CT scan of the brain is an informative and common research method. With its help, various pathological conditions are diagnosed. Accessibility, painlessness, accuracy of the study and quick results are the undoubted advantages of computed tomography. Using CT, a three-dimensional image of the brain is obtained with the ability to study the organ layer by layer. Contrast enhancement increases the diagnostic information content of the method.
Yusupov Hospital conducts all types of computed tomography of the brain. The clinic is equipped with modern equipment that allows diagnostics to be carried out in the shortest possible time.
The essence of the method
Computed tomography of the brain is a research method based on the use of x-rays. Using a series of images, a three-dimensional image of the brain is created. Various pathological conditions are diagnosed in this way. The advantage of CT is the ability to study the organ layer by layer. Tomography is used in various fields of medicine. The method has a small number of contraindications, which allows it to be used for various conditions. To determine damage to the blood vessels of the brain, a computed tomography scan is performed using a contrast agent. This type of study allows you to most accurately determine the affected area.
How it works and why it is carried out
The essence of magnetic resonance imaging, which is usually denoted by the abbreviation MRI, is the effect on the human body of a magnetic field and radio frequency pulses that scan it section by section and allow one to obtain a highly accurate and clear image of internal organs and tissues in three projections - sagittal, axial, coronal.
Content:
- How it works and why it is carried out
- Indications for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
- Who should not have an MRI of the brain?
- How to prepare for an MRI of the brain
- The process of performing an MRI of the brain
Initially, this technology owes its appearance to the phenomenon of NMR - nuclear magnetic resonance, discovered in 1946 during joint research by Harvard and Stanford specialists.
The phenomenon is that the nuclei of some substances, such as hydrogen, can absorb or launch the energy of radio frequency pulses, provided that these substances are in a magnetic field, and the frequency of the pulses coincides with the rotation frequency of these nuclei.
Each fragment and particle of the examined tissue or organ has its own NMR frequency. It is this value that is converted into the tomogram image.
Already in 1973, as a result of the analysis, study and development of this method, the first MRI image was obtained - an image of two vessels filled with water.
The author of the photo is Paul Lauterbur. His colleague, Peter Mansfield, was the first to show how a radio signal received from an MR spectrometer is converted into an image. Both scientists received the Nobel Prize in 2003 for their achievements in this field.
Since that time, the method of magnetic resonance imaging has gained popularity and is highly valued to this day.
It is prescribed in various situations for the following purposes:
- researching symptoms of probable or diagnosed head injuries;
- check for symptoms indicating the likelihood of brain damage from Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and other diseases. Such symptoms may include confusion, changes in consciousness, behavioral disturbances;
- checking for hydrocephalus;
- identifying and studying tumors, infectious lesions, abscesses, encephalitis or meningitis;
- testing the visual and auditory nerves.
MRI can be performed with or without contrast. In the first case, the subject is injected with special dyes, which in the photographs give a clearer and more detailed image of brain tissue.
MRI of cerebral vessels is distinguished as an independent type of examination - MR angiography. In terms of technique, preparation methods and contraindications, MR angiography does not differ from MRI of the brain, but it gives a complete picture of the condition of the arteries and veins of the brain, and MRI of the brain allows you to diagnose disorders in brain tissue. Both procedure options can be performed with contrast.
Advantages
Computed tomography has some advantages over other methods of studying the brain. The main ones include:
- Painless. Some discomfort may occur only after the administration of a contrast agent. This must be reported to your doctor.
- Accuracy. A layer-by-layer study of the brain allows us to detect initial changes in its structure. Contrast enhancement increases the information content of the method.
- Speed of research. The procedure takes on average one hour. Within an hour after diagnosis, the results are delivered to your hands.
- Possible for people suffering from claustrophobia.
Contraindications to the use of contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging
Gadolinium, which is part of the contrast agent, is a substance with a high safety profile. Despite this, the use of contrast agents in patients with severe renal failure and impaired renal function is not recommended. If the patient is receiving hemodialysis, an MRI with the introduction of contrast agents is performed before the procedure in order to remove the drug from the body artificially and reduce the load on the excretory organs.
To minimize the possible impact of contrast on the human body, there is no need to overuse the method. Contrast does not affect the overall quality of the resulting images - MRI of the brain with contrast has strict indications (do not ask for a “higher contrast” image). In all other cases, magnetic resonance imaging without contrast is sufficient.
Contrast-enhanced MRI of the head is not recommended during pregnancy. Gadolinium crosses the placental barrier and can accumulate in the fetus. A detailed study of the effect of contrast agents during pregnancy has not been carried out, since such experiments are prohibited for ethical reasons.
Individual intolerance or allergic reactions to contrast agents for MRI and their components are a contraindication for the use of contrast. If necessary, the problem can be solved by prescribing antihistamines and corticosteroids.
Preparing for MRI of the brain with contrast agents
No special preparation is required for contrast-enhanced MRI of the brain.
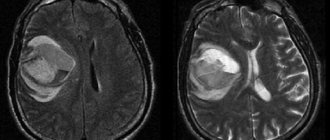
What does a CT scan show?
Computed tomography of the brain is prescribed for various conditions. Depending on the reason for the study, diagnostics are performed with or without a contrast agent. This diagnostic method is prescribed to identify the following conditions:
- bleeding;
- strokes and hemorrhages;
- neoplasms in the head and neck area;
- fractures of the base of the skull;
- hematomas and injuries;
- inflammatory process;
- pathologies of tissue development;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the area being examined.
Indications
A CT scan of the brain is possible with or without a contrast agent. Computed tomography without contrast is indicated for the following conditions:
- Head injuries. This group of indications includes bruises, concussions, and damage to the bones of the skull.
- Dental examination. The dentist may prescribe a computed tomography scan to determine developmental disorders of the maxillofacial area. In addition, research is necessary before implantation.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident. If acute cerebrovascular accident is suspected, a CT scan of the brain is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Diseases accompanied by loss of consciousness. Syncope, accompanied by convulsive syndrome, requires a computed tomography scan of the brain.
A CT scan of the brain using a contrast agent is called angiography. It allows you to most accurately examine pathological formations in the brain area. This research method has the following indications:
- Determination of the area of stenosis. Angiography allows you to determine the area of vascular narrowing, as well as the degree of stenosis.
- Diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms.
- Suspicion of ischemic stroke.
- Checking for vascular patency. Using tomography, obstruction is diagnosed due to thrombus formation or blockage of the lumen of the vessel by an embolus.
In what cases is an MRI of the brain done?
Tomography can be either the main diagnostic method or an additional one. Indications for the procedure are the following conditions and diseases:
- neoplasms;
- developmental anomalies;
- injury;
- stroke;
- intense headache of unknown origin;
- pathology of the pituitary gland;
- vascular abnormalities;
- multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system;
- dementia;
- epilepsy;
For frequent or persistent headaches, MRI is used if:
- the attacks became more frequent and more severe;
- coordination of movements is impaired;
- there is a connection between headaches and coughing and sneezing;
- there is an oncological disease of another localization;
- attacks occur at night, interrupting sleep.
Tomographic scan of the brain
Magnetic resonance imaging is also successfully used to diagnose the following pathologies:
- Acute cerebrovascular accident. This can be an ischemic attack, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, post-traumatic hemorrhage.
- Intracranial space-occupying formations. Tomography is the main method for:
- primary diagnosis of extra- and intracerebral tumors;
- differential diagnosis of tumors, abscesses and other pathologies;
- assessing the success of tumor removal, postoperative complications, and continued tumor growth.
- Metastatic lesions of the central nervous system. For tumors with a high frequency of metastatic brain damage (lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma and others), magnetic resonance scanning is included in the mandatory examination protocol.
- Multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the white matter of the brain. MRI is the most accurate diagnostic method in this case. The use of intravenous contrast allows one to visualize lesions, determine their size, and monitor the progress of treatment.
- Dementia and memory disorders. Tomography is necessary for:
- exclusion of possible tumors, hemorrhages;
- determining the duration and nature of the process;
- assessing the success of treatment.
- Epilepsy. MRI of the brain is a mandatory examination procedure for patients suffering from epilepsy. It helps to exclude tumors, pathologies of the brain and blood vessels, the consequences of injuries, and inflammatory processes. To visualize minor structural changes, images of thin sections (1–3 mm) are taken using additional signal amplification modes (according to the epileptic protocol). The second most common possible cause of epilepsy is benign tumors. Detecting them on MRI gives the patient a chance for recovery with surgery.
- Pathology of the pituitary gland. The main examination method is tomography with intravenous contrast.
Indications for CT scan of the head and neck
Computed tomography of the head carries a certain radiation load on the body, so scanning is recommended no more than 3 times a year for emergency indications.
The interval between studies should not be less than 4 weeks. For preventive purposes, experts do not recommend undergoing examination, as the X-ray load on the body increases. The main indications for CT of the head and neck are:
- dizziness and tinnitus, the causes of which have not been established;
- anomalies in the development of bone structures of the head, blood vessels;
- suspicion of the development of a hernia in the cervical spine;
- neck and head injuries;
- suspected tumors of the head and neck;
- headache;
- identifying dilation of blood vessels in the neck and head;
- signs of cerebrovascular insufficiency.
When contacting specialists at the Yusupov Hospital with these signs, patients receive advice on the scope of diagnostic measures to identify the causes of the pathology, after which they are sent for diagnosis.
Make an appointment
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
The first thing a doctor pays attention to when a new patient comes to see him is his complaints. Suspicious symptoms, for example, pathological deviations in behavior, consciousness, sensations, reactions, may be the basis for referral to an MRI of the brain. Such deviations include:
- regular, frequent headaches of unknown etiology;
- periodic fainting;
- confusion of thoughts, clouding and disturbances of consciousness;
- feeling of dizziness with minor exertion or at rest;
- causeless decrease in hearing and visual acuity, tinnitus;
- sensitivity disorders of the facial nerves, pain, tingling, numbness of the facial muscles;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- decreased ability to concentrate.
Single manifestations of such conditions are unlikely to be a cause for serious concern, but if there is regularity and/or persistence of symptoms, a combination of several of the above sensations, the doctor may need magnetic resonance imaging data.
In addition, an examination will need to be carried out if, for other indications, the doctor suspects multiple sclerosis, parasitic, infectious or inflammatory lesions, tumors and neoplasms in the brain, acute or chronic cerebrovascular accident, cerebral aneurysms, pituitary tumor, vascular pathologies.
Contraindications
Despite the well-tolerated procedure and its painlessness, computed tomography of the brain has some contraindications. These include:
- Pregnancy. Since the research method is based on the use of X-rays, there is a possibility of negative effects on the fetus. Carrying out a CT scan of the brain in a pregnant woman is justified only in cases of threat to her life.
- Excessively heavy weight. Obesity, in which weight reaches above 200 kg, is a limitation for performing computed tomography of the brain.
- Mental illnesses. During the CT scan, you must remain motionless. Mental illnesses accompanied by inadequate reactions make diagnosis difficult.
- Individual intolerance to the components of the contrast agent.
- The presence of severe renal or liver failure. This contraindication is due to the need to remove the contrast agent. In cases of insufficient liver or kidney function, excretion becomes difficult.
Prohibitions and restrictions for MRI
MRI of the brain is a safe and effective procedure. Despite this, it also has its own categorical contraindications for:
- the presence of metal prostheses or implants, electronic equipment (for example, a pacemaker) on the patient’s body that cannot be removed;
- a person’s condition that does not allow transfer to a tomograph (coma, being on artificial life support).
It is not advisable to carry out diagnostics using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, however, with the permission of a doctor, it is possible in the following cases:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- uncontrolled body movements;
- claustrophobia or panic attacks when in a tomograph;
- availability of modern dentures;
- pain in which it is difficult to remain motionless for a long time;
- renal or liver failure.
In some of the above recommendations for refusing MRI of the brain, certain actions can be taken to lift the ban. For example, you can temporarily stop breastfeeding. 2 days is enough. Breast milk can be expressed and the baby can be fed formula or milk from a pre-created “bank”.
Preparation
No special preparation is required to perform a CT scan of the brain. If it is necessary to use a contrast agent, the last meal should be 5 hours before the examination. Before a CT scan of the brain, it is recommended to consult with your doctor about the need to stop taking medications during the study.
Progress of the study
The procedure for performing a CT scan of the brain consists of the following steps:
- The patient is placed on a conveyor.
- The head is fixed using special devices. This is necessary to ensure maximum immobility during the examination.
- After starting the tomograph, a series of images are taken, with the help of which a three-dimensional image of the brain is formed.
- Computed tomography is a painless diagnostic method. During the examination, the patient hears only clicks. This factor is eliminated with the help of earplugs.
- If contrast enhancement is necessary, a special substance is injected into the body. It stains the blood vessels, which allows for a more accurate diagnosis of the brain. The contrast agent may cause a metallic taste in the mouth, nausea, or headache. This must be reported to the doctor conducting the study.
On average, a CT scan of the brain takes from 30 minutes to an hour. The duration of the study depends on the type of diagnosis and the general condition of the patient. The results are deciphered immediately after the procedure. It takes about 1-1.5 hours depending on the complexity of the tomography.
Decoding the results
After the tomography, the doctor evaluates the resulting layer-by-layer images. The presence or absence of neoplasms, areas of hemorrhage or ischemia are taken into account, and brain structures are assessed. A computed tomography scan is considered normal if there are no signs of pathological neoplasms, brain structures are age-appropriate, there are no areas of fluid accumulation, and there are no violations of the integrity of bone tissue.
Any deviations from the norm are recorded in the conclusion and require further consultation with a specialist. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are deciphering all types of computed tomography of the brain. The latest equipment makes it possible to accurately determine the initial changes in the organ.
Price
The cost of a head and neck CT scan varies depending on the qualifications of the specialist, the equipment used and other factors, which include the administration of a contrast agent. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients have access to a wide range of diagnostic services, and also have the opportunity to undergo scanning with contrast.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital guarantee obtaining clear, high-quality images that will allow you to fully evaluate the area under study. If you need a head CT scan, there are many diagnostic centers in Moscow. However, services that meet European standards are provided at the Yusupov multidisciplinary hospital located on Nagornaya Street. If you need a specialist consultation for a head CT scan, please make an appointment by phone.
Make an appointment