Stroke is a serious disease that causes destructive changes in brain cells as a result of circulatory problems. The most severe form of pathology is an extensive stroke, as a result of which several areas of brain tissue are affected, which leads to the formation of persistent irreversible disorders, including death. The consequences of a major stroke are serious, so the chances of survival and further prognosis are quite unfavorable, although everything depends on timely, high-quality treatment, a set of rehabilitation measures and the desire of the patient.
At the Yusupov Hospital, experienced neurologists diagnose and treat major strokes. For this purpose, modern medical equipment is used. It allows you to quickly and accurately determine the localization of the pathological focus. Based on the data obtained, doctors develop appropriate treatment. For this purpose, all conditions have been created in the neurology department:
- modern diagnostic equipment that allows you to quickly identify the type and location of a stroke and the degree of brain damage;
- a team of specialists, which includes professors and neurologists of the highest category with experience in treating major strokes;
- the presence of high-class life-support equipment that supports the vital functions of the body;
- modern effective drugs;
- the desire of all clinic staff to give the patient a chance to recover after a stroke;
- the use of innovative methods for restoring lost functions by rehabilitation clinic specialists;
- the possibility of performing minimally invasive neurosurgical interventions in partner clinics;
- psychological support for relatives of patients who have had a major stroke.
What is a major stroke
In the international classification of diseases ICD-10, acute cerebrovascular accident is coded I60-I69. A major stroke is the most dangerous type of cerebral blood flow disorder, leading to the death of several areas of the brain. The term “extensive” is due to several characteristics:
- large areas of the brain are affected;
- the formation of the disease is caused by damage to large arteries;
- the possibility of the appearance of many pathological foci.
Loss of oxygen and nutrients leads to rapid death of nerve cells. A large amount of damage during a major stroke leads to the loss of important functions and abilities of the body: vision, hearing, motor activity, etc. The consequences of minor injuries with quick and effective treatment can be completely eliminated, which allows the patient to return to normal life and restore lost functions, but the likelihood of recovery for large lesions is quite small.
Extensive lesions are characterized by a high rate of development of clinical signs, severity and the development of serious irreversible consequences, so the prognosis for the patient is rather disappointing. According to statistics, approximately 15-20% of victims have a chance of recovery.
Stroke Prevention
Most often, during the rehabilitation period, in addition to drug therapy, the patient is prescribed a set of physical therapy exercises. They will allow a person to learn to stand firmly on his feet again, maintaining his balance. Additionally, it is possible to use special simulators that allow you to restore the functions of your arms and legs. Classes on them can be carried out at home. If, after a stroke, a person is paralyzed and unable to stand up on his own, sessions are prescribed with a massage therapist who will develop the mobility of the limbs.
Treatment for stroke should be done with caution and should be done by a board-certified physician. Self-medication can only worsen the condition
Myocardial infarction is considered the main cause of death in patients after stroke. In order to avoid it, you must follow the preventive measures prescribed by your doctor. Cerebrovascular accident is a serious disease
It is important to know about all the signs of a stroke in a woman in order to be able to provide timely assistance and prevent irreversible consequences
Error type: "Forbidden". Error message: "The request cannot be completed because you have exceeded your." Domain: "youtube.quota". Reason: "quotaExceeded". Did you add your own Google API key? Look at the help.Check in YouTube if the id PLw28qKAVv_b4A8cRjf_48D_LiZk6Krk9b belongs to a playlist. Check the FAQ of the plugin or send error messages to support.
Symptoms, clinical picture
Precursors of a stroke may appear weeks and even months before an acute cerebrovascular accident. Among the obvious first symptoms of a stroke are:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- darkening of the eyes with sudden movements;
- episodic global memory loss (amnesia);
- sudden short-term disorientation.
The main signs of a major stroke appear several hours before an acute cerebrovascular accident or directly during an attack. Depending on the type of stroke, within a day the patient experiences pronounced symptoms of brain damage:
- drowsiness followed by excitement;
- stunned;
- loss of consciousness;
- increasing sharp headache;
- nausea and vomiting.
Patients are concerned about pain in the eyeballs, a feeling of heat, sweating, increased heartbeat, dry mouth, and convulsive syndrome develops. One of the most common symptoms of a major stroke is coma. It indicates significant and deep damage to brain structures. After treatment and rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital, 37% of patients who suffered a stroke live a full life, 25% regain consciousness, but there remain residual disturbances in speech and motor functions, which are also gradually corrected in the rehabilitation clinic.
General cerebral symptoms of a major stroke include:
- Strong headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- dizziness;
- stunned state;
- sopor;
- rarely coma;
- pale skin;
- cardiopalmus;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- convulsive syndrome;
- hyperthermia.
Focal symptoms depend on the location of the pathological focus. When the right hemisphere is damaged, motor and sensory disorders occur in the left half of the body, and vice versa. Among the main symptoms are:
- violation of superficial and deep sensitivity;
- inability to independently flex and straighten limbs;
- drooping corner of the mouth;
- inability to smile;
- impaired speech and swallowing;
- deviation of the tongue towards the affected side;
- memory loss;
- mental disorder;
- decreased visual acuity;
- dry mouth.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital pay special attention to the symptoms of a major stroke. The clinical picture, together with the diagnosis, allows us to determine the type of cerebrovascular accident and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Causes
Major stroke has several risk factors:
- Atherosclerosis. Reducing the lumen of the arteries due to cholesterol deposits disrupts the process of blood circulation in the tissues of the brain. This provokes the development of ischemia;
- Hereditary predisposition. If one of the relatives had a history of an episode of cerebrovascular accident, then subsequent generations are at risk;
- Taking certain medications. Oral contraceptives and other drugs thicken the blood, increasing the risk of spontaneous thrombosis;
- Arterial hypertension. High blood pressure has a strong impact on the vascular wall. As a result, arteries rupture with subsequent hemorrhage into the brain cavity;
- Frequent transient ischemic attacks;
- Diabetes mellitus complicated by cerebral vascular angiopathy;
- Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Drug use;
- Metabolic syndrome;
- Excess weight (more than 30% of normal).
The chances of surviving a major stroke depend on whether treatment for the disease is started within 3-4 hours of the onset of the first symptoms. Finding out the causes of major stroke is necessary to develop the most effective treatment regimen. In addition, eliminating provoking factors will reduce the risk of developing a recurrent cerebrovascular accident.
A major stroke is one of the most dangerous pathologies that occurs due to circulatory problems in several areas of the brain at once. As a result, the patient develops a number of complex pathological abnormalities, in some cases incompatible with life.
The most dangerous type is considered to be hemorrhagic stroke. In this case, problems arise with blood circulation in the brain, leading to hemorrhages. Blood entering the cranial cavity causes swelling of the surrounding tissues, as a result of which vital functions are disrupted. Ischemic stroke has favorable prospects. It is expressed in a short-term disruption of vascular conductivity, which, with proper therapy and care, is eliminated over a certain period of time.
The symptoms of a major stroke are characteristic: the patient loses coordination, inadequately perceives reality and the speech of others, completely or partially loses the ability to reproduce words and arrange them in logical chains. The main symptom is a severe headache.
If any of these manifestations occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. The sooner measures are taken, the greater the chances of recovery, and in some cases, life. The consequences of a major stroke are truly dangerous; most patients cannot fully recover their health for the rest of their lives. At the Yusupov Hospital, the examination takes minimal time, and a comprehensive treatment plan is prescribed in accordance with the type of extensive stroke and the extent of brain damage.
Make an appointment
Probability of relapse
Chances of surviving after a major myocardial (heart) infarction, consequences, how to improve the prognosis
Many people are interested in the question: “How many strokes can an elderly person suffer?” It is impossible to give an exact answer, as it depends on many factors. But a maximum person can survive 3 strokes, which is extremely rare.
What is the probability of relapse? Even if a person fully recovers from a stroke, the likelihood of the disease reoccurring is very high. Relapse is accompanied by more severe symptoms and causes even more severe consequences of stroke in old age. In almost all cases, the person loses motor and mental abilities.
If a person has a stroke for the third time, it is a catastrophe for life. People rarely survive such a blow. Typically, patients no longer recover either physically or mentally, remaining disabled.
Most often, a recurrent stroke occurs due to the fault of the patient himself, since many patients do not follow doctors’ recommendations while at home. The following rules will help you avoid relapse:
- Eat properly.
- Do not overload the body physically.
- Do physical therapy.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Take all medications prescribed by your doctor on time.
- Contact your doctor immediately if your health conditions worsen.
Stroke is a dangerous pathology that causes many serious consequences. It is not always possible to restore full functioning of the body. Often patients remain disabled, losing the ability to move, vision, hearing and other important functions.
Acute cerebrovascular accident is a dangerous pathology that leads to the most tragic consequences. Experts warn that stroke is especially dangerous in old age, since in adulthood it is almost impossible to prevent cell damage and the occurrence of brain dysfunction. According to statistics, thousands of citizens die from this disease every year, and those who manage to survive most often become disabled. That is why every person should understand why a stroke occurs, how it manifests itself, and what measures need to be taken to avoid trouble.
Kinds
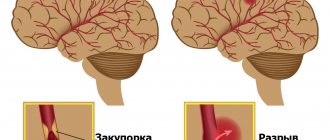
Acute cerebrovascular accidents are divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic. In the first case, the lumen of the artery closes, in the second, blood escapes from the damaged vessel. Various reasons lead to the development of these types of stroke. In addition, they differ in pathogenetic mechanisms and clinical presentation. Extensive stroke is divided into the following types:
- Hemodynamic. Vasospasm provokes a decrease in the amount of oxygen that reaches the brain tissue. The cause of this condition is often hypotension.
- Microocclusion. A stroke develops due to a local disturbance in blood flow.
- Lacunar. In the brain, due to increased pressure in the vessel, a cavity is formed. It is filled with liquid.
- Cardioembolic. Arrhythmias lead to the detachment of a blood clot. As a result of uneven contraction of the myocardium, blood turbulence occurs. The detached blood clot enters the brain vessel, causing the development of a stroke.
- Atherothrombotic. The cause of acute cerebrovascular accident is the blocking of the artery lumen by an atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis is formed due to changes in the lipid composition of the blood.
Types and classification
A major stroke occurs when large arteries are damaged, including the carotid arteries - they take part in the blood supply to the cerebral hemispheres. As a result of their blockage or rupture, the power supply to one or even two hemispheres may completely stop. This leads to a sharp deterioration in nervous activity, and in the absence of medical assistance within the first few hours, to death. It is important to determine the type of stroke and its causes - these factors influence the selection of further treatment and rehabilitation after a stroke.
Ischemic major stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs in 80% of patients. Its main reason is the deterioration of blood conductivity through the vessels, while their walls remain undamaged. Ischemia is oxygen starvation of tissues, which is especially dangerous for the brain. This type of stroke can occur suddenly or develop gradually, against the background of the main predisposing factors:
- blockage of a vessel by a thrombus, including atherosclerosis and plaque formation;
- vascular spasm, as a result of which blood cannot flow freely to the brain tissues;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure - in such conditions, a small amount of oxygen-enriched blood reaches the nervous tissues.
With an ischemic stroke, there is still a chance of full recovery. If the walls of the vessel remain intact, in the first few hours all possible measures should be taken to restore blood circulation.
Extensive hemorrhagic stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke is a stroke that occurs when an artery ruptures. Its second name is non-traumatic cerebral hemorrhage. This is a dangerous phenomenon that can be fatal even if emergency care is provided in a timely manner. An extensive hematoma deprives brain tissue of the ability to receive and transmit nerve impulses, which can result not only in deterioration of memory, attention, skills and reflexes, but also coma and complete suppression of nervous activity.
There are several types of hemorrhagic stroke, which differ in the location of the hematoma and the degree of danger for the patient.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage is the most common type. Blood enters the brain matter and damages nerve cells that are responsible for various skills and functions in the human body. Risks to the patient's life are present, but they are minimal compared to other types of hemorrhagic stroke. The main causes are hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis and thrombosis. P
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a pathological condition in which blood enters the subarachnoid space, between the membranes of the brain. It often occurs spontaneously and can be fatal, even with prompt medical attention. Among the causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage, in addition to hypertensive crisis, are smoking, excess weight and alcohol abuse - all these factors lead to weakness of the vascular walls.
The danger of hemorrhagic stroke is that not every patient is able to fully restore lost skills. Even if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the nerve tissues undergo necrosis and cannot perform the function of transmitting nerve impulses.
Brainstem stroke
Both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes can be located in the brainstem center. Here are vital centers that are involved in the regulation of breathing, swallowing, and heart rate. If blood enters this area, it can be instantly fatal due to the cessation of breathing and heartbeat.
Mechanism of ischemic stroke
Another name for ischemia is cerebral infarction. As a result of a sharp restriction of blood supply, brain tissue dies. This condition often occurs due to rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, blockage of the lumen of a vessel by an embolus or thrombus.
The cause of atherosclerosis is the deposition of cholesterol in the inner layer of the artery. A blood clot forms due to increased blood viscosity. This condition often occurs against the background of concomitant diabetes mellitus and tumor formations. A cerebral infarction develops due to a sudden cessation of blood flow to the brain tissue. The changes that occur become irreversible 5–8 minutes after the onset of pathological symptoms. In the absence of correct treatment, the affected area increases. Therefore, it is important to seek medical help in time to preserve as much viable tissue as possible.
With the development of ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere, sensory disturbances and motor disorders appear on the right. Damage to the right hemisphere is accompanied by speech disorders. General cerebral symptoms include dizziness, nausea, loss of consciousness, and in rare cases, coma. Specific signs of ischemic stroke are considered to be a decrease or complete loss of sensitivity in the right half of the body, limited or absent movements in the limbs, problems with swallowing, and drooping of the corner of the mouth.
Ischemic stroke is divided into 5 subtypes:
- atherothrombotic – develops slowly due to atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries;
- cardioembolic – occurs when a cerebral artery is completely or partially blocked and develops rapidly;
- lacunar – occurs due to damage to perforating arteries, develops within several hours;
- hemodynamic – occurs due to a sharp decrease in blood pressure, is sudden, affects all areas of the blood supply;
- microocclusive - develops due to a violation of the coagulation and anticoagulation system.
Consequences of stroke depending on its type
Extensive stroke is divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic. Extensive stroke consequences and consequences of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke are similar. The difference is in the speed and severity of their development.
Ischemic stroke is characterized by a disruption of the blood supply to parts of the brain due to blockage of an artery by atherosclerotic plaque. Ischemic stroke has a more favorable prognosis for the patient's recovery. The consequences of an ischemic stroke are usually manifested by impaired motor activity, muscle weakness, loss of control of motor activity, problems with coordination, difficulties in concentration and perception, speech disorders, loss of sensation, and epilepsy.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a consequence of a ruptured vessel, resulting in bleeding in the brain. As a result, cerebral edema occurs and an acute inflammatory process develops, which leads to brain necrosis and death. Very often it happens due to high blood pressure, at a critical level.
Hemorrhagic stroke is very dangerous, difficult to treat, characterized by high mortality; with extensive brain damage, coma and death can occur. The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke are usually disappointing: a person can become disabled, remain blind, deaf, insensitive to pain and heat, smells and speech addressed to him for the rest of his life. A person is not able to care for himself - he cannot eat, and he cannot control bowel movements and urination. The general condition of the patient is lethargy.
With a major stroke, it is important for the patient’s condition how quickly he receives help. The consequences depend on the degree of brain damage
With a major stroke, the left side of the body can be paralyzed, memory and thought processes can be affected, and reactions can slow down. The facial muscles will be affected – the patient’s facial expressions will be skewed and distorted. On the mental side – apathy, a feeling of detachment and hopelessness. Persistent paresis occurs, sensitivity suffers, and eye movements may be impaired.
It all depends on the age of the patient - the elderly condition aggravates the diagnosis, the severity of the lesion, the strength of the body, and gender. During the first days after a stroke, approximately 25% of patients who have suffered a major stroke die. When vital parts of the brain are damaged by an extensive stroke, 95% of patients die immediately, and the remaining 5% fall into a coma. Recovery from a major stroke without consequences is possible in only 5% of patients. Unfortunately, they are not immune from a second stroke; within a year after the first attack, it occurs in 25%, and in 40% after 5 years. Being older increases your chance of having another stroke.
The consequences of a stroke are divided by type:
- Motor: paralysis of the limbs, paresis, increased muscle tone, paralysis of part of the body - left or right side, problems with swallowing;
- Disorders of the vestibular apparatus: impaired coordination, orientation, balance, dizziness;
- Visual impairment: blindness - partial or complete, impaired eye movement, strabismus, visual agnosia, double “picture” in the eyes;
- Hearing impairment: the occurrence of hallucinations, hearing loss or reduction, auditory agnosia;
- Loss of smell, loss of pain, disturbances of tactile sensitivity, or, on the contrary, the appearance of hypersensitivity;
- Cognitive: decreased and impaired attention, decreased intelligence (dementia), logic, memory impairment or loss (amnesia), information perception, speech problems;
- Mental: anxiety, aggressiveness, instability of the psyche and emotional background, depression, apathy.
The consequences of a stroke in old age very often lead to dementia, because the destroyed brain cells are replaced by connective tissue.
Mechanism of hemorrhagic stroke
Among the main causes of hemorrhagic stroke are:
- uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- excessively thin blood;
- congenital deformations of the vascular wall.
Rupture of blood vessels with subsequent leakage of blood into the brain cavity most often provokes a sharp rise in blood pressure. In addition to the listed etiological factors, aneurysm, traumatic brain injury, physical or emotional stress can cause hemorrhagic stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by a sudden and rapid onset. Symptoms include severe headache, rapid breathing, confusion, and possible development of coma. The skin becomes cold to the touch, the corner of the mouth droops, and blood pressure rises. Against the background of hemorrhage in the brain, the tone of the muscles of the limbs decreases, strabismus may appear, the pupils dilate, and swallowing is impaired. Hemorrhagic stroke has a less favorable course and is often accompanied by complications.
There are 2 types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- intracerebral. Occurs due to thinning of the arterial walls and a sharp jump in pressure. The risk group includes persons aged 45 to 60 years;
- subarachnoid. Occurs when a cerebral artery aneurysm ruptures and blood escapes under the arachnoid membrane of the brain. The risk group consists of people aged 30-60 years, abusing alcohol and smoking, and having excess body weight.
Diagnostics
Major stroke is a condition requiring urgent diagnosis and treatment. For this, the Yusupov Hospital uses the following methods:
- Collection of complaints and medical history. The doctor finds out the time of onset of pathological symptoms, their severity and speed of spread. It is necessary to establish predisposing factors.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate. These are indicators by which the severity of the patient’s condition is assessed.
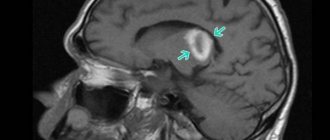
- MRI. Allows visualization of cerebral tissue. Today, tomography is considered the most informative method for diagnosing acute cerebrovascular accident.
- EEG. Evaluates brain activity. In the affected area, the waves received will be below normal.
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck. It is carried out to determine the nature of blood flow in the brain area.
- Clinical and biochemical blood test. Prescribed to detect cholesterol concentrations. The standard of research includes a lipid profile.
The listed diagnostic methods can be expanded depending on the individual characteristics of the disease. The Yusupov Hospital uses modern medical equipment for examinations. Thanks to this, it is possible to quickly and accurately determine the pathological focus. Based on the data obtained, neurologists select a treatment and rehabilitation program for each patient. This approach allows you to reduce the length of hospital stay and minimize the risk of complications and recurrent stroke.
Make an appointment
Treatment
Treatment for a major stroke should begin as early as possible. Irreversible consequences for the brain develop rapidly. To prevent stroke complications, comprehensive treatment is necessary. Self-therapy is excluded. The patient needs to be urgently hospitalized. The following drugs are used to treat major stroke:
- Hypotensive. Prescribed to lower blood pressure. In inpatient settings, antihypertensive therapy is emergency. In the future, a permanent treatment regimen is selected for the patient.
- Anticoagulants. Prevents thrombus formation and improves the rheological properties of blood.
- Diuretics. Against the background of a major stroke, the risk of developing cerebral edema increases. It occurs due to an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in certain areas. Diuretics help remove excess fluid from the body and alleviate the condition.
- Statins. Prescribed to reduce blood cholesterol levels, as well as prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
- Angioprotectors. Protect the vascular wall from the exogenous effects of provoking factors.
- Cerebrovascular drugs. Improves blood circulation in the brain and restores metabolic processes.
Surgery for stroke is indicated in the presence of an extensive hematoma. The purpose of the operation is to remove liquid connective tissue. This is necessary to reduce the risk of developing compression of healthy nerve structures. The surgical operation is performed through trepanation.
After treatment and relief of the acute period, patients are transferred to the rehabilitation period. At the Yusupov Hospital, experienced exercise therapy instructors and physiotherapists develop an individual rehabilitation treatment plan.
Consequences
It is impossible to accurately predict the consequences of a major stroke. It all depends on the volume and location of the damage. The human body is designed in such a way that when one hemisphere loses activity, the other is activated, which allows one to maintain vital functions and increase the chances of survival. With such a severe form of pathology, persistent disorders often develop that are difficult to correct:
- paralysis of limbs;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- inability to self-service;
- mental disorders;
- loss of vision;
- memory disorders;
- loss of learning ability;
- speech impairment, etc.
A major stroke is characterized by an unfavorable course. Untimely treatment can lead to the development of incurable complications. The disease occupies a leading position in the structure of disability. The most common consequences of a major stroke include:
- Movement disorders. Such complications occur in 80% of cases. In this case, the ability to move the upper or lower extremities is impaired or completely lost;
- Speech disorders. Doctors identify several options for speech complications;
- The ability to speak and write independently is lost, but the speech of the interlocutor is perceived adequately;
- There is a loss of perception of one’s own and others’ speech;
- Visual impairment. The image may be completely distorted or partially missing.
- Cerebellar dysfunction. Characterized by dizziness at rest. In this case, causeless and uncontrolled vomiting, increased blood pressure and tachycardia occur.
To help patients with a major stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital begin treatment and rehabilitation immediately after the patient’s admission to the neurology clinic. First, the vital functions of the body are ensured with the help of modern equipment that allows you to control breathing and cardiac activity. Then the type of stroke is clarified and drugs are prescribed that restore the function of brain cells in the stroke area and neurons located around the lesion.
In case of hemorrhagic stroke, patients at partner clinics undergo minimally invasive neurosurgical operations to reduce compression of the brain. This is the only effective treatment for hemorrhagic stroke and helps patients recover and regain lost functions.
In the presence of extensive ischemic stroke, pathogenetic therapy is carried out, aimed at improving the passage of blood through brain tissue, and treatment with neuroprotectors that protect brain cells from damage. Treatment begins within three hours of the onset of the stroke. The severity of the positive dynamics depends on the speed of dissolution of the blood clot: neurological functions are better restored with rapid, almost instantaneous lysis of the blood clot. The most rapid and complete dissolution occurs in cardioembolic major stroke. Slow restoration of blood flow occurs with atherothrombotic damage to the artery.
It is not accompanied by a significant improvement in clinical dynamics. For most blockages of medium- and large-sized arteries, thrombolysis is the treatment of choice. It provides early restoration of blood flow in 30-40% of cases. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors use the most effective drug for thrombolysis - recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. It is administered intravenously to patients.
One of the promising directions for restoring blood flow through a thrombosed artery is surgical removal of the thrombus - endovascular extraction or excision. The operation is performed in partner clinics. After surgery, blood supply to the brain is restored in 81% of patients within the first 24 hours. In the first days of atherothrombotic stroke and with confirmed cardiogenic stroke, patients are administered heparin. In the presence of atrial fibrillation, after heart valve replacement or concomitant myocardial infarction, patients are prescribed warfarin.
Drugs with complex vascular-metabolic action, of which Cavinton is a representative, have a positive effect on the state of blood supply to the brain. In cases of extensive stroke, drugs that have a nootropic effect, as well as neuroprotectors, are prescribed. Rehabilitation of patients with a major stroke after restoration of consciousness is carried out in a rehabilitation clinic. The hospital is equipped with modern equipment, and a multidisciplinary team of specialists takes an individual approach to the treatment of each patient. If you have symptoms of a major stroke, call an ambulance and call.
When the patient arrives at the Yusupov Hospital, doctors will be ready to immediately begin providing specialized medical care that promotes recovery after a stroke. You can increase your chances of survival and reduce the consequences of a major stroke using rehabilitation techniques. You can get diagnosed and treated for a major stroke at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic has modern medical equipment and a professional team of doctors. This allows for timely and high-quality treatment of cerebrovascular accidents.
Each patient is provided with an individual approach. Rehabilitation is carried out by experienced exercise therapy instructors. You can sign up for a consultation and ask any questions you may have by phone.
Consequences of damage to the cerebral hemispheres
Based on the developing symptoms of a stroke, one can assume the localization of the damage. With a major stroke, the blood supply to one of the hemispheres is often disrupted, which makes it possible to predict possible consequences. The left hemisphere is responsible for analytical and logical functions, verbal communication. After damage to this area of the brain, problems with speech and pronunciation are likely to develop, loss of the ability to analyze events, loss of visual memory, decreased sensitivity of the right half of the body, psycho-emotional disorders, aggression, apathy, and reluctance to live. According to studies, it turned out that damage to the left hemisphere is less life-threatening, and the chances of recovery are quite high if you provide timely assistance and undergo full rehabilitation.
The right hemisphere is responsible for the perception of surrounding information and thinking, therefore, when it is damaged, the following complications develop: memory impairment (up to loss of short-term memory), motor disorders of the left half of the body, mental disorders, aggressiveness, increased excitability, disorders of the perception of space and time. Rehabilitation for such disorders can last several years, and the likelihood of returning even a small proportion of lost functions is low.
Consequences for the elderly
In case of coma after a stroke in the elderly, the prognosis is more severe:
- hemorrhagic stroke of the brain often ends in death;
- after an ischemic stroke, even if the coma was short-lived, the consequences for the elderly will be severe (disability group I or II and dependence on the care of third parties).
If a patient has experienced a major stroke and was able to recover from a coma, the following complications are often observed:
- tactile disorders;
- vision problems;
- the appearance of abnormal reflexes;
- limited mobility;
- psychical deviations;
- speech disorders;
- memory loss;
- inability to self-service.
A deep coma at 80 years of age almost always ends in death or vegetative existence, and the chances of survival in the elderly at 90 years of age are minimal.
But these are just general statistics. Some ninety-year old people who suffered hemorrhage and were in a coma for 10 days or longer were able not only to come to their senses, but also to partially restore their lost skills. Cases of recovery are rare, most often the prognosis is severe.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing a recurrent major stroke, you must follow the preventive recommendations:
- Monitor blood pressure levels daily;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress;
- control weight;
- adhere to the principles of rational and balanced nutrition;
- carry out planned surgical correction in the presence of congenital aneurysms.
Odds and Predictions
According to statistics, with major strokes the chances of survival are no more than 65-70%. At the same time, the majority of patients (80%) develop persistent irreversible disorders leading to disability; only in 5% of cases is there a possibility of complete recovery. In addition, 15% of patients develop a recurrent attack, worsening any prognosis, often leading to death. The chances of survival after a major stroke depend on many factors. The older the patient, the worse the prognosis, which is associated with the speed of metabolic processes and the presence of concomitant pathology. Bad habits also adversely affect the recovery of patients. Life expectancy and prognosis directly depend on the speed and quality of care.
If you suspect a stroke, you can contact specialists at the Yusupov Hospital. They organize emergency hospitalization of the patient in a specialized department, where the patient will receive emergency care and create an effective rehabilitation program. Rehabilitation after a major stroke includes a set of measures in accordance with age, indications and contraindications. The success of the procedures depends on the attitude of the patients, the active support of family and friends, and the implementation of all medical recommendations. The coordinated work of professionals at the Yusupov Hospital allows us to achieve excellent results that improve the quality and length of life. You can find out more about the treatment and rehabilitation of patients after a stroke by phone.
Make an appointment
Rehabilitation begins on the first day
— When can you start rehabilitation after a stroke?
- After completion of treatment of the acute phase, that is, in fact, on the first day after the stroke. Even if the patient is still lying down, he can and should move - turn his head, move his arms and legs, try to sit up.
Even with bedridden patients, you can and should do passive exercises.
The rehabilitation program begins in the hospital and continues at home (or in a sanatorium, medical center). Every day after a stroke is work on the road to recovery.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
— What should be the first step in the recovery process?
— First of all, you need to work on correct body positioning: this facilitates the restoration of motor abilities, prevents muscle injuries, contractures, and reduces pain. Main principles of positioning:
- maintain the maximum possible symmetry of key points (shoulders, shoulder blades, pelvis), keep the head, shoulders, hips in the correct position.
- golden melt - the patient lies on either side, but not on the back.
- do not ignore the immobile part of the body. The bedside table is placed on the affected side so that when moving, for example, behind a mug, the patient reaches across the affected side and uses it. Learn to use your weak hand - for support, support, opening a door, turning on a light. It is important to develop a strong habit of using your weak hand as much as possible.
— Does the patient need physical therapy?
- Necessarily. Exercise therapy is necessary to restore movement skills and prepare for the moment when you can move more fully. As a result of regular exercises, shortened muscles of the hand, forearm, and back of the legs will be stretched, weakened arm muscles will be activated, the amplitude of movements will increase, and balance while sitting and standing will improve. If the patient has speech impairment, articulation exercises are necessary (for the tongue, lips, lower jaw muscles, facial muscles). Vestibular gymnastics is needed to restore coordination of movements, exercises for rehabilitation for movement disorders. Having mastered these exercises under the guidance of a doctor, you can do them at home - first with the help of relatives, then on your own. The main thing is regularity: 5-6 times a week, 30-40 minutes a day.
Advice to the patient’s relatives: treat his complaints wisely and do not allow him to succumb to laziness and despondency.
A patient in this state is most often inclined to lie down, but your task is to insist that he moves. Adequately assess his condition, and if he can get to the toilet on his own, do not place the dry closet near the bed. If the patient is able to feed himself, do not spoon feed him.