Unfortunately, a disorder such as stroke is very common. And if previously older people suffered from damage to the blood vessels of the brain, today young people also turn to specialists for help. In our information article we talk about the consequences of the disease, in particular about strabismus and how to restore vision.
In this article
- What is a stroke?
- Types of lesions
- What are the causes of stroke?
- What are the symptoms of a stroke?
- What are the consequences of a stroke related to the visual organs? How to recover? What will be the treatment?
- How to treat strabismus during a stroke?
- What does drug treatment include?
- Gymnastic exercises for the treatment of strabismus
- Surgery to treat strabismus after stroke
- Recommendations
What is a stroke?
Experts call a stroke an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain, which entails focal damage. Unfortunately, every year the disease becomes younger and more common: people after thirty years of age often experience a stroke. It manifests itself as sudden weakness in the limbs and disturbance of consciousness, as well as facial asymmetry, impaired speech and vision, and other signs that we will discuss below. It is important to diagnose this disease in time and begin treatment. Will the body be able to fully recover? It is difficult to answer this question unambiguously, since it will depend on physiology and age, as well as a number of other factors. In any case, treatment is necessary to correct cardiac, respiratory and metabolic disorders and combat cerebral edema. Also, a person after a stroke needs specific pathogenetic, neuroprotective and symptomatic therapy that will prevent complications.
Types of lesions
Experts distinguish two types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic. They are radically different from each other, as they have different mechanisms of action and principles of treatment. So, the first type can be called a cerebral infarction in another way. What happens at this moment? The work and patency of the cerebral arteries is disrupted, which leads to prolonged ischemia and changes in brain tissue in the area of the blood supply to the affected artery.
In turn, a hemorrhagic stroke is provoked by a pathological (atraumatic) rupture of a cerebral vessel with hemorrhage into the cerebral tissue. Neurologists summarize that ischemic stroke most often affects people after fifty years of age, while hemorrhagic stroke can also occur in the younger generation. For example, at the age of 40 years.
Reasons for appearance
Cerebral infarction is always associated with damage to blood vessels or disruption of their normal patency. The dynamics of the blood and its composition change. The catastrophe affects the basin of the middle (right) cerebral artery and provokes exogenous and endogenous factors.
Right hemisphere stroke occurs due to:
- Constant use of alcohol, drugs, smoking.
- Intense physical activity, frequent stress.
- Hypertension, hypotension.
- Excess weight, which sharply increases cholesterol levels.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Aneurysms, atherosclerosis, tumors.
- Diseases of the kidneys, cerebral vessels, heart.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives without control is the cause of right-sided stroke in women, accompanied by severe consequences.
- Hereditary or congenital pathologies of the heart (defect), endocrine system, blood are the cause of cerebral hemorrhage in children.
Depending on the type of blow, the factors that provoke hemorrhage change:
| Type of pathology | Causes | Consequences |
| Right hemisphere ischemic stroke is a disruption of the blood flow to the brain. Partial or complete blockage of blood vessels occurs. | Thick blood, embolism, thrombosis, atherosclerotic and cholesterol plaques, vascular compression, arterial hypertension, pressure surges, heart problems. Tension during childbirth, strong emotional outburst. | The brain does not receive the required amount of oxygen. Nerve cells die, starve, tissue necrosis. |
| The type of hemorrhagic stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain is considered fast-moving and aggressive. A catastrophe associated with rupture of blood vessels supplying tissue. | High blood pressure, hypertensive crisis, intracranial pressure. Changed structure of blood vessels, previous head injuries. | Rapid cerebral swelling, coma, disability, paralysis. Microstroke, when a small lesion is affected, but only in a targeted manner. |
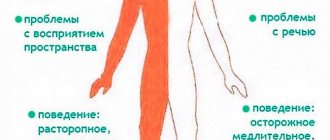
Right-sided stroke in men, women, and children provokes the loss of essential skills for a normal life. Recovery takes a long time, often you have to learn to walk, talk, write again, and regain sensitivity in the upper and lower extremities.
What are the causes of stroke?
What is the cause of stroke? Given the statistics, there may be various reasons. For example, arterial hypertension or atherosclerosis. Plus, unhealthy diet, dyslipidemia, alcoholism, severe stress, etc. Heredity also plays an important role.
An ischemic stroke develops as a result of a disruption in the passage of blood through one of the blood vessels supplying the brain. For example, due to occlusion of the carotid arteries. The cause of a sharp deterioration in cerebral blood supply may be a minor vascular spasm or thromboembolism. In turn, the cause of the latter is often cardiac pathology. The occurrence of the second type of stroke, that is, hemorrhagic, may be associated with the presence of various vascular pathologies. For example, cerebral atherosclerosis, systemic vasculitis and collagenosis. Rarely, but there are still cases when this type of stroke directly depends on blood clotting or incorrect therapy with anticoagulants and fibrinolytics.
Causes of diplopia
The appearance of such a pathology can be provoked by various factors: ophthalmological, infectious, neurological. For example, double vision can occur after eye injuries, when the axis of the eyeball is displaced as a result of an impact. Diplopia can result from damage to the optic nerve due to intracranial tumors.
This disorder is also noted during infectious processes: rubella, mumps, when the brain stem is affected. Even strong alcohol consumption can cause diplopia—drunk people often see double—or drug intoxication. Image displacement is also observed in botulism, multiple sclerosis, and thyrotoxicosis. Diplopia can also be a type of complication after eye surgery.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
Of course, the symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke are different, but they also have common signs. First of all, it is worth noting that the first type of disease develops more slowly than the second. At first, focal and general cerebral symptoms signal a stroke. In turn, the hemorrhagic type develops more rapidly, begins with general cerebral manifestations, against the background of which focal symptoms appear and progressively increase. In the case of subarachnoid hemorrhage, meningeal syndrome is typical.
Now about all the symptoms in more detail. By general cerebral pain we mean severe headaches, nausea, and often loss of consciousness. Focal signs depend on where in the brain the stroke occurs. If in the carotid artery, then there is a decrease or complete loss of muscle strength in the limbs of one side of the body. Homonymous hemianopsia is also possible, that is, loss of the same halves of the visual fields of both eyes. In some cases, photopsia (false appearance of light flashes, sparks, luminous lines) and visual hallucinations are noted. With a stroke in the vertebrobasilar area (it forms the right and left vertebral arteries that supply the cerebellum, trunk and occipital lobe of the brain), dizziness, diplopia, visual field defects, hearing impairment, oculomotor disorders, dysphagia (inflammation of the oral cavity, pharynx of the esophagus) are noted. Since without medical help it is impossible to understand where exactly the stroke occurred, one should rely on general cerebral signs. Once the diagnosis is made, surgical treatment is necessary.
Eye stroke: symptoms and treatment
Blood vessels deliver nutrients and oxygen to every cell in your body. When the vessels become narrowed or blocked by a blood clot, the blood supply is cut off. As a result, a stroke may occur. It affects not only the brain, but also the eyes. This condition is called central retinal artery occlusion. Symptoms may develop slowly over hours or days, or they may occur suddenly.
How to determine the disease?
- Only one eye is affected.
- Floaters, gray spots and flashes appear in the field of vision.
- There is pain and pressure in the eye, but strokes are often painless.
- Blurred vision or complete loss of vision.
If you have these symptoms, consult your doctor immediately. Even if it seems like you're feeling better. Left untreated, central retinal artery occlusion can lead to permanent vision loss.
What are the risk factors?
- Diabetes.
- Elderly age.
- Male gender.
- Glaucoma.
- Problems with blood pressure.
- Increased cholesterol levels.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Blockage of the carotid or cervical arteries.
- Smoking.
What complications can there be?
- Macular edema.
The macula is the central part of the retina, which is responsible for visual acuity. Swelling can lead to its loss. - Neovascularization of the cornea.
A condition in which blood vessels form where they should not exist. In severe cases, the retina may completely detach. - Neovascular glaucoma.
A sharp increase in pressure in the eye due to the formation of new blood vessels.
How is an eye stroke diagnosed?
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT). A non-invasive method that helps detect retinal edema.
- Fluorescein angiography. The patient is injected intravenously with a contrast agent, which allows the vessels in the eye to be examined using a special camera.
An ophthalmologist may also order additional tests to look for glaucoma, diabetes, or heart problems, since underlying conditions can cause a stroke.
How is an eye stroke treated?
Treatment depends on complications and the patient's overall health. The doctor may prescribe:
- Eye massage.
- Corticosteroids and other drugs.
- Panretinal laser coagulation of the retina is a laser treatment for eye pathologies.
How to prevent eye stroke?
- Visit your ophthalmologist regularly.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels.
- Keep an eye on your blood pressure.
- Check your cholesterol levels.
- Stop smoking.
An eye stroke is an extremely dangerous condition. Take care of your health and do not delay visiting your doctor. The sooner you start treatment, the better your chances of saving your vision.
How to treat strabismus during a stroke?
Since strabismus after a stroke is one of the most common problems, the question of how to cure strabismus after a stroke becomes the most pressing. To restore visual function after a stroke, there are several time-tested techniques. These include:
- drug therapy;
- therapeutic and preventive gymnastics for the eyes;
- operation.
What the treatment will be is decided by the ophthalmologist together with the neurologist, taking into account the type of disease, how the stroke progresses, the individual physiological characteristics of the patient and many other factors. In some cases, a comprehensive approach is used to achieve maximum recovery. Below we will talk about each method of treating strabismus after a stroke.
What does drug treatment include?
Despite the great development of medicine, there are still no special drugs aimed specifically at restoring vision after a stroke, but there are drugs that can solve local problems. The effect of medications after a stroke is usually aimed at the following results:
- normalization of blood flow in the brain;
- regeneration of rheological properties of blood;
- elimination of metabolic disorders;
- reducing the volume of necrotic tissue;
- normalizing oxygen delivery to the brain and reducing the sensitivity of cells to its lack.
Using such an integrated approach, it is possible not only to minimize the number of necrotic neurons, but also to restore some sections that were slightly damaged. The ophthalmologist also recommends taking medications aimed at relieving tension and blockage of blood vessels, which will help regulate blood supply. But usually such drugs are used in the first few hours after a stroke in order to eliminate focal signs as soon as possible.
Vasoactive drugs are used to reduce the volume of necrotic tissue. If the patient has increased sensitivity of cells to hypoxia, then vitamin E is prescribed. It is a powerful antioxidant.
Gymnastic exercises for the treatment of strabismus
This method is certainly one of the simplest, but quite effective. Especially when it comes to strabismus. However, you need to be patient, since eye gymnastics is not the fastest method of restoring vision. The ophthalmologist will tell you more about the exercises that are necessary after assessing the situation. It is worth noting that in most cases, gymnastics only relieves tension from the eyes, eliminates redness and burning, but cannot completely restore vision. It is recommended to train not only the visual organs, but also all parts of the body that have atrophied as a result of the stroke.
Causes and complications of diplopia
As we noted earlier, the causes of monocular and binocular diplopia can be different diseases and conditions.
The main causes of monocular diplopia include:
- Astigmatism is a visual defect caused by the curvature of the lens, cornea or eye, which causes a person to lose the ability to see objects clearly.
- Keratoconus is a disease of the eye in which the cornea thins and takes on a cone shape.
- cataract - clouding of the lens;
- dry eye syndrome - a lack of tear fluid that moisturizes the surface of the eye. Symptoms of dry eye include burning, redness, itching and vision problems.
— pterygium is the growth of degenerative tissue in the area of the inner canthus.
Binocular diplopia disappears if you close one eye. This indicates that your eyes cannot work together and indicates a problem with the brain or nerves. The most common causes of binocular diplopia include:
Nerve damage – The optic nerves are responsible for communication between your eyes and your brain. Inflammation and any other types of damage can cause double vision.
Diabetes is one of the most common diseases that causes nerve damage.
- cranial nerve palsy due to diabetes or high blood pressure;
— myasthenia gravis is an immune disease characterized by pathologically rapid fatigue of striated muscles. In the case of the eyes, we are talking about weakness of the eyelids, which leads to double vision.
- Graves' disease, diffuse toxic goiter or Graves' disease - all these are names for one condition, the cause of which is dysfunction of the thyroid gland. About 30% of people suffering from this disease experience vision disorders, including diplopia.
- squint.
Diplopia can cause complications , both temporary and chronic.
Some people who suffer from double vision experience nausea and dizziness. For others, double vision is accompanied by a feeling of tension in the eyes and sensitivity to light.
It is important to understand that headaches accompanied by visual disturbances may be a symptom of infections or brain tumors.
Surgery to treat strabismus after stroke
Often, for strabismus after a stroke, doctors resort to surgical intervention. It is important to understand that the operation will not eliminate the causes of strabismus and the consequences of a stroke, but will return the eyes to their natural position and reduce the risk of diplopia, that is, double objects, so that a person can normally perceive the world around him. At the moment, there are several types of elimination of strabismus after a stroke. But what type of operation the specialist chooses will depend on the type of strabismus and the general condition after the stroke.
Recommendations
Stroke is an extremely serious disease that leads to damage not only to the visual organs, but also to other organs. Therefore, immediate contact with specialists at the first signs of a stroke is of paramount importance. It is also important to note that an independent disease such as an eye stroke often occurs. In this case, a separate course of treatment is prescribed. The recovery period will directly depend on how quickly medical care was provided and, of course, on the degree of damage and the age of the patient. Today, strabismus after a stroke can be cured in various ways or using an integrated approach. What kind of therapy will be determined solely by the ophthalmologist.
Symptoms and signs of double vision
The patient complains of double vision: complete, partial, at a certain point in the visual field.
This symptom also depends on the distance from which a person looks at the object. There are cases when double vision occurs when looking at close or distant objects.
There is a difference in the contrast and brightness of parts of one object in question.
A frequent accompaniment of diplopia is dizziness.
It is difficult for the patient to move in space, drive a car and simply move various objects. This occurs due to a slight loss of orientation.
In addition to all of the above, when the image is doubled, painful sensations occur in the eyes.
Useful video
Treatment for double vision: