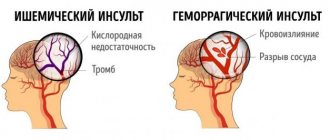
Stroke is a serious brain disease characterized by circulatory disorders, focal lesions of brain tissue, and death of neurons. A stroke can be hemorrhagic or ischemic. Hemorrhagic stroke is less common than ischemic stroke and is characterized by rupture of blood vessels and hemorrhage in brain tissue. Ischemic stroke is more often diagnosed in older people and is characterized by impaired blood flow in the cerebral arteries and the death of neurons in the area of blood supply to brain tissue by the affected artery. When a stroke develops, the patient requires emergency care: the sooner the patient is admitted to the hospital, the more effective the care provided by doctors will be.
In addition to drug treatment of stroke, great importance is attached to rehabilitation therapy, which begins to be carried out in the acute period of the disease. At the Yusupov Hospital, various methods of physiotherapy and exercise therapy are used to restore patients after a heart attack and stroke. With the help of a comprehensive rehabilitation program, the patient is rehabilitated - restoration of motor activity, coordination of movements, visual function, sensitivity. The neurorehabilitation department of the hospital is equipped with modern devices, verticalizers and various simulators, including robotic ones.
The influence of exercise therapy on the patient’s nervous system
Therapeutic exercise is the performance of certain physical exercises, which begin with the simplest movements of the patient after he regains consciousness, then the physical activity gradually increases, the exercises become more complex. Exercise therapy helps improve blood circulation in organs and tissues, accelerates the process of restoration of various body functions, and improves metabolism. Physical therapy exercises for each patient are selected individually depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and concomitant diseases. An individual physical therapy program at the Yusupov Hospital is drawn up by a rehabilitation doctor.
Make an appointment
Why does the hand stop moving after a stroke?
A stroke occurs due to an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, in which a portion of it dies. Depending on which part of the brain is affected, a person’s brain function is impaired. Because of this, various organs may stop functioning, including limbs - for example, a hand. Because the nerve pathways cross, the left arm will be affected if the stroke occurs in the right hemisphere, and vice versa.
At the same time, there is another dependence: the closer to the right hemisphere the stroke occurred, the more painful the damage to the limbs is felt. This happens because it is in the right hemisphere of the brain that the nerve centers responsible for the motor activity of the body are located. Therefore, a stroke, after which the left arm fails, usually requires longer rehabilitation.
Both types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic - can cause such lesions and impair the motor activity of the hand. Disturbances can be different: pain, loss of sensitivity and coordination, complete paralysis of a limb.
Passive and active rehabilitation after stroke
The first classes with the patient are conducted by a physical therapy instructor in the ward. The patient performs simple movements with his arms and legs with the help of an instructor - this type of rehabilitation is called passive. Passive rehabilitation of the upper and lower extremities begins with the development of large joints with a gradual transition to small joints. Rehabilitation therapy begins with the shoulder and hip joints. After developing the hip joint, the instructor helps the patient flex and extend the lower limb, develops the knee, then the ankle joint, and lastly the doctor develops the joints of the foot.
The rehabilitation specialist performs massage from the foot to the thigh. During hand rehabilitation, exercises begin with the development of the shoulder joint, then flexion-extension and rotational movements of the hands are carried out in the area of the elbow and hand joints. Massage of the upper limbs is performed from the fingers to the shoulder. A set of exercises combined with massage stimulates brain function. With partial restoration of motor function, exercise therapy exercises become more complex, and the patient begins to perform the exercises independently. The time for gymnastics increases from 10 minutes to half an hour, and active rehabilitation of the patient begins.
If the brain damage is significant, the patient is paralyzed, sensitivity is lost, rehabilitation is carried out with the help of medication, massage, electromagnetic stimulation of nerve cells, acupuncture, and reflexology. After partial restoration of motor function, the rehabilitation doctor introduces therapeutic exercises into the program.
How to restore an arm after a stroke
A positive attitude and support from family have an impact on rapid recovery from illness. Partial paralysis of the arm is a common occurrence after a stroke and is characterized by stiffness of movement and limited motor ability of the arm. Functional paresis (partial paralysis) refers to neurological syndromes, caused by disruption of the nervous system, damage to the nervous system pathway due to damage to the cerebral cortex after a stroke. Paralysis of the arm is the complete absence of voluntary movements of the limb. Such conditions require the help of rehabilitation specialists. The neurology and rehabilitation clinics of the Yusupov Hospital treat patients after stroke. The hospital’s specialists are a team of neurologists, psychotherapists, massage therapists, and therapeutic exercise specialists. Individual sessions with the patient are carried out taking into account the severity of his condition.
Recovery from a stroke may involve the hand or the entire limb. With partial paralysis, the ability to move the arm or hand freely is impaired; the person cannot fully care for himself or perform basic actions. To restore motor ability, the patient must perform daily exercises for finger motor skills and limb motor skills. Specialists at the rehabilitation department of the Yusupov Hospital use special simulators to help restore brain function, sensitivity and motor activity of the limbs. The rehabilitation process after a stroke is not quick and requires patience. Exercises to restore motor activity of the hand will need to be performed at home, after discharge from the hospital.
Rehabilitation exercises on simulators
The Yusupov Hospital uses two types of simulators for the rehabilitation of patients after a stroke - mechanical and robotic. Mechanical exercise machines include exercise bikes, treadmills, and exercise machines for restoring balance and gait. Robotic simulators are equipped with electronic biosensors that stimulate activity by influencing the affected limbs. Robotic simulators have wide functionality; they are programmed taking into account the patient’s needs, promote the transmission of nerve impulses from the brain to the injured limb, and stimulate motor activity.
Rehabilitation exercises after a stroke are performed using multifunctional exercise equipment and sports equipment. There are different types of simulators:
- To restore motor activity, use a flexion/extension simulator, a simulator for developing the joints of the limbs, exercise tracks, and exercise bikes.
- For bedridden patients, exercise equipment in the form of a bed or bicycle is used.
- To restore balance, gait, and motor activity, a horizontal simulator is used.
- For patients who cannot yet stand, a seated exercise machine has been created to develop and strengthen the back muscles.
A set of measures to restore the hand after a stroke
Restoration of hand motor skills after a stroke occurs under the supervision of physiotherapists. The list of measures includes procedures in different areas:
- physical rehabilitation therapy;
- drug treatment;
- psychological counseling.
Physical rehabilitation therapy
Physical rehabilitation is a critical part of restoring arm movement after a stroke. It involves doctors of various specializations, but primarily physiotherapists, neurologists and rehabilitation specialists. Treatment is aimed at developing and strengthening everyday motor abilities.
The process uses:
- physical therapy and gymnastics
: physical exercises on the arm - from the simplest gradually to more complex, developing fine motor skills; - action and observation therapy
- during these procedures, the patient watches another person performing some actions with his hand (in person or on video), and then repeats after him. The method triggers the work of similar areas of the brain, and this helps restore motor skills of the hand; - mirror therapy method
- within the framework of this rehabilitation technique, a mirror is placed between the patient’s hands in such a way that the image of the movement of the healthy limb creates the illusion of the same normal movement of the affected arm; - tekar therapy
- radio wave exposure to the body to produce endogenous heat. This helps reduce pain and speed up the tissue healing process; - massage techniques
; - acupuncture, modeling
from dough, plasticine or clay; - hydrotherapy methods
: hydromassage baths, contrast and circular showers.
The rehabilitation department has an occupational therapy department and a neuromotor department for the upper limbs. Robotic technologies are used here, including virtual reality. Neuromotor rehabilitation using such high-tech systems is a modern method of restoring hand motor abilities.
The greatest effect is achieved when the doctor competently combines all these methods. In this case, the specialist must first assess the extent to which the patient’s condition allows him to undergo these measures.
Drug treatment
In most cases, rehabilitation of the hand after a stroke requires drug treatment. However, it must be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
There are no universal dosages and regimens; each patient needs his own therapy. To make a decision about which drugs and in what doses the patient needs, the specialist studies all available information about him. In particular, medical history, anamnesis, data on clinical manifestations, results of previous examinations and tests.
The doctor may also change your medication regimen during treatment if he has reason to believe that the current dosage is ineffective or insufficient. The basis is new biometric data, information from the patient’s daily records (“diary of a stroke patient”). First of all, we are talking about the dynamics of blood pressure, heart rate, as well as side effects from medications.
Types of drug therapy that are used to restore limb activity after a stroke:
- intramuscular and intravenous injections
, which are aimed at increasing vascular activity and strengthening neurons. These include Botox injections, which significantly reduce muscle spasticity; - lymphotropic drugs
, which are injected directly into the lymphatic system so that the active substance gets into the arm faster; - analgesics
(to reduce pain in the arm),
muscle relaxants
(to relax the muscles of the limb),
anticoagulants
(to prevent the formation of blood clots),
antidepressants
(to treat depression that has developed due to illness) and other drugs, including antibiotics, vitamins and potent drugs - of necessity.
Psychological counseling
The patient’s internal state greatly influences the process and result of restoring the activity of the arms and legs.
Rehabilitation in a specialized center forces a person to change his usual way of life: he distances himself from society, loses independence and independence even in everyday worries. This cannot but affect the psychological state and leads, at a minimum, to discomfort, and at most to the development of depression.
The patient needs understanding, respect and care, but may also experience anger and powerlessness due to loss of control over his own body. To deal with this, a psychotherapist is needed. He will develop the correct technique for working with the emotional state and select a communication method for the family. The doctor will also prescribe pharmaceutical treatment to the patient if it is necessary and fits into the overall drug treatment plan.
Hand exercises for stroke rehabilitation
Hand exercises improve motor activity and help restore lost functions. In severe cases and in the absence of early rehabilitation, hand functions are often not restored or partially restored. In some cases, rehabilitation does not help; doctors carry out bipolar stimulation - an effect on immobile joints and muscles of the body using artificially created impulses from the brain to the body. This helps restore reflexes and sensitivity, improve blood circulation in the tissues. Then the patient undergoes rehabilitation using exercise therapy and other methods.
The motor activity of the hands and the motor skills of the fingers are most difficult to restore. You can often see trembling hands in a patient after a stroke; he cannot hold a ballpoint pen in his hand, cannot write, and does not grasp objects well. Especially for such patients, they conduct classes in modeling from plasticine, with a Rubik's cube, teach them to write again, and work on a silicone simulator. Doctors use reflexology if a patient has suffered a severe stroke. This helps restore fine motor skills, improve grasping movements, flexion and extension of fingers, and joints of the hand. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients undergo rehabilitation on computerized simulators using a comprehensive recovery program, which includes massage and physical therapy exercises.
Hand exercises are not complicated and do not require special exercise equipment or devices; the patient can perform them at home:
- Lie on the bed, move your arms back and grab the headboard. Tighten the muscles of your arms and body, imitating a pull-up. Raise your legs up or stretch them straight.
- Using rotational movements of bent arms, knead the shoulder joint.
- Sit upright on the bed, place your hands behind your back as close to each other as possible, tilt your head back, then return to your previous position.
Restoring an arm after a stroke at home
For complete rehabilitation, the patient’s psychological mood is important. A psychotherapist at the rehabilitation center of the Yusupov Hospital will help restore psychological balance. Restoring sensitivity and motor activity begins with the prevention of muscle spasticity. The arm muscles shorten after a stroke and lose their elasticity due to prolonged inactivity. Classes begin with passive gymnastics for the joints of the limb, which should be performed in a position comfortable for the patient. When the patient can make the first movements with his hand, the joints will already be ready for motor load. Restoring an arm after a stroke at home will be faster if the patient is helped by loved ones.
Classes begin with the formation of a message from the brain to the limbs - the patient must mentally imagine the movement of the limb. Regardless of whether one or both limbs are damaged after a stroke, the exercise should be performed with both limbs. Such exercises activate areas of the brain responsible for the functioning of pathways. Mentally imagining hand movements is an exercise that can be performed throughout the day, an unlimited number of times.
Performing gymnastics with the help of various objects - a ball, a rolling pin, small objects that improve the motor skills of the fingers, allows you to speed up the recovery of brain function. Exercise with a stick - bending, extending the arms, allows you to regain lost skills. When performing gymnastics, in most cases, the help of loved ones is required - they can give commands to perform movements, help perform movements for the first time, bend and straighten a limb, and give massage. Gymnastics often causes pain and irritation in the patient. Despite the pain, the load should gradually increase, the exercises should become varied. Over time, the patient must perform gymnastics without assistance, fully bearing the entire load when moving.
For the shoulder joint
Restoration of the forearm and shoulder joint takes place with the help of flexion and extension exercises, rotation, push-ups, muscle tension and relaxation, clapping, and massage. To do this, use exercise machines, dumbbells, and various devices. First, the arm is kneaded, then a set of exercises is performed; therapeutic exercises are always combined with a massage of the limbs. A set of exercises for the shoulder joint:
- The patient lies on his back, arms extended along the body. The instructor holds his hand at the elbow to avoid bending, takes the patient's palm with his other hand and moves the patient's arm up and down.
- The instructor performs circular movements with the patient's arm fixed in a straightened state.
- The patient lies on his back, with his arm slightly to the side. The instructor turns the straightened arm over, palm down, then up.
For lower limbs
Exercises for the lower extremities begin to be performed as soon as the patient regains consciousness. At the initial stage, the instructor helps to bend and straighten the lower limbs; over time, the patient will be able to imitate walking in a prone position, then get out of bed, learn to maintain balance, and walk without support. Exercises for patients in the supine position:
- The patient is in a supine position, the leg is straightened. The instructor turns the leg with the foot inward, then outward.
- The patient is in a supine position, the leg is bent at the knee. Holding one hand under the knee, the instructor performs circular movements with the limb, holding and pressing with the other hand in the hip joint area.
- The patient is in a supine position, the affected leg is bent at the knee. The instructor fixes the leg at a right angle, holding it with the other hand under the knee, bends and straightens the lower limb.
- The patient is in the same position on his back, with the leg fixed at a right angle. The instructor, holding the patient's leg under the knee, moves it away from the body and returns it back.
These exercises are performed by the patient after he is allowed to sit:
- In a half-sitting position, holding the edges of the bed with both hands, stretch both legs forward as evenly as possible, bend over, throwing your head back. While stretching your limbs, take a deep breath, return to your previous position and exhale.
- Remain in the same body position, keep your breathing calm and deep, slowly lift your right leg up and lower it back, then your left leg.
- In a half-sitting position, bend your leg, pull your bent leg at the knee as close to your chest as possible (you can help with your hands), and tilt your head forward during the exercise. Bending the leg, inhale, straightening the limb, exhale, return to the previous position.
Exercise therapy to restore visual function after stroke
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients with visual impairments will be able to undergo examination, treatment, rehabilitation, and, if necessary, surgical treatment in a network of partner clinics. Rehabilitation after a stroke includes exercises that you can then do at home. Depending on the type of visual impairment, rehabilitation therapy is carried out:
- If lateral vision is impaired, intensive medical and restorative treatment is carried out, undamaged areas of the cerebral cortex take over the lost function, and vision is restored. In this case, the doctor marks with a red line a passage of text on the page of the book on the side of which lateral vision is weakened. Before starting to read, the patient must look for the red line - this will be the beginning of the text.
- With oculomotor nerve palsy, the patient cannot look straight and his eyes look in different directions. Such a disorder can resolve over time with proper and timely treatment and rehabilitation. With paresis of the oculomotor nerve, accommodation may be impaired. Over time, the patient gets used to using only central vision. To determine the impairment of perception of objects at far and near distances, the following test is performed: the doctor takes a pencil in each hand and brings one of the pencils closer to the patient’s face, then moves his hand back.
- If atrophy of the oculomotor nerve develops, the patient's function of the upper eyelid muscle is impaired. Nystagmus or trembling of the eyeballs may occur. Often this condition leads to visual impairment.
To restore vision, the doctor asks the patient to draw the other half of an object in a drawing or take part in a certain type of computer game. The patient is asked to follow with his gaze the pencil in the doctor’s hand, which moves in front of the patient’s face to the right, then to the left, up or down. The patient should follow the pencil without turning his head. To improve blood circulation, eye massage is necessary and beneficial. The eyes are closed, with gentle movements in a circle the patient massages the eyeballs, lightly pressing on them. The exercise should be performed for 10-20 seconds.
To restore visual function, a number of eye exercises are performed:
- Rotate the eye to the right, then to the left - repeat several times.
- Look up, then down - repeat the movement several times.
- Movement of the eyes in a circle - to the right, then to the left.
- Take a short break with your eyes closed, open your eyes and blink frequently for a few seconds.
- Close your eyes tightly and relax - repeat several times.
- Fix your eye on the object, then turn your head to the right and left without taking your eyes off the object - do this several times.
Types of mobility impairments
Neurologists note that after an ischemic attack on the brain, the arms and legs may move incorrectly, sensitivity decreases, and in the most difficult cases, total immobility develops. Ischemic or hemorrhagic - it doesn’t matter what kind of stroke was diagnosed: restoring the arm will require professionalism, patience and unconditional adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
- Paresis is an incomplete loss of motor function, the arms become weaker.
- Hemiparesis is a malfunction of a limb on one side of the body (right or left); with paraparesis, both limbs are affected; with monoparesis, only one limb is affected.
- Paralysis (plegia) - due to central damage to muscle tissue, the ability to move is completely lost.
- Paresthesia - in this case, the hand does not hurt after a stroke, it ceases to feel anything: touch, pain, cold or warmth.
Restoring fine motor skills after stroke
Fine motor skills are restored with the help of simple exercises that allow you to restore fine hand movements and finger flexibility. The most effective activities for restoring fine motor skills are putting together puzzles, various objects from small parts of a construction set, drawing, fastening buttons on clothes, and lacing shoes. To restore the function of the hand and fingers, the patient is asked to take two nuts in his hand and roll them with the movement of the palm and fingers. Recommended for patients after a stroke to develop fine motor skills:
- Sort through the beans and peas, separating the peas from the beans.
- Use special silicone hand trainers with spikes to massage your palms and fingers.
- Tighten and unscrew nuts, close and open the lock with a key, turn on and off the lights in the room, write texts.
What exercises are used after a stroke to restore paralyzed limbs?
The basis for the treatment of paralysis and paresis of the limbs is exercise therapy. A special set of exercises is being developed for the arm after a stroke, including the use of medical simulators.
Moreover, modern robotic simulators with extensive data analysis capabilities make it possible to gradually develop paralyzed limbs without pain. The sensor system sensitively diagnoses muscle contraction, pulse, etc., which, in turn, allows you to adjust the load during exercise after a stroke so as to eliminate pain.
A physical therapy instructor should supervise the patient’s exercise on exercise machines. After a stroke, during exercise it is necessary to monitor all indicators of the condition - blood pressure, heart function, breathing, etc., in order to eliminate the possibility of complications.
During rehabilitation after a stroke, mobile simulators are used for a bedridden patient. For example, Motomed can be used to develop a paralyzed arm after a stroke, and Artomot can be used to develop knee and hip joints. The verticalizer provides walking or joint function, as well as the necessary range of motion even in completely paralyzed patients.
In exercise therapy after a stroke there is a set of exercises to develop and maintain muscle tone without the use of exercise equipment. In addition to daily gymnastics with an instructor in the rehabilitation center, the set of exercises after a stroke includes art therapy, during which patients develop fine motor skills - sculpt, paint, work with scissors, needles and other small objects. This is especially valuable for restoring hand mobility after a stroke and helps normalize the functioning of the central nervous system.
For recovering patients, a health path has been created on the territory of the center - paths for daily race walking with dosed exercise.
Restoring speech after a stroke
Speech function after a stroke is restored much worse than motor function. Its recovery can take a long time, over several years. Speech therapists at the Yusupov Hospital are developing a program and working with the patient to restore speech throughout the entire period of his stay in the hospital; after discharge from the hospital, his relatives are involved in the patient’s rehabilitation. To restore speech, the following techniques are used:
- Pronunciation of an incomplete word - the patient must complete the word independently.
- If speech function is completely lost, rehabilitation begins with the pronunciation of individual sounds.
- When the patient learns to pronounce words, he is forced to repeat short poems and sayings.
- Singing is considered one of the best methods of speech restoration.
- In order for the patient to learn to speak faster, the facial muscles and tongue muscles should be trained. For this purpose, the patient is taught to curl his lips into a tube, stick his tongue out of his mouth as far as possible, and lick his lips with his tongue, first in one direction, then in the other. Lightly bite your lower lip, then your upper lip, and bare your teeth.
Make an appointment
Rehabilitation of the patient at home
Before the patient is discharged from the hospital, relatives receive recommendations on caring for the patient after a stroke. Recommendations for rehabilitation will be provided by the attending physician. The rehabilitation exercise program is performed every day without breaks, 2-3 times a day. Performing physical exercises should not tire the patient or cause him pain. Exercises in a sitting position help prepare the patient for walking.
When the condition improves, exercises are performed in a standing position; they help eliminate neurological disorders as much as possible by restoring fine movements. The patient performs exercises with an expander. From a standing position, he bends down and picks up a matchbox from the floor. Performs breathing exercises with raising your arms up while inhaling, standing on your toes, then lowering yourself onto your entire foot, lowering your arms, exhaling, leaning forward. A comprehensive recovery program is aimed at reducing muscle tone, improving blood circulation, preventing joint contracture, restoring and maintaining fine motor skills, speech, preventing the formation of bedsores and the development of inflammatory processes.
The Yusupov Hospital uses modern rehabilitation methods, uses various types of exercise equipment, and physical therapy exercises. Rehabilitation doctors develop an individual rehabilitation program for each patient.