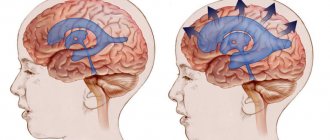
Babies, as a rule, often fall in the first year of life, when they are learning to walk or due to the neglect of adults, falling out of bed is very common. If this occurs, it is important to calmly assess the situation and pay close attention to signs of injury.
Although it may look scary, falling out of bed usually does not cause serious harm. However, injuries can occur, so parents should know the signs that indicate their child needs medical evaluation after a fall.
What to do first
If your child falls out of bed, it is important to remain calm. As long as the child’s fontanelles are not closed (the large one in the middle of the crown and the small one at the back of the head), in the event of an impact they will protect the baby from a fracture of the cranial bones.
When a baby or toddler falls out of bed, it is important to remain calm and quickly assess the situation.
Call 911 immediately without touching the child if:
- He lost consciousness
- The child is motionless (before the fall he was active, perhaps crawling and rolling over, after the fall he lies motionless).
- Convulsions appeared (the child’s arms and legs involuntarily twitch, eyelids tremble).
- Coordination is lost. This symptom can be observed in a child who already knows how to sit and perform actions with toys. For example, before the fall, he skillfully put objects into some container, but after the fall he cannot stand or stumbles every 2-3 steps.
- Vomit
- Sudden severe lethargy and drowsiness of the child.
- Strong crying
- Bleeding from the nose (this can be a rather dangerous condition, which indicates a serious injury to the cranial bones. Bloody or, conversely, clear discharge may appear from the ears).
Moving a child with a head or spinal injury can cause serious complications. However, if the child is in an area where there is a risk of further injury, he or she can be carefully moved to a safer location.
If your baby is vomiting or having a seizure, gently turn him onto his side. Make sure your baby's neck is straight while you turn.
Check him over carefully, paying close attention to his head and any bumps, bruises or other injuries. Check the rest of the baby's body, including the arms, legs, chest, and back. If you see damage, under no circumstances should you adjust the joints yourself or touch or press on the bones. You can apply cold to the site of the bruise - any food from the freezer will do for this. They need to be wrapped in a soft towel and held where the redness has formed. If there is a wound, it must be treated with hydrogen peroxide to stop the bleeding, apply a sterile bandage and wait for the doctor to arrive.
If the child does not show any visible signs of injury, observe him for a short time to make sure nothing changes.
Cyanosis (blueness of the skin)
Iron deficiency
22165 January 26
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Cyanosis: causes of appearance, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
In many cases, the condition and color of the skin are an important diagnostic criterion for the doctor. Blueness of the skin (the medical term is cyanosis) indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood. Unfortunately, with the gradual development of cyanosis, a person and the people around him often do not notice a progressive change in skin tone, while the doctor is especially wary of cyanotic skin, which may indicate diseases of the vital organs of a person.
Types of cyanosis
Cyanosis is classified according to several parameters, each of which is important for the diagnostic search.
Depending on the prevalence of cyanotic coloration of the skin, total
cyanosis, characterized by a change in color of the entire surface of the skin, and
local
, localized in certain areas of the skin.
Local cyanosis may be central
and
peripheral
. Central cyanosis includes cyanosis of the oral mucosa (perioral cyanosis), nasolabial triangle, and area around the eyes (periorbital cyanosis). In addition, peripheral cyanosis, or acrocyanosis, is distinguished, which is characterized by a bluish coloration of the parts of the body most distant from the heart, located on the periphery - cyanosis of the fingers and toes, cyanosis of the earlobes, etc.
Depending on the speed of development, acutely emerging
cyanosis (rapidly progressing) and
chronic
cyanosis, which develops gradually and is present in a person for a long time.
Possible reasons for the development of cyanosis
The color of the skin is formed by two main factors: the presence of coloring pigments (for example, melanin) and the condition of the superficial blood vessels (the degree of opening of their lumen and the color of the blood in them).
The bluish tint of the skin is determined primarily by the color of the blood.
It is known that one of the most important functions of blood is the transfer of oxygen by attaching it to the protein hemoglobin, which is part of red blood cells.
Blood enriched with oxygen in the lungs is called arterial and has a scarlet tint.
As the cells of organs and tissues become saturated with oxygen, there is less oxygen in the blood and it takes on a cherry hue. Blood poor in oxygen is called venous. It is the accumulation of venous blood in the tissues that determines the characteristic bluish tint of the skin.
There are two main reasons for the accumulation of venous blood in tissues. The first reason is a circulatory disorder, in which the outflow of venous blood from the cells is disrupted. This mechanism underlies the development of cyanosis of the skin in diseases of the heart and blood vessels. The second reason is a violation of the enrichment of blood with oxygen in the lungs, which occurs with diseases of the respiratory system, with damage to the respiratory center (the functional structure of the brain and spinal cord that regulates the functioning of the respiratory muscles) or with a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the air, for example at high altitudes.
What diseases cause cyanosis?
Cyanosis in most cases is a manifestation of pathology of the cardiovascular or respiratory systems.
Among heart diseases, it is worth noting a group of congenital heart defects, which are formed during the intrauterine development of the fetus and are manifested by cyanosis from infancy, and a group of acquired heart diseases, which includes a wide range of diseases leading to the development of heart failure. We list the main ones:
- Coronary heart disease, which includes, among others, angina pectoris and the consequences of myocardial infarction. The basis of this disease is insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
- Cardiomyopathies are primary lesions of cardiac muscle cells.
- Arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation.
- Infectious myocarditis is an inflammatory lesion of the heart muscle of infectious origin.
- Heart valve defects, such as aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation, etc.
Among other diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is worth noting a violation of the patency of the peripheral veins, as a result of which there is a retention of venous blood in one or another segment of the body with the development of local cyanosis.
An example is chronic venous insufficiency of the lower extremities, in which varicose veins and a bluish discoloration of the skin of the feet and legs are observed.
Diseases of the respiratory system, often leading to the development of respiratory failure with the appearance of cyanosis, include:
- Pneumonia (pneumonia).
- Bronchiolitis (inflammation of the smallest bronchioles - the airways).
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Bronchial asthma, not controlled by taking special medications, and other rarer diseases.
It must be taken into account that the primary cause of circulatory and respiratory disorders can be explained by pathologies of other organs and systems, for example, endocrine glands, the central nervous system.
Which doctors should I contact if cyanosis develops?
Often, diseases of the circulatory and respiratory organs are treated jointly by several specialists. A therapist almost always appears among them. It is to him that you need to contact if a bluish tint of the skin appears. After the examination, the issue of referral to doctors of a narrow specialization is decided, for example, a cardiologist, pulmonologist (a doctor specializing in lung diseases), an allergist, an endocrinologist, a surgeon.
Diagnosis and examinations for cyanosis
The success of diagnosing the disease that led to the development of cyanosis largely depends on the conversation between the doctor and the patient and on the clinical examination. The patient needs to be told when cyanosis appeared, how intensively it developed, and on which parts of the body it manifested itself at first.
It is necessary to describe accompanying complaints, for example, cough, shortness of breath, interruptions in heart function, swelling, etc.
As a rule, acute cyanosis is accompanied by other significant manifestations, and it is these that serve as a reason to consult a doctor.
After the conversation, the doctor will examine the condition of the cardiovascular system, respiratory system and rule out damage to other organs. As a rule, already at this stage the doctor assumes one or another disease, the presence of which can be confirmed using laboratory and instrumental research methods:
- An exercise electrocardiogram can help diagnose heart disease and suggest lung disease.
Possible injuries
Several possible injuries can result from a fall, including:
Shake
A physician should evaluate head injuries for concussions.
A concussion is a type of head injury that usually occurs when a blow to the head causes the brain to receive a jolt inside the skull. It is difficult to detect a concussion in a toddler because they cannot describe their symptoms.
Signs of a concussion in an infant include:
- loss of consciousness
- inconsolable crying
- vomit
- excessive sleepiness
- long periods of silence
- refusal to eat
- temporary loss of recently acquired skills
- irritability
Damage to soft tissues.
The scalp is the skin that covers the head and contains many small blood vessels. Even a minor cut or injury can bleed profusely, making the injury appear more serious than it is.
Sometimes, an internal hematoma under the scalp can cause swelling on the baby's head, which can last for several days.
Skull fracture
The skull is the bone that surrounds the brain. Possible skull fracture if falling from a high place.
Infants with a skull fracture may have:
- depressed area on the head
- clear fluid coming from the eyes or ears
- bruises around the eyes or ears
Take your child to the emergency room immediately if he has any of these signs.
The brain is a delicate structure that contains many blood vessels, nerves and other internal tissues. Falls can damage these structures, sometimes severely.
Parents have powerful intuition. If something seems wrong with your child, it is important to understand it so you can contact a doctor. It's always better to be safe and make sure there are no serious injuries.
First aid
The first thing to do is call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, you must:
Provide the victim with peace (you can cover him with a blanket).- If the child has lost consciousness, it is necessary to lay him on his right side, bend his left arm and leg.
- If damage is detected on the skin, they are treated with hydrogen peroxide. You can also apply cold to the injured area of the head.
- If bleeding occurs, cotton-gauze swabs will help to cope with it.
Important! It is strictly not recommended to give the victim any medications before the doctors arrive.
In any case, if the temperature increase is insignificant, then there is no need to bring it down. And temperatures above 38°C should be reduced gradually, using the doctor’s recommendations.
A concussion is a serious and dangerous injury. Self-medication can lead to complications. After providing first aid, further actions should be performed only as prescribed by doctors.
Usually the victim is prescribed vitamin complexes. A slightly elevated temperature (about 37°C) can persist for up to two weeks. There is no need to knock it down.
Important! During home treatment, if the temperature exceeds 38°C, the general condition worsens or any individual symptoms intensify, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Most often, the victim’s condition completely normalizes after 3 weeks. If all medical instructions are followed, the concussion goes away without complications. The child can return to his previous lifestyle again.
Home care
The doctor may recommend rest for your child after a fall.
Your child may need some sleep after a fall, especially if it happens during or after a nap. It may be helpful to let your child rest. However, your doctor may recommend waking your baby at regular intervals to check on him.
Waking up your baby may make it easier to spot any signs of a more severe head injury. The child must:
- breathe normally
- acknowledge your parents or guardians
- easy to wake up
If not, contact your doctor or seek emergency medical attention.
Falling out of bed can cause headaches, neck or body pain in a child. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen may help calm your child. It is best to check the type of medication and dosage with your doctor .
Rest is the best treatment after a head injury. Parents should maintain quiet activities for several days and ensure that the child avoids active play.
Prevention
Fall prevention is the best way to keep your child from getting a head injury. However, accidents do happen. After a fall, it is important to reevaluate the safety and security of children at home.
Never leave a child unattended on an adult bed, even if the pillows are in place, to prevent them from getting close to the edge. In addition to falls, adult beds pose a risk for other types of accidents, including entrapment and suffocation.
Also, do not place a car seat or booster seat on top of a raised surface, even after you have secured your child.
Always put your baby in a crib when leaving him alone in the room. There should be no soft bedding in the crib that could crush or suffocate the baby.