Causes of stuttering
Stuttering is a disorder provoked by psychological and physical factors. The medical name for this speech problem is logoneurosis; it is studied by both medical workers and psychologists, grouped into groups.
Biological prerequisites (heredity)
It is noted that if the mother or father suffered from stuttering, then the child’s chance of developing logoneurosis from early childhood increases. Also, this speech disorder can be transmitted through generations if the grandparents had mild or complicated stages of the pathology.
Physiology
In most cases, somatics influences:
- the brain is functionally affected;
- there were head injuries while in the womb;
- past infectious disease;
- disorder of the autonomic nervous system, etc.
In addition, stuttering is provoked by general physical or nervous exhaustion, a weakened immune system, defects in the formation of the speech apparatus, insufficient development of motor skills, etc.
Social influence
The social factor influencing a person disturbs and changes the general internal and external state. Children suffer from disturbances in the functioning of the speech apparatus due to communication problems:
- quarrels and misunderstandings in the family;
- any aspects of education are not covered;
- do not find a common language with their peers.
Psychology
Children and adults are susceptible to psychological factors that influence their future interactions with others. Logoneurosis can develop due to:
- psychological trauma;
- acute emotional experiences (they can be both positive and negative);
- severe fear;
- psychological fatigue;
- information exhaustion;
- stressful situations, etc.
These factors depend on the person; not all life circumstances can lead to disorders and problems. If you set your priorities correctly and cope with psychological barriers, then speech disorders can certainly be avoided.
Those who stutter are most often withdrawn, which prevents them from correcting and restoring correct speech skills. Logoneurosis, which arose due to psychological reasons, is treated faster and easier.
First, the prerequisites for the onset of the problem are examined, and then a comprehensive treatment method is prescribed. Logoneurosis must not only be eliminated physiologically, the psychological causes of stuttering must be eradicated so that in the future they do not again contribute to the development of pathology.
Causes
Today, scientists distinguish two main types of stuttering . The first occurs in children with a defect in the nervous system. The reasons for such stuttering are: hereditary predisposition, trauma during childbirth, difficult pregnancy of the mother, frequent illnesses in the first years of life. Outwardly, the child seems quite healthy and smart, but he stutters. And during a neurological examination, such children usually show signs of increased intracranial pressure, changes in reflexes and increased convulsive readiness.
The second type of stuttering occurs in children with an initially healthy nervous system. They become stutterers as a result of neuroses caused by severe overwork and stress. The causes of neurotic stuttering can be very diverse: a cat suddenly fell from the closet was frightened, he overworked himself by memorizing an excessively large number of poems at the request of his parents, he was upset because of his grandfather’s illness. Of course, not every child will stutter after watching a film about Freddy Krueger, but an impressionable and nervous child will. With this type of stuttering, the speech defect can intensify with emotional excitement and neuropsychic stress.
There are also exotic causes of stuttering. It happens that a child begins to stutter in order to become like a stuttering relative or acquaintance. And some children become stutterers forever after they are forcibly retrained from left-handed to right-handed.
A speech disorder such as scanned speech may be similar to stuttering, in which the patient speaks sometimes quickly, sometimes slowly, sometimes loudly, sometimes quietly - such pronunciation is characteristic of a disease of the cerebellum and is otherwise called speech ataxia. True stuttering increases with excitement, weakens in a calm environment, people who stutter sing well.
Statistics
Logoneurosis is considered a problem that arises more often in childhood than in adulthood. According to statistics, around one to three percent of children worldwide stutter. These statistics vary depending on location, age, and nationality.
Boys are four times more likely to develop a stutter than girls. Many people do not know what logoneurosis is and whether they have it, since the pathology can manifest itself in a milder form.
It has been proven that stuttering in adults, which they suffer from since childhood, is much more common in people who grew up in orphanages and boarding schools. It is obvious that early separation from parents and an unfavorable social climate affect the further psychological state and development of a person.
Also, people living in villages and towns are less susceptible to speech defects than those living in a metropolis. This is due to the calm environment. Adults who stutter account for only 1% of the population, which indicates the successful treatment of this pathology.
Siblings adopt this disorder in 18% of cases. Moreover, stuttering occurs in 32% of dizygotic twins, and in 77% of monozygotic twins.
Phases of pathology development
Phase I
Stuttering with short episodes, shortening the period of smooth speech regularity. Characterized by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty in pronunciation at the beginning of a word and when constructing a sentence.
- Stumbling in speech occurs in the pronunciation of short parts of speech, conjunctions and particles.
- Stuttering occurs as a result of “Communicative pressure” (excitement, a person is in a hurry to say something, etc.).
- There is no speech phobia observed.
II phase
- A chronic form of pathology appears.
- Pronunciation is difficult when speaking quickly and in complex word combinations.
- Awareness of a speech defect, but this does not interfere with normal communication.
III phase
- Obvious convulsive syndrome. But the person does not yet perceive this as a problem.
- Some sounds and syllables cannot be pronounced.
- Speech inhibition, as attempts begin to replace some words with others that are less problematic.
IV phase
- Stuttering develops into a major personal problem. The person understands that he has serious speech impairments and avoids contacts and difficult situations where communication is required. If at earlier stages words and expressions sometimes changed, now this happens all the time.
- Anticipation - a person waits for his speech errors.
- Chronic problem in pronouncing words. Development of fear of communication.
Types of stuttering
The division concerns convulsive forms, clinical manifestations and the course of the pathology.
Convulsive forms of stuttering in adults and children have the following divisions:
- The clonic form is a short-term spasm, followed by a second similar one, which leads to involuntary repetitions of phrases and letters.
- Tonic form - long-term or short-term muscle contraction. As a result, a person does not pronounce one word for a long time.
- Mixed stuttering in the form of parallel clonic and tonic forms.
In addition, in addition to the functionality of the speech apparatus, facial expressions suffer: they may be accompanied by cramps of the facial muscles and parts of the limbs.
Course of stuttering
- Long-term - when the defect manifests itself on a permanent basis in all words and in any situation.
- Intermittent - some psychological situations provoke stuttering (excitement, joy).
- Relapse - after treatment, the problem appears after some time. It doesn’t matter whether a person is cured completely or partially.
Clinical form of stuttering
Logoneurosis manifests itself in two clinical forms: neurotic and neurosis-like. Each of them has its own cause with a developing mechanism.
Neurotic stuttering
Stuttering in adults and children was not caused by birth or postpartum trauma. These are not physical disorders in the cerebral cortex. This form of disorder includes the psychological and social factors described above. With this type of pathology, the patient is easier to cure than with a neurosis-like form. The problem is mainly dealt with by a psychologist. Adults are more often susceptible to the chronic form of this pathology.
Characteristics of a person with neurotic stuttering:
- A person with a stutter is immediately visible: he is silent, timid and agitated, he invents worries, he is often offended, irritated, he is withdrawn, his far-fetched fears interfere with life. These are melancholic people.
- This patient has no physical developmental abnormalities.
Neurosis-like form
It appears unexpectedly, most often in the medical history there are birth problems. For example, the mother suffered a difficult pregnancy: complications, birth injuries. As a result, the functioning of the brain and central nervous system is disrupted, treatment takes longer, and a 100% guarantee of recovery is not always given.
Often, each part of the speech apparatus is susceptible to severe forms of convulsions. When talking, people can accompany their speech with sharp nods of the head, twitching of the hands, and contraction of the facial muscles. All this happens involuntarily.
A person gets tired after a long conversation, so such people are more silent. In addition to exhaustion, the patient complains of poor memory, orientation in space and time.
You need to work with a specialist in a comprehensive manner, taking special medications. The lengthy recovery procedure can take several years.
Stuttering
Stroke
Encephalitis
4452 March 30
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Stuttering: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Oral speech is a complex multicomponent process in which not only the structures of the maxillofacial apparatus, but also the brain centers located in the cerebral cortex take part. It is in these structures that in most cases certain pathological processes leading to the development of stuttering are localized.
Stuttering (stammering) is understood as a speech feature characterized by frequent repetition or prolongation of sounds, syllables or even words in combination with frequent pauses, which disrupts the fluency of oral speech.
Today, different figures are given that characterize the number of people who stutter - from 1 to 5%. However, all experts are unanimous that among males stuttering occurs 4 times more often than among females, and also that in 90-95% of cases stuttering occurs between the ages of 2 and 7 years.
This speech defect often leads to problems in communication, which consist not only in the difficulty of perceiving such speech on the part of the listener, but are also associated with the internal emotional experiences of a stuttering person.
Types of stuttering
There are the following types of stuttering:
- Neurotic stuttering, the development of which is usually based on some psychotraumatic factor. This type of stuttering is psychogenic and is not based on structural damage to the brain or peripheral parts of the speech apparatus.
- Neurosis-like stuttering - unlike neurotic stuttering, it develops against the background of organic damage to the nervous system.
- Mixed stuttering develops against the background of both a psychogenic factor and true damage to the nervous system.
Possible causes of stuttering
Stuttering is based on various muscle spasms of the speech apparatus. They develop due to abnormal impulses emanating from the motor speech centers of the brain. The cause of the pathological functioning of these parts of the central nervous system can be both structural and functional disorders. The latter are characterized by the presence in some part of the brain of a focus of excitation, which activates the motor speech center and leads to the development of convulsive readiness of the muscles involved in articulation and voice formation.
If tonic convulsions develop, a prolonged muscle spasm occurs, resulting in speech delay. Unlike tonic convulsions, clonic convulsions are a series of short-term convulsions that lead to involuntary repetition of sounds or syllables.
Both types of seizures lead to impaired speech fluency and stuttering.
Diseases that cause stuttering
Among the factors influencing the development of stuttering, doctors identify the following diseases and conditions:
- emotional lability and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system;
- mental trauma;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- infectious brain damage;
- stroke;
- perinatal damage to the central nervous system of the child, associated, as a rule, with a violation of the supply of oxygen to brain structures in the prenatal period of development, during childbirth and in the first hours and days of life.
Which doctors should I contact if I stutter?
Traditionally, the initial examination of a patient with stuttering is carried out. After a detailed interview with the patient, the purpose of which is to clarify the circumstances of the appearance of stuttering and possible provoking factors, the doctor specifically examines the nervous system for the presence of other signs of neurological abnormalities. In the treatment of stuttering, doctors resort to the help of a speech therapist and psychologist. Often, to treat stuttering, especially in the absence of organic damage to the nervous system, the neurologist refers the patient to a consultation with a psychiatrist in order to identify some mental abnormalities that lead to the development of stuttering.
Diagnosis and examinations for stuttering
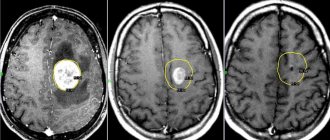
Diagnosis of stuttering begins with a neurological examination, during which a neurologist may suspect the presence of a structural brain lesion or, conversely, receive no evidence of the presence of organic damage. In this case, the doctor resorts to additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods in order to confirm or exclude various organic lesions. EEG and neuroimaging methods are coming to the fore.
Electroencephalography (EEG) is one of the integral methods of additional research of a patient suffering from stuttering. EEG helps differentiate neurotic and neurosis-like stuttering by identifying signs of convulsive activity in individual areas of the brain.
How does stuttering develop?
This process has not been fully studied; at the moment there is a version. Depending on the prerequisites for dysfunction of the speech apparatus, Broca's center is affected (the vocal center responsible for the work of the muscles and ligaments involved in speech). As a result of overexcitation of Broca's center, the speed of its work increases. The functioning of the so-called speech circle (Broca's center, Wernicke's area and associative center) is disrupted.
This causes a convulsive effect (tongue, lips, soft palate and others). A person develops stuttering due to impaired coordinated functions of the speech apparatus when reproducing words, syllables and phrases that are caused by a spasm. The spasm begins in one of the sections of the speech apparatus.
If Broca's center is highly overexcited, this is reflected in nearby areas of the brain. As a result, involuntary movements and spasms of the limbs, etc.
It is interesting that nerve impulses during an excited nervous system and consonant sounds (especially voiceless ones) are similar in frequency. Therefore, stuttering mainly occurs on consonants and is extremely rare on vowels.
Symptoms
Photo: detki-pogodki.ru
There are two clinical forms of stuttering: neurotic and neurosis-like. Each of these forms has its own mechanism for the formation of the disease and its own symptoms of manifestation.
For example, there are children prone to developing a neurotic form of stuttering.
In this case, parents notice that their children become timid, anxious, touchy, irritable, and whiny. Such children's mood changes sharply, often downward (for no apparent reason). Sleep is disturbed, children have difficulty falling asleep, and are afraid to sleep with the lights off.
The mental, physical and mental development of children is not impaired and corresponds to their age. However, the formation of speech occurs somewhat earlier than in other children. By 10 months of life, the first words appear, by 16-18 months the first phrases are pronounced. 2-3 months after the formation of phrasal speech, the first complex sentences and speech structures appear.
In the case of the development of stuttering, which, as a rule, occurs between the ages of 2 and 6 years, the child can speak without hesitation (light interval), then periods of stuttering appear. This occurs as a result of some kind of mental trauma, which can provoke mutism (the child stops answering questions or talking), after which hesitations in speech appear.
Another reason that contributes to the development of a neurotic form of stuttering is the early introduction of a second language of communication. Some children, due to their individual characteristics, do not always have time to master their native language by the right age, then the early introduction of a second language will be stressful for the child.
This form of stuttering is highly treatable if parents pay attention to the symptoms in a timely manner and seek help from a doctor. But it is possible for the disease to become chronic. In this case, children, realizing their illness, begin to withdraw into themselves and are reluctant to engage in conversations because they do not want to make an unfavorable impression on others. Logophobia develops - an obsessive fear of speech associated with stuttering.
Adults also have logophobia. Such people feel socially inferior, choose professions with minimal communication, and are prone to loneliness, since the existing illness causes fear of communicating with other people.
Children prone to a neurosis-like form of stuttering are characterized by a lag behind their peers in physical development. Such children develop a lack of coordination of movements, a delay in speech development occurs (they begin to speak later, vocabulary accumulates slowly, phrasal speech is formed late, the construction of complex sentences is difficult).
Such children are easily irritable, whiny, do not tolerate stuffiness and heat, and their sleep is disturbed.
Stuttering of a neurosis-like form appears at the age of 3-4 years. Initially, children speak with hesitations, which gradually increase (become more frequent and longer), and the “bright gap” (when the child speaks without hesitation) shortens. Then, extra words and phrases appear in the child’s speech that do not carry a semantic load. The pace of speech changes: it becomes either accelerated or slowed down. In addition, spasms of the facial muscles of the face or hands may occur.
Since the neurosis-like form of stuttering is associated with organic damage to the brain, symptoms such as decreased memory and performance, increased fatigue, hyperactivity, and headaches are added to the existing symptoms.
In adults, the chronic form of neurosis-like stuttering is accompanied by convulsions in all parts of the speech apparatus. The speech of such a person is often accompanied by nodding movements of the head, monotonous movements of the fingers, and swaying of the body from side to side. Communication with other people has a tiring effect on a person, because of this he is not able to carry on a conversation for a long time, and often answers in monosyllables.
In addition, there is often a decrease in memory, attention, increased fatigue and decreased performance.
Specialists
Treatments for stuttering in children and adults are similar. Depending on the determination of the cause of the speech defect, the attending physician is appointed. There are several of them, sometimes two or more specialists deal with one patient.
- A neurologist and psychiatrist prescribe medication to solve the problem of stuttering.
- The psychotherapist prescribes psychotherapy depending on the characteristics of the person: hypnotization, training.
- A psychologist studies psychosomatics and human personality. First, the patient is removed from the psychological barrier. He is trained to be in society and make decisions in stressful situations.
A speech therapist is a specialist who corrects speech in parallel with the provision of assistance by another specialist. It helps improve speech, use breathing exercises, and pronounce letters and sounds.
The goal of his therapy is not to correct incorrect pronunciation, but to help in realizing that words can be constructed easily in a sentence, regardless of pathology. The patient reduces his fear of stuttering.
An acupuncturist works to improve blood circulation. The sessions used are responsible for a specific organ; in general, the technique helps with mild stages of stuttering. Stuttering is a fairly rare occurrence and can take a long time to correct. If you start to fight the pathology in time and diagnose the correct factor in the development of the problem, then the chances of getting rid of this speech disorder increase sharply.
Correction methods
Stuttering, like other diseases, is easier to correct in the early stages. In some cases, it is possible to get rid of this speech disorder in just a few weeks. But most often it takes much longer.
As mentioned above, treatment should begin with a visit to a neurologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, the purpose of which will be to identify the causes of speech dysfunction. If stuttering is caused by a malfunction of the central or peripheral nervous system, then the patient will be prescribed adequate drug treatment. In addition, the following specialists will treat stuttering:
- reflexologist. To eliminate stuttering, it is important to get rid of muscle tension localized in the shoulder girdle, neck and abdomen;
- psychotherapist. Modern psychotherapeutic techniques will help to identify the psychological causes of the problem and eliminate them. As a result, you can not only normalize speech, but also completely change your life for the better. Become more confident in your own abilities, learn to get out of difficult life situations, improve relationships with people around you, etc.;
- speech therapist. Special speech therapy exercises will allow you to develop correct speech breathing, learn to pronounce sounds, control the speed of speech and its tempo.
Comprehensive treatment and constant work on yourself will allow you to achieve lasting results in the shortest possible time.
It should be remembered that a one-time visit to a speech therapist will not help. You should also not count on the fact that the doctor will give you a “miracle pill” and your stuttering will disappear. This speech disorder will only go away if the stutterer strictly follows the recommendations of all specialists throughout the course of treatment.