The radial nerve runs along the back surface of the shoulder, as if in a spiral, and gives off branches that provide movement of the muscles responsible for extension of the forearm and hand, outward rotation of the forearm, sensitivity of the skin of the back surface of the shoulder and forearm. Among other nerves of the hand, neuritis occurs most often in it.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Why does radial neuritis occur?
This is usually caused by damage to the nerve trunk due to prolonged compression. This may be due to the following reasons:
- "Saturday Night Paralysis" . This interesting name appeared due to the fact that neuritis and other damage to the radial nerve often occur in people who like to spend their days off drinking alcohol and then fall asleep with their hand under their head or under their torso.
- "Honeymoon Paralysis" . It occurs after sleeping in an embrace, when the head of one person lies on the hand of another for a long time.
- “Crutch paralysis” occurs in some people who constantly use crutches.
- Fracture of the humerus. In this case, bone fragments can damage nerve fibers.
- Injections into the outer part of the shoulder . Most often, injury to the radial nerve occurs if it is located unusually, or if the injection is given incorrectly.
- Strongly pulling the arm with a tourniquet for a long time when trying to stop bleeding.
- Infections. A rarer reason. Neuritis can be caused by: influenza, pneumonia, typhus and some other infectious diseases.
- Poisoning, for example, alcohol, lead.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
Given the limited space in the carpal tunnel, any swelling in this area can put pressure on the median nerve, causing symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. There are many different reasons that lead to the development of this syndrome, but often the exact cause cannot be determined. Some people have an anatomically narrower carpal tunnel to begin with, making them more at risk for developing carpal tunnel syndrome. It is believed that this tendency may be genetically determined, and if there is a family history of this syndrome, then the likelihood of pressure on the median nerve increases significantly. You are also more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if you are overweight, smoke, or drink excessively. Another risk factor is age – the older a person is, the higher the likelihood of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Women are more predisposed to this syndrome than men due to the narrower carpal tunnel. There is also a greater tendency to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if there has been a wrist injury (rupture or sprain) or there are diseases such as:
- diabetes
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- hypothyroidism
It is possible that hormones play a role in the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, as some women develop the syndrome during pregnancy or menopause. Hormones produced during pregnancy can lead to fluid retention, which in turn can cause swelling in the wrist. It has been noted that performing certain types of activities can lead to the development of this syndrome. People who do a lot of heavy manual work or repetitive movements of the wrist, such as on an assembly line or working with their hands in cold temperatures, also have a greater risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. But the probability increases significantly if the load is combined with the presence of systemic diseases.
Treatment of neuritis of the radial nerve of the hand
Depending on the causes of the disease, the doctor may prescribe:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antibiotics - if the pathology is caused by an infection.
- Drugs that normalize metabolic processes in nervous tissue.
- Means for improving blood flow in small vessels that supply nerve fibers.
- In case of poisoning - intravenous infusions of solutions through a dropper to remove toxic substances.
- Physiotherapy: magnetic therapy, UHF.
If the damage to the nerve fibers is caused by injury, it is necessary to carry out timely and correct treatment: straighten the dislocation, match the fragments of the broken bone and apply a plaster cast.
For severe injuries, surgical treatment may be considered.
The prognosis is usually favorable; with timely treatment, after some time, complete restoration of impaired functions occurs. Often, after conditions such as “Saturday paralysis,” recovery occurs on its own without therapy. If the disturbances persist, it is better to see a neurologist.
For effective treatment of radial nerve neuritis, which will help restore its functions as quickly and fully as possible, contact a neurologist. Do not engage in self-diagnosis, especially if movements and sensation in the hand are severely impaired, and these disorders persist for a long time. You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Medica24 international clinic at any time of the day and any day of the week by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Symptoms of radial neuritis depend on the level at which it is damaged:
In the armpit area and at the top of the shoulder:
- The thumb and index finger are connected.
- It is difficult to straighten the forearm and hand.
- It is difficult to rotate the forearm outward when the arm is extended.
- Sensitivity on the skin in the area of the thumb, index and middle fingers is reduced, “crawling goosebumps” and numbness occur.
In the middle of the shoulder:
- Extension of the elbow joint is not impaired.
- The sensitivity of the skin of the shoulder is preserved.
- All other symptoms that are described above for neuritis of the radial nerve in the upper part are present.
At the bottom of the shoulder and at the top of the forearm:
- The sensitivity of the skin on the back of the forearm is not impaired.
- The sensitivity of the skin on the back of the hand is reduced.
- It is difficult to straighten the hand.
Treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome
The choice of treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying medical condition that may be causing the symptoms.
In the first stage, treatment usually includes rest, immobilization of the wrist in a brace, and sometimes local cold. If the patient’s profession involves stress on the wrist, then it is necessary to change activities for a while. In addition, it is possible to improve the ergonomics of the workplace, for example, you can adjust the computer keyboard and the height of the chair and optimize the load on the hands. These measures, as well as periodic episodes of rest and wrist stretching exercises, can actually prevent the development of carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms, which are caused by repetitive, excessive movements of the wrist. If there are systemic diseases or injuries, then individual treatment of these diseases is carried out. Fractures may require orthopedic correction (plaster, orthosis). Overweight patients should be advised to lose weight. For rheumatoid arthritis, specific treatment is carried out for the inflammatory autoimmune process. Wrist swelling, which may be associated with pregnancy, disappears after the baby is born.
Drug treatment
Several types of medications may be used to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is quite often prescribed in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome and, although the mechanism of therapeutic action is not entirely clear, nevertheless, many doctors note a certain effect of using this drug. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may also be helpful in reducing inflammation and pain. But these drugs have side effects and therefore this must be taken into account when prescribing them. Corticosteroids may also be used. They can be given orally or as injections into the affected wrist joint. Corticosteroids can lead to rapid relief of symptoms, but the side effects of these drugs do not allow them to be prescribed long-term and in the presence of some conditions (for example, in diabetes mellitus, their use can lead to a worsening of the condition). They should also not be prescribed in the presence of infections. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy and acupuncture also provide a certain therapeutic effect. Most patients with carpal tunnel syndrome can be treated with conservative therapy. But sometimes chronic pressure on the median nerve can lead to permanent numbness and weakness. To avoid serious and permanent nerve and muscle damage, surgical treatment may be recommended in such cases. Surgery involves excision of tissue putting pressure on the median nerve. This surgical procedure is called a "carpal tunnel release." Currently, such an operation can be performed using endoscopic techniques, which allows for minimal tissue trauma and rapid restoration of nerve conduction. After surgical treatment, it is necessary to use exercise therapy to restore hand function.
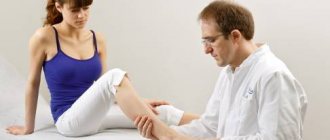
How to identify symptoms of radial neuritis?
There are some simple tests that help detect characteristic signs of the disease:
- Stand up, lower your arms along your body so that they are in an extended state. Try turning your forearms outward so that your palms “look” forward. In this case, you will have difficulties.
- Place your hands on the table so that your palms are on top. Try moving your thumbs to the sides. This will create difficulties.
- Place your hands on the table with your palms facing down. Try lifting your middle finger and placing it on top of your index or ring finger. This will not be possible.
- Place your hands together with your palms facing each other. Try spreading your fingers out to the sides. In this case, the fingers on the sore hand will not move to the side, but, on the contrary, will bend and slide along the healthy one.
- Stand up and raise your arms forward. In this case, the hand on the sore side will hang down.
If you find yourself with similar symptoms of radial neuritis, and they do not go away long enough, contact a neurologist at the clinic.
How is the diagnosis made?
Most often, a doctor diagnoses the disease by assessing the symptoms of radial neuritis during a neurological examination. In some cases, additional tests and studies and consultations with other specialists may be required.
Only a neurologist can correctly assess the symptoms and prescribe treatment. Therefore, you should not engage in self-diagnosis. Visit a specialist: you can make an appointment with a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24 by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome can be made based on symptoms and characteristic areas of numbness in the hand. But at the same time, it is often necessary to exclude other possible causes of symptoms that simulate carpal tunnel syndrome. This could be a neck, shoulder or elbow problem. The doctor examines the wrist to detect swelling, local fever, pain, and discoloration. Sometimes pressing on the front of the wrist can produce a tingling sensation in the hand and this is called the Tinel sign, characteristic of carpal tunnel syndrome. Symptoms may also occasionally be reproduced by flexing the wrist forward (called Phalen's sign). A definitive diagnosis can be made with ENMG. Typically, with carpal tunnel syndrome, there is a slowdown in nerve impulse transmission after the nerve passes through the wrist.
Extremity muscle testing, an electromyogram, is sometimes performed to rule out or detect other conditions that may mimic carpal tunnel syndrome.
Laboratory tests may be performed to help diagnose conditions associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. These tests include thyroid hormone analysis, general blood tests, blood sugar levels, etc. X-rays of the hand may also be ordered to determine the presence of bone changes (abnormalities of the bones and joints of the wrist). MRI is necessary in cases where it is necessary to visualize changes in ligaments and cartilage.