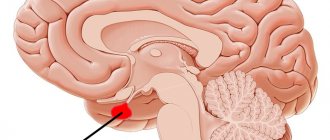
Causes of pituitary tumors
Today, modern medicine cannot give an exact answer to the question of tumor development, but scientists have put forward some assumptions about this. In many cases, hereditary or genetic factors influence. This disease is caused by various inflammations and infections of the nervous system, injuries to the head, chronic inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (chronic sinusitis), and any other infectious diseases that are provoked by various types of bacteria and viruses. The cause of a pituitary tumor is often also the excessive influence of toxic harmful substances on the body, as well as any pathologies during pregnancy or childbirth (premature birth, infection in the amniotic fluid, cancer of the fetal membrane, etc.).
Hormonal tumors, most often pituitary tumors. With uncontrolled growth of cells that produce growth hormone, this type of disease can appear.
There is an opinion that the progression of abnormal pituitary tissues can be activated due to the unproductive activity of the peripheral glands of the endocrine system or an excess of the hormone secreted by the hypothalamus.
Therapeutic measures
For any brain tumor, including pituitary adenoma, when prescribing a treatment plan, the possibility of surgery is first considered. If for some reason surgical removal of a pituitary tumor is not possible, drug therapy is often prescribed with drugs designed to reduce the effect of excess hormones on the body, and radiotherapy can also be used.
The development of modern technologies makes it possible to actively and effectively use stereotactic radiation therapy, in particular, with the use of the CyberKnife apparatus, for pituitary adenoma. It has the highest precision and allows you to remove the tumor using a non-surgical method. The procedure is practically painless and does not require hospitalization, and its cost is more affordable than similar procedures in clinics in Europe and Israel. You can make an appointment for a consultation in Moscow by phone. +7 (495) 085-79-02 or 8 (800) 5-000-983.
Symptoms of pituitary tumors
The reason for worry and contacting a specialist is for a woman a disruption in the menstrual cycle, light discharge from the nipples, and for a man - a violation of sexual growth and potency.
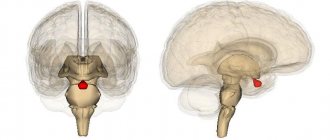
Symptoms of pituitary tumors can be completely different and this is due to their size. For example, neoplasms about 19 mm in size are called macroadenomas, and even smaller ones are called microadenomas. These macroadenomas tend to press against other nearby tissues.
Symptoms of neoplasms affecting surrounding tissues:
- acute headaches, frequent and sudden;
- fatigue, weakness of the body;
- deterioration or loss of vision;
- frequent constipation;
- gag reflexes, nausea;
- problems related to sexual life;
- hair loss;
- the patient gains weight or, on the contrary, loses weight.
There are pituitary tumors that produce their own hormones in addition to the pituitary gland. They are called hormonally active.
Neoplasms that produce somatotropin predetermine the occurrence of acromegaly in mature individuals, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- disturbance of scalp growth;
- double vision;
- discomfort in joints and muscles;
- headache;
- increase in the size of the palms and feet.
When such a disease is detected in a child, he often suffers from gigantism, abnormal development of the body structure (excessively large height, small head, elongated limbs). All this entails various pathologies on the part of sexual function, mental and physical development lags behind.
Unnatural development is determined by prolactin-secreting tumors:
- men suffer from enlargement of the parenchyma of the mammary glands (gynecomastia);
- infertility caused by the absence of menstruation in women (amenorrhea) or irregular menstrual cycles (oligomenaria);
- secretion of breast milk in men and women, which is accompanied by decreased sexual desire, fever, and sudden headaches (galactorrhea);
- men experience disruption or complete loss of sexual relationships with women.
Some adenomas that produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) can cause excessive production of adrenal hormones, which is the source of Cushing's disease. The following symptoms are noted:
- improper distribution of adipose tissue, its placement in the face, as well as the neck, torso, but at the same time the limbs remain thin;
- the skin becomes exhausted, thin, dry and inflamed;
- acrocyanosis;
- the skin is prone to intense pigmentation, bruises and stretch marks appear;
- Diabetes mellitus or osteoporosis may occur;
- arterial hypertension;
- persistent mental defects, euphoria or depression;
- amyotrophy;
- the face becomes moon-shaped.
Thyrotropin-producing adenomas provoke the appearance of hypothyroidism. The development of the disease can begin with functional insufficiency of the thyroid gland. Gonadotropic tumors of the pituitary gland are characterized in women by frequent uterine bleeding and systemic menstrual irregularities.
The larger the tumor, the more pronounced the manifestations and symptoms of the disease can be, which will worsen in the future with the increase in tumors. If they are not corrected in time, the result can be fatal for the patient. Such adenomas cause sudden loss of vision or its deterioration, optic nerve atrophy. In the most severe cases, complete loss of vision is possible.
When adenomas affect the cranial nerves, there is a risk of damage to the nervous system. Clinical symptoms in this case are:
- sudden spasms of some parts of the body;
- nystagmus;
- severe headaches, high intracranial pressure;
- the patient's consciousness becomes impaired.
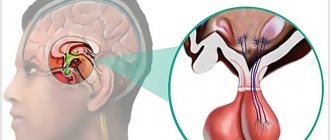
Pituitary adenoma has a very detrimental effect on the ventricles of the brain, namely, it puts pressure on them. In this case, dropsy of the brain or hydrocephalus is formed. This outcome entails disorders: paralysis of the eyeballs (ophthalmoplegia) or double vision (diplopia). The development of a harmful tumor downwards will lead to rupture of the sella turcica, as well as the spread of pathology to the sinus area, and cerebrospinal fluid leaks from the nose.
Stages of pituitary tumors and their symptoms
A low-quality tumor begins its formation with the so-called pre-invasive cancer. In these cases, the patient does not notice any symptoms; the tumor-like formation can exist for a long time without the active growth of cancer cells.
At this stage, a pituitary tumor in Israeli cancer centers is detected during preventive examinations.
Oncopathology at the first stage is mostly asymptomatic - this can continue for 2 or 3 years. Once diagnosed, it can be successfully treated.
In the second stage of the disease, rapid growth of a tumor-like formation in the pituitary gland is recorded. A sick person feels the first signs of illness: weakness and dizziness, headaches and nausea, sleep disturbances and increased fatigue.
The third stage of pituitary cancer is characterized by a significant increase in the tumor and damage to the occipital lymph nodes. At this stage, pronounced symptoms of the disease are noticed; usually the patient seeks medical help with the following symptoms:
- decreased visual function, temporary or permanent blindness due to compression of the visual center in the brain;
- headaches that are aching in nature;
- loss of consciousness and memory impairment;
- decreased sensitivity in the upper and lower extremities, as fluid circulation in the spinal cord is disrupted;
- hormonal imbalance;
- cachexia (severe exhaustion of the body).
Although the third stage is more difficult to treat, it is necessary to fight the tumor to prevent further complications.
At the fourth stage of a low-quality pituitary tumor, it reaches a large size with metastasis. Patients experience mental disorders, epilepsy and other serious symptoms.
Depending on the type of tumor, when treating pituitary tumors in Israel, doctors prolong the life of patients in 98% of cases, and in the most difficult situations provide palliative care.
Diagnosis of pituitary tumors
At the first sign of a pituitary tumor, you should immediately contact highly qualified specialists. At the clinic, doctors will conduct examinations for hormonal and ophthalmological disorders. To do this, you will need to take a blood and urine test. This is done to determine the level of hormones.
As for the ophthalmological examination, it will help determine the size of the adenoma, as well as the direction of its formation. Next, the spinal cord fluid must be examined for the presence of proteins in it, since this may be an indirect sign of the presence of an adenoma in the brain.
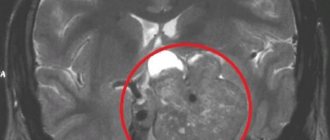
The next step will be radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography of the brain, which neurovisualizes neoplasms of the pituitary gland. But, in the case of a small tumor in size, radiography will be meaningless, since it only detects adenomas that have a clear effect on the surrounding tissue.
The exact location and volume of minor tumors are diagnosed by computer tomographs. Doctors also often use the radioimmunological method. Since, as already mentioned in the article, this disease of the pituitary gland is extremely difficult to detect, doctors use complex diagnostics to accurately determine the diagnosis.
Principles of disease treatment
Let’s make a reservation right away: with this diagnosis, the patient needs highly qualified medical care and constant monitoring. Therefore, there is no need to rely on chance, believing that the tumor will resolve and everything will pass. The outbreak cannot go away on its own! In the absence of adequate therapy, the danger of becoming disabled with irreversible functional impairment is too great, and deaths from the consequences also occur.
Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, patients are recommended to solve the problem surgically and/or conservative methods. Basic therapy procedures include:
- neurosurgery
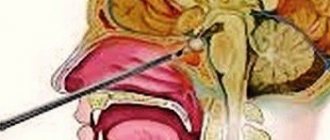
- removal of adenoma by transnasal access (through the nose) under endoscopic control or transcranial method (standard craniotomy is performed in the frontal part) under the control of a fluoroscope and microscope;
90% of patients are operated on transnasally, 10% require transcranial ectomy. The latter tactic is used for massive tumors (more than 3 cm), asymmetric growth of newly formed tissue, extension of the lesion beyond the sella, and tumors with secondary nodes.
- treatment with medications
- the use of drugs from a number of dopamine receptor agonists, peptide-containing agents, targeted drugs for hormone correction; - radiotherapy (radiation treatment)
– proton therapy, remote gamma therapy using the Gamma Knife system; - Combination treatment
– the program course combines several of these therapeutic tactics.
The doctor may not use surgery, but recommend observation of a person diagnosed with pituitary adenoma in the absence of focal neurological and ophthalmological disorders and the tumor is hormonally inactive. Such a patient is managed by a neurosurgeon in close collaboration with an endocrinologist and an ophthalmologist. The patient is systematically examined (1-2 times a year), sent for MRI/CT, eye and neurological examinations, and measurement of hormones in the blood. In parallel with this, the person undergoes courses of targeted maintenance therapy.
Since surgery is the leading method of treating pituitary adenoma, we will briefly highlight the course of the surgical process of endoscopic surgery.
Treatment of pituitary tumors
There are several types of treatment for pituitary tumors:
- drug treatment, which is prescribed in the early stages of the disease, when doctors can do without surgery (they usually use cyproheptadine, caberglobin, bromocriptine - they regulate the level of hormones in the body);
- interstitial or external beam radiation therapy (carried out in the presence of such features in which the tumor does not allow surgical intervention);
- surgical intervention - doctors resort to this method in the most severe cases, when the disease is severely advanced or the adenoma is large. After this procedure, the patient is prescribed hormone therapy and additional radiation therapy.
Removal of adenoma by instrumental means in our time is carried out using endonasal transsphenoidal intervention, in other words, through the nasal passage. This is a completely safe method, since penetration is carried out by an endoscopic probe and miniature instruments, which avoids any infections and incisions during the operation.
Symptoms
Unfortunately, making a diagnosis is often difficult, since with a tumor such as a pituitary adenoma, the symptoms are often unclear or contradictory. Among them: headaches, narrowing of the field and visual acuity, and less often - disturbances of consciousness. With hormonally active forms the following may be observed:
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease, as a result of which the adrenal glands produce excessive doses of cortisol, sugar metabolism is disrupted, bones become brittle and a number of other negative changes are observed;
- heart rhythm disturbances, muscle weakness and atrophy, specific obesity;
- disproportionate increase in the size of the feet and hands, enlargement of facial features, in children - excessive growth or, on the contrary, dwarfism;
- increased sweating, protruding eyes, tachycardia.
With pituitary adenoma, the symptoms in women differ from the manifestations of the disease in men. The former may experience colostrum discharge from the nipples, male pattern hair growth, cessation of menstruation and infertility. In the latter, testicular atrophy, decreased potency and libido, and breast growth are possible.
Prognosis for pituitary tumors
Pituitary tumors, according to statistics, account for 15% of intracranial neoplasms. In most cases, these are benign tumors that slowly increase in size (which reduces the number of relapses); they do not extend beyond the sphenoid bone (also known as the sella turcica, where the pituitary gland is located). But there are also malignant ones, that is, those that have a cancerous nature of development.
Scientists have found that the age at which this type of disease is most often diagnosed in women and men is 30-40 years. Children very rarely suffer from this disease.
In 80% of cases, asymptomatic development of the disease is observed. It is possible to rehabilitate visual processes only at the initial stages of the development of abnormal processes.
It is difficult to make a prognosis for this disease, since it directly depends on timely recognition and initiation of treatment. Therefore, it is worth consulting a doctor promptly and undergoing routine medical examinations on time. But it is worth saying that in 25% of cases, patients with somatotropinomas and prolactinomas have a successful outcome of the disease, while the remaining adenomas are successfully cured in 80% of cases.
Preventative measures to prevent pituitary tumors
The exact reasons for the formation of tumor-like growths in the pituitary gland, as well as the development of other types of cancer in the brain, have not yet been established, therefore, to eliminate the risk of their occurrence, doctors recommend:
- undergo prompt diagnosis and treatment of any dishormonal disorders or chronic diseases;
- prevent traumatic brain injuries;
- take preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of neuroinfections;
- try to control the intake of hormonal drugs and not take oral contraceptives for a long time.
You must also adhere to the general rules of a healthy lifestyle (normal sleep and a rational daily routine, a balanced diet and giving up bad habits).
Prevention to exclude relapse after surgical and radiotherapeutic treatment of cancer abroad requires an annual examination and systematic use of prescribed medications.