Features of the formation of neurosis in a child
Next, consider the origin of childhood neuroses.
Their peculiarity in children is their formation against the background of personality immaturity. To understand, the personality of children is determined by the type of upbringing in the family.
It is worth highlighting the main “inadequate” types of upbringing:
- Insufficient attention to the baby is “hypocustody.”
- Excessive attention is “overprotection”.
- Cruel upbringing.
- Authoritarian parenting.
As a rule, improper upbringing can harm the development of a child’s personality and temperament. As a result, negative character traits and inadequate reactions on the part of the child appear. Sooner or later, this leads to a feeling of inferiority, against the background of which any negative external influence can lead to neurosis. The role of a negative factor can be: a rude word, a loud remark, a change in living conditions and much more.
Given the immaturity of personality in children, typical forms of neurosis rarely develop. More often they have simpler disorders - systemic neuroses. They can manifest themselves in any organ and organ system. It is believed that the choice of damage to one or another organ depends on the hereditary susceptibility (weakness) of the organ or body system. Such weak points in children are often the speech-motor system (formation of stuttering) and the urinary system (development of enuresis).
There is also another development mechanism: a combination of increased nervous tension and the performance of a certain action or movement at this moment. So, this action or movement can lead to the formation of tics in the baby. Thus, neuroses in childhood most often manifest themselves as tics, stuttering and enuresis. In the absence of treatment, systemic neuroses with age often become “classical”, as in adults.
Stuttering is common in children with neuroses.
Patient reviews
Doctor: Evsyunina Natalya Borisovna
Source: prodoctorov.ru
Good doctor! She loves her job and is attentive to young patients and their parents. I won't describe our case. I will say that I did not regret visiting this doctor. I recommend! We visited the IMMA clinic on Bratislavskaya. Thank you that there are still such doctors and it doesn’t matter whether you applied for a fee or for free, the professionalism is immediately clear.
Doctor: Evsyunina Natalya Borisovna
Source: prodoctorov.ru
We are very grateful to Natalya Borisovna for treating our daughter with due attention. After going to the clinic, my hair stood on end and I decided to go to an alternative specialist. I wanted to hear an opinion not just as a sweet pill, but a real opinion. She looked at the baby very carefully, made recommendations and we really breathed out. We highly recommend this specialist.
Doctor: Evsyunina Natalya Borisovna
Source: prodoctorov.ru
Doctor Evsyunina is competent. We had a routine checkup. I didn’t expect special attention, but I must pay tribute, Natalya Borisovna was very pleased not only with her attitude, but also with her knowledge. The consultation was informative, the examination was thorough, and the advice was useful. I have no complaints about this specialist. The price of the appointment is not overpriced, as it seemed to me at first, everything corresponds to the quality. Thank you.
Doctor: Evsyunina Natalya Borisovna
Source: prodoctorov.ru
We contacted a neurologist with my son, he is 4. We just came for a routine examination, I was bothered by the remarks of the treating pediatrician that we were allegedly lagging behind in development. At the reception, I heard a competent opinion from Natalya Borisovna and received a lot of practical advice for the future. She is a very good doctor, attentive and interested in helping people. She was very friendly towards my child, he behaved calmly during the examination, which is rare for us. We will contact this doctor for physiotherapy. I like Evsyunina and inspires confidence, so I am ready to recommend her to other people.
Causes
The main factors contributing to the development of neuralgia in children:
- Lack of oxygen during fetal formation
- Maternal smoking during pregnancy
- Birth injuries and premature birth
- Low hemoglobin level in the expectant mother
- Stress during pregnancy
- Injuries in a child that caused pinched nerves
- Hypothermia
- Spinal diseases
- Infectious diseases
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Symptoms of neuralgia
The main symptom of neuralgia is a burning, shooting or aching pain that spreads along the nerve trunk or is localized in the area of the affected nerve.
Additional symptoms include:
- Facial muscle twitching, tics, seizures
- Temperature increase
- Weakness in the lower extremities
- Increased secretion of salivary glands
- Increased irritability
- Headache
- Bad dream
- Excessive sweating
- Hyperactivity
- The baby's inability to open his jaw when crying
Types and symptoms of neuroses
There are such types of general neuroses as:
- Hysteria . In children, this condition manifests itself as an excessive, inadequate reaction to dissatisfaction with something. Children with hysteria often “fake it.” They can achieve what they want by manipulating their parents. Manipulation may involve simulating symptoms of the disease. At the same time, the doctor, examining the baby, does not find objective signs of the disease.
- Neurasthenia . In children it manifests itself as irritability and weakness. It is not uncommon to experience violent reactions to minor remarks or actions. Characteristic symptoms of neurasthenia are also: mood swings, increased fatigue, decreased performance, headache, palpitations, sleep disturbance. Pediatricians, examining these children, often identify well-known vegetative-vascular dysfunction.
- Obsessive states . They develop in children with certain psychological characteristics: fearfulness, suspiciousness, indecisiveness. The formation of various fears is typical from an early age. Most sick children develop a variety of defensive reactions in the form of obsessive actions (flapping hands, frequent hand washing, jumping, etc.). At an older age, obsessive thoughts, doubts, and more may appear. At the same time, children may realize the absurdity of their actions and try to fight them.
Below we consider the most common forms of neuroses in children:
- Tiki . Often preceded by obsessive states and actions. They are characterized by stereotypical contractions of individual muscle groups. At an early age, frequent eye blinking often occurs. As it progresses, other muscle groups may be involved in the process (twitching the nose, opening the eyes, raising the eyebrows, lifting the shoulders, and much more). After suffering from acute respiratory viral infections, such children may develop respiratory tics: coughing, coughing, snorting, etc.).
After suffering from acute respiratory viral infections, children may develop respiratory tics (coughing, coughing, snorting, etc.).
- Stuttering . You can also come across another name - logoneurosis. They are synonymous words. Stuttering is a speech disorder associated with convulsive contraction of individual muscle groups of the speech-motor apparatus. You can find out more about the manifestation and treatment of this problem in our article.
- Enuresis . Represents bedwetting. Enuresis is a neurosis only if it develops against the background of psychological trauma or changes in living conditions (visiting kindergarten for the first time, the birth of a brother or sister, etc.). The connection with the environment and situation in which the baby may be is quite characteristic. Over time, children develop a feeling of inferiority due to their illness. At an older age, negative character traits may appear: lack of restraint, anger, irritability. In some cases, enuresis can develop along with encopresis (fecal incontinence).
Neurosis, like other diseases, goes through a number of conditional stages. The effect of treatment depends on the timeliness of assistance. A fairly simple rule: the earlier the help is provided, the more favorable the effect of treatment .
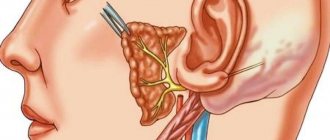
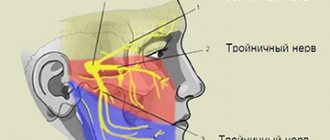
Trigeminal neuralgia in children: diagnosis and treatment
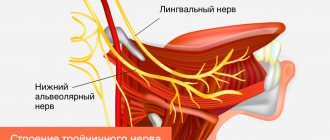
The trigeminal nerve is one of 12 nerves that arise from the brain.
Dividing further into branches, the trigeminal nerve provides communication with the central nervous system of the upper, middle, lower areas of the face and the oral cavity. In the practice of neurologists of the medical network in Kaspiysk, Makhachkala, as well as in other cities, this disease is more common among the female half of the population, aged 50 years and above. Trigeminal neuralgia in children is less common, but nevertheless the problem remains relevant and requires attention from parents, since the child is not always able to adequately describe his sensations.
What is neuralgia?
Neurologists diagnose trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminal neuralgia), the main symptom of which is severe, acute, paroxysmal pain in the area of the connection with the central nervous system (innervation), for example, in the cheek or jaw. The attacks themselves can be of short duration, but with a high frequency of repetitions. In some cases, before attacks there is a feeling of tingling or numbness in the facial area.
The following two types of pathology are noted:
- Typical. In which a severe attack of burning pain occurs unexpectedly and disappears very quickly.
- Atypical, when the pain is aching in nature, causing the patient suffering over a long period of time.
Both types of disease bring a lot of suffering to the sick child and adult. An attack of pain can be triggered by any, even minor, irritation of the area where the inflamed nerve passes, for example, shaving, chewing food or drinking liquid, pronouncing words, an ordinary smile, crying, and even just lightly stroking the face.
Causes of neuralgia
At present, the reasons due to which trigeminal neuralgia develops in children and adults have not been specifically established. However, it is possible to identify risk factors and pathologies that can lead to the disease. These include:
- compression of the nerve where it exits the brain;
- hypothermia;
- nerve damage due to injury or surgery;
- chronic infections of the facial part (caries, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, sinusitis);
- metabolic diseases (gouty arthritis, diabetes);
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- mental disorders;
- atherosclerosis;
- tumor formations in the brain;
- infectious diseases (syphilis, herpes, tuberculosis);
- allergies;
- helminthic infestation
- cardiovascular diseases, etc.
Attacks are provoked by any irritation of the innervation zone of the trigeminal nerve: washing, shaving, using cosmetics, chewing food, talking and, unfortunately, much more.
Consequences of trigeminal neuralgia and diagnostic methods
Among the complicated consequences of neuralgia, if timely or adequate treatment measures are not taken, neurologists name the following pathologies:
- facial nerve paresis;
- hearing loss;
- paralysis of facial muscles;
- chronic pain;
- nervous system disorders;
- loss of facial symmetry.
To diagnose neuralgia, a sick child must first undergo a consultation with a neurologist at a children's clinic. After which the attending physician will determine the need for further examinations, which include:
- radiography of the skull and teeth;
- magnetic resonance therapy (MRI);
- electromyography;
- laboratory blood test.
In some cases, you may need additional consultation with specialized specialists - an ophthalmologist, dentist, otolaryngologist or pediatrician.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
With timely treatment, the prognosis is usually positive. The main method of treating neuralgia in children in Kaspiysk and Makhachkala includes drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, and surgery. During drug treatment, anticonvulsants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, and drugs to reduce muscle tension are prescribed. During physiotherapy, our Healer clinics in Kaspiysk and Makhachkala effectively carry out acupuncture, magnetic therapy, laser and ultrasound treatments, as well as electrophoresis with medications prescribed by a doctor.
The need for surgical treatment of a child may arise when it is necessary to eliminate the cause of nerve compression and it is impossible to achieve the desired result by other means. Currently, minimally invasive operations such as radiosurgery are widespread. The specific type of surgical intervention depends on the characteristics of the disease. But the main thing you need to know is that the sooner the operation is performed, the greater the effect can be achieved.
Musaeva Raisat Magomedkadievna, pediatric neurologist in Kaspiysk.
Works at the clinic “Healer-Kaspiysk” at the address: st. Ordzhonikidze, 6a.
Opening hours: Mon, Tue, Thu, Fri, Sat – from 13.00 to 15.00.
Telephone number for making an appointment in Kaspiysk: +7.
Indications for use of Mydocalm
Tablets and injections are prescribed for the following pathological conditions:
- hypertonicity of the skeletal muscles with damage to the central nervous system of an organic nature - stroke and diseases of the pyramidal tracts of the brain, multiple sclerosis, encephalomyelitis, etc.;
- cerebral palsy;
- contracture that occurs against the background of osteochondrosis, osteoarthrosis, spondylosis;
- stiffness of movement, impaired speech due to spasticity of skeletal muscle tissue;
- muscular dystonia;
- spinal dystrophy;
- inflammatory processes in the spinal cord and brain against the background of intoxication of the body, allergies and viral damage;
- after spinal cord injury and surgery;
- cervical and lumbar syndrome;
- arthrosis of large joints.
Mydocalm is prescribed in complex therapy as an adjuvant for the following pathologies:
- obliterating diseases of the circulatory system - thromboangiitis, diabetic angiopathy, arteriosclerosis, Raynaud's syndrome, diffuse scleroderma;
- pain during menstruation;
- cholelithiasis;
- haemorrhoids;
- colic in the kidneys;
- threat of miscarriage with high uterine tone;
- impaired vascular innervation - intermittent angioedema dysbasia, acrocyanosis;
- diffuse scleroderma with fibroids;
- complications of diabetes.
Types of nervous tics in children
Each child has his own individuality, and therefore nervous tics that arise for one reason or another are different.
Tic manifestations generally have two types:
- Motor (motor). They are detected by spasms of individual muscles, their groups or movement of limbs and other parts of the body.
- Voice (vocal). They can be recognized in the form of frequently repeated individual sounds, syllables, exclamations, words and even phrases.
Both groups are divided into simple and complex tics. Everything is clear here. A simple form - one short movement or sound, a complex one - several muscle groups are involved, if there are vocal disorders, progress is also observed in them.