Oligophrenia in adult women is a persistent disorder of intellectual, mental, emotional and volitional development that is observed from birth or occurs during life as a result of injuries and illnesses. Characterized by adaptation disorder, poor adaptability to the environment, problems in the process of social interactions.
To schedule a consultation, just call 8(969)060-93-93.
THE ESSENCE OF THE PROBLEM
Mental retardation is a serious limitation in the skills necessary for daily life, social and intellectual activities. Such individuals experience problems with speech, motor development, intelligence, adaptation, emotional-volitional sphere, and cannot interact normally with the environment.
This definition was given by AAIDD - the American Association for Developmental and Intellectual Disabilities, which changed its approach to this problem. It is now believed that providing ongoing, personalized support can improve the quality of life of a mentally retarded person. Yes, the term itself was replaced with a more tolerant and inoffensive one – “intellectual disability”.
In addition, such a disease is now not considered mental. And it should not be confused with developmental disabilities. The latter covers a broader area, but is very closely related to the first: autistic disorders, cerebral palsy, etc.
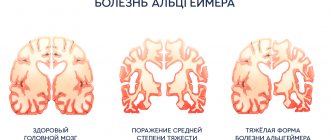
Oligophrenia is a chronic non-progressive disease that occurs as a result of brain pathology in the prenatal period or after birth (up to three years).
Despite the achievements of modern medicine and serious preventive measures, it cannot give an absolute guarantee that this disease will not appear. Currently, 1 to 3% of people worldwide suffer from UO, but most suffer from a mild form (75%).
There is also acquired mental retardation - dementia. This is a separate “age-related” pathology in older people, a consequence of natural brain damage and, as a result, the collapse of mental functions.
Degrees of mental retardation
The most effective diagnostic method for identifying mental retardation is determining the IQ. Based on the results obtained, the following stages of mental retardation are distinguished: debility, imbecility, and idiocy. However, today such a classification is rarely used by doctors based on ethical considerations. Doctors prefer to indicate the stages of oligophrenia in neutral terms. Pathology in this case is also classified based on the obtained IQ. In this division of oligophrenia, three stages have the following degrees:
- light – 50-70 points;
- moderate – 35-50 points;
- severe – less than 20 points.
As you can see, the higher the IQ values, the less pronounced the stage of the pathology. However, the traditional division of pathology allows us to give a clearer picture of the disease. In this case, how is oligophrenia divided into stages? The three stages are distributed as follows: debility corresponds to the mildest and most common form of the disease, imbecility to the average, and idiocy to the deepest. Let's take a closer look at them.
CAUSES
Intellectual disability is the result of genetic diseases and many other factors, or rather, their combination: behavioral, biomedical, social, educational.
| Causes | Factors | |||
| biomedical | social | behavioral | educational | |
| Intrauterine development of the fetus (prenatal) | -age of parents; - diseases in the mother; -chromosomal disorders; -congenital syndromes | the mother's miserable existence, she was subjected to violence, was poorly fed, did not have access to medical services | parents used alcohol, tobacco, drugs | parents are not prepared for the birth of a child, are cognitively incompetent |
| Birth of a child (perinatal) | -prematurity; - birth injuries | poor baby care | child abandonment | lack of medical supervision |
| Later life (postnatal) | -bad Education; -brain injuries; -degenerative diseases; -epilepsy; -meningoencephalitis | -poverty; -poor family relationships | -domestic violence, harshness towards the child, isolation; -failure to comply with safety measures; -bad behavior | -poor quality medical care and late diagnosis of diseases; -lack of education; -lack of support from other family members |
No one can accurately name the specific “culprits,” even despite fairly scrupulous research and early diagnosis. But, if you analyze the table, the most likely cause of oligophrenia may be:
- any genetic failures - gene mutations, their dysfunction, chromosomal abnormalities;
- hereditary developmental disorders;
- malnutrition;
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy - syphilis, rubella, HIV, herpes, toxoplasmosis, etc.;
- premature birth;
- problematic childbirth - asphyxia, mechanical injuries, hypoxia, fetal asphyxia;
- insufficient upbringing of the child from birth, parents devoted little time to him;
- toxic effects on the fetus leading to brain damage - parental use of strong drugs, drugs, alcoholic beverages, smoking. This also includes radiation;
- infectious diseases of the child;
- skull injury;
- diseases affecting the brain - encephalitis, whooping cough, meningitis, chicken pox;
- drowning.
Causes of mental deviation
Among the factors that influence the occurrence of mental pathology are the following:
- genetic predisposition to the disease. In approximately half of cases, mental retardation is inherited;
- chromosomal disorders, gene abnormalities, their mutation due to radiation, infectious diseases, maternal use of toxic substances during gestation;
- severe labor, which led to injury to the child (especially in the case of head injury), asphyxia, cerebral hypoxia;
- premature birth;
- infectious diseases affecting the central nervous system;
- lack of education, negative atmosphere in the family, psychological trauma at an early age, late diagnosis of the disease, etc.
It should be noted that to date scientists have not been able to find a single cause of mental retardation. As a rule, the occurrence of the disease is associated with several unfavorable factors that occur simultaneously or alternately.
DEGREES OF MENTAL RETARDATION
Intellectual disability is divided into 4 stages. This classification is based on special tests and is based on the IQ level of intelligence:
- mild (moronicity) – IQ from 70 to 50. Such an individual has impairments in abstract thinking and its flexibility, short-term memory. But he speaks normally, albeit slowly, and understands what is said to him. Often such a person cannot be distinguished from others. But he is not able to use the acquired academic skills, for example, financial management, etc. In social interactions, he lags behind his peers, so he may fall under the negative influence of others. He can perform everyday simple tasks himself, but more complex ones require outside help;
- moderate (not very pronounced imbecility) – IQ 49–35. A person needs constant continuous patronage, including for establishing interpersonal relationships. Spoken speech is very simple, and he does not always correctly interpret what he hears;
- severe (severe imbecility) – IQ from 34 to 20. A person does not understand speech well, numbers, the concept of time is not available to him - for him everything happens here and now. Speaks in monosyllables, vocabulary is limited. Needs constant monitoring and care in terms of hygiene, clothing, nutrition;
- deep (idiocy) – IQ level less than 20. Speech, its understanding and sign language are very limited, but are able to express simple words and instructions, as well as their desires and emotions using non-verbal communication. Severe sensory and motor problems are present. Completely dependent on others.
It should be noted that with long-term and persistent training of people with any degree of dementia, they can achieve basic skills.
Stages and degrees of debility
There are three stages depending on IQ:
- easy : IQ 65-69 points;
- moderate : IQ 60-64 points;
- severe : IQ 50-59 points.
The following types of debility are also distinguished:
- Atonic . It is characterized by the fact that patients demonstrate strange, motiveless behavior.
- Asthenic . Patients are emotionally unstable, quickly get tired and become mentally and physically exhausted.
- Stenic . This degree has two poles. On one: good-natured, sociable, lively people. On the other: hot-tempered, emotionally unstable, uncontrollable.
- Dysphoric . This is the most dangerous degree of the disease: the mood of patients in this group is aggressive, often aimed at destruction and pogrom.
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA
According to DSM-5 (the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders), intellectual disability is a neurodevelopmental disorder, characterized and defined by the following symptoms:
- Deficits in intellectual functioning. Difficulties with abstract thinking, reasoning, decision making, and learning. All this must be confirmed by appropriate tests.
- Deficit of adaptive behavior. Inconsistency with accepted cultural and social standards, inability to live independently, reduced social responsibility, difficulties with communication. That is, the individual cannot communicate and serve himself and needs care wherever he is.
- A person finds it difficult to perform tasks that require memory, attention, speech, writing, reading, mathematical reasoning, and is unable to gain practical skills.
- Problems in the social sphere. Does not have socialization skills - communication with people, cannot make friends and maintain relationships. Doesn't understand his feelings and thoughts.
- Problems in the practical field. Poor ability to learn skills, lack of control over one’s own behavior, inability to take care of oneself, irresponsibility, etc.
Other signs
Together with the mentioned criteria, the presence of any stage of CP can be determined by the following criteria.
In the primary period of development, a healthy child masters simple skills, which, as they grow older, are well mastered and move on to more complex ones. Adaptive and intellectual problems become noticeable as the child develops. When they appear depends on the type, cause and degree of mental retardation.
The stages of development (motor skills, speech, socialization) of children with intellectual disabilities are the same as those of healthy people, but they progress much more slowly, that is, they reach a certain level much later. With a mild form of mental retardation, the lag behind peers becomes noticeable only at the beginning of school (learning difficulties), and with a severe form - in the first years of life.
As a rule, if intellectual disability is inherited (by genes), it affects the person’s appearance.
Oligophrenics are more likely to have physical, neurological and other health problems. For such individuals, sleep disturbances, anxiety disorders, and schizophrenia are also common. Diabetes, obesity, sexually transmitted diseases, and epilepsy are common.
People with mild to moderate intellectual disabilities speak much less well than their younger peers. The higher the level of disorder, the worse the speech.
Behavioral disorders characteristic of oligophrenics are associated with the discomfort they experience when communicating, the inability to communicate their thoughts to others, and a misunderstanding of their desires and needs. In addition, they suffer from social isolation. This is where manifestations of excitement, anxiety, nervousness, etc. follow.
Diagnosis of oligophrenia
As a rule, the symptoms are pronounced, and it is not difficult to diagnose mental retardation in children. If a child has a delay in physical and psychological development, these are signs of mental retardation in children. Based on this, a diagnosis is made.
Also, to make a diagnosis, the doctor communicates with the child, determines the emotional and mental background. The specialist monitors the baby’s speech, notes how quickly he answers the question, how he reacts to communication with the doctor, and what emotions he expresses. What matters is the baby’s vocabulary and his abstract thinking. Also, the doctor’s task is to determine the child’s attitude towards himself and the environment, for example, towards peers and adults.
Diagnosis of mental retardation includes a test of thinking. The child is given a saying, a metaphor, a sentence. The doctor asks the child to give them an explanation, to explain the meaning of what was said. We also work with images. The specialist shows the child a picture and asks him to tell what he sees in it. At the same time, the doctor monitors not only speech activity, but also the emotional state of the baby. During the diagnosis, the child's memory is checked. The doctor lists words or gives a short story, after which he asks the baby to reflect what was said.
In order to establish the cause, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, you need to comprehensively study the problem. This is the main task of the specialists of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg).
Patients are prescribed an MRI, which allows them to examine the brain, and tests are taken to check for congenital syphilis.
When to see a doctor
If any of the listed symptoms occur, you should consult a neurologist or neurologist.
Seeing a doctor depends on what additional symptoms accompany the disease; for example, in case of speech defects, it is recommended to make an appointment with a speech therapist. To check the child’s development, you need to make an appointment with a child psychologist, who will help you understand what causes problems in communicating with peers and other people. Our clinic is located in the center of Moscow.
Treatment and rehabilitation for oligophrenia
Treatment of oligophrenia is a complex process. If a child is developmentally delayed, mental development can be corrected only in the early stages of the disease. If the disease was diagnosed in late stages, symptomatic therapy is prescribed. It is important to fully examine the patient, which will help to understand whether he has infectious diseases or not. If they are detected, additional treatment is prescribed.
Complex treatment necessarily includes a cycle of taking vitamins and medications that help improve metabolism in the brain. Specialists such as a psychologist, neurologist, and speech therapist work with the child. It is also important to involve teachers. These specialists are faced with the task of preparing the child for society, adapting him, and teaching him to serve himself independently.
Doctors note that a child suffering from oligophrenia, although he lives and is among people, behaves aloof, rarely communicates with adults, and has difficulty making contact with peers. This is due to the fact that it is difficult for a child to understand the people who surround him, and as a result, those around him, in turn, do not understand him well. This problem may be due to the fact that the child received little attention from loved ones, so he developed this pattern of behavior.
An important nuance: after the doctor announces the diagnosis, experiences are typical not only for the parents, but also for the child himself. At this stage, he withdraws into himself and stops communicating with peers and close people. You need to understand that this is also psychological stress for him.
To eliminate the problem, experts recommend working with the child, having conversations with him, and playing educational games. Parents first of all need to learn how to find contact, as a result of which the child will respond in kind when communicating with loved ones. Gradually, this model of behavior and communication will move to another level, the child who has been diagnosed with mental retardation will begin to communicate with peers.
If a child has problems with speech development, he is referred to a speech therapist for correction. The most difficult thing is to correctly introduce a child into a team, for example, into a class, a group in a kindergarten, to prepare him for communication with peers. Here the main task facing doctors, parents, and teachers is to teach the child to care for himself independently.
In the future, a patient with oligophrenia is sent to study in a special school, a group, where they help him choose and instill professional skills. For each patient, the doctors of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) select an individual plan of classes and treatment, taking into account the degree of mental retardation and the patient’s development (including physical). Also (if any) neurological disorders and the emotional state of the patient are taken into account.
Further life and treatment depend on when the diagnosis was made, what degree of the disease, what level of mental retardation was diagnosed, when treatment began. With a mild form of oligophrenia, patients can take care of themselves, master simple professions, exist independently in society, and communicate with people. People with moderate to severe illness can be taught to perform light household chores. If a patient has been diagnosed with a deep form of oligophrenia, he needs constant care and assistance.
SYNDROMES COMBINED WITH DIFFERENT DEGREES OF IR
Down syndrome is the most common genetic cause of intellectual disability. It is caused by a chromosomal abnormality - if normally there are 46 of them, then in this case there is an unpaired 47th chromosome. People with this syndrome can be identified by an abnormally short skull, flat face, short arms and legs, short stature, and small mouth. They process the information received poorly and remember it, they lack the concept of time and space, and their speech is poor. Moreover, such individuals adapt well to society.
Martin-Bell syndrome (fragile X chromosome). The second most common genetic cause of mental retardation. It is recognized by the following external features: increased mobility of joints, an elongated face, an enlarged chin, a high forehead, large, protruding ears. They start talking late, but poorly, or don’t speak at all. They are very shy, hyperactive, inattentive, constantly moving their hands and biting them. Men have more cognitive impairment in this category than women.
Williams syndrome (“elf face”). It occurs as a result of hereditary chromosomal rearrangement, the loss of genes in one of them. The patients have a very interesting appearance: the face is narrow and long, blue eyes, flat nose, large lips. Usually suffer from cardiovascular diseases. Rich vocabulary, good memory, excellent musical abilities, and social interaction skills. But there are problems with psychomotor skills.
Angelman syndrome (happy doll or Parsley). Caused by a change in chromosome 15. Very light eyes with characteristic spots on the iris and hair, the head is small, the chin is pushed forward, the mouth is large, the teeth are sparse and long. Severe delay in psychomotor development, significant impairment of speech and movement (poor balance, walks on stiff legs). He often smiles and even laughs for no reason.
Prader-Willi syndrome . It is characterized by the absence of a paternal copy of chromosome 15 and a number of other disorders. He is short in stature, has small arms and legs, suffers from compulsive overeating, and, as a result, obesity. Problems with short-term memory, speech, information processing.
Lejeune's syndrome (cry of the cat or 5p syndrome). A very rare and serious disease caused by the absence of the short arm of chromosome 5. The head is small, the face is round, the lower jaw is underdeveloped and the bridge of the nose is wide, so the eyes are located far from each other. The feet are turned out, the hands are small. The larynx is underdeveloped, there are vision problems, in particular, strabismus. She often cries and makes a sound similar to a kitten meowing. Motor development is delayed, and the ability to pay attention is limited.
In addition to the syndromes mentioned, intellectual disability can coexist with cerebral palsy, deafness and blindness, autistic disorders, epilepsy and other somatic and mental illnesses.
Treatment of oligophrenia
Treatment of oligophrenia in the stage of debility and imbecility consists of correcting existing intellectual defects with the help of:
- correctional schools;
- speech therapists, teachers specializing in the development of speech, thinking, social skills and attention.
For mental retardation in the idiocy stage, treatment is reduced to caring for the patient in a psychiatric hospital or a home for the mentally retarded/disabled.
Neurologists, defectologists and psychologists working with mental retardation sufferers set themselves the goal of maximally adapting them to self-care and life in society. Very often, sick children live in isolation. Even their closest relatives do not understand them, which only aggravates the situation.
A rehabilitation plan for each patient is developed individually. This takes into account the degree of mental retardation, the presence/absence of somatic and neurological disorders, and characteristics of physical development.
CHILDREN WITH INTELLECTUAL DISABILITIES
Society must be tolerant of people with mental retardation; a special approach and teachers are needed who know the specifics of the work, who can give intellectual disabilities an education and help them realize their potential.
Children with disabilities need the support of others, especially parents, who must provide such children with psychological comfort, development, and improve their quality of life.
In infants, it is quite difficult to identify mental retardation, especially its mild form, since they are almost no different from others. But their activity is impaired: they begin to hold their heads up late, babble, sit, and crawl.
But as the child grows up, when he begins to go to kindergarten, it becomes noticeable that he has difficulty maintaining a daily routine, communicating with peers, and mastering new skills. For example, a three-year-old child cannot assemble a pyramid on his own, although he repeated this many times with the teacher. My classmates succeeded after 1-2 lessons.
Oligophrenic children are not inquisitive; they cannot sit in one place for a long time, but they get tired very quickly. Their speech is poor, they confuse letters (especially consonants). Since their phonemic hearing and analysis are poorly developed, they pronounce words incorrectly, and then write incorrectly. The development of auditory discrimination and the articulatory speech apparatus lags behind - hence slurred speech.
Gross and fine motor skills suffer as the central nervous system develops abnormally. The baby's movements are uncertain and sluggish, he manipulates objects chaotically. For a long time he cannot determine the “main” hand; he moves both of them inconsistently.
Difficulties with the “pinch” and “tweezer” grip do not allow the child to hold a pencil and pen correctly and learn to write. Underdevelopment of fine motor skills also makes it difficult to care for oneself.
The child cannot concentrate and remember something. This negatively affects cognitive activity and mental activity. The baby does not see or hear what is said to him due to attention problems.
Studying is difficult for such children: they learn the material slowly because they do not remember it and cannot reproduce the information received. They cannot apply the skill or knowledge they have learned after repeated repetitions and quickly forget it.
The child is not able to express feelings verbally, because he has poor speech, but he expresses emotions through facial expressions, touches, and gestures. He is incapable of empathy. His will is weak, so he is trusting of any person, easily suggestible, and this is very dangerous.
Contact a specialist (neurologist) without delay if your child behaves unusually or you do not understand what is happening to him. The benefit of this is double - in the best case, all doubts about the adequacy of your child will be dispelled, and in the worst case (which, however, is also not bad) - early diagnosis will allow you to immediately take measures to solve the problem. This will allow such a child to be better socialized and adapted to life.
The doctor will examine the little patient, ask the parents about the symptoms, when they appeared, about the child’s practical and social skills, adaptive behavior, etc. An intelligence test is required to find out how teachable the child is, how he can solve problems and think abstractly. An IQ below 70 may indicate the presence of intellectual disability and its level.
Tips for parents
The following recommendations can be given to mothers and fathers of special children:
- Of course, hearing such a diagnosis for your child is a terrible blow, causing negative thoughts. There is a feeling of guilt, resentment at fate, anger, despair, melancholy. But you still have to accept this fact, come to terms with it, and communication with other parents who have a similar problem can be a good support. It’s also a good idea to visit a psychologist.
- You need to clearly separate your capabilities from what is impossible to do and, without giving up, look for ways to solve problems and means.
- Consult with specialists. It is also advisable to collect as much information as possible from serious sources about mental retardation, how and how you can help the child, what exactly should be done, where to go. The experience of families with an oligophrenic child is invaluable, communicate with them.
- Learn about and take advantage of government and community services for families with children with mental retardation.
- Think not about limitations, but about your child’s capabilities, what he can do and what he needs, how to please him. It is in your power to help him become independent and socialize as much as possible.
- Under no circumstances isolate your child from other people, neither children nor adults.
- Despite the fact that the level of development of your child at certain stages is lower than that of his peers, you need to communicate with him not as with a baby, but in accordance with his age.
- It is necessary to regularly conduct developmental and training sessions. The goal of education is social adaptation, that is, the child must master speech, writing, and everyday independence.
Don’t expect anything special from all your efforts, some super-result, be happy with the smallest progress. But we shouldn’t stop there either. Even if you understand your child by individual words, this is not enough for communication with others and social adaptation. Move on, don't give up and don't indulge your child's laziness.
To reduce the likelihood of having a mentally retarded child, a pregnant woman should:
- DO NOT drink, smoke or take drugs;
- take folic acid;
- visit a doctor regularly;
- Eat a diet containing fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and foods low in saturated fat.
After the baby is born:
- carry out screening of the baby - this will identify diseases that can provoke mental retardation;
- visit your pediatrician regularly;
- do all scheduled vaccinations;
- allow him to ride a bicycle only with a helmet, and to ride in a car until the required age only in a car seat;
- Avoid contact of your child with household chemicals and lead-based paints.
Support by specialists
A child with an intellectual disability needs comprehensive support throughout childhood from the following specialists:
- child psychologist and psychiatrist;
- speech therapist;
- neurologist;
- speech pathologist.
If there are other disorders (blindness, deafness, cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disorder), then a rehabilitation specialist, an ophthalmologist, a massage therapist, and a physical therapy teacher are added to the above-mentioned professionals.
Symptoms of oligophrenia in children
Symptoms of mental retardation in children are expressed in a complex manner; it can be not only mental retardation, but also other manifestations, for example:
- motor;
- speech;
- memory problems;
- poor concentration;
- problems with imaginative thinking.
Against this background, the child develops neurological disorders, problems with expressing emotions, and will. If an adult has been diagnosed with mental retardation, his thinking and development will resemble the thinking and development of a small child.
In mild to moderate forms, the symptoms are less pronounced. At the same time, the child will not be able to go beyond the situation in which he now finds himself. The ability to concentrate attention on specific things will also be reduced, abstract thinking will be impaired, initiative will be expressed weakly, have an immature, unclear character.
Children with mental retardation may exhibit both good and poor memory. In most cases, it is weakened, but there are situations when a sick child shows good memory for mechanical memorization of small information, for example, names, numbers, titles. Children have a weak vocabulary, their speech is simplified, phrases will be short, simple, words in sentences may be arranged in the wrong order.
With a mild degree of oligophrenia, children can read, remember what they read, display, and repeat fragments of what they read. If a severe form of the disease has been diagnosed, the child will not be able to read the proposed material or will read it, but will not be able to remember it and will not display it. In most cases, even if a child knows the letters, he will not always be able to put them together.
Dealing with everyday issues is a difficult task for a child with mental retardation. Here, too, everything depends on the degree of the disease. Such children will not be able to independently make purchases in a store, prepare lunch, make tea, clean the house, or choose clothes in accordance with weather conditions. Children with mental retardation are often guided by the opinions of other people and do what others tell them. The physical development of a child is not always normal. There are children whose physical development level can be considered above average, but the majority are behind the norm.
The development of oligophrenia in children depends on age. Clearly expressed signs of the disease are formed at 6-7 years of age. The first sign is excessively increased irritability. Such children make little contact with adults and communicate little with peers. It takes more time to learn basic actions; for example, it is more difficult to teach a mentally retarded child to use a cutlery than a healthy one.
Children with mental retardation show less activity and interest; for example, starting from the age of three, healthy children begin to show interest in toys. Patients with mental retardation do not show such interest. When healthy children move to a new level of development - imitating the behavior of adults, patients with mental retardation are just beginning to show interest in toys.
Activities such as appliqué, working with plasticine, and drawing do not attract children with mental retardation. It is difficult for a child to recognize the properties of objects and compare them with the outside world. In order for the information to stay in your head, you need to repeat it many times and go through all the steps again. Patients do not express their emotions as clearly as healthy children. On the contrary, non-standard, inflated emotions may appear.
IS OLIGOPHRENIA CURABLE?
Treatment and correction of this disease is not an easy task; it will require a lot of effort, time, and patience. In addition, different levels of mental retardation and the age of the patient require their own methodology. However, if the tactics are chosen correctly, a positive result becomes noticeable within a couple of months.
Unfortunately, complete relief from intellectual disability is impossible. The thing is that certain parts of the brain are damaged. The nervous system to which it belongs is formed during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus. After the birth of a child, its cells almost do not divide and are not able to regenerate. That is, the damaged neurons will not recover and mental retardation remains with the person for the rest of his life, although without progressing.
But, as already mentioned, children with a mild degree of the disease respond well to correction, receive self-care skills, education, and can work quite normally, performing simple tasks.
Prevention of oligophrenia
Since mental retardation is very often caused precisely by problems of intrauterine development, preventive measures include:
- registration in the housing complex before 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- regular visits to the pregnant gynecologist, timely testing, ultrasound diagnostics;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- taking daily walks in the fresh air;
- quality rest (sleep at least 8 hours a day);
- rational and balanced nutrition;
- the use of gentle methods of obstetrics, refusal of obstetric forceps.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
SUPPORT FOR PEOPLE WITH ID
This disease develops in different ways, but it is very important to diagnose it as early as possible. In this case, specialists will begin to work closely with such a patient at an early age, which significantly improves his condition and quality of life.
Such assistance is necessarily personalized, that is, it is planned taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, his needs and desires. People with this diagnosis are not the same, therefore, help for each of these individuals in the sphere of life and certain activities should have its own type and intensity.
In many countries of the world, including ours, special programs have been developed whose goal is to improve the quality of life of people with mental retardation. They are integrated, “dissolved” in society. Children with mild degrees of the disease go to auxiliary schools and kindergartens, inclusive classes in regular educational institutions. There are even groups in vocational schools where you can get an education and then work in your specialty.
Who is he, a person with mild dementia?
Moronism is the most common and mildest variant of mental disability.
The severity of the disease can be mild, moderate or severe. According to the dominant manifestations: atonic, sthenic, asthenic, dysphoric. Patients remember any information slowly and forget quickly. They do not know how to generalize, do not master abstract concepts. The type of thinking is concrete-descriptive. That is, they can only talk about what they saw, without making any conclusions or generalizations. Their understanding of logical connections between events and phenomena is impaired.
Patients with oligophrenia to the extent of debility are practically the most honest people in the world. But not for high moral reasons. These people are simply not capable of fantasizing. With the exception of rare, pathological cases described in judicial practice, they can only talk about what they saw.
During a conversation, one immediately notices: speech disturbances, monotony, lack of emotion, poor vocabulary, primitive sentence construction.
Sometimes such a phenomenon as giftedness in some areas is added against the background of general pathology: the ability to mechanically memorize large texts, absolute pitch, genius in mathematics, artistic gift.
Patients do not like change of environment. Only in a familiar environment do they feel confident, protected and even capable of independent life.
They are highly suggestible, which is why they are easy prey for criminals who use them like zombies. It is easy to convince a gullible oligophrenic of something, to impose your point of view, which they will perceive as their own. From among them often emerge uncontrollable and unreasoning fanatics who never change “their” beliefs.
Will and emotion are almost undeveloped. They are guided by instincts: sexual, food. Sexual promiscuity is an unpleasant phenomenon that causes disgust among others.
In persons suffering from debility, instincts are almost impossible to control and correct. Food instinct is the basis. They eat a lot, are indiscriminate in their food, and have a poorly developed sense of fullness.
In general, with successful socialization, they are excellent spouses (suggestibility), not prone to conflicts, and very obedient (no judgment of their own).
They are easy to manage. Because of their suggestibility and controllability, they can be both completely adequate members of society and absolutely asocial, maliciously vindictive and cruel.
They can have a very attractive character: kind, like children, warm-hearted, devoted to those who care about them. Along with them, there are individuals who are aggressive, angry, stubborn, and vindictive.
Moronism is expressed both in excessive excitability and in obvious inhibition (in common people the latter are called “brakes”).
Persons diagnosed with “moronism” do not serve in the army, do not drive cars, do not have the right to purchase and store weapons, and work in state and municipal institutions is not for them. Systematic observation by a psychiatrist increases their chances of adapting to the outside world.