Find out more about diseases starting with the letter “O”: Fainting (syncope); Occlusive hydrocephalus; Occlusion of the carotid arteries; Olivopontocerebellar degenerations; Optico-chiasmatic arachnoiditis; Neuromyelitis optica; Brain tumors; Cerebellar tumors; Tumors of peripheral nerves; Spinal cord tumors; Brain stem tumors; Central nervous system tumors; Tumor of the cauda equina; Tumor of the pineal gland; Oromandibular dystonia; Osteocondritis of the spine; Brain swelling; Carbon monoxide poisoning; Ophthalmoplegic migraine.
A cerebellar tumor is a pathological formation in the cerebellum, benign or malignant in nature. It may have an independent origin or be a secondary disease of a metastatic nature. The diverse clinical picture is divided into 3 groups - cerebral, cerebellar and brainstem symptoms.
Establishing a conclusion about a tumor is based on data from magnetic resonance scanning of brain structures. The diagnosis is confirmed after receiving the results of a histological examination of the formation material. Treatment of a cerebellar tumor involves surgery with absolute removal of the lesion, restoration of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, and elimination of compression of the brain stem.
general information
Of the total number of diseases with brain tumors, cerebellar tumors account for approximately 30%. A detailed histological study makes it possible to determine more than 100 morphological types of cerebellar formations. The results of numerous studies by neurologists, neurosurgeons, and oncologists confirm that in the vast majority of cases—70%—glioma develops.
The possibility of developing pathology does not have limited age criteria. However, medulloblastoma is diagnosed more often in children, hemangioblastoma, astrocytoma - in middle-aged people, in older patients - glioblastoma, metastatic neoplasms. The risk of developing cerebellar cancer is higher in Caucasian men.
What is cerebellar cancer
Cerebellar cancers include tumors that contain mutated cells. The disease is malignant in nature and causes serious complications.
Cerebellar cancer is manifested by headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, respiratory function, convulsions, paresis, tremor of the upper extremities, vomiting, and increased fatigue.
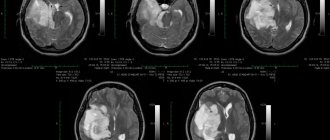
The disease can be confirmed by CT, MRI, radiography, and neuro-ophthalmological examination.
Treatment is standard - chemotherapy and radiation therapy, surgery, medications.
According to statistics, pathology is detected in 30% of cases of brain formations. Using histological examination, more than 100 types of neoplasms are determined.
Cancer of the cerebellum can occur regardless of age. Certain types are typical for middle-aged and older patients, and some types of tumors are detected only in children.
Pathogenesis and causes of disease development
Factors promoting the development and growth of tumor cells are not known. According to medical research, it has been determined that with the primary disease of Recklinghausen's neurofibromatosis, 10 of the patients develop a hereditary tumor of the cerebellum. It is generally accepted that tumor provocateurs can be exposure to radiation, oncogenic viruses (herpes, human papillomas, some adenoviruses), and the effect of carcinogenic chemical compounds on humans. The risk of developing malignant tumors increases in patients undergoing immunosuppressive treatment (for example, HIV-infected patients).
The mechanisms of neoplasm development occur in the following directions:
- Damage to the cerebellar substance occurs due to compression by the tumor with further death. This process is accompanied by focal cerebellar symptoms.
- The longer the tumor develops, the more it fills the fourth ventricle and compresses the brain stem, which is accompanied by dysfunction of the cranial nerves and brain stem clinical signs.
- Increasing hydrocephalus of the brain is accompanied by a general cerebral clinical picture and an increase in intracranial pressure. The cerebellar tonsils descend and become pinched in the posterior cranial fossa. The medulla oblongata is located between the occipital bone and the cerebellum. These processes cause bulbar disorders, complications from the cardiovascular system and breathing.
Tumor stages and metastasis
Among the many factors that influence the prognosis of the disease, the extent of the tumor is extremely important. Two main parameters are taken into account here: the size and infiltration of the primary tumor (T-stage) and the degree of its dissemination or metastasis (M-stage).
T stage
T1 - tumor less than 3 cm in diameter: in the roof of the IV ventricle, vermis, or cerebellar hemisphere.
T2 - a tumor more than 3 cm in diameter, affects one nearby structure or partially fills the fourth ventricle.
T3a - affects two adjacent structures or fills the fourth ventricle with spread into the cerebral aqueduct or the foramina of Magendie and/or Luschka.
T3b - the tumor grows into the bottom of the fourth ventricle and fills the cavity of the fourth ventricle.
T4 - the tumor spreads further through the cerebral aqueduct and affects the midbrain and third ventricle.
M stage
M0 - there are no signs of subarachnoid or hematogenous metastases.
M1 - tumor cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
M2 - a node in the cerebellum or subarachnoid space, or in the third or lateral ventricles.
M3 - nodes in the spinal arachnoid space.
M4 - extracranial metastases.
The T stage is determined during surgery, when the surgeon can directly determine the boundaries and extent of the tumor. In most cases, T3-T4 stages of the disease predominate. Their share ranges from 50% to 65%. Medulloblastoma tends to metastasize along the cerebrospinal fluid pathways and, less often, extracranially. In general, at the time of diagnosis, 20%-30% of patients already have metastases. In young children this figure reaches 50%. Moreover, about 15% of metastases are supratentorial, about 12% are spinal. In approximately 10% of cases, extracranial metastases are detected - most often in the bones (up to 80%), less often - in the lungs, liver, and peritoneum.
Stages M2-M3 are determined on the basis of MRI and CT with contrast enhancement of the brain and spinal cord, spinal metastases are detected using myelography.
Extracranial metastases are detected by ultrasound of internal organs, scintigraphy, and examination of a puncture biopsy of the bone marrow.
Classification
Cerebellar tumors, like all tumors, regardless of location, are divided into malignant and benign. Medulloblastoma is a tumor characterized by rapid growth and invasion of the subarachnoid membranes. In children, it is the most commonly diagnosed type of cerebellar malignancy.
The second place is occupied by cerebellar sarcoma, according to general data on prevalence. Locally spreading hemangioblastomas and astrocytomas with infiltrative growth are the most common benign tumors of the cerebellum. In most cases, they have a cystic modification and consist of a small node and a cystic cavity of significant size.
With any form of tumor, the brain stem is subject to compression due to the small lumen of the posterior cranial fossa. This is risky in any case, so the division of neoplasms into benign and malignant is very arbitrary.
Based on the source of development, tumor processes of the cerebellum are divided into 2 significant groups - primary and secondary neoplasms. The primary tumor is formed from the cells of the cerebellum, as a result of persistent replacement of cells of its substance with pathological cells (the process of metaplasia starts).
Primary tumor foci can be benign or malignant. Metastatic origin is characteristic of secondary cerebellar neoplasms. They can develop in breast cancer, thyroid cancer, malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract and lungs. Secondary tumors invariably have a malignant nature.
Classification of cerebellar hemangioblastoma
It is worth understanding: based on the area of the lesion, a distinction is made between microscopic and macroscopic cerebellar hemangioblastoma (CM – this is how we will further denote the disease).
- Pure cell tumors are characterized by yellow cells appearing on abnormal vessels.
- Transitional tumors consist of stromal cells as well as capillaries. The ratio is approximately equal, as practice shows.
- Juvenile tumors are characterized by the fact that they represent a dense clot of capillaries, the walls of which are thin.
The classification is quite extensive, there are other points. However, all details will be provided by the attending physician.
Symptoms
The picture of the disease in cerebellar tumors consists of general cerebral, cerebellar symptoms, and phenomena of damage to the brain stem. Very often, all three groups of symptoms appear simultaneously.
Sometimes the onset of the disease is manifested by symptoms of one type. General cerebral phenomena occur first if the tumor is localized in the cerebellar vermis. The process taking place at this time directly in the tissues of the cerebellum may not produce any symptoms and remain in the compensation stage for a long time. Symptoms of cranial nerve damage or indications of brainstem compression may also be the first manifestations of the disease.
Tumor diseases of the cerebellum have the same general cerebral symptoms as tumors of the cerebral hemispheres. Patients report constant headaches, sometimes of a paroxysmal, progressive nature. The headache comes in the morning, is widespread, and is less often centralized in the back of the head. The feeling of nausea comes regardless of food. At the peak of the headache, vomiting, dizziness, stunned state, and drowsiness are possible.
Patients complain of fatigue. Sometimes hallucinations of the olfactory, auditory or light type develop. The more the tumor blocks the vessels through which the cerebrospinal fluid passes, the more the clinical picture increases. The patient is forced to take a position that alleviates his condition - tilt his head forward or backward, knee-elbow position with his head down.
Attacks of nausea and vomiting come more often. If the patient suddenly changes the position of the head, sudden blocking and the onset of a hypertensive-hydrocephalic crisis are possible.
Focal (cerebellar) signs depend on the location of the tumor process. Cerebellar ataxia is the main clinical factor. If the process is located in the cerebellar vermis, instability and gait disturbances are observed. When walking, the patient stumbles, staggers, and spreads his legs wide. To maintain balance, the patient balances with his hands. The patient may skid when turning.
Involuntary movements of the eyeballs are observed - nystagmus. Cerebellar speech disorders develop. It has an intermittent and chanting character (divided into syllables). When the cerebellar hemispheres are involved in the tumor process, disorders of coordination and proportionality of movements are noted on the affected side. The patient cannot perform finger-nose, knee-heel tests. There are changes in handwriting to a more sweeping, larger one, as well as dysmetria and intention tremor.
A cerebellar neoplasm can grow from one hemisphere of the cerebellum to the other, from the hemisphere to the vermis and vice versa. Impaired coordination and confusion of symptoms of damage to the cerebellar structures are manifested in a variety of clinical pictures.
Damage to the brain stem has its own signs of compression, as well as dysfunction of individual cranial nerves. Patients experience trigeminal neuralgia, neuritis of the facial nerve, hearing impairment, pathologies of taste perception, speech impairment, and complete loss of sensitivity of the soft palate.
Vomiting not associated with headache is a typical manifestation of brainstem lesions. It is caused by irritation of the receptors in the posterior fossa of the skull and can appear due to sudden movements or changes in body position. Long-term compression of the brainstem provokes motor restlessness, irregular heartbeat, double vision, increasing nystagmus, oculomotor disorders - gaze paresis, divergent strabismus, drooping eyelid, mydriasis.
Possible autonomic disorders, tonic convulsions, arrhythmia. Impairment of respiratory activity is possible until breathing stops completely, which can lead to the death of the patient.
Cerebellar tumors
Most of the known neoplasms can develop primarily or metastatically in the cerebellum. As a general rule, for cranial tumors in such cases there will be symptoms of three categories:
- socket, i.e. cerebellar,
- distant,
- general cerebral.
All of them are closely confused with each other, and the cerebellar component, unfortunately, often does not occupy the first place and is often lost in the motley and complex picture of the disease. There is no point in describing each group of symptoms again in every detail - they are all already known to you. We can only emphasize individual particulars and briefly touch on the question of combining all the features together.
Of the general cerebral symptoms, stagnant nipples deserve mention. It develops relatively quickly and can be strongly expressed. Probably the reason is the proximity to the tumor of large venous reservoirs in the form of sinuses and v. Magna Galeni; such proximity, one must think, contributes to circulation disorders in the skull and is one of the reasons for congestion in the retina.
Another general cerebral symptom - headache - is most often observed in the back of the head, but can also be localized in other parts of the head. In addition to a stagnant nipple, apparently, there may often be phenomena of the so-called “stagnant labyrinth”, i.e. symptoms of labyrinthitis: they greatly interfere with diagnosis, introduce extraneous elements into the cerebellar syndrome and thus deprive it of its clarity and purity. Due, probably, to congestion in the labyrinth, dizziness with cerebellar tumors can be very pronounced, reaching levels that, generally speaking, are not characteristic of this organ. At the end of the disease, changes in the general senses are very pronounced - a disorder of consciousness, hibernation.
Long-term symptoms are very numerous. These are paralysis of the cranial nerves - V, VI, VII, VIII pairs, less often of the bulbar nerves. Then the symptoms from the pyramids are central paresis and paralysis, convulsions, contractures.” Sensitivity is upset less frequently and weaker.
Finally, the last group of symptoms is focal, that is, in this case, cerebellar. Here you can find different elements of cerebellar syndrome in the most variegated combinations. It is impossible to list all such combinations, especially if we take into account the symptoms of other categories: there seem to be an infinite number of them, although this is probably a kind of optical illusion. Probably, we simply do not yet know those typical symptom complexes into which cerebellar tumors develop. It is possible to indicate only the roughest outlines of two main types of disease in connection with the localization of the tumor: processes up to the midline, i.e. in the vermis, and processes in the hemisphere. When the tumor is localized in the worm, the so-called worm syndrome occurs. It is dominated by balance disorders - a typical “drunk gait”, lateropulsion, retropulsion. Standing, even sitting, can be upset. Incorrect postures of the head and torso are very pronounced. In addition, there is a noticeable speech disorder. A constant or almost constant symptom is nystagmus.
When localized in the hemisphere, the unilateral cerebellar syndrome predominates - at least at the beginning of the disease: all those elements that I have listed are quite clearly expressed on the side of the tumor. Of course, these types are somewhat distinct mainly at the beginning of the disease. Then the tumor, no matter where it is, compresses everything and gives a mixed picture - total cerebellar syndrome. the course of the disease is slow, chronically progressive, as with any tumors. Tumors rich in blood vessels, especially after specific treatment, sometimes give noticeable remissions. The total duration of the disease is from 1 to 3 years. Treatment, as with any tumors, is exclusively surgical. Everything that has been said on this subject regarding abscesses applies here too. Only the results of the operation are even more modest: in round numbers, success is observed in 20% of all cases, and the remaining 80% of patients die. Experiments are now being made with radiant energy treatment, but the results of this method have not yet been determined.
Diagnostics
An examination by a neurologist does not always make it possible to determine the presence of a cerebellar tumor, since specific manifestations may be absent. Identification of cerebral symptoms is the reason why the patient is referred to an ophthalmologist for consultation and ophthalmoscopy. Hydrocephalus is indicated by congestion of the optic nerves. A CT or MRI of the brain is required. The examination results provide complete information about the location of the tumor and its size.
It is necessary to differentiate cerebellar tumors from cerebellar cysts, aneurysms of cerebral vessels, brain abscesses, and stroke.
Treatment of cerebellar hemangioblastoma
Neurosurgery has made major breakthroughs in the treatment of diseases of both the spinal cord and the brain. Rare diseases, such as GM, are also successfully treated. But what ensures the efficiency of all operations? Firstly, a professional approach to each client. It is achieved through qualified specialists, often working in teams. Here, every doctor values the health of his clients and values his reputation. Therefore, he makes every effort to ensure that the treatment is successful; Numerous clients of the clinic were convinced of this, many of whom doctors saved from death. Secondly, after the procedures, you can stay in a specially prepared center. We are talking about rehabilitation. This task is important because shows doctors' complete control over the situation. It's better to stay here for a while to avoid relapses. This will help you be sure that your health will stay with you and it will go away. The City Clinical Hospital pays special attention to diagnostic issues. After all, before starting treatment, you need to determine the disease, its form or degree. And the general condition of the body needs diagnostics. Only after careful checks and tests does the doctor choose the most rational method of treatment.
It is noteworthy that not only surgical intervention is used. Conservative treatment is also a priority. Again, everything directly depends on the type of disease, its form and degree of neglect. The individual characteristics of the patient’s body are also taken into account.
Returning to the issue of equipment and equipment, we note that efficient and modern devices are available. In general, the toolkit is rich. This allows you to judge the accuracy of the data and perform the most complex operations. The clinic does not skimp on equipment, because a lot depends on it: with professional “tools”, doctors will be able to perform the most complex operations at the European level. And you don't have to travel far. After all, the State Clinical Hospital is located in Moscow. Details can be found on the official website. It also contains information regarding contact details; You can call to find out the answers to all your questions. Friendly specialists will help solve your problems and make an appointment with a doctor. Therefore, do not delay treatment.
Treatment
Surgical treatment is the main treatment for cerebellar tumors. The question of the need and extent of the operation is considered by a neurosurgeon. Radical removal of the tumor is considered the most effective. A contraindication to surgery is considered to be tumor growth into the brain structures, into the fourth ventricle. In such a situation, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is restored and the possible volume of tumor formation is removed. It is advisable to perform shunt manipulations, ventricular puncture, external ventricular drainage, depending on the symptoms.
The material obtained during the operation is subject to histological examination to determine the degree of malignancy. Based on the results, further treatment tactics, chemotherapy and radiation treatment are determined. If necessary, painkillers, diuretics, sedatives, and antiemetics are prescribed.
The presence of a cerebellar tumor can be detected using MRI. You can find a clinic that allows you to undergo tomography using modern equipment on our website. Here you can find hundreds of clinics with high ratings and affordable prices. Making an appointment through the website gives you the opportunity to receive a discount on the examination.
Methods for diagnosing and treating cerebellar tumors according to stages
Examination of a person does not always suggest the presence of a tumor of such a localization, because there may not be specific signs. Radiation research techniques are considered the most informative in diagnosis. CT scan (even better - MRI with intravenous contrast supplement) allows not only to identify a tumor, but also to differentiate this disease from others with manifestations of cerebellar lesions already present in the patient. Using MRI, it is possible to examine the structure of the tumor, its location in relation to the network of blood vessels, and identify other signs that help specialists carry out interventions to eliminate the tumor formation.
The key way to get rid of a cerebellar tumor is surgery, usually with the absolute elimination of tumor structures, but this is not always possible from a technical point of view. If the tumor has spread to the nearest tissue, the fourth ventricle, it cannot be completely eliminated. In this situation, they try to remove more tumor tissue. The doctor performs a set of actions to restore cerebrospinal fluid circulation. To do this, sometimes sections of the occipital bone and the first cervical vertebra are removed (this measure helps to get rid of compression of the brain stem).
In case of low-quality formations of the cerebellum (this is determined histologically), after surgery the patient is recommended radiotherapy, the task of which is to eliminate the atypical elements that can survive. Possible use of chemicals. The types and extent of therapy are determined by the histology of the tumor.
If the formation is not completely removed, after a certain time it grows again, giving typical clinical symptoms.
To overcome such tumors, they also resort to drug therapy to carry out treatment aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease (antiemetics, painkillers, hormonal drugs, etc.). They do not always affect the tumor itself directly, but they help improve the patient’s condition. The cost of cancer treatment abroad depends not only on the degree of development of the pathology, but also on other indicators (methods, drugs used, etc.) - so, usually the patient is offered program options suitable for his case.
Symptoms and signs
Malignant tumors that form on the tissues of the cerebellum are accompanied by a variety of symptoms, which are divided into three categories: cerebral, distant and local. They all flow in parallel, intersect and merge with each other.
General cerebral
They appear in the early stages of tumor development. One of the most pronounced disorders is called congestive nipple. This condition is accompanied by changes in blood supply and circulation of brain fluid. As a result, retinal congestion occurs.
A nonspecific general cerebral symptom is headache. It can manifest itself both in the early stages and not in later stages. In addition, the symptom is characteristic of cancerous and benign neoplasms.
Painful sensations are localized in the occipital part, over time it covers the entire head. Headaches are often associated with the occurrence of a “stagnant labyrinth,” which has serious consequences and makes it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis.
Patients complain of dizziness, decreased quality of vision, and breathing problems. Symptoms appear against the background of compression of neighboring structures, when the neoplasm increases in size.
When pressure is applied to the respiratory center of the brain, asphyxia can occur while the person is sleeping.
Distant signs
They appear at later stages and have a pronounced character. The most common signs are paralysis and seizures.
When the tumor affects the cerebellum, patients experience unilateral symptoms. The disease has a slow course. But as a result of the influence of certain negative factors, an exacerbation occurs, which leads to the spread of the pathological process to neighboring structures.
When the tumor reaches a large size, blockage of the outflow tract of liquor fluid is noted. In this case, all symptoms intensify.
Patients experience symptoms such as loss of coordination, hand tremors, and increased intracranial pressure. There is a decrease in hearing and vision up to their complete loss.
In addition, at stages 2 and 3 severe headaches, vomiting, weakness of muscle tissue, and wobbling of the eyeballs appear.
Nesting
Symptoms in this category are similar to general cerebral and distant signs, but are more pronounced.
They are also accompanied by dysfunction of many organs affected by metastases.
Features of surgery to remove a tumor of the cerebellopontine angle
Removal of the tumor of the cerebellopontine angle is carried out surgically. Before surgery, patients of this profile undergo general clinical and neurootological examination, CT and MRI. According to indications, myo- and angiography and neuropsychological testing are prescribed.
Removal of a tumor of the cerebellopontine angle is performed using modern methods of endoscopic microsurgery under conditions of constant neurophysiological monitoring (including stimulation and EMG of the facial nerve). After neuroimaging, the doctor develops a surgical plan, determines its volume and the point of best access. The intervention is carried out using high-speed drills and pneumatic drills, which ensure minimal invasiveness and reduce the extent of damage to nearby tissues.
Removal of a tumor of the cerebellopontine angle is carried out under endotracheal anesthesia in a closed circuit using Propofol and inhalational anesthetics (Sevoflurane, Isoflurane). Necessary conditions for the operation, which is performed in a sitting position, are also Doppler ultrasound of the heart and a special surgical table with supports for the surgeon’s hands. During the removal of a tumor of the cerebellopontine angle, it is possible to perform a rapid analysis of the removed fragment of the tumor with subsequent correction of the course of the operation.
The final result of surgical intervention is determined by the characteristics of tumor growth, the degree of damage to the base of the skull, and its fusion with neurovascular structures. In most cases, I, together with a team of assistants at the N. N. Burdenko Research Institute of Neurosurgery, manage to solve all the problems facing us.
Clinical picture
Timely removal of tumors of the cerebellopontine angle is complicated by the slow development of the disease without severe clinical manifestations. The patient may experience noise in one ear for several months or even years (so-called cochleovestibular syndrome). Then comes a period when the signs of the disease become more pronounced (deafness, facial nerve paresis). In most cases, diagnosis and then removal of tumors of the cerebellopontine angle are carried out precisely at this stage.
Other consistently occurring symptoms of the disease include:
- headache;
- loss of corneal and conjunctival reflexes;
- cerebellar phenomena - unilateral hemiataxia and general cerebellar ataxia, adiadochokinesia, unsteady gait, decreased muscle tone, dizziness;
- paralysis of limbs.
Treatment of brain astrocytoma
The diagnosis of astrocytoma is a direct indication for surgery. If the disease is diagnosed at the beginning of its development, the doctor can observe the tumor for some time and when it reaches stage 2, perform surgery to remove it. Modern oncology and neurosurgery provide several methods for treating astrocytoma, which allow the operation to be performed with maximum precision and minimize possible complications.
The Burdenko Neurosurgical Clinic in Moscow offers a range of services for the diagnosis and treatment of astrocytoma. The center performs complex operations using modern equipment, as well as chemotherapy and radiosurgical techniques. The clinic's doctors are high-level professionals with many years of experience.
If the tumor size does not exceed 3 centimeters, stereotactic radiosurgery can be used. The operation is performed under tomography control and allows for complete or partial resection of the formation. This procedure does not provide a 100% chance of recovery, but it can reduce intracranial pressure and alleviate the patient’s general condition.
At the Burdenko Institute of Neurosurgery, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. Surgical treatment of astrocytoma consists of endoscopic craniotomy. This operation allows you to preserve important body functions while removing the tumor through a small incision. The procedure takes from 2 to 6 hours. Treatment in the clinic using the latest equipment eliminates possible complications and reduces relapses.
Treatment of brain cancer is carried out in accordance with international medical standards. After removal of the astrocytoma, the patient spends a long time in the clinic, undergoes rehabilitation, and is under constant medical supervision. A few days after the operation, a control MRI is prescribed, which allows you to assess brain function and exclude complications. It is recommended that patients undergo diagnostics almost every 6 months, this will allow them to monitor whether there are any new foci of tumor.
The rehabilitation program after surgery is developed by a rehabilitation doctor, neurosurgeon and nutritionist. It consists of physical therapy, diet, massage, speech therapy correction and other techniques that can improve the quality of life. The recovery period can last from 3 to 6 months.