If you suspect a concussion or the diagnosis has already been established, you will need to be examined by a neurologist. If any studies have been previously performed, be sure to take their results for consultation, incl. the pictures themselves. If studies have not been performed, they will be recommended and performed based on the results of the examination.
- Symptoms of a concussion
- What to do if you have a head injury
- Concussion Screening
- Trauma to the cervical vertebrae due to concussion
- Nose injury due to head injury
- What happens if a concussion is left untreated?
- Treatment of concussion at the Echinacea Clinic
Symptoms of a concussion
Symptoms of a concussion (one or more of the following):
- Headache;
- agitation or drowsiness;
- Poor tolerance to bright light and loud sounds;
- Confusion;
- Dizziness and coordination problems;
- Loss of consciousness - from a few seconds to hours;
- Memory impairment (events immediately before the injury and/or immediately after the injury are usually lost from memory);
- Slurred speech;
- Noise in the ears, double vision;
- Convulsions;
- Different pupil sizes
- Disorientation in time, space, self, etc.
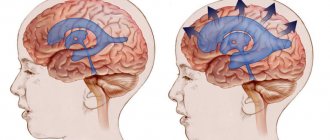
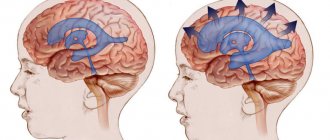
A poorly treated concussion is dangerous, first of all, because of its long-term consequences , which occur 6-18 months after the traumatic brain injury. If you doubt the presence/absence of a concussion, it is better to play it safe and clarify the situation with the help of a neurologist. In doubtful cases, we will clarify the patient’s condition using magnetic resonance imaging , brain evoked potential studies and other highly sensitive diagnostic methods.
When can a concussion occur and how is it treated?
A concussion is characterized by minor hemorrhages and swelling of its substance, which is not accompanied by a violation of the bone integrity of the skull.
What are the main causes of this pathological condition?
The main reason, and indeed the only one, is head trauma. Another thing is that it can be obtained under various circumstances (for example, during a car accident, a fight, during a sports competition). However, there have been rare cases of a concussion occurring without a direct blow to the skull, but with sudden braking of head movement, for example, in the case of sudden braking of a car. But at the same time, a mandatory condition for confirming the diagnosis of a concussion is loss of consciousness.
What symptoms accompany this pathology?
Usually, immediately after an injury, a person loses consciousness for several seconds or even minutes. Upon regaining consciousness, he may feel severe nausea, which will lead to vomiting. There is a severe headache accompanied by dizziness. There is also general weakness, drowsiness, ringing in the ears, sweating, transient strabismus, nervousness and many other general cerebral symptoms. The victim's breathing movements become more frequent, the heart rate increases with frequent occurrence of arrhythmias. Temperature reactions are usually not observed. All of the above symptoms usually go away soon.
Regarding the headache, it can last for several days, its character is usually pulsating and localized in the back of the head. With concomitant hypertension, these pains become even more pronounced.
If the injury is severe, the patient may experience antetrograde amnesia, when he cannot remember events that occurred a couple of minutes before the injury and some time after it was received.
What additional research methods can be used to diagnose a concussion?
In addition to all the symptoms listed above that most often accompany this condition, as well as the stories of witnesses of the incident that led to it, doctors use some additional research methods. They allow us to determine the anatomical and functional state of the brain. These include:
- EEG (or electroencephalographic study), which shows electrical activity and brain potentials recorded on graph paper;
- ophthalmoscopy performed by an ophthalmologist. With this method, he examines the fundus of the eye, where he can see signs of increased pressure inside the skull, which often occurs with a concussion;
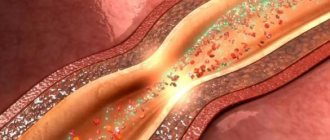
- Ultrasound of the head with Doppler, which allows you to determine the quality and speed of blood flow in the cerebral vessels;
- a study by a neurologist who examines the vestibular apparatus of the victim, and also diagnoses possible disorders of the systems of smell, hearing and taste.
How to properly treat a concussion?
Therapeutic measures in this case should be started immediately. First you need to lay the victim down with the head end slightly raised. If you lose consciousness, turn your head to the side to avoid aspiration of vomit.
You need to lie down more for two to three days.
Among the medications, drugs are prescribed that eliminate headaches, dizziness, sleep disorders, in other words, normalize the functional activity of the brain. Such medications include, for example, Actovegin, piracetam, Cavinton, Cerebrolysin. Also usually prescribed are sedatives (Corvalol, valerian, glycine), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ketorolac), a combination of B vitamins (Neuromax, Neurobion). Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
What to do if you have a head injury
Immediately after an injury? If one or more of the listed symptoms appear after an injury, you must call an ambulance. If there are no strict indications for hospitalization or if you refuse hospitalization, you can get the necessary help in our clinic.
What help can you provide yourself?
- Lay the victim on his side; this will prevent inhalation of vomit even during loss of consciousness;
- Apply cold to the head to reduce the increase in brain swelling;
- Unfasten clothing that is blocking breathing, belt, trouser waistband;
- Stay close to the victim, because Possible vomiting, psychomotor agitation, and falling when trying to stand up.
After being discharged from the hospital.
If the patient remains unwell after discharge from the hospital, there is usually a persistent increase in intracranial pressure and/or damage to the joints and ligaments connecting the skull to the cervical spine. This is easy to establish using magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and x-ray examination of the cervical vertebrae. This will require a slight correction of the course of treatment (special exercises and medications), which usually leads to improvement within 1-2 weeks. The total planned course of medication after a concussion is at least two months.
Signs of a concussion in children
The main signs of a concussion are loss of consciousness for a short period of time, poor spatial orientation, headache, dizziness and weakness. In some cases, vision may deteriorate. Symptoms of a concussion in a child also depend on age.
Clinical manifestations of this condition in infants are as follows:
- frequent regurgitation (possible single vomiting);
- pale face;
- decreased appetite and refusal to eat;
- swelling of the fontanelle;
- poor sleep, moodiness, crying for no reason.
Signs of a concussion in children from three to six years of age: possible short-term loss of consciousness, nausea and vomiting (one-time), dizziness, bradycardia, pale skin, sweating. The child can show where it hurts and what exactly happened.
How does a concussion manifest in schoolchildren?
- obvious loss of consciousness (10 to 15 minutes);
- Strong headache;
- severe lack of coordination;
- constant nausea and vomiting;
- presence of neurological symptoms;
- The temperature during a concussion in children remains normal.
Please note that a characteristic feature of concussion in childhood is an increase in symptoms. If immediately after the injury the child’s condition can be described as quite satisfactory, then over time it noticeably worsens.
If you have a head injury, consult a specialist! Timely diagnosis and treatment will help avoid many complications and serious consequences. On our website you will find a list of doctors and diagnostic measures that a child may need after a concussion.
Concussion Screening
Why do you need a concussion evaluation? To promptly notice and treat possible dangerous conditions that often accompany a concussion:
- The release of blood into the membranes and substance of the brain;
- Fractures of the bones of the skull, orbits, face, cervical vertebrae;
- Hemorrhage in the orbital tissue and eyeball;
- Inner ear injury;
- Foci of death of brain matter.
MRI and X-ray computed tomography of the brain will show brain swelling, hemorrhage, traumatic changes in the brain, damage to the bones of the brain and facial skull.
To assess the mobility of the vertebrae after injury, an x-ray of the cervical spine with the head tilted forward and backward (fractures, dislocations and subluxations of the vertebrae are clearly visible).
Evoked potentials of the brain are the most accurate research method today, providing information about disturbances in the conduction of impulses in various parts of the brain (visual, auditory, sensory, motor pathways of the nervous system).
Trauma to the cervical vertebrae due to concussion
Injuries to the cervical vertebrae often go unrecognized because their symptoms are similar to those of a concussion.
The skull is firmly fixed to the first cervical vertebra by joints and ligaments. Therefore, the impact force acting on the skull is necessarily transmitted to the cervical vertebrae . Most often, with a concussion, the ligaments and joints connecting the cervical vertebrae are affected (traumatic subluxations). Fractures and dislocations of the cervical vertebrae are less common.
If, after hitting your head, you continue to experience dizziness, unsteadiness, pain in the back of your head or underneath it, pain in the eyes, visual disturbances, or pain when moving your neck for a long time, we will definitely perform an X-ray or MRI scan of the cervical vertebrae. Traumatic subluxations of the cervical vertebrae are usually easily removable ; their symptoms resolve within a few hours after reduction.
Read also
Neuralgia
Neuralgia is a disease that is a lesion of the peripheral nerve.
It manifests itself as a strong, burning, acute pain that is felt in the area of innervation of the affected (along) nerve. Types… Read more
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
The first description of the disease in the literature appeared in 1953. J. Anderson described a case from practice: a 47-year-old man with lung cancer experienced symptoms similar to myasthenia gravis. After tumor removal...
More details
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
– “One of the most terrible human diseases... 3 letters...” – “Cancer” – “Not suitable...” Yes, dear ones, there is something worse than cancer. And this disease is called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or...
More details
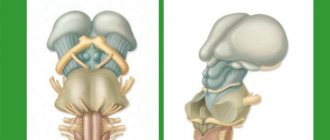
Chiari malformation
What is Chiari Malformation? Chiari malformation (formerly Arnold-Chiari malformation) is a congenital defect of brain development that involves the dislocation of the cerebellar tonsils into the spinal canal through the large…
More details
Clubfoot
Clubfoot should not be understood as just one foot disorder. This is a group of deformities of the foot and ankle joint with their pathological setting. Clubfoot is a deformity in which...
More details