© Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Cystic formations in the cranial cavity always cause well-founded concern among both specialists and their owners. One of the variants of such cavities is a retrocerebellar cyst, which is detected in approximately 4% of healthy people and gives symptoms in only a fifth of its carriers.
Having set out to learn more about this cyst, the reader will find a large amount of information on the Internet, but not all of the information corresponds to reality. Most dubious sources present a retrocerebellar cyst as a kind of intracerebral accumulation of fluid in the place of dead neurons, but in reality it is a cerebrospinal fluid cyst lying outside the brain rather than inside it.
Intracerebral cysts, in other words, cerebral cysts, actually form in the brain itself after necrosis due to a stroke, tumor or injury. The cerebrospinal fluid cyst owes its appearance to the pathology of the arachnoid membrane, therefore it is also called arachnoid, and identifying it with a cerebral cyst is fundamentally incorrect.
The term “retrocerebellar” is not a characteristic of the cyst itself, but an indication of its location behind the cerebellum (cerebellum), in the region of the posterior cranial fossa, as shown by MRI data, through which these same cysts are detected.
Thus, a retrocerebellar cyst is a cavity formation in the back of the skull, formed by the arachnoid mater, collagen fibers, containing cerebrospinal fluid and lying between the surface of the brain and its arachnoid membrane.
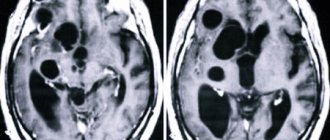
example of cystic expansion of the retrocerebellar arachnoid space
In most cases, a retrocerebellar cyst is discovered accidentally, in young adults who, for one reason or another, have had an MRI. As a rule, the reason for examination is neurological symptoms, which are not always associated with a cyst. A small-sized retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst can be asymptomatic and is extremely rarely accompanied by any negative effects on the brain itself.
Indications for the study
The presence of a retrocerebellar cyst can be suspected by some characteristic symptoms:
- Severe headaches that do not go away even after taking painkillers;
- Unreasonable loss of consciousness or fainting state;
- Sensation of squeezing and pulsation in the head;
- Deterioration of hearing or vision;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Numbness of the limbs;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Epileptic seizures.
Magnetic resonance imaging is required if surgical intervention in the brain area is necessary.
Note that the clinical picture and severity of symptoms depend on the exact location and size of the retrocerebellar cyst.
Classification of brain cysts
Cysts are divided according to the type of acquisition into the following types:
- Primary or congenital - found in newborns already in the maternity hospital;
- Secondary or acquired - these brain formations are a consequence of various pathological abnormalities or the result of surgical intervention.
The localization of the formations under consideration largely determines their variety. The most common are arachnoid and retrocerebellar cysts.
- If the location of the cyst is determined between the brain and its arachnoid membrane, then the cyst is called arachnoid.
- If the cyst occupies a certain part of the brain, then we are talking about an intracerebral (cerebral) cyst.
What is a retrocerebellar cyst of the brain? In particular, the name of this type of disease comes from its location, where the connection is determined with the cerebellum.
A retrocerebellar or intracerebral cyst develops at the site of death of areas of gray matter, that is, in the thickness of the brain, and not in its shell or on the surface. Speaking about this type of neoplasm, they can be located in any part of the brain, so there is a certain classification of the disease in question depending on their location (for example, superior and inferior retrocerebellar cyst).
A similar clinical picture is observed in the presence of a tumor.
The causes of brain meningioma are hormonal changes after 50 years. Read our article about who is more susceptible to this disease and what preventative measures need to be taken. From birth, babies may develop a malignant tumor, such as neuroblastoma. Signs of the development of neuroblastoma in a child can be seen in this article.
The provoking reasons for the development of this type of cyst are:
- Deficiency of oxygen and the required amount of microelements entering the brain;
- necrosis of nerve cells (strokes);
- previous operations in the cranial area;
- development of inflammation of infectious origin;
- injuries and mechanical damage (concussion).
Retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst
The arachnoid membrane refers to one of the three meninges located between the dura superficial mater and the soft deep mater of the brain.
Thus, a pathology in which a bubble of liquid content (cerebrospinal fluid) is formed, located, as a rule, between the meninges, is called an arachnoid cyst.
Factors for the development of this type of cyst:
- the process of inflammation of the meninges;
- increased liquid filling pressure;
- brain injuries.
Retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid cyst
A cyst is a formation that has a wall and some contents. If its filler is liquid, then they talk about a cerebrospinal fluid cyst
, which is a consequence of processes such as:
- the process of inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- injuries;
- stroke and hemorrhage;
- undergone surgical procedures.
CSF cysts of the brain occur in approximately 4-5% of the population, while only 2 out of 10 patients experience a severe course of the disease. Retrocerebellar arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the brain is divided into forms
:
- Congenital
– a consequence of a disturbance in the intrauterine state of the fetus (birth trauma). - Acquired
- the development of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst is caused by inflammation of the superficial membranes of the brain (damage, trauma, etc.).
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is safe for the body only if all contraindications are excluded.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended in the following cases:
Very often, to obtain more informative images, doctors prescribe additional contrast. In this case, you must ensure that there are no following contraindications:
- Pregnancy of any stage.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Kidney failure.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Allergic reaction to components included in contrast agents.
Symptoms
What sizes are dangerous: a cyst manifests itself clinically when its size exceeds 3 cm in diameter. Retrocerebellar cyst of the brain is characterized by the following syndromes:
- Syndrome of increased intracranial pressure. Signs: bursting headache, dizziness, loss of appetite, sleep disturbance, irritability, emotional lability, decreased visual accuracy, tinnitus. Psychomotor development may be delayed in children.
- General cerebral symptoms: throbbing headache, drowsiness, stupor, memory loss, increased distractibility, seizures, tremors of the limbs. Patients answer questions slowly and are disoriented.
- Neurological deficit: decreased sensitivity, weakened muscle strength in the arms and legs.
- Focal symptoms. It is caused by mechanical compression of the cerebellum by the cyst. In this case, a retrocerebellar cyst of the cerebellum is manifested by impaired coordination, decreased accuracy of movements and gait disorder.
Preparation rules
During a routine examination, doctors recommend following a few simple recommendations:
- If it is necessary to administer contrast, you must come to the clinic on an empty stomach, that is, do not eat food for 7-8 hours.
- If you are afraid of research or confined spaces, be sure to consult with a specialist. Your doctor may prescribe you sedatives to make the examination process more comfortable.
- Do not bring any metal products inside the tomograph. For this reason, doctors recommend removing metal accessories in advance.
- Prepare a change of clothes that do not have metal or metal-containing accessories.
- The duration of the diagnostic test is about 40 minutes. Empty your bladder in advance to avoid discomfort during the procedure.
About the disease
Cysts are neurological in nature.
A retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst is a benign cavity formation that appears at the site of destruction of nerve tissue due to some pathological process.
The formation algorithm is simple and clear: a certain abnormal process occurs in the brain, during which brain tissue begins to die.
A lesion forms at the affected area, which is surrounded by connective tissue - this is the wall of the formation.
Gradually, dead cells accumulate in it, surrounded by liquid. An increase in the size of the cyst affects the patient’s well-being: the larger the formation becomes, the more pressure it puts on the brain and poses a greater danger to life.
The formation is localized between the surface of the brain and the arachnoid (arachnoid) membrane. Its walls are formed precisely from the tissue of the arachnoid membrane, and the cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The more it is, the larger the cyst.
Typically, arachnoid cysts are distinguished - those located between the gray matter and the membrane, and intracerebral (cerebral), located in a certain part of the brain. A retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst simultaneously affects both the intracerebral and arachnoid spaces.
How is an MRI performed?
To ensure that the procedure is as informative as possible and that the images are clear, experts recommend performing magnetic resonance imaging in closed-type tomographs. Before starting the study, the patient must change into clothes without metal structures, take off his shoes and lie down on a retractable table. If the doctor has prescribed additional contrast enhancement, a special drug is injected into a vein, which is distributed throughout the circulatory system in just a few minutes. Then the table moves inside the tomograph, where the research process takes place.
Maintaining immobility is the main requirement for the patient! Remember that even minimal movements can lead to a decrease in the information content of the procedure.
It is also worth noting that when performing magnetic resonance imaging, a specific loud noise is observed. If this scares you, you can use earplugs.
Patients generally tolerate MRI well. Inside the tomograph there is good lighting and ventilation, there is a loudspeaker, as well as a panic button for emergency stop of the study.
How dangerous is the disease?
It is quite obvious that everything that happens in our body not from nature is not good, especially when it comes to the brain.
The appearance of a cyst in the thickness of nerve cells or the arachnoid membrane significantly affects a person’s lifestyle and activities.
Due to constant aching pain and dizziness, a person cannot work, but experiences constant fatigue .
If any center of the brain is damaged, hearing, vision, tactile sensations, and balance are impaired, which also greatly affects life. It is difficult for a person to see for himself where to go, get dressed, or get to the metro.
Convulsions and paralysis make it impossible for a person to live independently: in order to eat normally and go to the toilet, you will need the help of a specialist.
The cyst can progress at high speed and lead to swelling of the brain, as a result of which blood circulation and breathing are severely impaired and the person may die.
REFERENCE! A retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst of the brain, located in the posterior fossa of the skull, grows faster and quickly leads to an undesirable result.
MRI with contrast
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed with contrast, especially if any neoplasm is suspected. This makes it possible to examine the tumor in detail and distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one.
The contrast agent clearly highlights the vessels, which allows you to see any tissue pathologies. Don't worry, contrast agents are safe for the human body. Most patients tolerate this procedure well. You must first consult a doctor and exclude all possible contraindications.
Diagnosis of brain cyst
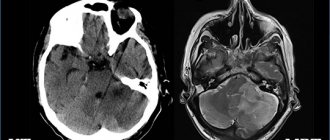
Recognition of the presence of a cystic formation is carried out using the following diagnostic methods (tomography):
- magnetic resonance;
- computer
These methods are the most accurate in diagnosing the pathology in question, since they provide the most complete description of the course of the disease. Additional research methods include:
- USDG (ultrasound Doppler scanning);
- ECG, Echo-CG;
- blood pressure monitoring.
To differentiate a cyst from a tumor, a diagnostic procedure is performed that requires the introduction of a special contrast agent. In newborns, an ultrasound scan of the brain is prescribed in the first week of life, which excludes the presence of congenital pathological formations.
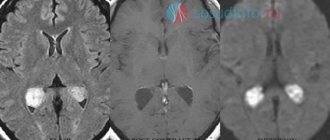
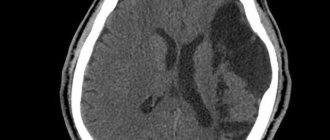
The following photo clearly shows the location of the retrocerebellar cyst:
Decoding the results
A retrocerebellar cyst is located in the brain behind the cerebellum, in the posterior cranial fossa. During magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to clarify the exact location and size of the formation.
The report will contain all the information, but the MRI specialist cannot make a diagnosis - this must be done by your attending physician. If the diagnosis of retrocerebellar cyst is confirmed, the doctor will determine treatment tactics. For benign tumors, it is often possible to do without surgical interventions - they are required only in cases of large tumors or rapid growth. To avoid serious consequences, consult a doctor at the first alarming symptoms. Be healthy!
Diagnosis and treatment of retrocerebellar cyst
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using diagnostic research methods, such as CT and MRI.
If the cyst is small, does not give any symptoms and is discovered by chance, during a routine examination or diagnosis of another disease, then treatment is not required; observation by a neurologist and monitoring of tumor growth is sufficient.
If symptoms appear and the cyst increases in size, surgical intervention is necessary. Before surgery, the size of the cyst, its causes, location features, and the risk of surgery are assessed. After which a decision is made to use one of three types of surgical intervention:
- Endoscopic puncture is the least traumatic type of surgery using an endoscope. A puncture is made in the skull and the cyst is removed or fluid is pumped out. This type of surgery is not always acceptable due to the location of the cyst.
- Neurosurgical surgery with craniotomy is a traumatic type of operation during which the skull is completely opened and the cyst is removed.
- Shunting is performed when hydrocephalus occurs, that is, a constant flow of fluid into the cyst. The operation is performed using a shunt, which drains fluid from the cyst into the natural reservoirs of the body.
Possible complications
If a person postpones a visit to the doctor for a long time, ignores the symptoms, in general, does everything to ensure that the disease reaches an advanced stage, serious complications may arise.
The main ones are:
- Incessant pressing headaches;
- When a specific area of the brain is damaged, any functions are lost (for example, the vestibular apparatus, speech center, etc.);
- Convulsive and epileptic seizures (mainly in children);
- Increased intracranial pressure , sensitivity to long journeys;
- Weakening of the immune system , and as a result - frequent illnesses;
- Deviant behavior or communication difficulties, increased or decreased activity.
No additional growths, tumors or formations in the human body can be useful or even harmless. If there is an excess of something somewhere, then you need to find out the cause and eliminate it.
A retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst is located deep in the skull, and, of course, it is impossible to detect it on your own. It is important to listen to your body and pay attention even to a symptom such as a headache.
Sometimes even a few hours play a role between the time when taking medication can still save you and the time when urgent surgical intervention is required.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Retrocerebellar arachnoid and cerebrospinal fluid cysts, reaching a diameter of no more than 2 mm, are so asymptomatic that an adult does not even think about a serious problem.
The tumor, falling under negative factors (trauma, infectious disease, poor circulation in the brain), begins to grow, and this already provokes the appearance of unpleasant symptoms:
- frequent headaches of a paroxysmal nature, the appearance of regular migraines;
- insomnia, causeless irritability, manifestation of chronic fatigue;
- disturbances in coordination of movements, frequent dizziness, accompanied by darkening of the eyes, loss of balance;
- hearing impairment, partial loss of vision;
- increased intracranial pressure, drowsiness, sudden attacks of nausea and even vomiting;
- slow reactions, memory loss.
Diagnosis begins with interviewing the patient. Doctors can clarify the symptoms based on the person’s story, compile a history of complaints and an anamnesis of the development of pathological phenomena. Often the symptoms are so different that their description alone cannot accurately formulate a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Then the patient is referred for detailed diagnostics.
The patient takes a blood test for cholesterol, the degree of blood clotting and the general condition of the body. If cholesterol is elevated, and blood clotting is the opposite, this means an existing cerebrovascular accident. What other research is needed?
The next blood test is to detect other pathologies: infectious lesions of the central nervous system, sclerosis, the presence of arachnoiditis. Doctors regularly monitor blood pressure levels, since strokes often lead to the development of a tumor.
A well-known method for making a diagnosis is MRI. During the examination, a special substance is injected into the brain near the cerebellum, which helps doctors determine the size of the cyst and its location, and exclude the presence of malignant cells.
A popular research method is Doppler ultrasound examination. Diagnostics evaluates the patency of the main “army” of the brain – blood vessels. If they are too narrowed, it means that the brain is experiencing a lack of nutrients, which can lead to necrosis of brain tissue.
Why can a tumor appear?
A number of main reasons for the formation of brain cysts:
- ischemic damage to the cerebral cortex, resulting from impaired local circulation;
- abnormalities in the structure of the head and brain (for example, the absence of natural partitions between the hemispheres);
- hereditary factors;
- brain injuries as a result of unsuccessful operations or mechanical impacts;
- past infectious diseases leading to disorders in the central nervous system: encephalitis or meningitis.
A serious cause of the appearance of a congenital tumor is considered to be the use of medications by a pregnant woman, which affect the intrauterine formation and development of the fetus, and prolonged exposure to an environment with poor environmental conditions.
What sizes are dangerous?
A retrocerebellar cyst occurs in the affected areas of the brain and directly in the thickness of this organ. To correctly determine the size of the pathology, the patient undergoes a series of examinations. It occurs as a result of various provoking factors; it is also worth considering that new foci of infection and even a micro-stroke can provoke an increase in formation.
This type of cyst can also grow due to impaired blood flow in the brain. Even small sizes at the initial stage of occurrence can provoke serious irreversible consequences for the patient, including the complete death of this organ.