Diseases of the nervous system, incl. neuroinfections, brain cysts and arachnoiditis are the specialization of our clinic. We will clarify the reason for the formation of the cyst in your case, conduct an examination for neuroinfections and the necessary treatment of the brain cyst, etc. We will be happy to help you.
- Brain cyst is a consequence of the disease
- Do brain cysts grow?
- Symptoms
- Examination and diagnosis
- Brain cyst: treatment at the Echinacea Clinic
Brain cyst is a consequence of the disease
There are two main types of cysts:
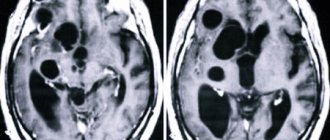
1. An arachnoid cyst is a bubble of fluid accumulated between the adherent layers of the meninges. Such cysts remain after inflammation of the meninges , hemorrhage or injury. Arachnoid cyst of the brain is not a completely correct redundant expression, since the name “arachnoid” comes from the name of the arachnoid membrane of the brain (arachna - spider). If the fluid pressure in the arachnoid cyst is higher than the general intracranial pressure, it can compress the cerebral cortex and cause unpleasant symptoms.
MRI scan of the brain. The brain is shown in grey, the fluid in black. 1 – normal slit-like fluid space between the temporal and parietal lobes of the brain. 2 – arachnoid cyst of the brain, an accumulation of fluid is visible in the substance of the brain.
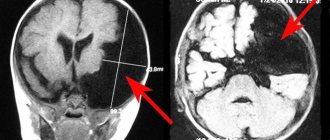
2. Cerebral or intracerebral cyst (corpus callosum, subcortical nuclei, hemispheres, cerebellum, brain stem, etc.) is an accumulation of fluid at the site of a dead area of the brain. Thus, the fluid replaces the lost volume of brain matter. The cause of death should be clarified, and further destruction of the brain should be prevented. Common causes of cysts are cerebrovascular insufficiency, stroke, trauma, inflammation (encephalitis), and surgery in the cranial cavity.
MRI scan of the brain. 1 – normal fluid cavities (ventricles of the brain). 2 – Intracerebral fluid cyst at the site of a dead area of the brain.
An arachnoid cyst of the brain is always located on the surface of the brain, in the area of the membranes. Cerebral intracerebral cyst - in the thickness of the brain substance.
Causes
Primary (congenital) cysts are formed due to abnormalities in the developing fetus, most often this occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- intoxication of the fetus with narcotic substances, alcohol, nicotine, medications that have a teratogenic effect;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus with viruses;
- irradiation;
- severe overheating of the body during pregnancy.
In addition, the formation can occur with Marfan syndrome - this is an anomaly of connective tissue, as well as with pathologies of the corpus callosum.
Secondary pathologies can develop when:
- brain injuries;
- pathological processes in the brain, for example, degenerative;
- in the presence of infections;
- deterioration of cerebral circulation.
In addition, pathology can be observed after surgery.
The mechanism of development of this neoplasm is quite complex and is associated with impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. As a result, a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid is formed.
Do brain cysts grow?
A brain cyst is not a cancer. The size of the cyst can be easily monitored using MRI or CT scanning. If the size of the cyst has become larger over time, it means that some damaging factor continues to act on the brain. In this case, we look for and treat the causes of cysts.
The main reasons for the growth of arachnoid cysts in the brain:
- The fluid pressure in the cyst increases;
- Inflammation of the meninges continues (arachnoiditis, infection);
- Concussion in a patient with a previously formed cyst.
The main reasons for the growth of intracerebral cysts (and/or the appearance of new cysts):
- Cerebrovascular accidents continue, new foci of micro-strokes appear;
- The infectious or autoimmune process of destruction of brain matter continues (multiple sclerosis, multiple encephalomyelitis, neuroinfection).
The causes of the appearance or growth of brain cysts can usually be determined by the results of MRI, blood tests, and studies of blood flow through the vessels of the brain. Treatment is based on research results.
What is the danger of a retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst?
A long asymptomatic course of the disease in combination with the slow growth of the cyst is in itself dangerous. Parents may not realize that their child has a tumor in the brain. Although the tumor is benign, if left untreated it can have life-threatening complications. For example, one of these complications is the rupture of a cyst, in which the cerebrospinal fluid filling it spills into the brain tissue, which leads to death.
In addition, no one can give an absolute guarantee that the tumor will not degenerate into malignant. And this is already a serious danger to life.
Symptoms of a brain cyst
Symptoms are determined by the underlying disease that caused the cyst to appear. Therefore, they are diverse and nonspecific.
One or more of the following symptoms may occur:
- Headache;
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the head;
- Sensation of pulsation in the head;
- Noise in the ear with intact hearing;
- Hearing impairment (sensorineural hearing loss);
- Visual disturbances (double vision, spots before the eyes, etc.);
- Symptomatic epilepsy;
- Paresis (partial paralysis) of an arm and/or leg, permanent or transient;
- Episodes of loss of consciousness;
- Balance imbalance;
- Numbness of any part of the body, permanent or transient.
If the brain cyst is a trace of a long-term illness, there may be a complete absence of any symptoms.
Signs
You can suspect the presence of a pathology in the head based on characteristic manifestations. Some people can ignore warning signs for a long time, explaining them by fatigue, individual characteristics of the body, weather changes and other safe factors.
Such behavior cannot be considered correct, because if any unpleasant symptoms appear, it is important to consult a doctor.
Manifestations of a cyst:
- Constant headaches. They are extremely difficult to eliminate with the help of various analgesics.
- Nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Insomnia, anxiety during sleep.
- Mental disorders. A person may suffer from apathy, negative thoughts, and increased aggression.
- Noise in ears.
- Problems with coordination, it is difficult for a person to maintain balance.
- Speech disorders.
- Decreased sensitivity of the skin.
These signs can be noted in adult children. At the same time, it is more difficult to find out about the presence of a neoplasm in newborns . This is due to the fact that they cannot talk about their condition, so they have to judge only by external signs. These include lethargy of the limbs, excessive regurgitation, and blurred vision.
As soon as characteristic signs are detected, you will need to consult a doctor. A specialist will be able to conduct an examination and also refer you for the necessary examinations. Based on their results, it will be possible to clearly understand what kind of pathology we are dealing with.
Examination and diagnosis
MRI or CT will provide unambiguous information about the presence, size and location of the cyst. A study with intravenous contrast helps to distinguish a cyst from a tumor You can perform such a study at the Clinic of the Academy of Sciences .
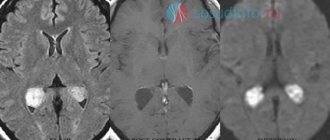
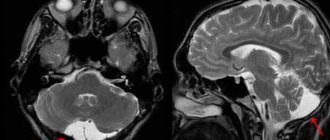
MRI scans of the brain. 1. Cyst after cerebral hemorrhage 2. Cerebellar cysts after ischemic stroke (blockage of cerebral arteries) 3. Cystic adhesive arachnoiditis
To avoid the enlargement and appearance of new cysts , we must clearly understand and treat the root cause of their occurrence. Therefore, we carefully examine you for circulatory disorders, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
Doppler ultrasound of the head and neck vessels (USDG) will help detect narrowing of the vessels that supply the brain with arterial blood. Lack of blood supply can lead to focal death of the brain matter and the appearance of cysts.
Heart studies (ECG, Echo-CG) . The brain may not have enough blood supply due to rhythm disturbances or heart failure.
Blood test for clotting and cholesterol. An increase in cholesterol concentration in the blood and increased clotting are the main causes of blockage of brain vessels with subsequent formation of cysts. This problem is easily solved with the help of modern medications.
Blood pressure monitoring. Episodic increases in pressure are a common cause of strokes and post-stroke cysts. A monitor is a small device that is constantly with you for 1 day and records your blood pressure on a memory card. The data is then read by a computer and gives the doctor a complete picture of the pressure for the day.
blood tests for infections and autoimmune diseases of the nervous system in cases of suspected neuroinfections, arachnoiditis, and multiple sclerosis.
Symptomatic manifestations
This cystic neoplasm is characterized by an asymptomatic course .
Most often, such neoplasms are detected during a patient examination for neurological pathologies with similar symptoms.
The clinical signs of the cyst are nonspecific; their severity depends on the size of the tumor and its location. Patients may complain of general cerebral symptoms, which are associated with compression of brain areas. A focal clinical picture is observed in rare cases, and is most often caused by the presence of hygroma or rupture of the cystic cavity.
The main features are:
- dizziness , which are not associated with pregnancy, taking certain medications, severe fatigue, iron deficiency, and so on;
- vomiting , which is also not associated with gastrointestinal poisoning, taking medications, and so on;
- mental disorders, hallucinations ;
- convulsive syndrome;
- loss of consciousness;
- hemiparesis , decreased sensitivity in the limbs;
- failure to coordinate the activity of the body muscles;
- headaches that are not relieved by painkillers;
- a feeling of fullness , pressure, compression and increased pulsation in the affected area;
- visual and hearing problems;
- extraneous sounds in the ears;
- heaviness in the skull;
- painful or uncomfortable sensations when turning the head.
Reference! Secondary arachnoid cystic neoplasms may be accompanied by symptoms of injury or primary disease, which served as an impetus for the development of the disease.
Brain cyst: treatment at the Echinacea Clinic
The first thing we will do is find out whether your cyst needs treatment and whether your poor health is associated with it. More than half of all cysts do not require treatment at all. Treatment is necessary if the cyst causes any symptoms, increases in size, or is at risk of developing new cysts. Treatment of a brain cyst is carried out regarding the underlying disease that caused its formation.
Resorption of adhesions of the meninges in arachnoid cysts - more details on the page of our website about arachnoiditis. For this purpose, we use two powerful absorbable drugs: Karipain (Karipazim) or Longidaza.
If we are talking about an infectious or autoimmune process , it is necessary to find and eliminate chronic foci of inflammation in the body. Treatment with antibiotics alone is practically useless. If arachnoiditis occurs, it means there is a gap in the immune defense, and first of all it is necessary to restore the body’s immune shield and reduce autoimmune aggression. All of our neurologists have specialized training in immunology. Based on the results of a blood test for immune status and infections, we will offer you a consistent and safe course of anti-infective and immunomodulatory treatment.
Treatment of cerebrovascular accidents requires the fulfillment of three conditions: reduction of coagulation, reduction of blood cholesterol concentration, normalization of blood pressure. Nootropics ( improve the supply of brain cells with oxygen and glucose) and Antioxidants (increase the resistance of brain cells to increased intracranial pressure) are used
In our clinic you can contact any neurologist. Be sure to take with you all the medical documents available to you, even those that, at first glance, are not related to the brain .
Diagnostic methods
The difficulty in identifying the disease is that the symptoms are largely similar to those of other diseases. In the case of a cyst in a child, especially an infant, it is not possible to identify it based on a simple survey. Modern examination methods are designed to ensure diagnostic accuracy. MRI of the brain, ultrasound, computed tomography, electroencephalography, echo and rheoencephalography are performed. The most informative method in making an accurate diagnosis is MRI - magnetic resonance imaging. With its help, the doctor can not only determine the presence of a tumor, find and accurately determine its location, but also understand the nature of the tumor.
How to treat a cyst?
If the arachnoid cyst does not grow or develop, then treatment is not required. A person will need to register with a neurologist and undergo an MRI examination every year. This will make it possible to monitor the growth and development of the cyst, if it occurs.
When the cyst progresses and causes neurological symptoms, it requires treatment. Drug correction comes down to taking medications that normalize cerebral circulation (nootropics, vasotropics, antioxidants). Sometimes the patient is prescribed drugs that dissolve adhesions (Karipain, Longidaza). The help of a surgeon is needed when taking medications does not solve the problem.
Surgical intervention is designed to reduce intracranial pressure; it is implemented in three ways:
- Shunting. The result of this procedure is the formation of pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cyst cavity into the peritoneal cavity.
- Fenestration. This method involves aspiration of the contents of the cyst and further creation of holes. They connect the cystic cavity with the cerebral ventricle or subarachnoid space.
- Drainage of the tumor using needle aspiration.
Modern neurosurgeons prefer to use endoscopic interventions, as they have minimal brain trauma.
Surgery is prescribed only if other treatment methods are ineffective. If there is hemorrhage in the area of the cyst, or if it ruptures, removal of the tumor is required. The operation is performed by trephination, which is associated with a number of complications. The rehabilitation period is quite complex and time-consuming.
Characteristics by location
The cyst in question may be located:
- in the temporal lobes;
- in the parietal part;
- in the frontal region;
- in the region of the cerebellum;
- in the spinal canal;
- in the spinal column;
- in the lumbar region.
In the posterior cranial fossa
This cyst in the posterior cranial fossa (posterior cranial fossa) is accompanied by symptoms:
- persistent headaches;
- vomit;
- failure to coordinate movements;
- intermittent paralysis of body parts;
- convulsive syndrome;
- mental disorders;
- hallucinations.
According to statistics, tumors of this type are more often observed in men, in addition, the increase in the volume of the cystic cavity in men occurs more actively than in women. With a very large cyst, speech defects, hearing loss, and temporary memory problems may occur.
In the sacral canal
An arachnoid type cyst in the sacral region is a cavity. In it, the spinal membrane forms web-like walls. If the cyst size is more than 1.5 cm, the patient may complain of:
- lower back pain with increased loads;
- numbness, paresis, impaired functionality of the limbs;
- headaches, blood pressure surges, dizziness;
- if the cyst is located at the S2 level, sexual function is impaired, and intestinal problems also arise.
In the temporal lobe
A cyst in the temporal lobe is most often observed on the left side. This is due to the more delicate structure of the left-sided meninges and their increased sensitivity to infections. A person with a cyst in this area experiences:
- unsteady gait;
- lack of motor coordination;
- deterioration of sensitivity of the limbs;
- convulsions;
- blackouts;
- mental disorders.
These symptoms are caused by hydrocephalus - the accumulation of fluid in the skull. A cyst of the right frontal lobe is accompanied by a similar clinical picture.