Sclerosis of cerebral vessels is a systemic disease, as plaques, blood clots, and emboli block the lumen. The pathology has become generalized due to its localization in several parts of the body simultaneously - the lower limbs, brachycephalic trunk, vertebrobasilar arteries (VBA), anterior and posterior cerebral arteries.
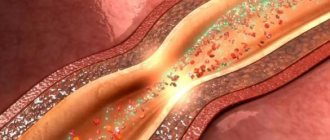
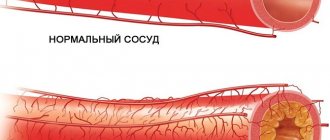
Sclerotic changes occur due to damage to the vascular wall, overgrowing of the defect with coarse connective tissue fibers. Loss of elasticity, conditions for subsequent deposition of cholesterol and calcium salts (atherosclerosis) are formed.
Sclerosis of the cerebral arteries
For the development of pathology, a change in the permeability of the vascular wall is required under the influence of an external factor - the deposition of cholesterol accumulations, vascular clots, neurogenic spasm of the artery. Fat molecules and blood cells penetrate into areas of defects.
Which cerebral vessels are affected by sclerosis:
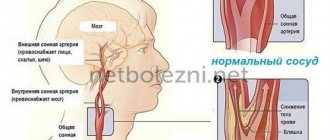
- Internal and general external carotid;
- Vertebral;
- Subclavian;
- Brachycephalic.
Prolonged spasm of the components of the brachiocephalic trunk causes chronic disruption of intracerebral blood supply. Numerous disorders lead to strokes and cerebral infarctions. The condition provokes oxygen hypoxia of brain tissue. Lack of microcirculation provokes ischemic conditions. Severe blockage of arterial patency causes a stroke.
Chronic cerebrovascular accident persists for a long time and is therefore accompanied by local defects. Clinical symptoms depend on the location of the pathological site.
Treatment
Therapy involves the use of medication (conservative) and surgical techniques.
Surgery
If an ultrasound reveals more than 70% reduction in the diameter of a cerebral artery, the question arises about the need for surgical treatment of the damaged vessel. The most commonly used method is carotid endarterectomy. During the procedure, the vessel is dissected at the site of the blood clot, which is removed, and the integrity of the vessel is restored using sutures.
Other methods are endovascular operations, stenting.
Drug treatment
It is prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account contraindications, medical history and based on the results of studies and tests.
Therapy for cerebral atherosclerosis is aimed at:
- harmonization and restoration of lipid metabolism;
- lowering cholesterol levels (find out the norm from the table);
- elimination of metabolic disorders;
- treatment of concomitant diseases.
To solve these problems, several groups of medications are prescribed:
Statins are an active group of drugs that block cholesterol synthesis in the body, reduce its amount and prevent the formation of plaques. These drugs are Lovastatin, Mevacor, Fluvastin, Mekafor, Simvastatin, Pravastatin.
Means for improving microcirculation , dilating blood vessels, relieving spasms and at the same time preventing platelets from aggregating (sticking together) into clots:
- "Actovegin", "Cavinton", "Curantil".
- “Parmidin”, “Anginin”, “Aspirin” restore blood flow in small vessels, reduce the permeability of the walls, suppress the adhesion of platelets into clots, stimulate the resorption of blood clots, and prevent the deposition of fats and cholesterol on the vascular wall.
Vasodilators:
- “Nicotinic acid”, Nikoshpan” - expand small capillaries, strengthen the cells of the arterial wall, and effectively help reduce cholesterol concentrations. From simple standard means - “Papaverine”, “Eufillin”.
- Among the more progressive medications: Isoptin, Lomir, Amlodipine, Diazem. Cinnarizine and Nimodipine are suitable for long-term use.
- Medicines containing the alkaloid of the periwinkle plant - Vinpocetine (Cavinton, Bravinton) allow you to dilate blood vessels and stimulate metabolism.
- Dietary supplements based on the Gingko Biloba plant are good at relieving vasospasm, stimulating the work of brain cells, and reducing blood viscosity. Taking Gingium, Tanakan, Ginkor Fort is not combined with medications containing aspirin (Trombass, Cardio-magnyl) due to the risk of a serious increase in blood flow and bleeding.
Nootropic drugs activate the process of energy exchange in brain cells, improve memory, mental activity, cerebral circulation and cell resistance to oxygen deficiency.
They treat problems of mental disorders, senile dementia: Piracetam, Nootropil, Bemitil, Cerebrolysin, Aminalon, Sermion (nicergoline), Meclofenoxate, Phezam, Biotredin, Vinpocetine.
Medicines that activate energy metabolism and remove lipids - Lipostabil, Omacor, Eikonol, Thioctic acid.
Medicines to prevent the formation of blood clots when blood viscosity increases and the content of prothrombin in it increases - “Trental”, “Aspirin-cardio”, “TrombASS”, “Pentoxifylline”, “Cardiomagnyl”.
Doctor's advice
There are risk factors for developing stroke and heart attack in the next 5 years that have long been studied and taken into account, called the “SCORE Scale”, in which the higher the cholesterol, the greater the risk. Accordingly, cerebral atherosclerosis increases the risk of sudden cardiovascular accidents. In the first place in the treatment regimen are statins - drugs that lower cholesterol and help reduce the volume of plaques.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Additional tools:
Fibrates – suppress the formation of fats and total cholesterol: “Clofibrate”, “Gemfibrozil”, “Fenofibrate”, “Atromid”, “Bezafibrate”, “Atromidine”.
Fibrates currently cause much controversy in the treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis. When used uncontrolled, fibrates are dangerous, so the dosage regimen and therapy regimen are agreed upon with a cardiologist.
“Nicotinic acid” and “Enduracin” are recommended in cases where atherosclerosis is associated with an increased amount of high-density cholesterol. They dilate blood vessels, but cause a rush of blood to the skin, so their use should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Hypocholesterolemic drugs - Neomycin, Guarem, Colestipol, Probucol, Lipostabil, Eikonol, Benzaflavin - reduce cholesterol, stabilize metabolism, and suppress the formation of blood clots.
In addition to the main treatment medications, it is advisable to take:
- Antioxidants that suppress oxidation processes: Mexidol, vitamins A, E, Aevit, P (strengthen the walls and increase the density and elasticity of blood vessels), microelements - potassium, silicon, selenium, vitamin C, which prevents the formation of fat deposits on the walls of arteries , group B improves the functioning of nerve cells. The use of Ascorutin (vitamin C plus rutin) requires monitoring the level of blood viscosity.
- For neurological manifestations and depression, antidepressants are used: Paxil, Azafen, Amitriptyline.
- When phobias, panic attacks, or severe anxiety appear, tranquilizers are prescribed: Alprazolam, Diazepam, Atarax, Phenazepam.
- If sleep is disturbed, sleeping pills and antidepressants (Donormil, Nitrazepam) are prescribed.
- For headaches and myalgia, the use of drugs that relieve pain and spasms is indicated: “Spazgan”, “Spazmalgon”, “Pentalgin”.
Among the more progressive medications: Isoptin, Lomir, Amlodipine, Diazem. Cinnarizine and Nimodipine are suitable for long-term use. Nootropics are prescribed with caution for dementia, as well as in older people - they activate the nervous system, and thus, as a side effect, can cause hyperexcitability, irritability, and aggression.
Physiotherapy for cerebral atherosclerosis
Aimed at activating blood circulation in the brain and processes in nerve cells, increasing arterial tone, and improving adaptive capabilities. This:
- Electrophoresis with medications.
- Hydrotherapy using carbon dioxide, oxygen, iodine-bromine, sodium, radon baths.
- Electrosleep procedures to strengthen and restore the nervous system.
- Special therapeutic exercises to improve and stimulate proper motor skills, motor functions, and relieve muscle spasms.
Diet therapy
The main provisions of the diet for cerebral atherosclerosis:
- Salt per day up to 3 g.
- Meals are frequent, in small portions.
- The amount of fat is no more than 65 g per day, of which 72% is vegetable.
- The amount of protein is not limited. Animal protein prevents fatty liver and cholesterol deposits in blood vessels.
What you can do:
- lean veal, pork, beef, turkey, fish;
- eggs in the amount of 1 pc. per day: in the form of steamed, baked, soft-boiled omelettes; milk, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, peas, beans, buckwheat, wheat, oatmeal;
- once a week a little caviar and tongue are allowed. 10-20 g per week of butter is allowed;
- sunflower, rapeseed, corn, cottonseed, olive seeds promote intestinal motility and remove excess cholesterol;
- seafood is very healthy (up to 6 times a week): fish, squid, shrimp, mussels, seaweed, kelp;
- vinaigrettes, salads from cucumbers, zucchini, cabbage, tomatoes, potatoes, pumpkin, soybeans, eggplant, pumpkin, dill;
- You can have low-fat sausage, ham, mild cheeses, dry cookies, marmalade, dried fruit candies, muesli.
What not to do:
- animal fats, offal products saturated with cholesterol, including liver, brains, kidneys are excluded;
- limit sweet dishes, fresh white bread, pure sugar, jam, honey, jams, cakes, buttery sweet cookies;
- Rich meat and mushroom soups, cream, ice cream, butter and custard creams, mayonnaise and sauces based on it, dark chocolate, strong coffee, tea, and alcohol are not recommended.
Folk remedies
In complex therapy of atherosclerosis, traditional methods are used with caution and after consultation with a doctor. They must be combined with medications
Among them:
- Collection for spasms of cerebral vessels, nervous tension. A collection is prepared from valerian root, cudweed, and St. John's wort in equal parts. Drink as an infusion.
- Honey and lemon juice are mixed equally with vegetable oil and taken a teaspoon in the morning (dangerous for allergies and gastritis).
- Drink 100 g of freshly squeezed potato juice for frequent headaches (harmful for stomach diseases).
- An alcohol tincture with garlic and lemon along with zest is known (extremely dangerous for gastritis, peptic ulcers, inflammation of the pancreas).
- Dill seeds (teaspoon), brewed in a glass of boiling water. Drink as tea for headaches.
Despite the fact that atherosclerosis occupies only the walls of blood vessels, the consequences for the brain, the entire body, psyche and intellect are devastating. A person gradually loses his personal qualities and turns into a thoughtless organism that requires constant care and regular feeding.
To prevent such an existence, you should pay attention to the very first signs of the disease, do all the necessary examinations and take timely the whole range of measures aimed at recovery.
How to recognize and how to treat cerebral atherosclerosis, watch the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://www.angiolsurgery.org/recommendations/2013/recommendations_brachiocephalic.pdf
Rate how helpful this article was
4.5 10 people voted, average rating 4.5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Causes of vascular sclerosis of the cerebral arteries
Lack of oxygen and nutrients contributes to the development of cystic cavities and scars. At the site of the destroyed adventitia, fibrous scars are formed, which over time in case of CNM provoke complete obstruction of the artery with the subsequent development of ischemic stroke.
Pathology intensifies under the influence of provoking factors:
- Violation of fat metabolism;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Frequent nervous tension;
- Emotional experiences;
- Hypertension (high blood pressure);
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Private stressful situations;
- Overweight;
- Diabetes;
- Smoking;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Eating disorder;
- Loss of artery fragility with age.
Age-related changes are characterized by the presence of several factors simultaneously. Preliminary prevention helps prevent dangerous conditions.
Diagnostics
Correct treatment of the pathology is possible only after the following diagnostic measures:
- MRI and CT of the brain.
- Complete blood test (sugar, creatinine, blood electrolytes, vitamin B1 level).
- Study of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones.
In addition, a neurologist examines the medical history and collects information about a possible genetic predisposition to the development of this pathology.
Degrees of chronic sclerosis of the cerebral arteries
Mortality from ischemic stroke ranks second in Russia after diseases of the cardiovascular system. The cause of death is six million people in Russia. Approximately every minute and a half in the Russian Federation, one person suffers a stroke. It is impossible to cure the disease. Only prevention prevents brain hypoxia.
Degrees of chronic intracerebral insufficiency according to Pokrovsky:
- The first stage is minor ischemia with an asymptomatic course, no significant changes in the cerebral arteries;
- The second stage is accompanied by a neurological deficit with signs of mild neurological disorders. The probability of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) with CNM within an hour after a deterioration in blood circulation reaches 80%. The pathology is transient. Symptoms disappear within 24 hours;
- The third degree is accompanied by vertebrobasilar insufficiency and general cerebral neurological symptoms. In medical terms, a complex of changes in pathology is called “dyscirculatory encephalopathy”;
- The fourth degree is a complete or completed stroke with multiple changes that persists for more than a day. Clinical signs depend on the predominant location of neurological manifestations.
The extreme degree of sclerosis of the cerebral arteries is a stroke. Nosology leads to disability. Complete blockage of the lumen of the vessel is accompanied by severe tissue hypoxia. Obstruction of the vertebral and carotid arteries in the neck leads to the death of a significant part of the brain parenchyma.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) leads to stroke in 90% of people within a year. Neurologists consider pathology to be the first signal of subsequent dangerous, life-threatening changes in the brain matter.
Timely treatment for symptoms of vascular atherosclerosis
Treatment of pathology is especially effective in the early stages. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease and minimize the negative consequences.
An important role in treatment is played by the qualifications of the doctor and the class of equipment used in the clinic. Modern diagnostic equipment detects even minor changes in the vascular system, and treatment of complex cases is possible without surgical intervention - using innovative, low-traumatic methods.
The first signs of cerebral atherosclerosis
Before the transient attack, focal neurological disorders are observed:
- Transient paresis and paralysis of the limbs;
- Blindness;
- Fainting conditions;
- Memory loss;
- Intellectual function disorders;
- Speech pathology;
- Periodic headaches.
The appearance of the described symptoms indicates a violation of cerebral circulation, which can be detected using Doppler ultrasound of the base of the skull.
Manifestation of stage I stenosing sclerosis of the cerebral arteries
Nosology has three degrees of severity.
Signs of the 1st degree:
- Chronic fatigue;
- Persistent depression;
- Dementia;
- Memory loss;
- Constant excitability;
- Moodiness;
- Periodic dizziness;
- Fainting;
- Doubling of objects before the eyes;
- Unilateral or bilateral tinnitus;
- Emotional disorders.
With intense physical activity and stressful situations, symptoms worsen. Long-term persistence of CNM for several years in a row leads to irreversible changes. It is possible to restore the patency of the cerebral artery only through surgical intervention to stent the damaged area.
Symptoms of stage II sclerosis of the cerebral arteries
The second stage occurs due to a moderate lack of intracerebral microcirculation.
The main signs of stage II cerebral sclerosis:
- Poor concentration;
- Loss of speech skills;
- Decreased performance;
- Difficulty performing daily work;
- Lack of articulation;
- Memory disorders;
- Weakening of intellectual activity.
The second degree of atherosclerosis of the carotid, vertebral, and cerebral vessels leads to a pronounced disturbance of the microcirculation of the cerebral parenchyma.
Signs of stage III atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
Deposition of cholesterol plaques inside the carotid or vertebral arteries of the neck leads to a decrease in microcirculation of 25% of brain structures. The vessels provide blood supply to the base of the brain. Lack of blood flow through the basilar basin causes hypoxia, a lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Signs of stage IV cerebral sclerosis
A dangerous list of symptoms occurs in the third stage:
- Ischemic heart attack or stroke;
- Fainting;
- Coma;
- Paralysis and paresis of the limbs;
- Disability;
- Unsuitability.
Full recovery after the third degree is impossible. The consequences depend on the extent and depth of damage to the brain parenchyma.
Multiple sclerosis - how it differs from the vascular type
Demyelination is the destruction of myelin in nerve sheaths, which occurs in inflammatory, autoimmune, and prion diseases. The nosology differs from classical vascular thrombosis, embolism, and atherosclerosis in morphological manifestations.
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by the destruction of myelin. Unprotected nerve sheaths overlap each other, causing damage to signal transmission. Every year, the manifestations of the nosology increase, which leads to muscle paralysis and paresis of the limbs.
Atherosclerosis leads to blockage of vascular patency. The deposition of cholesterol plaques in the artery wall reduces patency. Initially, local changes appear without symptoms. An increase in hypoxic conditions leads to neurological disorders. Doctors will be able to conduct a differential diagnosis of nosologies based on clinical manifestations.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
Disorders of fat metabolism contribute to excessive accumulation of cholesterol inside the cerebral arteries. Consistent violation of microcs
circulation leads to a number of pathological symptoms:
- Night sleep disturbance;
- Intense headache;
- Nightmares;
- Constant excitability;
- Speech disorders;
- Chronic fatigue;
- Difficulty swallowing.
The initial manifestations of the disease are ear noise, headaches, memory loss. Feeling better after rest, intensifies in the afternoon.
The first signs of atherosclerosis:
- Increased suspiciousness;
- Speech deterioration;
- Unsteady gait;
- Depressive state;
- Twitching of arm muscles.
A specific sign of second-degree atherosclerosis is an individual’s overestimation of his own capabilities.
The final stage of cerebral atherosclerosis is decompensation. It occurs due to multiple disorders due to lack of blood supply. The nosology is characterized by a high risk of stroke, heart attack, and transient ischemic attack.
Complete cessation of microcirculation develops with severe obliteration of the vessel by atherosclerotic plaque. The death of the parenchyma is accompanied by a lack of nutrition and oxygen supply. With extensive death of intracerebral parenchyma, neurological manifestations can be traced:
- Weakness of limb movements;
- Disorders of the sensitive area;
- Loss of coordination;
- Speech disorders;
- Severe dizziness;
- Difficulty swallowing reflex;
- Headaches and dizziness.
Cerebral sclerosis is characterized by multiple changes in which additional pathological conditions develop. Atherosclerotic changes in the main arteries of the head cause multiple symptoms.
Symptoms of sclerotic changes in the coronary and carotid arteries
Lack of blood circulation to the base of the brain may be due to blockage of the cervical vessels. Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the neck (spondylosis), instability of the vertebrae provokes compression of the vertebral artery arising from the brachycephalic trunk. The vessel supplies blood to the lower part of the base of the brain.
Common symptoms of cerebral atherosclerosis
Clinical picture of the main symptoms of cervical sclerosis:
- Decreased mental activity, constant fatigue, chronic fatigue;
- Short-term loss of consciousness with a sudden movement of the head;
- Poor concentration;
- Instability of the emotional sphere, instability of the mental sphere;
- Tendency to depression;
- Insomnia;
- Behavioral disorders;
- Constant anxiety, excitability;
- Dizziness and headaches;
- Epileptic disorders, muscle cramps;
- Manifestations of synesthopathy are pain in the back of the head, loss of sensation in the lower extremities;
- Periodic Cheyne-Stokes breathing (shallow with certain cycles of inhalation and exhalation);
- Cerebellar ataxia occurs due to damage to the cerebellum and trunk;
- Visual, auditory, speech disorders;
- Transient paralysis of the legs.
Some people with atherosclerosis of the vertebral, carotid and carotid arteries develop a protective reaction to light and loud sounds. Organic damage to brain tissue due to chronic disruption of cerebral microcirculation leads to dementia. A cerebral or hypertensive crisis develops in patients with a combination of CNM and essential hypertension.
The rapid progression of vascular atherosclerosis in diabetes mellitus is caused by impaired glucose absorption due to a lack of insulin supply.
Prevention of intracerebral sclerosis
Sclerotic damage to intracerebral arteries can be prevented only at the initial stage. Ischemic disorders in hypertension are prevented by correcting blood pressure levels with medications. Stable maintenance of numbers prevents hypertensive crises. Only a doctor can choose the right medications.
An atherosclerotic diet includes low-fat foods, consumption of vegetable oils, and optimization of the daily menu. Limiting bread and sugar normalizes intracellular metabolism and reduces the load on the pancreas.
Diagnosis of cerebral vascular sclerosis
The development of sclerotic changes in cerebral structures is diagnosed at the initial stage by the following methods:
- MRI of the brain with contrast - examination of the arteries after intravenous administration of a contrast agent. The procedure shows the structure, areas of vasoconstriction are identified;
- Neurosonography – ultrasound of the brain arteries;
- X-ray cerebral angiography - performing radiography of the skull after intravenous administration of contrast;
- Transcranial duplex scanning (two-dimensional) - a special ultrasound of the blood circulation of the cranium;
- Biochemical and general blood test.
Computed tomography (CT) is prescribed after traumatic brain injury to verify skull fractures and detect hematomas.
Diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis
Suspicion of this disease arises when examining the patient based on characteristic symptoms in accordance with the stage of the disease and his age.
A refined diagnosis is made based on the results:
- duplex ultrasound examination of extracranial vessels (assessment of their condition, absence or presence of narrowings, lipid plaques, blood clots);
- transcranial Dopplerography (analysis of the condition of intracranial arteries);
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- angiography of veins and arteries.