Motor neurons, upper and lower
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the most common type of motor neuron disease.
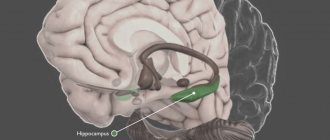
Motor neurons are cells that carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles. They can reach 1 meter in length.
Upper motor neurons are located in the cerebral cortex. Their processes (axons) descend into the spinal cord, where they contact the neurons of the spinal cord.
Neurons in the spinal cord (lower motor neurons) use processes to transmit signals to the muscles and control their contractions. Depending on their location, they are responsible for the movement of the arms, legs, torso, contraction of the diaphragm, breathing, swallowing, etc.
In ALS, motor neurons in both the brain and spinal cord are affected and killed.
The average age of patients is 45 years, but there are also much younger patients. Thus, American composer and guitarist Jason Becker was diagnosed with ALS at the age of 20.
The disease occurs in 5-7 people per 100 thousand population. Every 90 minutes, a new case of ALS is diagnosed around the world.
There are twice as many cases of men as women.
Muscle weakness and joint stiffness
What's happening? When the number of signals from motor neurons to muscles decreases, the latter are used less and less and lose mass over time. This leads to a feeling of weakness and can cause problems with balance and gait, which increases the risk of falling.
What can be done? A decrease in muscle mass cannot be stopped by physical exercise, because... the disease progresses irreversibly. However, exercise helps maintain joint flexibility and mobility, which helps maintain muscle function, balance, and body posture. To get a referral to a physical therapist who can create an appropriate exercise program, you must contact your primary care physician. A nutritionist can also help and advise you on how to eat properly to maintain your body weight and further slow down the rate of muscle loss.
Learn more about ways to combat muscle weakness and fatigue
Famous people with ALS
Mao Zedong.
Photo from pinterest.ru Mao Zedong (1893-1976) - Chinese politician. At the age of 80, he was diagnosed with ALS, but died two years later from a heart attack.
Lou Gehrig (1903-1941) was an outstanding American baseball player. He was diagnosed with ALS at age 36, in 1939.
Dmitry Shostakovich (1906-1975) is a great composer. He suffered from ALS for about ten years and died of a heart attack.
Stephen Hawking (1942-2018) is a famous British physicist. Lived with ALS for over 50 years.
Vladimir Migulya (1945-1996) – composer, author of music for the songs “Grass at the House”, “Talk to Me, Mom”, “Stuntmen”, etc. The disease was discovered in 1993.
Jason Becker (born 1969) is an American composer and guitar virtuoso. He fell ill with ALS at the age of 20, in 1989.
Fernando Ricksen (born 1976) is a Dutch footballer. He was diagnosed with ALS in 2013 and lost the ability to speak in 2021.
Gehrig's, Hawking's and Mao Zedong's disease
This disease was first described in 1869 by the French psychiatrist (by the way, the teacher of Sigmund Freud himself) Jean-Martin Charcot. Science and medicine have advanced greatly since then, but ALS is still considered one of the most mysterious diseases of the 21st century.
ALS is also known as the most common form of motor neuron disease (MND). Internationally, this disease is also known as motor neurone disease, motor neuron disease, and Lou Gehrig's disease. The latter option is most often used in the United States and Canada, since in 1939 ALS was diagnosed in the then famous American baseball player Lou Gehrig. For his endurance, this man was nicknamed “The Iron Horse”; He played all his life for the New York Yankees and set more than one record. But at age 36, Gehrig was diagnosed with ALS. The disease immediately cut short his career and took his life: Gehrig died in 1941.
At one time, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis also affected such people as composer Dmitry Shostakovich, Chinese leader Mao Zedong. But, of course, ALS became widely known later, when the whole world learned about a man named Stephen Hawking. This English physicist and cosmologist was remembered not only for his outstanding discoveries, but also for his extraordinary life expectancy for such a diagnosis: he managed to live with ALS for more than 50 years - longer than anyone in history. Moreover, the scientist became the father of three healthy children.
Stephen Hawking. Photo: PA Images/TASS Today, worldwide incidence rates of ALS or MND are estimated to range from 0.86 to 2.5 per 100,000 people per year. This is a very rare disease, and it is impossible to cure or stop its course; it will only progress. The only thing doctors can do is to alleviate the patient’s condition and, at different stages, slightly improve his quality of life.
In Russia, until 2012, ALS patients had nowhere to turn for help. In 2012, a service to help people with ALS began its work in Moscow - then it was one of the charitable projects of the Orthodox help service “Mercy”. Three years later, in 2015, on the initiative of ALS patients themselves, the “Live Now” foundation was established - it remains the only organization in the country that develops a system of assistance to such patients. The Moscow service for helping people with ALS now operates on the basis of the foundation: people from all over Russia receive help here.
Every year, the foundation holds all-Russian patient conferences on ALS, in which specialists from around the world take part. The last such conference was held in April of this year with the support of a Grant from the Mayor of Moscow. She gathered in one hall dozens of patients with ALS and specialists in various fields of knowledge: neurologists, psychologists, speech therapists, teachers, geneticists - in a word, all those who understand the specifics of this difficult disease and know how to help. Hundreds of participants watched the broadcast online.
Contrary to expectations, the conference was opened not by the director of the foundation, but by one of the patients, Nailya Bikkulova
. The young woman is confined to a wheelchair and can hardly speak. Despite this, she addressed the audience with an opening speech - using her eyes. Nailya uses the same technology as Hawking: she types text on a computer that reads her eye movements.
“The response to my appeal to the fund was immediate,” says the robotic female voice of the computer program. “Coordinator Mlada called me back and immediately began offering help, consultations, and rehabilitation means. Thanks to such participation, you understand that you can and should live. When you feel that someone wants to help you not in words, but in deeds, then the patient and his relatives gain confidence, because there is practically no information about the disease and its course.”
The desire and even some kind of urgent need to live is something that Naila definitely has. Her eyes literally glow, a smile appears on her lips every now and then - gentle, quiet and calm, like Mona Lisa. A smile behind which hides a lot of pain, already experienced and not yet known. But Nailya is not alone in this pain: every minute her beloved husband is next to her, ready to help and support.
Nailya Bikkulova with her husband. Photo: Artem Danilov/MIR MTRK
There are a lot of people in the hall, but identifying patients with ALS is not so easy: not everyone has breathing tubes inserted into their throats, some speak and even walk on their own. Only by indirect signs can one understand that a person is unwell: a cane placed on a chair, slightly closed eyes, cautious and slightly slow movements. And every time you look at them you think: it will get worse.
Who's at risk
Stephen Hawking.
Photo from pinterest.ru The disease was first described in 1869 by the Frenchman Jean-Martin Charcot, but it is still poorly understood. In each case, its triggering mechanisms may be different.
There are hereditary forms of ALS, and then the main cause is a mutation in a specific gene. When making a diagnosis, a neurologist usually asks whether any other family members have suffered from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or frontotemporal dementia (the same genetic “breakage” leads to it).
But in the vast majority of patients (90-95%), none of the relatives suffered from these diseases. Moreover, in 10% of these people the mutation is still detected - it occurs for the first time in them, and is not transmitted from their parents.
There is a hypothesis that there is a connection between the non-hereditary form of ALS and certain injuries, high stress in sports, and agricultural chemicals.
But clear conclusions have not yet been made, since many data are inconsistent with each other.
The only known risk group is children of sick parents with an established mutation that caused the development of ALS. They inherit the damaged gene with a 50% probability. But a gene mutation does not necessarily lead to ALS.
Mysterious mutant gene
Why does a person get ALS? Nobody knows this. Or rather, there are many assumptions, but doctors still don’t know how exactly this disease occurs. Genetics can provide the most information, since ALS is essentially a genetic mutation.
One of the conference guests was Christian Lunetta, scientific director of the NeMo Center for Neuromuscular Diseases in Milan.
. He said that ALS most likely begins in a person many years before the first symptoms appear.
“When the patient is finally diagnosed, the level of damage is most often already very significant. Of course, there must be some risk factors for ALS - perhaps external. We can say for sure that a powerful risk factor is the presence of a familial form of ALS, that is, a genetic mutation. And recently, this is the most difficult part of the research - to determine the genes in which there are faults,” said the doctor.
Christian Lunetta. Photo: Irina Fomochkina/MIR MTRK
With the familial form, everything is more or less simple - this is when a gene with a mutation is inherited, explains biologist, founder of the Clinical Bioinformatics Laboratory Fedor Konovalov.
“When we talk about the genetics of ALS, we primarily mean, of course, familial cases, of which there are about 10%. This is a direct transmission to descendants (not through a generation) with a probability of 50%. Moreover, this does not depend on gender. The patient has a mutant gene on one of his chromosomes, while the other chromosome is normal. A person passes on only one of each pair of chromosomes to each child, the second from the second parent. Thus, it turns out that the patient has a 50% probability of passing on the defective chromosome to any of his descendants,” explains Konovalov. But sometimes mutations arise, as geneticists say, de novo: both parents are healthy and will never develop ALS, but one of their children develops the disease. This form of ALS is called sporadic.
“And it can be hereditary in nature,” Konovalov clarifies. – From the point of view of family history, the case is sporadic, but de facto it is hereditary. The mutation appeared either during the embryogenesis of this person, or during the formation of germ cells in the parents. The important thing is that when this happens, the mutation, having occurred in a sporadic case, can then be inherited as a family one.”
Photo: Irina Fomochkina/MIR MTRK
Weakness in the legs
Dmitry Shostakovich.
Photo from pinterest.ru ALS is very difficult to diagnose. Firstly, because it is a rare disease that doctors are poorly aware of. Secondly, early symptoms are quite minor: clumsiness, clumsiness in the hands, slightly slurred speech. Thirdly, the disease manifests itself differently in each patient.
The first and most common symptoms of ALS are weakness in the arms or legs. Objects begin to fall out of the hands, the person stumbles when walking, and drags his foot. There is a sensation of muscle contractions under the skin (fasciculations). Painful cramps and spasms may occur. Fatigue increases.
Difficulties begin with speech, swallowing, and chewing. It becomes difficult to breathe.
Some ALS patients may cry or laugh involuntarily. The reasons for this are not psychological, but physiological: the disease affects areas responsible for emotional reactions. Sometimes there are problems with memory and concentration.
What tests are performed to make a diagnosis?
Photo: Flickr.com/ec-jpr
If the therapist suspects that a person has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, he will send him to a neurologist, who will prescribe a series of examinations:
– a blood test (will show whether the level of creatine kinase, an enzyme that is produced when muscle tissue is destroyed), is elevated;
– magnetic resonance imaging (does not reveal specific changes in ALS, is used to exclude diseases with symptoms similar to ALS);
– electroneuromyography (registration of electrical activity of muscles);
If necessary, additional examinations such as a lumbar puncture or muscle biopsy may be performed.
Forecast
The prognosis for the recovery of patients suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is pessimistic. Treatment of the disease is aimed at improving the quality and increasing the patient’s life expectancy. The only drug that affects the mechanism of development of the disease is not imported into the Russian Federation. The most unfavorable prognosis is for high and bulbar forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Care and palliative therapy for patients suffering from ALS are provided at the neurology clinic and hospice of the Yusupov Hospital. Doctors in the intensive care unit use modern equipment to support the patient’s vital functions. To get complete information about the disease, the cost of treatment, and to make an appointment with a neurologist, call the contact center phone number. It works 24 hours a day without days off and lunch breaks.
Make an appointment
What happens to the patient
Photo from the site syl.ru
The average life expectancy for ALS is from two to five years from the moment the first symptoms appear. There are cases when the disease lasts several decades. For example, Stephen Hawking lived with ALS for more than 50 years. And there are patients who leave a few months after the diagnosis is made.
As ALS progresses, a person experiences increasingly serious difficulties with moving, speaking, swallowing, and breathing. Therefore, doctors advise relatives to immediately adapt housing for the patient and buy special equipment.
If the disease begins in the legs, then at first it becomes difficult for the patient to walk and maintain balance; he may lean on pieces of furniture, so they must be stable. Then the patient begins to use a walker or wheelchair, and it is important to free up space in the house for this.
Gradually, it becomes difficult for a person to raise his arms, so it is recommended to place all necessary things no higher than 1 m from the floor. There are adapted forks, spoons and knives with thicker handles and even with straps; they allow the patient to go longer without assistance when eating.
To communicate with the outside world, such patients eventually have to resort to special devices. Stephen Hawking, for example, used a special computer system that was controlled by the cheek muscle. And Jason Becker uses a board with letters that he points to with his eyes. Many people benefit from the Tobii device, which connects to a regular computer and allows you to move the cursor and type on the keyboard with your eyes.
Sooner or later, a person's respiratory muscles are affected and he loses the ability to breathe on his own. Then there is a need for breathing equipment.
What helps with ALS
Photo from als-info.ru
ALS remains an incurable disease. Doctors can only prolong a patient’s life and improve its quality.
Riluzole is a medicine that can slightly slow down the progression of ALS (provided the person starts taking it in the early stages of the disease). This drug is not registered in Russia.
Mechanical ventilation also increases the life expectancy of people with ALS. In addition, it improves sleep, reduces shortness of breath and fatigue. There is non-invasive pulmonary ventilation (NIV), in which a special device pumps air into a face mask. Invasive ventilation uses a tracheostomy, which almost completely deprives a person of the ability to speak.
Many people with ALS find it very difficult to eat and drink. To compensate for the lack of calories and fluid, special therapeutic nutrition is used. When it becomes difficult for a person to swallow even homogeneous food, a gastrostomy is placed - a special tube through which food enters directly into the stomach.
A neurologist may prescribe medications to the patient to reduce muscle spasms, as well as medications to reduce fasciculations. Morphine-containing drugs are prescribed to reduce the feeling of suffocation. Sometimes patients with ALS are given antidepressants.
Massage, aromatherapy, and acupuncture help relieve stress and pain. (Naturally, these methods do not treat the disease itself). Physical exercise allows you to maintain muscle function, a sense of balance, and joint mobility longer. However, excessive stress can cause harm, so a set of exercises should be developed under the supervision of a physical therapist or exercise therapy doctor.
What is ALS?
The nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord that are involved in regulating muscle function are called motor neurons.
ALS is characterized by a violation of this type of regulation. A decrease in muscle activity leads to a decrease in strength, and subsequently to muscle rigidity (inelasticity) and a decrease in muscle mass.
ALS greatly shortens a person's life; gait, speech, swallowing and breathing are impaired. The personal experience of everyone who has encountered this disease is unique: not all symptoms may appear and not necessarily in the specified sequence. However, symptoms progress over time: in some people quite quickly, in others - more slowly.
ALS is a rare disease that affects adults. And despite occasional cases of this diagnosis in young people, most often the disease occurs in the age group from 50 to 70 years.
At the moment, no effective treatment for ALS has been developed. However, a number of medical and social services specialists can help manage symptoms to ensure the highest possible quality of life for the patient and his family.
Find out more in the section "What is ALS"
Is Kennedy's disease a type of ALS?
Kennedy's disease is another disease that also affects motor neurons but, unlike ALS, causes only weakness. Because the disease progresses slowly, the life expectancy of people with Kennedy's disease is not reduced.
Since the symptoms of Kennedy's disease and ALS are similar, diagnostic errors are possible. However, Kennedy disease has a clear and well-described genetic mutation that can be identified through genetic testing. Additionally, Kennedy's disease usually affects men, while women are only carriers of the genetic mutation. Cases of the development of symptoms in women have been described, but they are extremely rare.
The following information will also be helpful to those caring for someone with Kennedy's disease.
What causes ALS?
Unambiguous causes of ALS have not been established, since in each individual case various factors may be decisive. Most people with ALS do not have family members who have been diagnosed with ALS. In such a situation, it is believed that the disease is of a polyetiological nature with the participation of both genetic and environmental factors (in this case, the participation of genes is less pronounced). Among the environmental factors are the influence of nutrition and air composition, heavy physical labor, participation in military conflicts, smoking, lead intoxication and contact with chemical fertilizers. Since external factors are always different in each individual case, it is impossible to clearly establish the specific cause of ALS.
Research is currently being conducted into the disease, its causes and progression. Thus, understanding of the disease is gradually expanding.
Find out more in the material “Causes of ALS”
What if several family members have ALS?
In a small number of cases, a mutation in the corresponding gene is inherited. However, it is believed that for the full manifestation of the disease, the presence of other factors is necessary.
If a person with ALS or their relatives are concerned about the possible hereditary nature of the disease, they can seek genetic counseling. A geneticist will explain all the nuances of the disease and provide the most accurate information about the impact of ALS on family members of the patient.
Find out more in the material “Inherited Causes of ALS”
The doctor will also tell you about a method called genetic testing. But you need to take into account that this is an expensive procedure that does not provide 100% answers to all questions. The fact is that only a few individual genes responsible for the formation of ALS are usually tested. However, not all such genes are currently known.
The decision to undergo genetic testing can be difficult as it affects other family members. Not all relatives may want to know about the risk of developing ALS. It is recommended to undergo genetic counseling with the participation of a neurologist with experience in working with ALS.
Find out where to get genetic testing in the ALS Help section.
What are the most common symptoms of ALS?
As a rule, the disease begins with damage to the muscles of the upper and lower extremities, as well as the muscles of the mouth. Not all of the muscles listed are affected at the same time.
ALS is characterized by:
- weakness and decreased motor activity of the limbs;
- muscle twitching and scratching sensation under the skin;
- muscle rigidity and spasms (sometimes painful);
- breathing problems and feeling tired;
- problems with speech, swallowing and salivation;
- changes in behavior and thinking.
Some people experience paradoxical emotional reactions in the form of crying against a background of elevated mood or laughter against a background of sadness. This phenomenon is called emotional lability and can be very unpleasant, but medical and social services staff will always be able to provide the necessary support. This symptom does not occur in all people with ALS.
Find out more in the material "Emotional Disturbances"
ALS usually does not affect the following organs/systems:
Sense organs : vision, hearing, smell, tactile and taste sensitivity.
Bladder and intestines. However, a decrease in the level of physical activity complicates the process of going to the restroom and also contributes to the development of constipation. People with ALS sometimes experience a false urge to urinate, even though the bladder is empty. Consult your doctor or neurologist about drug therapy for this symptom.
Sexual function. Although sexual dysfunction is not typical for ALS, fatigue, decreased motor activity and the state of emotional stress caused by the presence of the disease contribute to the appearance of some difficulties during sexual intercourse. Find out more in the material “Intimate life and relationships”
Ways to control symptoms include exercise and drug therapy. However, a person may have other symptoms not listed above, or other diseases not related to ALS, such as viral, physical, or injury. You should always consult your doctor or health care team with any questions.
Find out more in the material “ALS Symptoms”
What research is being done to beat ALS?
Image from the site syl.ru
In motor neurons affected by ALS, pathological clots (aggregates) of protein molecules are found. Typically, proteins stick together as a result of some defect in the gene that encodes them.
In 20% of cases of hereditary and in 2% of sporadic forms of ALS, the disease is caused by a mutation of the SOD-1 gene. This mutation was first discovered in 1993.
A mutation in the TAR DNA binding protein (TDP-43) gene has been found in some families of ALS patients. In 3-5% of patients with a hereditary form of ALS and in 1% with a sporadic form of ALS, a mutation of the FUS protein gene occurs.
In 2011, scientists discovered the C9ORF72 gene mutation. It turned out that it is present in 25−40% of families where there is a patient with ALS, and in 7−10% of patients with a sporadic form of the disease.
In 2014, thanks to the IceBucketChallenge flash mob, when thousands of people around the world were doused with ice water, more than $100 million was raised to research the causes of ALS and find a cure for this disease.
Research is going in two directions. The first is the search for genes that cause the hereditary form of the disease. The second is the identification of “susceptibility genes” that increase the risk of the disease in a family where no one has previously had ALS. Understanding the mechanisms of the disease will help find a cure for it in the future.
What help does the patient and his family need?
Photo by Yuri Mozolevsky from the website sb.by
A person with ALS may need consultations with a neurologist, a respiratory support specialist, a physical therapist, an occupational therapist, a nutritionist, a speech therapist, a music therapist, a psychologist, a palliative physician, as well as the help of a medical and visiting nurse.
The family will have to provide him with certain equipment. This could be a wheelchair, walker, multifunctional bed, ventilator or NIV, aspirator (saliva ejector), cougher, lift (for example, for moving from a bed to a wheelchair or from a stroller to a bath). In addition, the patient needs medicine, nutritional therapy, hygiene products, etc.
Each patient with ALS needs an individual route of care, as the disease can progress in different ways.
How the State Duma expanded the federal list of orphan diseases
At the beginning of April, Yulia Retina, a consultant at the Office for Organization of Medical Equipment Provision at the Samara Region Ministry of Health, told Ilya Frolov that the procedure for purchasing a cough cougher was long and would take two months at best. “The process of signing a purchase agreement can last up to 20 days, after that it takes a month or a month and a half for the purchase itself, and there are May holidays, and besides all this, supply disruptions due to coronavirus cannot be ruled out,” Ilya Frolov lists possible reasons for which his grandfather may not live to receive a cough cougher. - We had the first recommendation for a cough cougher in January - and by the end of May we may be waiting for the device! They explain to me that the region does not purchase equipment for future use, only after the fact, when someone needs it. But we actually needed the device in January - and then we really could have waited a month or a month and a half. And now we can’t wait. Sputum in the bronchi is a risk of pneumonia. This will kill grandfather. Now, without a cougher, he can’t even use NIV normally: as soon as sputum accumulates, the NIV becomes clogged.” As a quick alternative, the Ministry of Health of the Samara Region offered the Frolovs - once again - hospitalization in the intensive care unit. But the family believes that Vladimir will not survive life in intensive care.
“Grandfather doesn’t talk, he communicates with his family through notes,” explains Ilya. “In intensive care, without his family, no one will understand him.
At home, when he begins to choke on phlegm, we tap his back - we cannot leave him for a minute. If he goes to the hospital, no one will do this - he will simply be intubated, he will be on a ventilator. But they won’t let us into intensive care because of the threat of coronavirus.”
A person with ALS can live a long time on a ventilator, but it is a painful life, oh. Today, patients with this disease have the right to refuse intubation and connection to mechanical ventilation, choosing a palliative route, in which death occurs from natural causes and the patient is at home with his family. However, Vladimir Frolov is being deprived of this right - without the necessary equipment, the last months or weeks of the life of a patient with ALS can be so painful that relatives will be forced to agree to intubation in intensive care.
“Nurses from the palliative department are now coming to us, noting that we have better care for him at home than in the hospital,” says Ilya. “The chief freelance neurologist of Syzran, Evgeniy Kirilin, told us that the main thing for grandfather is care. There is no cure for ALS, and care slows the progression.”
On April 9, the Live Now charity foundation, with the participation of the Samara charity foundation Evita, bought a cough cougher for Vladimir Frolov.