Perinatology is a science leading from obstetrics to pediatrics. Studies the period of intrauterine development of a child from the 22nd week of a woman’s pregnancy.
Perinatal practice often diagnoses a choroid plexus cyst in a newborn. Education does not have a negative impact on a child. The danger lies in diseases that provoke neoplasms. Perinatology scientists argue: some call choroid plexus cysts a marker of chromosomal abnormalities, but without confirming this.
To avoid consequences, expectant mothers undergo timely diagnosis and find out the causes of the pathology. Based on the size and location of the cysts, the doctor prescribes treatment. Therapy helps eliminate cysts completely or slow down their growth.
What is a choroid plexus cyst?
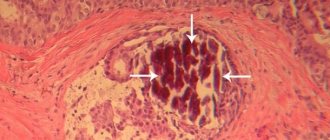
A choroid plexus cyst is a cavity in the brain. Its walls are formed from cells and tissue. They have clear rounded borders. Inside, the cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid.
The overwhelming majority of pathology cases are benign. Disorders appear due to the rapid growth of the cystic sac. The neoplasm compresses nearby tissues. This disrupts cerebral circulation and negatively affects nerve cells.
To detect a bubble with liquid, screening is performed. It is a complex of studies to identify the risks of developing diseases in the fetus. Diagnosis is carried out after 20 weeks of pregnancy. The discovery of cysts does not cause concern to doctors, because they have almost no effect on intrauterine development.
This terrible word "Cyst"
Infrequently, in about 1 in 30 pregnancies, an ultrasound scan of the fetus may reveal a cyst of the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle of the brain. The word “cyst” usually causes tremors and panic in our population, as it is associated with the need for surgery or cancer.
However, as for the choroid plexus cyst of the brain, there is no need to panic. Typically, this is a benign finding, can be diagnosed from 15 weeks of pregnancy and usually continues to be observed until 28-32 weeks of pregnancy, after which most cases of these cysts resolve on their own.
Why then does the doctor mention these cysts if everything is so simple and safe? Wouldn't it have been easier to remain silent and ignore this discovery? - you ask.
The fact is that a cyst in the choroid plexus of the brain can appear for other reasons - for example, as a result of hemorrhage into this same choroid plexus, or as a consequence of an infectious process in the brain, or as a manifestation of a vascular aneurysm, and even as a manifestation of the cystic component of the tumor brain
That is why, when a choroid plexus cyst of the lateral ventricle of the brain is detected, not complacency should dominate the mood of the doctor and the patient, but alertness, and only a detailed analysis of the state of the brain and blood circulation in it, analysis of systemic indicators of fetal blood circulation, analysis of the results of infectious screening and screening of the state of all systems and fetal organs will be able to give an answer about the degree of danger of the detected cysts.
Choroid plexus cysts can be single or multiple, unilateral or bilateral, and their sizes also vary , but in general the prognosis of these cysts depends on other risk factors for fetal disease combined with them, for example, such as an increase in the thickness of the nuchal translucency or cervical fold , the presence of skeletal dysplasia, other malformations of the brain and heart, kidneys, facial structures of the fetus, etc.
You need to understand that the choroid plexus and the lateral ventricle of the brain are not dimensionless , and when the size of the cyst is more than 9-10 mm, the fetus develops secondary ventriculomegaly (i.e., expansion of the lateral ventricles of the brain), which is accompanied by intracranial liquor hypertension and hydrocephalus.
According to statistics, cysts disappear by 28-30 weeks of pregnancy. This is also not entirely and not always true, and we provide photo examples from our own practice demonstrating choroid plexus cysts in both fetuses and newborns.
The same medical statistics note that in the presence of cysts of the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles of the brain, such a formidable chromosomal disease of the fetus as trisomy 18, known to us as Edwards syndrome, is more often detected. Much less frequently, in the case of choroid plexus cysts, trisomy 21 (Down's disease) can also be detected. Therefore, the task of the doctor-ultrasound researcher when identifying a cyst of the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle of the fetal brain is not just to state this fact, but to exclude other probable signs (markers) of these formidable genetic diseases.
And further. In postpartum ultrasound screening, a newborn undergoes a series of ultrasound examinations of the whole body (and in the case of an appointment at our center - ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography), echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart), ultrasound of the stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, ureters, bladder, hip joints, and in an expanded version - additionally the thymus gland, thyroid gland, intestines, reproductive organs (organs of the scrotum or uterus with appendages).
So, when performing neurosonography (ultrasound of the newborn’s brain), brain cysts are often discovered that were not detected during prenatal examinations. The point here, of course, is not the inattention of the ultrasound doctor, who “overlooked” the cysts during the examination of the fetus.
The detection of these cysts indicates trauma or infection suffered by the baby during childbirth, or in the early postpartum period. Cysts can also be found in the choroid plexuses, but their heterogeneous structure indicates the hemorrhagic nature of the cyst.
More often, newborn brain cysts are of a different nature and have a different localization. Thus, periventricular and subepindeminal cysts are found in children who have had cytomegalic or herpes infection, and in children who have had meningoencephalitis, cysts of the brain parenchyma are found due to necrosis (death) of tissues affected by the inflammatory process, as well as in children who have suffered severe ischemic-hypoxic brain damage . And don't forget about the possibility of subarachnoid cysts.
In newborns who have suffered hemorrhages into the brain parenchyma during the birth period due to resorption of hematomas, porencephalic cysts also form. This type of cyst has a periventricular, subcortical localization and does not affect the choroid plexuses of the lateral ventricles of the brain.
Thus, only a thorough ultrasound screening performed by an experienced specialist and using high-quality equipment allows: - to clearly determine the presence of a choroid plexus cyst;
— determine its prognostic value;
- exclude dangerous chromosomal diseases associated with the cyst, primarily disease
Down and Edwards disease;
- exclude hydrocephalic syndrome in the fetus
— trace the dynamics of cysts as pregnancy progresses
- determine delivery tactics
— after the birth of a child, during an ultrasound scan of the brain (neurosonography), a detailed assessment of the anatomy of the brain and the characteristics of blood circulation in it.
Only this approach to the health of the fetus, in the event of detection of choroid plexus cysts in the brain, WILL ENSURE THE BIRTH OF A HEALTHY, DESIRED CHILD.
Good health to everyone! R. Shukhnin.
In the photo from my own practice:
Unchanged choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle of the brain
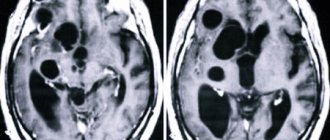
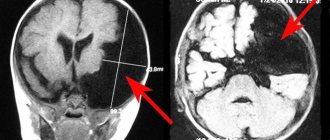
Pregnancy 16 weeks. Small cyst of the choroid plexus of the right lateral ventricle of the brain
Ultrasound screening 2nd trimester: Cysts of the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle of the brain at 18 weeks of pregnancy
Ultrasound 21 weeks pregnancy. 2 choroid plexus cysts of the left lateral ventricle of the brain
Pregnancy 28 weeks. Quite a large cyst of the choroid plexus of the left lateral ventricle of the brain
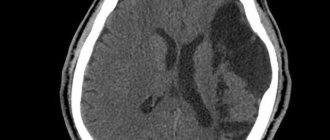
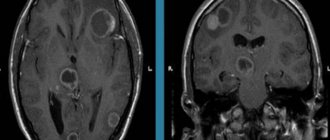
Newborn brain – choroid plexus cyst in the right lateral ventricle of the brain
Newborn brain – 3 small choroid plexus cysts in the right lateral ventricle of the brain
Newborn brain.
Subepindemal cyst of the lateral ventricle Down's disease hydrocephalus brain infections choroid plexus cysts of the brain meningoecephalitis porencephalic cyst screening Pyatigorsk subarachnoid cyst ultrasound pregnancy 4d ultrasound newborns Pyatigorsk
What are the causes of cyst formation?
Based on the time of formation, cysts are divided into two types. When detected at 20 weeks, it is the intrauterine type. In other cases, the cystic sac of the brain is fixed after birth.
In the fetus
The choroid plexus is a paired system. It originates in the ventricles. A pair of plexuses indicates the formation of the left and right hemispheres in the fetus. The vascular plexuses do not have nerve endings. Their main function is to produce cerebrospinal fluid to nourish the brain.
The part of the child’s brain is actively developing and accumulating fluid. During the formation of a cystic sac, the cerebrospinal fluid is located between the plexuses. Then it forms into bubbles. Sometimes this indicates mutation ability. Doctors rarely associate neoplasms with mental disorders. Failure of chromosome division leads to the formation of cavities with fluid.
In 90% of cases, by 28 weeks the cysts resolve on their own and do no harm. But in rare pathologies, the cystic sac remains in the head cavity. For a long time there are no symptoms. In adults, it is diagnosed only on MRI or CT scans.
In a newborn
A choroid plexus cyst in an infant develops under the influence of infectious diseases. In the plexuses of blood vessels, cystic sacs form against the background of negative situations. More often this influence on the mother’s body while carrying a child:
- Herpes virus.
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza, measles).
- Oxygen starvation of the fetus.
- Birth injuries.
- Change or disruption of blood flow.
Education will not affect the brain function of a newborn. The doctor will prescribe treatment only in rare cases of complications when the cyst develops rapidly. Then the child needs constant supervision of parents and a specialist. Signs of complications include frequent excessive regurgitation or vomiting, poor coordination of movements and increased or decreased muscle tone in the child.
In rare cases, the baby suffers from strabismus and convulsions. Symptoms worsen the baby’s life and provoke negative physical development.
Choroid plexus cysts of the fetal brain on pregnancy ultrasound
?What are isolated choroid plexus cysts and how common are they?
The CSS is a small fluid-filled structure within the choroid of the lateral ventricles of the fetal brain. The choroid plexuses are complex structures in the brain that produce fluid that nourishes the brain and spinal cord. On ultrasound, CSS appear as anechoic cysts inside the echogenic choroid plexus.
CSS can be single or multiple, unilateral or bilateral, and most often have a diameter of less than 1 cm and are detected in approximately 1–2% of fetuses in the second trimester and are equally common in male and female fetuses
?What are the main clinical consequences of isolated CSS?
?CSS is not considered a structural or functional abnormality of the brain. When a choroid plexus cyst is identified, it is necessary to evaluate the presence of structural malformations and other sonographic markers of chromosomal abnormalities. A detailed examination of the brain, spine, fetal heart (4-chamber section and main vessels) as well as fetal biometry is necessary to exclude intrauterine developmental delay. If there are no other abnormalities, then the choroid plexus cyst is considered isolated.
The only problem with CSS is the connection with trisomy 18. Trisomy 18 (Edwards's syndrome) - in 30-50% of cases is accompanied by CSS and is characterized by delayed fetal development, limb abnormalities, abnormal head shape, combined disorders of the heart, kidneys and urinary system .
?If such disorders are detected in combination with CSS, genetic counseling is necessary. Ultrasound characteristics of choroidal plexus cysts (size, complexity, laterality and persistence) do not have a significant impact on the likelihood of trisomy 18. ?How should a woman with an isolated CSS cyst be monitored for throughout your pregnancy?
?More than 90% of choroidal plexus cysts resolve, most often by 28 weeks. Studies evaluating neurodevelopmental outcomes in children born after a prenatal diagnosis of CSS have shown no abnormalities in neurocognitive ability, motor function, or behavior.
?At the patient's appointment for an ultrasound scan of the fetus at 18-19 weeks of pregnancy. The study revealed cystic structures in the projection of the choroid plexuses; no other sonographic markers of aneuploidy or structural malformations were identified.
Types of vascular cysts
Perinatology divides cystic formations into three types. They are divided according to the process of formation and location in the head. There are pseudocysts on the left, right and bilateral. Depending on the type, treatment and further actions are adjusted.
Vascular cyst of an infant
Localization left and right
Pathology is determined before birth. Unilateral formation does not affect the nervous system. In 5% of cases, active accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid is observed. In infants they appear due to trauma and oxygen deprivation.
Bilateral pseudocysts
They have a complex development mechanism. They require careful monitoring by the doctor and parents of the child in the womb and after birth. There are three types of pseudocysts: choroidal, subependymal and arachnoid.
Choroidal cyst
This is a neoplasm of the choroid plexus of the 3-4 ventricles. The reasons for its appearance are ARVI or flu during pregnancy, hypoxia during childbirth. As education increases, the child experiences frequent and severe headaches, and there is a risk of seizures and twitching of the limbs.
Diagnosis is carried out using an ultrasound machine through the large fontanel. Treatment is most often surgical with the use of medications. This view needs to be removed. The probability of spontaneous resorption is only 45%.
Subependymal cyst
Pathology develops under the lining of the brain cavity. A possible cause is damaged walls of small vessels. They are injured when the child passes through the birth canal. 2-3 capillaries are damaged, and blood flows under the membrane.
The blood is replaced by cerebrospinal fluid, as a result of which a cystic sac appears in the vessels. With normal physical development of the child, it subsides and resolves. This takes approximately a year. A subependymal cyst in a child does not require monitoring or treatment. Dynamics of self-healing – 98%. Neurologists do not consider it necessary to re-diagnose.
Arachnoid cyst
Localized between the soft and hard membranes of the brain. The causes may be infectious diseases, complicated pregnancy and childbirth. A cystic sac does not cause any discomfort to the child. When enlarged, it puts pressure on the meninges on both sides and causes discomfort, as it can reach 0.9 mm.
Necessary treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. In this case, a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and select the right medications. Treatment is carried out by eliminating symptoms: headache, vomiting, restless sleep and seizures. Swelling of brain tissue is also prevented and the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is normalized.
Dr. Evgeny Komarovsky reassured parents whose children were diagnosed with cerebral pseudocysts. The doctor explained that ultrasound often diagnoses pseudocysts in infants. But medicine has not yet identified the reason for the appearance of round tumors. What is clear is that by the age of one year, the blisters resolve in the vast majority of babies. The doctor calls such findings a reason for parents to worry and unnecessary intervention.
Regardless of the type of cyst, you should consult your doctor. You need to carefully understand the diagnosis. According to ICD-10, disease code D32.0 should be checked. After this, decide whether the child’s treatment will be justified.
What is the difference between a cyst and a pseudocyst?
Domestic doctors use these concepts as synonyms. In fact, there are differences, but they are morphological, related to structure and have little effect on the outcome.
Cysts and pseudocysts are cavities filled with fluid, in the brain - with cerebrospinal fluid. Inside the cyst there is a lining of epithelium, but inside the pseudocyst there is no lining. This difference can only be detected with high-precision equipment with very high resolution, which is equipped in large medical centers. When doctors mention a cyst or pseudocyst, they mean that there are cavity formations in the brain.
Thus, a cerebral pseudocyst in newborns does not require separate treatment - it is a small bubble with fluid inside. Such children should be monitored over time by a neurologist.
What is a subependymal pseudocyst?
There are several ventricles in the brain. These are cavities for the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The liquor collects in them and washes the brain. Ependyma is a thin membrane that lines the inside of the ventricles and spinal canal. The cells that form ependyma belong to neuroglia or auxiliary nerve cells that perform a supporting and trophic function for nervous tissue.
The cavity formed under the ependyma (the prefix “sub” means “under”) is a subependymal cyst.
It has long been known in which places in the brain of a newborn child cavities are most often found. A subependymal pseudocyst forms in the lateral ventricles, namely in their lateral corners, as well as in the groove separating the optic thalamus and the caudate nuclei (extrapyramidal structures). It is these formations that are called pseudocysts. Bubbles located in all other places of the brain and spinal cord are usually called cysts.
Signal to parents
Statistics say that choroid plexus cysts are formed in 1-2% of cases. Their spontaneous resorption occurs by the 24th week in 90% of cases. Their size is considered small up to 5 mm.
Geneticists classify these formations as “soft” markers of chromosome abnormalities. This means that the child may have an inherited chromosomal abnormality, but does not have to. A more careful and thorough study is needed, using genetic molecular diagnostic methods.
If other developmental abnormalities are detected, it is advisable to perform amniocentesis - puncture of amniotic fluid with subsequent study of the chromosome set. The consequences of chromosomal abnormalities are incurable hereditary diseases, and parents should be aware of this.
Diagnostics
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes mandatory tests. The first signs of the disorder are detected in the prenatal period. Early screening allows changes in the choroid plexus to be monitored through repeat diagnostics.
During the first period of a child’s life, the child is monitored through ultrasound. This procedure is mandatory. Allows you to determine whether there is damage to the ventricle. In addition, ultrasound can show a bilateral formation.
If the cyst does not shrink and causes specific symptoms, an MRI or CT scan is used. This diagnosis is carried out one year after birth. Until this point, the cyst can resolve on its own. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the neurologist registers the child to monitor his condition.
Treatment of pathology
The prognosis for cystic formation of the choroid plexus is positive. No therapy or drug intervention is required. Treatment is prescribed in cases of rapid growth of cysts. This provokes an increase in intracranial pressure, disrupts blood circulation in the brain and the transmission of nerve impulses. The neurologist determines the treatment tactics: therapy or surgery.
Drug therapy
The reason that causes the pathological growth of the cystic sac is an infectious disease. In this case, the doctor prescribes antiviral and antibacterial drugs. They are indicated for a pregnant woman to prevent the growth of tumors in the lateral ventricle of the brain. An analysis is required to confirm the infection.
When prescribing treatment for a baby with an enlarging cystic sac, the neurologist is guided by test results and ultrasound. Treatment is adjusted depending on the symptoms. For headaches, medications are prescribed to normalize blood circulation. Diuretics reduce intracranial pressure. For convulsions and twitching of the limbs, anticonvulsants are prescribed. A mild sedative is prescribed if the child is overexcited and does not sleep well.
Surgical intervention
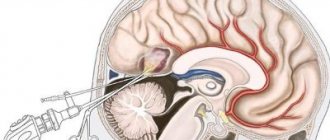
Prescribed in extreme and rare cases. Surgery prevents the risk of complications of symptoms. In the future he will maintain normal mental and physical development. Surgical intervention in this case can be of two types: bypass surgery and trepanation.
Bypass surgery is a procedure with minimal trauma. Fluid is pumped out of the cystic cavity through special tubes. There is a risk of infection, so antibiotic therapy is carried out. This eliminates the development of inflammation and damage to brain tissue. High probability of relapse.
Trepanation is an extremely dangerous method. Prescribed in case of ineffectiveness of other procedures. At a more mature age, neurological pathologies may appear.
Possible prevention of pathology
In the event of the birth of a child, the prevention of his health depends on the mother. A woman should try to avoid hypothermia and not visit crowded places where she can get an infection. Smoking, drinking alcohol and lack of physical activity pose a great danger. In this case, the fetus does not receive enough oxygen.
From the very beginning of pregnancy, it is necessary to register with a gynecologist. As prescribed by the doctor, go to specialists and take the necessary tests. If an infection occurs, you must carefully follow the instructions and recommendations of a specialist.