Description of the disease
Today, almost every fifth newborn child can be diagnosed with increased intracranial pressure. Although in most situations it does not have any tragic consequences. But it is still worth checking the head for the presence of excess fluid in the head of a newborn. And if the diagnosis is confirmed, then you should definitely think about taking all the necessary measures for treatment.
Hydrocephalus of the newborn (or dropsy in other words) is the name of a complication due to which in the area of the brain in newborns there is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, otherwise called cerebrospinal fluid. There are several variations of the disease, however, in children under two years of age, all its symptoms are very similar to each other.
The term "hydrocephalus" is derived from two Greek words that mean "water" and "head". In other words, this disease consists of excess fluid (water) in the head. This is where the second name of the pathology comes from, which sounds like dropsy of the brain. True, strictly speaking, this name is not entirely correct. The fact is that in the presence of hydrocephalus in the head of newborns, there is an excess not of water at all, but of cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid. Liquor is a liquid that is vital for the functioning of nerve tissues. It can be found in the spinal cord. We will consider the fluid levels in the head of a baby below.
In addition, it is also present in the brain. In it, a substance such as cerebrospinal fluid is concentrated in four ventricles, which are located in the center of the skull. The upper two are located in both hemispheres, and the lower ones are located along the central cerebral axis. The ventricles usually communicate with each other through a system of pipes called the cerebral aqueduct. In addition, cerebrospinal fluid can enter the subarachnoid space, which separates the meninges with special cisterns located at the base of the skull.
Hydrocele of the brain in a newborn
Dropsy of the brain, the symptoms of which are few, is characterized by an increase in the volume of the baby’s head. Due to the fact that the bones of the newborn’s skull are not fused, they begin to move apart, the head increases in size, and the skull becomes deformed. Over time, other symptoms appear:
- nausea and vomiting;
- severe headache, the child constantly cries, sleep is disturbed;
- muscle tone of the upper limbs increases;
- as a result of fluid accumulation and tissue compression, the normal functioning of the brain is disrupted;
- the child is developmentally delayed - delayed mental and motor development, lack of a step reflex.
Medical statistics show that about 70% of newborns suffer from hydrocephalus in one form or another; the hidden form of the disease is not always detected on time. The prognosis for children with hydrocephalus is favorable if the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner, adequate treatment is prescribed, or surgery is performed.
Types of disease
There are only three main forms of this pathology, in which fluid is observed in the head of a newborn:
- open hydrocephalus;
- closed, or occlusal form;
- hypersecretory form of pathology.
The closed type of the disease occurs in cases where there is a physical obstacle that interferes with the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial container intended for it into the systemic bloodstream. This type is mainly caused by cysts along with tumors or hemorrhages.
The open type of the disease is usually observed when the mechanism of absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the systemic circulation is disrupted. With this variant of the development of pathology, the cause of the disease is often previous infections. For example, meningitis or the presence of blood in the subarachnoid space.
Hypersecretory hydrocephalus is a relatively rare type of the disease in question and is observed in approximately five percent of cases. It usually occurs as a result of excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid. A similar situation can happen, for example, due to pathology of the choroid plexus.
What does “dropsy of the brain” mean in adults?
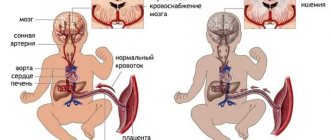
The causes of dropsy in adults are varied; it is a disease whose untimely treatment can lead to serious complications and even death. The causes of the development of cerebral hydrocephalus in adults can be various diseases, injuries, pathologies of cerebral vascular development, and tumors. As a result of brain injury or disease, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain is disrupted. The fused bones of the skull of an adult do not allow the size of the skull to change due to fluid pressure; the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain leads to compression of brain tissue and the development of severe complications.
Functions of fluid in the head
The volume of cerebrospinal fluid is, in fact, relatively small. Normally, in newborns it is, as a rule, 50 milliliters, and in adult patients - from 120 to 150 ml.
The functions of the fluid in the head of a newborn are very diverse:
- protection of nervous tissue from external mechanical influence;
- removal of harmful substances from the brain and delivery of nutrients to it;
- maintaining stable intracranial pressure values.
The fluid in the baby's head, like blood, can circulate inside the cranial cavity. Against this background, its composition is constantly updated. In adult patients, on average, this can happen three times a day, and in infants much more often - up to eight times a day. Every minute, adults produce 0.35 milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid, and approximately 500 milliliters per day. CSF pressure in adults can vary quite widely, namely from seventy to one hundred and eighty millimeters of mercury.
CSF is mainly formed in the ventricles of the brain. Two thirds of this fluid can be generated by their choroid plexus, and the rest - with the help of membrane elements and meninges. In special veins that are located inside the skull, in its occipital parietal part, namely within the venous sinuses, it is absorbed.
Consequently, if for some reason the circulation processes of the cerebrospinal fluid are disrupted, and it is formed in greater quantities than necessary, or is simply not absorbed quickly enough, then an excess of this fluid is observed in the newborn in the cranial cavity. It is this syndrome in children that is called hydrocephalus.
Excess cerebrospinal fluid can manifest itself differently in children and adults. For example, adults have hard skull bones, so excess fluid usually leads to increased intracranial pressure. The situation is completely different for young children under the age of three. They have rather soft skull bones, and therefore hydrocephalus very often manifests itself in the form of an abnormal expansion of the head circumference.
Causes of fluid in the head of a baby
Dropsy in newborns can develop from simple prematurity. And in addition, from the presence or previous infectious diseases. For example, factors such as smoking, drinking alcohol and other bad habits of the mother, not just during pregnancy, but also in everyday life, can contribute to the development of this pathology in the newborn.
During the first few years of life, any head injury is very dangerous, as it can lead to an increase in the production of cerebrospinal fluid. A tumor that occurs in the brain can significantly interfere with the healthy flow of fluid in the head of a newborn baby. Which, in turn, will create excess pressure.
How does this pathology manifest clinically?
The fluid in the head of a newborn must circulate in a correct and normal manner, and if this is disrupted, this will certainly lead to hydrocephalus. The most important symptom is a change in the shape of the head over a fairly quick period of time. In this regard, it will be necessary to visit a pediatrician every month, who must measure the head, checking the condition with the normal fluid levels in the baby’s head.
In addition, the fontanel in a newborn baby is characterized by an increased size, since the sutures of the skull are not yet fully formed. Over time, the symptoms may become more pronounced: a network of veins will appear on the face, and the shape of the forehead, in turn, will become more disproportionate. Cramps may occur from time to time. Newborns with hydrocephalus tend to be lethargic and cry frequently.
Such children are noticeably lagging behind in development, their psychomotor skills are impaired. This usually manifests itself in the fact that the child’s head is very poorly supported. In addition, such children begin to crawl, walk and sit up late. In addition, newborns with this disease often spit up and even vomit. Among other things, they experience constant drowsiness. All such symptoms may indicate that the baby has increased intracranial pressure.
However, you should not rush to make a diagnosis based on individual similar characteristic signs, since usually only the appearance of the entire complex of the listed symptoms can indicate the presence of hydrocephalus. Only the attending doctor, as part of the examination of the child, will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the required treatment for the accumulation of fluid in the head of the newborn.
Basics of diagnosis and therapy in newborns
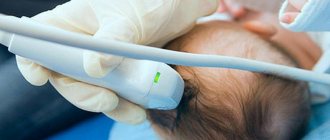
After determining the primary diagnosis, children are prescribed neurosonography along with ultrasound examination of the brain, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, ventriculoperitoneal shunting is often performed. The essence of this operation is that the cerebrospinal fluid from the cerebral ventricles of the newborn is sucked through silicone catheters into the abdominal cavity. Less commonly, fluid may be drained into the spinal canal or right atrium.
If the operation was performed on time, then the child has every chance of further normal life, which includes attending child care and school institutions. However, it is also necessary to take into account that the size of the head after surgery most likely will not decrease, since changes in bone tissue are always irreversible.
How to identify fluid in a baby's head?
Diagnosis of the disease
There are several ways to determine the development of hydrocephalus. It is worth noting that this disease is much easier to identify in children. But in adult patients, recognition of the described disease is sometimes difficult and problematic. Previously, many adults who suffered from hydrocephalus were diagnosed with various neurological and mental disorders. However, of course, their therapy was not very effective. Only after the advent of modern diagnostic techniques the situation changed radically. And for the better.
If there is a lot of fluid in the baby's head, this is mainly detected by the pediatrician during a thorough examination of the child. Doctors can turn their attention to obvious manifestations of hydrocephalus in the form of an enlarged head, bulging fontanel, divergence of the sutures of the skull, and in addition, changes in the appearance of the skin and characteristic neurological symptoms. To facilitate the diagnostic procedure, parents are recommended to record the baby’s head circumference values at a certain time interval. If a pathology is suspected, the pediatrician can write a referral to a neurologist, pediatric surgeon or neurosurgeon.
Treatment
Recently, great progress has been made in medicine in the treatment of hydrocephalus and the presence of fluid in the head of an infant. If just a few decades ago more than half of patients with this disease died, today the mortality rate is no more than five percent.
The choice of treatment method for hydrocephalus directly depends on the etiology of the pathology, and in addition, on its form and degree of development. In some situations, etiotropic therapy is possible. However, in most cases, treatment is aimed at removing fluid from the cranial cavity. Treatment of the progressive course of hydrocephalus in children can be carried out only by surgical methods. Unfortunately, conservative therapy is ineffective.
How to remove fluid from a baby's head? The operations that are performed for closed and open forms of hydrocephalus may differ slightly. Previously, open dropsy of the brain was considered an almost incurable pathology. But in the middle of the last century, new technologies were developed that make it possible to save the majority of young patients.
To remove excess fluid from the cranial cavity, shunting is usually performed. It consists of laying a kind of pipeline through which liquor is pumped to the rest of the body cavities. Such tubes are located under the skin surface for most of their length. Typically, the fluid is drained to the peritoneum (in ninety-five percent of cases), the chest area, or the atrium. In some situations, it has to be diverted not from the brain, but from the spinal cord, from where it is sent to the abdominal cavity.
When such an operation is performed on a child, as the baby matures and grows, the catheters will require lengthening and replacement. It is worth noting that modern catheters are equipped with special valves that allow you to regulate the fluid pressure in the brain vessels. If there is no threat to life, bypass surgery is performed as planned. As a temporary measure to reduce the pressure of brain fluid, a puncture in the spinal region is used.
Closed hydrocephalus often requires rapid surgical intervention, since in this form of the disease compression of the respiratory centers can occur. Therefore, in such a situation, a temporary operation can be performed with the installation of a special container to drain the cerebrospinal fluid.
If the patient has closed hydrocephalus, all the surgeon’s efforts are aimed at eliminating obstacles that interfere with the normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. In some cases, such an obstacle (in the form of a vascular aneurysm, cyst, hematoma, tumor) can be eliminated. Often, an endoscopic system inserted into the ventricular cavity is used for this purpose. The surgical operation is carried out using special instruments, a laser or an electrode, which allows the functions of the brain pipelines to be restored.
However, sometimes, for example, with tumors, regardless of their benignity or malignancy, such operations are simply impossible. In this case, the surgeon lays a pipeline from the container within which the cerebrospinal fluid accumulates into an alternative container, where it becomes possible to absorb it directly into the blood.
In absolutely all cases, the main goal of the operation is to restore the balance of cerebrospinal fluid output and generation that has been disturbed for various reasons. Of course, when the disease is secondary, then the main efforts must be directed to the treatment of the underlying disease, which caused an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment of hydrocephalus in children
Regardless of the child’s age, hydrocephalus at any stage of its development requires medical attention. Treatment of hydrocephalus in children and further tactics of patient management will depend on the severity of the patient’s condition, concomitant pathology and stage of the disease.
A group of diuretics - for the purpose of removing excess fluid through the renal barrier. Of the most commonly used, it is o, which helps slow down the production of cerebrospinal fluid by tissues. However, this drug actively removes potassium from the child’s body, so it is additionally necessary to prescribe Panangin or Asparkam, which contain this trace element.
Nootropics - to improve metabolic processes in brain tissue if there is developmental delay. The drug "Cogitum" is recognized as the most effective.
Only the attending physician has the right to prescribe a specific drug, taking into account the morphofunctional characteristics of the patient, the severity of his condition and the presence of possible adverse or allergic reactions to any of its components.
Conservative management of the patient is possible for no more than 4-5 months. If treatment does not give the desired effect, the patient’s general condition progressively worsens (decompensation), and according to instrumental studies there is a deterioration in the clinical picture of the disease, then it is necessary to lean in favor of surgical tactics.
The most effective and low-traumatic methods are:
- Installation of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt involves removing excess cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain into the abdominal cavity using a catheter.
- Ventriculostomy is the introduction of a device into the intrathecal space through incisions in the skin to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid. This type of invasive intervention is indicated for newborns, since the risks of complications in this situation are minimal.
- Surgical interventions aimed at restoring the natural outflow pathways of cerebrospinal fluid - removal of brain tumors, hematomas, etc.
- Surgical interventions aimed at reducing the production of cerebrospinal fluid - coagulation of the choroid plexus.
After surgical treatment, the child must be under strict dynamic supervision of the attending physician in a specialized hospital.
Complications of hydrocephalus
In the absence of treatment for the presence of fluid in the head of an infant, the disease in question can progress in most situations. This can lead to extremely negative consequences, which can also threaten the patient with death. The main complications of hydrocephalus are usually:
- the appearance of cerebral edema;
- the occurrence of epileptic seizures;
- displacement of the child's brain;
- development of coma, stroke and respiratory failure.
Not everyone knows why excess fluid in a baby’s head is dangerous. With the development of hydrocephalus in children during infancy, a slowdown and stop in the formation of new brain tissue are often observed. And this leads to a lag in the mental, mental and emotional development of the baby.
Hydrocele in a newborn: causes
The most common cause of hydrocele in children is a woman contracting an infection during pregnancy. Hydrocephalus develops for various reasons, which depend on the age of the baby:
- intrauterine hydrocephalus. This pathology is detected during diagnosis on ultrasound. Fetal hydrocephalus can be caused by various infections that the mother has: herpes virus, toxoplasmosis, cytomegaly. Most often, fetal hydrocephalus develops due to malformations of the central nervous system. It is extremely rare that the disease is associated with genetic disorders;
- hydrocele of the brain in a newborn. More than 70% of newborns suffer from hydrocephalus due to infectious infection of the mother or malformations of the brain and spinal cord. In 20% of children (mostly premature) the disease is a consequence of birth trauma, which was accompanied by intracerebral, intraventricular hemorrhage or the addition of an infectious brain disease. Brain tumors and malformations of cerebral vessels, which cause hydrocephalus, are very rare in newborns;
- the development of hydrocephalus in children over one year of age can be caused by inflammatory processes in the brain, infections, malformations of the brain and its vascular system, traumatic brain injury, genetic disorders, and cerebral hemorrhage.
Pathology prognosis
The prognosis for the development of hydrocephalus in a newborn directly depends on how quickly and, moreover, how timely the baby is diagnosed and therapy is started. Children with hydrocephalus can live a normal life, although, unfortunately, they face a number of problems associated with the maintenance of surgical shunts.
But if treatment for this disease in an infant is not started in a timely manner, its further progression threatens the baby with serious developmental delays, as well as speech impairment and irreversible changes in the brain, which will subsequently lead to disability.
Hydrocele of the brain in a newborn: consequences
If a child is diagnosed with hydrocephalus, he should be referred for consultation to a neurosurgeon. The consequences of cerebral hydrocele in a newborn are deformation of the skull, developmental delay, which cannot be compensated for later without taking timely measures. A consultation with a neurosurgeon will help you make a decision about surgical treatment of hydrocephalus. With the help of surgery, fluid is drained from the ventricles of the brain into other cavities of the body - the abdominal cavity, the right atrium, and the cistern magna.
An effective endoscopic operation (ventriculostomy) is also performed without installing a shunt system. The decision to perform such an operation is made by the doctor, since it is possible only in a small percentage of patients with certain forms of occlusive hydrocephalus.
The consequences of hydrocephalus in a newborn with age appear as:
- speech disorders;
- visual impairment, blindness;
- delayed physical development;
- mental retardation;
- severe headaches;
- epilepsy.
At the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, an examination is carried out that reveals dropsy of the brain, and doctors determine the stage of the disease. Depending on the results of the examination, the neurologist prescribes surgical or drug therapy. Highly qualified doctors treat patients with hydrocephalus. You can make an appointment by phone.
Advice from pediatricians
Hydrocephalus, or the accumulation of fluid in the head of a baby, is very often a congenital pathology. But is it possible to prevent such a condition long before its possible progression? In this regard, pediatricians advise, for the purpose of prevention, to examine both parents at once, and it is necessary to conduct research at the genetic level. Among other things, doctors recommend timely treatment of existing infectious pathologies and protect the mother’s body from their development throughout pregnancy.
In addition, in no case should you allow traumatic brain injury to a newborn during childbirth. It is necessary to carry out timely diagnosis and treatment of such pathological abnormalities as hydrocephalus. And it is best, according to pediatricians, for all parents to lead an exceptionally healthy lifestyle, and not just before planning a pregnancy.
The causes of fluid in the head of newborns are discussed. Thus, today every fifth newborn baby in the maternity hospital is diagnosed with increased intracranial pressure. But it is immediately necessary to reassure parents, since in ninety-nine percent of cases this diagnosis is made unreasonably and is put forward contrary to analyzes and research. But nevertheless, it is simply necessary to check suspicions of hydrocephalus. The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain cavity of a newborn must be treated.
The article described in detail the causes of fluid in the head of a baby. Get tested on time and stay healthy!
Treatment of the disease
Dropsy in the head in infants and newborns is treated in two ways: drug therapy or surgery. The use of drugs is aimed at maintaining the body and preventing the increase in head fluid. It is not possible to cure a child in this way.
If the identified cause of the pathology cannot be cured with conservative methods, a shunt is inserted into the brain or a hole is made in the ventricle. In any case, the liquid will be able to escape and will not accumulate. However, bypass surgery is performed every 2-3 years, and endoscopy will eliminate the problem for life.
Medication
To slow down the development of dropsy, reduce symptoms and improve the general condition of the child in the first stages of the disease, you can take medications.
Depending on the testimony of the specialists examining the child, a course of use of the following drugs is determined:
Diuretics, which help remove excess fluid.
Drugs to improve intracranial circulation.
Medicines with magnesium and calcium.
Nootropics.
This treatment will prepare the weakened body of the newborn for surgery and prevent serious disorders. Only a doctor can prescribe medications, because the age and condition of the baby must be taken into account. The patient's condition must be constantly monitored so that if complications threaten to develop, surgery can be performed.
Surgery
Removal of fluid from the brain is done through shunting or endoscopic surgery. Liquor from the ventricles or subcranial space is artificially removed to another place in the body that is free for fluid.
Types of operation:
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion. Silicone shunts move fluid from the brain into the peritoneal cavity.
Lumboperitoneal method. The excretory canal connects to the channels of the abdominal cavity.
Ventriculoarthrial method. The cerebrospinal fluid is transferred to the right atrium.
Operation according to Torkildsen. Transportation of cerebrospinal fluid into the cerebellomedullary cistern.
Ventriculostomy using an endoscope. Physiological restoration of blood flow using an artificially made hole in the ventricles.
Treatment of the disease with surgery allows the child to develop normally
However, it is important to notice the symptoms of the disease in time. Otherwise, the child will become incapacitated or die from intracranial pressure
Traditional methods
Treatment with traditional recipes will not lead to the baby’s recovery. However, it can relieve the symptoms of the disease without affecting the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Alternative medicine is not suitable for newborns, as there is a risk of developing allergies and digestive disorders.
For dropsy, it is recommended to drink freshly squeezed black radish juice, raw onion and pumpkin juice, a decoction of elderberry, clover or parsley. It is useful to eat more grapes and drink teas with lemon balm. These recipes help remove excess fluid from the child’s body, some have sedative properties.