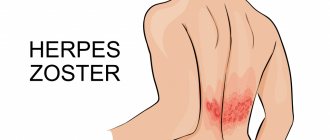
The causative agent of chickenpox belongs to the ubiquitous but small family of herpes viruses. All members of the family cause skin lesions in herpes simplex and genital, cytomegalovirus infection and herpes zoster. All of them, and chicken pox is no exception, begin penetration from the mucous membranes, and then hide in the nervous tissue for the rest of a person’s life, coming to the surface in the form of herpetic eruptions.
Our expert in this field:
Nagibina Margarita Vasilievna
Infectious disease doctor, doctor of medical sciences, professor
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
How and why does chickenpox get infected?
The source of the disease is a sick person during the period of rash formation. It is not necessary to meet the patient himself; it is enough to get a drop of saliva with a live virus floating in the air when coughing or talking.
The cause of the disease is the entry of the chickenpox virus into the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, where it immediately penetrates into the epithelial cell, multiplies and travels through the bloodstream to the lymph nodes, and then throughout the body.
Some signs of developing complications or severe disease
Any deterioration in the condition of a patient with chickenpox may indicate a severe course or the development of complications and requires prompt medical attention. What to pay attention to:
- An increase in the size of the blisters, their blueness, blood in the blisters, the appearance of new rashes 10 days after the appearance of the first signs of the disease;
- Body temperature above 37 degrees for more than one week, or a constant increase in temperature;
- Spread of rashes to mucous membranes: eyes, mouth, or genitals, because similar changes may occur in internal organs;
- The appearance of a cough or runny nose;
- The appearance of diarrhea and frequent vomiting.[3]
How to detect chickenpox virus?
Most people experience chickenpox in kindergarten; susceptibility to the infectious agent is almost 96%, so chickenpox in adults is very rare, and its course is mostly atypical. The symptoms are either too pronounced or almost not expressed, but not the classic version.
The infection is often mistaken for an allergic reaction; when no blisters appear, the process stops at the speckled stage. Often the symptoms of severe intoxication come to the fore, while the rash is barely noticeable. The general reaction is aggravated by concomitant chronic diseases and age-related decrease in immunity.
Infectious diseases specialists at the international clinic Medica24 will diagnose the pathology and help you cope with symptoms that worsen your quality of life.
The time from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease takes 10–21 days, but more often it takes 2 weeks.
The disease begins acutely, and the onset—the prodromal period—takes about two days. There are no characteristic symptoms at the onset of chickenpox, just intoxication. But in every third adult, the disease begins with severe symptoms: fever, headache, nausea, abdominal and lower back pain.
In some cases, the first symptoms of chickenpox may be catarrhal symptoms: sore throat, runny nose and dry cough.
Varicella (chickenpox) - symptoms and treatment
How long does chicken pox (chickenpox) last?
The incubation period lasts from 10 to 21 days. In typical cases (in children and adolescents), the disease begins acutely. On average, chickenpox lasts 7-10 days.
Symptoms of chickenpox in adults and children
Chickenpox in adults, due to the loss of lability of the immune system, manifests itself with a subacute and gradual onset (i.e., the main syndrome appears 2-3 or later days from the onset of the disease). Children, as a rule, tolerate the disease more easily.
Symptoms of chickenpox in children and adults:
- general infectious intoxication (SOII);
- vesicular exanthema;
- vesicular enanthema (aphthae);
- lymphadenopathy (LAP);
- persistent fever.
In typical cases, the height of the disease is preceded by a prodromal period lasting up to one day, mild, accompanied by slight weakness, low-grade fever, and rarely a small-spotted rash rash.
By the end of the first day, the height of the disease begins. The first symptoms of chickenpox include increasing intoxication, distinct weakness, and body temperature up to 38-39 ℃. During this period, the most characteristic sign that allows a correct diagnosis to be made is the appearance of a characteristic macular-vesicular rash. The first elements are localized on the scalp and behind the ears, then the rash spreads to the torso and limbs. It is typical that the face is affected later than other parts of the body. Elements of the rash appear in series with an interval of 12-48 hours, each new rash is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, new elements appear between the old ones and their number increases, which causes pronounced polymorphism of the rashes. As soon as the body temperature returns to normal, within 2-3 days we can talk about the healing process and the end of the period of rash.
The dynamics of the rash are very characteristic: first, a rounded reddish spot 5-10 mm in size appears, then a papule forms in the center, then a vesicle (bubble) with transparent contents up to 10 mm (single-chamber and collapsing upon puncture). Further, when secondary flora attaches, it may suppurate, after which it may dry out and form crusts, which fall off after 6-8 days, usually without subsequent defects. In rare cases (severe suppuration, scratching), scars may form.
Simultaneously with rashes on the skin, tender vesicles form on the oral mucosa, which, quickly opening, form aphthae (erosions) and can cause a feeling of discomfort and burning in the mouth.
Chicken pox in newborns
Infants rarely get chickenpox, since most of them are protected by maternal antibodies. If antibodies against the virus are passed on to the child from the mother, then the disease may be erased in a mild form. If there are no protective maternal antibodies, then chickenpox progresses rapidly: symptoms of intoxication are pronounced, convulsions are possible, consciousness is impaired, and complications arise from the internal organs and nervous system.
Chicken pox in pregnant women
Due to the wide spread of the disease, mainly in childhood and adolescence, by the time of pregnancy, women are in most cases immune to the chickenpox virus (i.e., if chickenpox was suffered before pregnancy, there is no risk of recurrence of the disease and no threat to the child; accordingly, there are no risks with contact of a pregnant woman with a patient with chickenpox or herpes zoster). In rare cases, when a pregnant woman does not have a titer of protective antibodies and comes into contact with a sick person, different outcomes are possible, depending on the stage of pregnancy. Acute chickenpox poses a significant danger to the pregnant woman herself (which is often forgotten by both the woman herself and the doctor who diagnosed the disease).
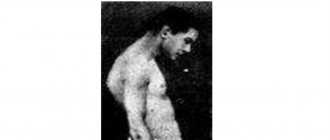
The most characteristic symptom of chickenpox
This is a rash that appears on non-inflamed skin. First, a rapidly growing spot appears, its middle gradually rises, and a bubble grows in it, like a drop of dew. The liquid in it soon becomes cloudy, and already on the 3rd day a crust forms. Bubbles of different sizes, from a point to a centimeter. The bubble will not necessarily grow; it may remain in the speck stage.
New bubbles appear in several stages, no more than four such waves with a break of a day or two, and for about a week they regularly “sprinkle” with new ones. The entire period of the rash takes no more than 3 weeks, during the third week crusts mainly form. There are no scars left.
Where can chickenpox rash appear?
First on the torso and limbs, but not on the palms and feet, and then on the face and head. It also happens in the mouth, causing pain when chewing and salivation; the blisters easily open, forming erosions that heal in 3 days. Blisters also appear on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Papules also grow in the eye and are tolerated quite easily; the vesicle quickly opens, forming an ulcer that goes away without a trace in a couple of days.
At the international clinic Medica24, examinations are carried out using high-precision equipment, which allows you to quickly make the correct diagnosis and begin treatment without delay.
Chickenpox symptoms
The disease has an incubation period of one to three weeks ; a child becomes contagious 2 days before the rash appears and remains contagious for about a week. Usually in children it starts with a rash, and other symptoms come later. The virus enters through the conjunctiva and respiratory tract. It multiplies in the mucous membrane of the pharynx and regional lymph nodes.
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- headache;
- elevated temperature (not in all cases);
- characteristic rash and severe itching. Source: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/varicella.pdf Chickenpox vaccine. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Vaccine information statement. Accessed September 14, 2017./span>
- The rash appears as fluid-filled blisters that burst easily, becoming ulcers. As it heals, it becomes crusty. Usually there are no traces left of it, but if the blisters are combed, scars remain. In very rare cases, the disease goes away without rash.
The onset of the disease is acute. Children develop an itchy rash, body aches, loss of appetite, headaches and disturbed sleep. Fever may persist for 2 to 7 days.
The first rash appears on the torso and face, then spreads to the limbs and scalp. Within 4-6 days, “spilling” still occurs. The lesions are usually 1-4 mm in diameter. The surface bubbles contain a clear liquid, and they themselves are surrounded by a red border. In every 5th patient, a rash may appear on the gums and mucous membranes of the mouth. In this case, the blisters quickly open and painful erosions appear. A rash appears on the conjunctiva in 2-5% of cases. Usually the cervical, submandibular, inguinal or axillary lymph nodes are enlarged. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5381807/ Varicella zoster virus infection Anne A. Gershon, Judith Breuer, Jeffrey I. Cohen, Randall J. Cohrs, Michael D. Gershon, Don Gilden, Charles Grose, Sophie Hambleton, Peter G. E. Kennedy, Michael N. Oxman, Jane F. Seward, and Koichi Yamanishi Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015 Jul 2; 1: 15016.
What other symptoms occur with chickenpox?
When a rash forms, the temperature rises, the rash comes in waves and the fever also comes in waves, but the temperature rarely lasts more than 5 days. With an extremely profuse rash, high fever and drowsiness, convulsions and loss of consciousness are possible. The rash, of course, itches a lot.
In almost half of the cases, the lymph nodes on the neck and submandibular areas are enlarged, which almost never occurs in children. The well-being of adults suffers more significantly than that of children, and the severity of clinical manifestations is more intense.
Pathogen information
The causative agent of chickenpox is Varicella zoster virus (VZV). This is a type III herpes virus that persists in the body after the initial infection. That is, “Varicella zoster virus” leads to “chickenpox”, and herpes zoster is the result of decreased immunity, the presence of concomitant diseases with immunodeficiency. The virus is unstable in the external environment; it is very sensitive to disinfectants, high temperatures, and ultraviolet radiation. Reproduction occurs in the affected cells of the body. Source: E.N. Sergienko Modern view of chickenpox in children // Medical news. — 2021. — No. 2. — P. 4-8.
Sources of chickenpox are patients with any form of this disease and with herpes zoster. The route of transmission is airborne . The virus is very volatile - you can become infected even if you are 20 meters away from the patient. Newborn babies have innate immunity from their mother, so chickenpox almost never occurs until six months of age. The main incidence occurs in children aged 0.5-7 years.
How does the infection usually progress?
Mild course with a few rashes, normal temperature or briefly rising to 38°C, blisters disappear within 3 days.
During a moderate infection with a temperature of up to 39°C, abundant skin formations disappear within 5 days.
Severe chickenpox is observed in patients weakened by chronic diseases; a fresh rash lasts for almost a week; the condition is severe with severe symptoms of intoxication.
If your condition worsens, you must immediately contact an infectious disease specialist, who is available seven days a week and on holidays at the international clinic Medica24. Registration is carried out 24 hours a day by telephone. Early initiation of special therapy will avoid irreparable consequences.
Chance of getting sick
The contagiousness of the chickenpox virus is truly unique - it is 100%. All age groups are susceptible to chickenpox. However, this infection most often affects children. About half of the diseases in childhood occur between the ages of 5 and 9 years; children aged 1–4 and 10–14 years are less likely to get sick. About 10% of the cases are people 14 years of age and older. Among this age group, over the past 5 years, the incidence of chickenpox has increased from 28 to 58 per 100 thousand population. Children in the first months of life are most often resistant to this infection. However, babies born prematurely and weakened by other diseases can become seriously ill with chickenpox.
The maximum incidence of chickenpox is observed in the autumn-winter months. Epidemic outbreaks are observed mainly in organized groups among preschool children. Children attending kindergartens and nurseries get chickenpox 7 times more often than unorganized children.
The risk group also includes patients with immunodeficiencies, including HIV infection. Severe cases of chickenpox have been described in children receiving hormonal therapy with steroid drugs. Cases of congenital chickenpox have also been described in children whose mothers had chickenpox in the first half of pregnancy; perinatal infection occurs in children whose mothers became ill 5 days before and 48 hours after the birth of the child.
In persons with severe immunodeficiency of various etiologies (in rare cases with HIV infection and in patients after organ transplantation; often with acclimatization, decreased immunity caused by severe stress), the disease may recur.
How else can the infection proceed?
Atypical forms are more common in adults. Thus, when treating an adult who has been in contact with a patient with immunoglobulin, which is practiced when there is an absolute probability of developing the disease, the symptoms of chickenpox are almost not expressed and this option is called erased.
In patients with severe chronic processes, tumors or after a transplant, on the contrary, severe forms develop like gangrene of the vesicles, with huge blisters - bullous, hemorrhagic with hemorrhages in the vesicles - in blood diseases. The generalized form is very difficult, when a rash forms even in the internal organs.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Treatment
Treatment of chickenpox mainly involves preventing bacterial complications. To prevent the spread of the virus, careful hygiene must be observed, including showering daily and trimming young children's nails (to prevent scratching and breaking up the rash blisters).
The use of antiviral agents during treatment, such as acyclovir, is only justified for premature infants, patients with compromised immune systems and adults (due to the greater severity of the infection). The traditional means of “treating” chickenpox – “brilliant” – is not any effective remedy; baths and trays with a small addition of soda, antihistamines and pain-relieving ointments to relieve itching are much more effective.
When is a patient considered cured?
Not until he feels himself recovering, but according to medical criteria:
- The patient should not have a skin rash and the mucous membranes should also be clean.
- There are no signs of intoxication.
- The temperature should be normal for at least three days.
- Blood test without abnormalities.
Most suffer from chickenpox in childhood; in adults, the infection is much more severe than in children, who feel well and are active even during the heyday of the disease.
The international clinic Medica24 uses the most effective domestic and foreign therapy methods, which can significantly improve the quality of life of our patients and maintain their activity. Get help from a specialist from our medical center by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01
The cause of the development of chickenpox is a virus from a small family of herpes viruses, it is designated as type 3. On the one hand, it is very gentle and cannot withstand not only ultraviolet radiation, but also just sunlight.
There is no need to treat surfaces in the patient’s room with antiseptics, because the virus getting on them leads to his death, but in the cold it persists for quite a long time and is easily restored after freezing. At the same time, the viral particle is very volatile and flies from person to person on particles of saliva.
Who is resistant to viral infection?
Chickenpox is a surprisingly sticky infection, which is why most people experience it during childhood. For some time, the newborn remains protected from the mother who had chickenpox a long time ago; the reason for this resistance is the antiviral antibodies inherited by the baby that circulated in the bloodstream of the pregnant woman. Once the antibodies are destroyed, the child becomes defenseless.
Immunity after illness is characterized as stable, almost lifelong, however, in the rarest cases, re-illness is possible. The fact is that the viral particle settles in the nerve ganglia, and even after a few years it can cause shingles or even recurrent chickenpox, and the antibodies circulating in the blood do not cause trouble for the suddenly activated herpesvirus type 3.
Only a qualified infectious disease doctor is able to quickly make a differential diagnosis and identify the cause of the pathological condition. Sometimes it is necessary to resort to modern diagnostic methods. All this is possible at the international clinic Medica24.
General information
Varicella (chickenpox) is an acute, highly contagious viral disease common throughout the world. Once one case occurs among susceptible individuals, it is very difficult to prevent an outbreak. While chickenpox is a relatively mild illness in childhood, it can become more serious in adults. It can be fatal, especially in newborns and those with weakened immune systems.
The causative agent, varicella zoster virus (VZV), is transmitted through respiratory droplets or direct contact, and patients are usually contagious for several days before the onset of the rash until the rash crusts over. Transmission of infection through third parties and household items is impossible.
VZV is a double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpes virus family. Only one serotype is known, and humans are its only reservoir.
The varicella zoster virus VZV enters the human body through the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and almost without exception causes clinical manifestations of the disease in susceptible individuals. After infection, the virus remains latent in the nerve ganglia and, as a result of VZV activation, can cause herpes zoster (herpes zoster), a disease mainly affecting the elderly and those with weakened immune systems.
Cause of infection: how is the disease transmitted from person to person?
It is unlikely that chickenpox can be caused by contact transmission - through touching a patient. But the viral particle is perfectly transmitted by airborne droplets using an aerosol, which is formed in the air from tiny droplets of saliva when a sick person coughs and talks.
Living infectious agents float in the smallest droplets of saliva; it is believed that the infection spreads through the ventilation system in the same way, because all it takes is one sick person in an apartment building, and all the residents who do not have immunity will get sick.
If a disease occurs, you must immediately contact a specialist who receives patients without weekends or holidays at the international clinic Medica24. Early initiation of therapy will avoid irreparable consequences.
Historical information and interesting facts
Chickenpox was first described in the mid-16th century in Italy by doctors Vidus-Vidius and Ingranus. For a long time, chickenpox was not recognized as an independent disease and was considered a type of smallpox. After the causative agent of chickenpox was discovered in the contents of chickenpox vesicles in 1911, the disease began to be considered a separate nosological form. The virus itself was isolated only in 1958. The chickenpox virus infects only humans, and the only reservoir of infection is also humans.
Why do spots and blisters form on the skin?
The main manifestation of chickenpox is a characteristic skin lesion. The chickenpox agent has a tropism for the skin; first of all, it rushes there, penetrates into cells and multiplies. While the particle is in the cell, the body reacts to the disorder by forming an inflammatory wave: nearby vessels expand, through which immune cells are actively arriving, filled with biologically active substances that dissolve all foreign substances. In general, inflammatory edema develops.
The breeding enemy agent and immune defenders together cause cell death. In place of the dead cell, a cavity is formed, which is filled with the surrounding inflammatory fluid, exfoliating the surface layer of the skin. This is how a bubble is formed from the speck.
When is a patient infectious to others?
The period from the penetration of the infectious agent to the development of symptoms of the disease with chicken pox lasts no more than 3 weeks. But already in the last few days of incubation, viruses multiply in the body of an infected person and are released into the surrounding space. At this time, a person does not yet know about his illness, but he is already capable of causing infection to other people a day before the rash appears.
For the entire time that new skin manifestations of chickenpox appear, a person is a source of infection. When new bubbles no longer appear, but crusts still remain, the person is no longer dangerous and can easily come into contact with people. On average, the entire period of formation and maturation of blisters lasts about a week, but in adults weakened by concomitant diseases, the infection can be atypical, long and difficult.
Specialists at the international clinic Medica24 always take into account not only the individual characteristics of the disease, but the capabilities and interests of each patient, so that the treatment is as comfortable as possible and actually improves the quality of life. If you are not healthy, have accidentally come into contact with a source of infection, or have an infectious patient in your family, call
Chickenpox is transmitted by the unusually volatile herpes virus type 3. In the medical literature, a high probability of transmission of infection is designated as virulence of 96%, but in life it looks like this: if a patient with chickenpox appears at the entrance of a house, then everyone who has not had it before will get sick.
Do you always need to get tested for chickenpox?
Diagnosis is simple, and tests are often not required to identify the causative agent of the infection. Chicken pox has very characteristic clinical manifestations, so diagnosis is carried out by an infectious disease doctor based on symptoms.
The high degree of transmission also speaks in favor of the infection; in most cases, it is possible to trace where the infection came from. Diagnosis of the pathogen may be required in the atypical course of the disease, when the manifestations are either less or more pronounced and do not resemble chickenpox.
Chickenpox vaccination
Vaccination is the best method of prevention. Children over 2 years of age are vaccinated once. It is shown:
- if the child has diseases that suppress the immune system;
- when taking immunosuppressants;
- before organ transplantation and radiation therapy;
- and etc.
Severe immunodeficiency is a contraindication.
The vaccine protects for life. Some components of the vaccine sometimes cause chickenpox, which is easily tolerated and does not cause complications.
Medical pediatricians strongly recommend vaccinating a child if he has not yet had chickenpox. For advice, you can contact the phone number listed on the website.
If the child is not vaccinated, then at the first symptoms it is recommended to consult a medical doctor, who will give recommendations on the correct treatment of the rash in order to prevent complications.
Sources:
- 1. E.N. Sergienko. Modern view of chickenpox in children // Medical news. — 2021. — No. 2. — P. 4-8.
- https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/varicella.pdfChickenpox vaccine. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Vaccine information statement. Accessed September 14, 2021.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5381807/ Varicella zoster virus infection. Anne A. Gershon, Judith Breuer, Jeffrey I. Cohen, Randall J. Cohrs, Michael D. Gershon, Don Gilden, Charles Grose, Sophie Hambleton, Peter G. E. Kennedy, Michael N. Oxman, Jane F. Seward, and Koichi Yamanishi Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015 Jul 2; 1: 15016.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
What diagnostic methods can a doctor prescribe for chickenpox?
With any infectious process, changes are noted in the general blood test, and with chickenpox too, but there are no manifestations specific only to this disease. In most cases, there is an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate - ESR.
To identify the pathogen, they take the contents of a vesicle or a scraping print from the erosion; after special silvering, microscopy determines clusters of viruses or giant cells with many nuclei. In the atypical form, manifested by catarrhal changes in the throat, these reactions are also performed.
Using test systems, molecular biological methods are used to detect antibodies to the virus in the blood, this is called a serological test. As a rule, diagnosis is performed in severe cases, however, the severity of the changes does not correlate with the severity of the disease.
The infectious disease specialist at the international clinic Medica24, having a broad clinical horizon, has at his disposal the most modern diagnostic methods and equipment with the ability to perform complex tests, which affects a favorable prognosis for the patient.
What diseases can the manifestations of chickenpox be similar to?
Differential diagnosis of chickenpox is carried out with other processes in which skin changes also occur in combination with symptoms of intoxication. First of all, with ARVI and herpetic infections: generalized herpes and cytomegalovirus infection.
They are looking for differences from pustular skin lesions - streptoderma and a dangerous infection of animals - foot and mouth disease, and other infections.
Only a qualified specialist with extensive diagnostic capabilities can quickly make a differential diagnosis and identify the cause of the pathological condition, and all this is possible in the infectious diseases center of the International Clinic Medica24.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
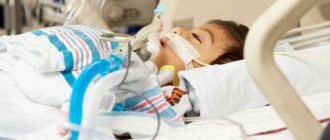
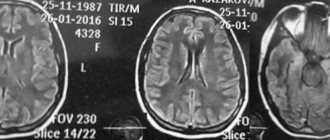
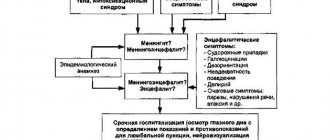
Treatment methods for encephalitis
Encephalitis is a serious and dangerous disease that requires timely and adequate treatment. Children with this disease must be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department or intensive care unit (depending on the severity of the disease). If necessary, the child is transferred to mechanical ventilation (artificial ventilation) and oxygen therapy is performed.
drug therapy individually for each patient, based on the causes and severity of the disease. The essence of drug treatment for encephalitis is to prescribe diuretics and glucocorticosteroids to reduce cerebral edema, drugs to correct water and electrolyte balance, antibacterial or antiviral drugs, depending on the etiological factor. In addition, symptomatic therapy is also important: anticonvulsants, antihistamines, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), blood pressure correction agents, etc. Etiotropic therapy consists of prescribing antiviral drugs (for example, for herpetic or cytomegalovirus encephalitis), as well as immunoglobulins.
After overcoming a life-threatening period, additional treatment methods : physiotherapy, massage. Drug correction of such consequences of encephalitis as parkinsonism, hyperkinesis or epileptic seizures is also carried out.
If someone in the family gets chickenpox: what are the preventive measures?
Most non-severe patients are treated at home.
- It is enough to isolate the patient in a separate room where ventilation is carried out regularly.
- The family member caring for the patient must follow normal sanitary and hygienic rules. Of course, he must have immunity, that is, he must have previously had chickenpox.
- There is no need to disinfect the room and objects used by the patient, since the virus is volatile, but not tenacious outside the body.
- When all the blisters have crusted over, approximately on the 6th day after the appearance of the last blister, the patient is no longer contagious.
What to do if there is no immunity to the infection, but there was contact with the patient?
Immunity after illness is lifelong. The quarantine period for chickenpox is 21 days, this time is enough for the virus to incubate.
In the first four days after contact with a patient, those who have not previously been ill and have not been vaccinated are vaccinated with the varicella-zoster vaccine.
If vaccination is contraindicated, ZIG or ZIP immunoglobulin can be used intramuscularly within 4 days.
All this will require time and effort; specialists at the international clinic Medica24 always take into account not only the individual characteristics of the disease, but the capabilities and interests of each patient, so that the treatment is as comfortable as possible and improves the quality of life. Call a specialist from the Center for Infectious Diseases 24/7
The material was prepared by an infectious disease specialist at the international clinic Medica24, Doctor of Medical Sciences Margarita Vasilievna Nagibina.