Neurologist
Chudinskaya
Galina Nikolaevna
Experience 29 years
Neurologist, member of the Association of Interdisciplinary Medicine
Make an appointment
Stroke is an acute cerebrovascular accident (CVA) that causes damage and death of nerve cells. The name itself comes from the Latin word “insultus”, translated as “strike, attack”. Previously, the pathology was called apoplexy (apoplexy), as the Greeks called paralysis - one of its main symptoms and consequences.
The disease is more common than acute myocardial infarction. Over 15 million cases are registered annually in the world. They account for 10% of all deaths (almost 6 million per year), which makes stroke the “No. 2 cause of death” on the planet after coronary heart disease (CHD). But in most episodes, the consequence of stroke is not death, but limitation of life activity; this is the leading cause of disability among people in the older age group.
About 60% of stroke patients have persistent neurological disorders that interfere with their normal lifestyle. Typical abnormalities include impaired movement and ability to move, difficulty swallowing, a high risk of speech and visual disorders, falls, and fractures. Emotional (depression) and cognitive (up to the stage of dementia) disorders are often observed.
Symptoms, signs of stroke
All symptoms of a cerebral stroke develop sharply, quickly, and appear suddenly:
- weakness, numbness, loss of sensitivity, paralysis of one half of the body or face, arms, legs;
- intense headache, described by patients as the worst in life;
- speech impairment (a person cannot speak or has difficulty doing so), misunderstanding of the interlocutor’s speech;
- deterioration in clarity of vision, it is unfocused or completely absent in one eye;
- dizziness, loss of coordination of movements, balance, walking, and sometimes loss of consciousness;
- nausea, vomiting.
Important: if you witness such symptoms, call an ambulance immediately! A stroke is an emergency condition that requires immediate emergency hospitalization!
Uninformed people can easily mistake such signs for alcohol or drug intoxication, so it is extremely important to know and distinguish the symptoms. After all, the speed of medical care plays a key role here - literally minutes count, death from stroke is directly related to delay. The sooner the victim is hospitalized, the less the consequences of a stroke will be and the higher the chances of saving life.
To make it easier to determine the occurrence of a stroke, doctors recommend using three basic recognition techniques. They are called the “UZP” rule, an abbreviation for the first letters of the words denoting the action that a person is asked to perform:
- U - smile. During a stroke, the smile often looks “crooked”, unnaturally skewed, when one corner of the mouth is lowered and the other is raised.
- Z – speak. Say a simple sentence like “Today they promised good weather.” Often (but not always!) there is incorrect pronunciation.
- P – raise your arms at the same time. If one arm involuntarily lags behind in movement or drops, there is a high probability of stroke.
When calling an ambulance, be sure to describe your symptoms to the dispatcher; such cases require calling a specialized resuscitation team and transporting them to a specialized clinic. You should not try to transport the patient to the hospital yourself, since not all medical institutions can provide the required set of emergency medical measures and precious time will be lost.
First aid for stroke
Before the medical team arrives, you need to provide assistance to the patient:
- Place in a horizontal position, raising the shoulders, neck and head 30° relative to the body (place a pillow, a cushion of clothing).
- Provide access to fresh air (unfasten tight clothing, open a window).
- Turn his head to the side to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
Under no circumstances should you give food or water - partial paralysis of the swallowing organs can cause food or drink to enter the respiratory system and subsequent suffocation. In other words, a person may choke or choke, which is likely to cause death due to stroke.
External signs of death from stroke
It is possible to determine that a person who has suffered a stroke is close to the end by external signs that indicate irreversible processes in the brain. Harbingers of approaching death are:
- disturbance of consciousness;
- unsteady gait, sweeping movements;
- the patient cannot speak, move, open or close his eyes;
- swallowing reflex is absent;
- there is inadequate motor activity, convulsions, twitching of the arms and legs, more like convulsions;
- increased body temperature - more than 40 degrees (indicates damage to neurons that regulate thermodynamics);
- eye movements are disturbed - by lifting the eyelid, you can see that the eyes seem to “float”, the pupil on the side of the hemorrhage is greatly dilated;
- high blood pressure, increased heart rate, bradycardia;
- appetite is reduced, stool is scanty and harder;
- urine is more concentrated and its quantity decreases;
- deep noisy breathing (Kussmauel breathing type), there are long pauses between inhalation and exhalation;
- breathing is sometimes deep, sometimes shallow.
Causes of stroke
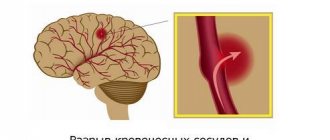
A stroke is caused by a disruption in the normal flow of blood to an area of the brain due to stenosis (narrowing), embolism (blockage), or rupture of a cerebral artery. If brain cells do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, they die.
Embolism and stenosis most often develop against the background of atherosclerosis, when an atherosclerotic plaque narrows the lumen of the vessel and promotes the formation of a blood clot. A detached blood clot completely blocks the vessel, this is called thromboembolism. Vascular rupture (essentially, intracerebral hemorrhage) can occur with arterial hypertension (high blood pressure), aneurysm, or severe traumatic brain injury.
There are a number of pathologies, the presence of which significantly increases the risk of stroke:
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- atrial fibrillation;
- myocardial infarction;
- high blood pressure;
- varicose veins;
- blood clotting disorder;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking, alcoholism.
The risk of developing this terrible disease increases after 30 years of age, especially in weather-dependent people, as well as in those exposed to chronic stress, regular overwork, and constant excessive physical exertion.
How not to miss a stroke in an old person
We have already said that a stroke in patients over 80 years of age has irreversible consequences. Therefore, as soon as you notice the above signs of illness in your loved ones or acquaintances who have crossed the eighty-year mark, immediately seek help from specialists.
If in young people, during a stroke, only a couple of symptoms appear, then in an old person, a stroke manifests itself in all its diversity, is bright and difficult.
You should be alert to general symptoms: dizziness, headache, poor coordination of movements, numbness on one side of the body.
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sudden and severe headache;
- rapid breathing accompanied by wheezing;
- redness of the skin, especially the face;
- a sharp increase in pressure;
- intermittent heartbeat;
- possible vomiting;
- numbness of the limbs and facial muscles.
In the first minutes of a hemorrhagic attack, immediately after a vessel ruptures, a person may lose consciousness. Depending on how the intracranial hemorrhage is localized, loss of vision and hearing can occur. Vomiting during a stroke can lead to aspiration in an old person, and therefore to respiratory arrest. In the most severe forms, patients experience seizures or even coma.
Signs of ischemic stroke:
- nausea and vomiting due to headache;
- sluggish, impaired movements, inability to lift or even move limbs;
- double vision when looking at objects, a blurry picture before the eyes;
- dizziness and disorientation;
- sensory disturbance;
- numbness of the mouth, inability to speak.
In the ischemic form, symptoms appear gradually. The acute phase is considered to be the first 6 hours after the attack.
If you suspect that an old person has had a stroke, then even before the team of doctors arrives, you can independently determine the primary diagnosis by performing simple tests:
- Ask the patient to smile. If a stroke occurs, one part of the face will remain motionless.
- Have the person try to simultaneously raise or at least stretch their arms forward. In case of a stroke, this can be done with only one hand.
- Try to talk to the victim, pay attention to his articulation. If cerebral circulation is impaired, it is almost impossible to pronounce words.
- Invite a person to stick out his tongue; the tip of the patient will certainly deviate to the side, in the direction of the lesion in the brain tissue.
Even if only one of the tests failed, the patient most likely had a stroke. In this case, there is no time to waste, but it is necessary to provide him with first aid.
Temperature during a stroke in an old person is an important indicator for determining the severity of the attack. The later a person’s temperature rises from the onset of a stroke, the more unfavorable the prognosis for the patient, and the greater the risk of death. High temperature is also a critical indicator that will subsequently prevent the body from recovering. This is due to the fact that hyperthermia worsens the hemorrhage and the hematoma begins to put pressure on the brain.
We recommend
“Recovery of older people after a stroke: tips and practical recommendations” Read more
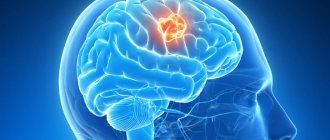
Classification of strokes
There are two types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic:
- Ischemic (also known as cerebral infarction) occurs when the lumen of a blood vessel in the neck or brain is narrowed or completely blocked by a blood clot.
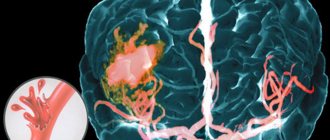
- Hemorrhagic - when hemorrhage occurs in the brain due to a rupture of the vessel wall, as a result of which nerve tissue is compressed, cerebral edema and displacement of brain structures are formed.
- Separately, a transient ischemic attack (TIA) should be mentioned - a short, from 10 minutes to several hours, disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. It is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of a stroke (headache, paresis, speech disorder, etc.), but differs in the short duration of their manifestations and the reversibility of the disorders. In most cases, TIA goes away on its own, without medical attention.
Sometimes people do not attach much importance to TIA due to the transience of this condition and the absence of complaints afterwards. But a TIA indicates a high risk of a full-blown ischemic stroke in the future, often within a few days or weeks. Therefore, such a patient must undergo a full examination to prevent stroke.
About 80% of all strokes are ischemic. There is a generally accepted classification of ischemic stroke according to the mechanism of development:
- Atherothrombotic - among all others, it is recorded in 40-60% of cases. Occurs as a result of atherosclerotic lesions of the precerebral or great cerebral artery. I get sick more often in people over 60 years of age. Often this type of stroke occurs during sleep, preceded by a TIA attack.
- Embolic stroke - develops against the background of mitral or aortic valve disease, after myocardial infarction, with endocarditis, paroxysm of atrial fibrillation, post-infarction aneurysm. The onset is sudden, in a state of wakefulness, the predominant age of patients is 50-65 years.
- Lacunar - due to damage to the small cerebral arteries that supply the deep parts of the brain. A type of stroke characterized by concomitant high blood pressure develops gradually over several hours.
- Hemodynamic – occurs in the presence of severe stenosis of the main arteries, subject to a sharp drop in blood pressure due to:
- orthostatic hypotension;
- deep sleep;
- hyperventilation;
- overdose of antihypertensive drugs;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart rhythm disturbances, etc.
Rapid death of a patient
There have been cases of immediate death from stroke in patients with extensive hemorrhage. It affects large areas of brain tissue, with deep penetration and damage to large vessels. Violating their integrity, the blood spreads to the hemispheres, thereby affecting the vital centers. A major stroke results from micro-strokes, persistently elevated blood pressure, repeated strokes, etc. Particularly dangerous and fraught with instant death is an extensive brainstem stroke - this is a type of disease characterized by damage to the nerve bundle of the brainstem. Unfortunately, this type of stroke in 95% of cases leads to paralysis and rapid death of the patient.
To avoid the re-development of various types of stroke, patients who have already suffered it once are recommended to frequently visit a doctor and be examined, as well as sanatorium-preventive treatment, rehabilitation appointments, and taking the necessary medications. Your life – health and longevity – depends on fulfilling the doctor’s requirements and recommendations. If you have a genetic predisposition to stroke or your health status indicates that you are likely to acquire the disease, you should make every effort to prevent the formation of conditions and environments for this.
Diagnosis of stroke
Since the therapeutic window for the treatment of acute stroke is limited in time, it is extremely important to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible. Examination of the patient by a specialist and diagnostic tests (including neuroimaging) are carried out almost simultaneously. The choice of neuroimaging method is based on the neurological status and condition of the patient; for example, about 40% of patients with stroke cannot undergo MRI due to contraindications.
Clinical examination remains an important part of diagnosis. At this stage, anamnesis is collected, a general examination, and a neurological examination. Information about the time of onset of symptoms and previous stroke is especially important. A neurological examination is intended not only to establish stroke and its causes, but also to exclude diseases that imitate it, and to differentiate it from pathologies with a similar clinical picture.
For people suspected of having a stroke or TIA, emergency computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is recommended.
Brain CT is today considered the international standard for diagnosing stroke; the accuracy of diagnosing hemorrhage with CT is almost 100%. Spiral CT reliably identifies most conditions simulating stroke (tumor, subdural hematoma, etc.) and distinguishes acute ischemic stroke from hemorrhagic.
MRI is more sensitive and can detect clear changes in the medulla, brainstem and cerebellum that are invisible with conventional CT. The procedure is especially effective in diagnosing stroke in the vertebrobasilar region, lacunar stroke, and acute ischemia. But MRI is less informative for hemorrhages.
Ultrasound methods help in diagnosing stenotic processes. Duplex scanning combines real-time ultrasound imaging to assess the anatomical structure of the arteries with pulsed Doppler analysis of blood flow at any part of the lumen of the vessel. This makes it possible to identify severe carotid artery stenosis at an early stage, for which catheterization angiography and surgery—carotid endarterectomy—are indicated.
Vascular imaging should also be performed as quickly as possible, including:
- CT angiography;
- MR angiography;
- catheter angiography;
- duplex ultrasonography.
Laboratory diagnostics should also be performed as an emergency; basic tests include:
- general clinical blood test with platelet count, hematocrit;
- determination of blood group, Rh factor;
- biochemical blood test: sugar, urea, creatinine, bilirubin, cholesterol, etc.;
- electrolytes (potassium, sodium);
- clinical urine analysis.
Other additional blood tests are possible as prescribed by your doctor.
Over 30 years, the incidence of stroke in the world has increased by 70%
Thanks to a detailed analysis of the situation with strokes, it was found that over almost 30 years, the incidence of this disease has increased by 70%, and the number of deaths has doubled. According to experts, Russians are at greatest risk of stroke. The situation is very seriously complicated by the emerging coronavirus pandemic. After all, the coronavirus, as it turns out, affects the brain, and its Indian version can cause multiple thromboses. All this ultimately leads to strokes and, accordingly, to an outbreak of disability among the population.
The systemic analysis carried out by scientists covered an almost 30-year period, from 1990 to 2021. The results were published in The Lancet Neurology. From 1990 to 2021, there were 101 million cases of stroke worldwide. In the study, this figure is noted as the prevalence of the disease. In 2021 alone, 12.2 million cases were reported. The death toll was 6.55 million people. Patients' disability-adjusted life years equivalent to years of "healthy life" lost due to deteriorating health, death or disability were also taken into account. As it turns out, between 1990 and 2019, humanity lost more than 140 million years of “healthy life.” As a result of calculations, it turned out that over 29 years the number of strokes in the world has increased by as much as 70%, and their prevalence has reached 85%. All these numbers do not inspire any good omens.
According to Irina Kondratova, a cardiologist at the medical network, the situation is very alarming and requires urgent intervention. Over the past decades, stroke has begun to affect not only older and mature people, but also young people. According to the expert, attention needs to be paid to the problem, as it seriously affects people’s productivity. The mortality rate from stroke is very high, as is the percentage of disability. Do not forget that only 20% of stroke patients are able to fully return to work.
Add AN to your sources so as not to miss important events - Yandex News
- The Russian Ministry of Health proposed importing unregistered vaccines and medicines into the country
- Taliban leaders are ready for war with Tajikistan
- In the Chelyabinsk region, 27 people died from Covid per day
- Residents of the Ivanovo region over 65 years old who have recovered from coronavirus will be paid 3,000 rubles
- How the state saves on disabled children
- Japanese scientist Fukushima said green tea can reduce the risk of cancer and stroke
- The state and prospects of pediatric oncology in Primorye were discussed in Vladivostok
- Actor Boris Tenin died at the age of 52
- Writer Alexander Lapin: “Three decades after the collapse of the USSR, we rolled back a whole century”
- In the Chelyabinsk region they do not rule out the introduction of compulsory vaccination
- Over 30 years, the incidence of stroke in the world has increased by 70%
- Rospotrebnadzor spoke about “easy” vaccination of pensioners against coronavirus
- The “pandemic” has become a breeding ground for a huge number of studies
- Morbidity and mortality from covid increased in the Chelyabinsk region
Become a member of the CLAN and every Tuesday you will receive the latest issue of “Arguments of the Week” with a discount of more than 70%, along with exclusive materials not included in the newspaper. Get premium access to a library of the most interesting and popular books, as well as an archive of more than 700 published issues for FREE. In addition, you will have the opportunity to benefit from free legal advice from our experts for a whole year.
- Enter your email address, then select any convenient payment method for your annual subscription
- Scan the QR. In the Sberbank Online application that opens, enter the annual subscription cost (490 rubles). Then send the confirmation code by email
Or
Stay with us. Add us to your sources and subscribe to our social networks.
Yandex Zen Telegram Google News MirTesen Twitter VKontakte Odnoklassniki Facebook
Stroke treatment
Modern approaches to the treatment of stroke are based on the fastest possible hospitalization of the patient; neurologists never tire of repeating: time = life. There is a concept of the so-called “therapeutic window” - 4.5 hours from the onset of an ischemic stroke, during which therapeutic intervention helps the regeneration of damaged cells and the creation of new synaptic connections by neurons to replace the lost ones. The procedure of thrombolysis or systemic thrombolytic therapy (STLT) is highly effective - the administration of drugs that destroy the blood clot and help restore normal blood flow.
The Ministry of Health has approved unified clinical protocols developed on the principles of evidence-based medicine, taking into account modern international recommendations. According to such protocols, the patient must be hospitalized in specialized stroke departments of multidisciplinary medical institutions, intensive care or emergency departments, which have the ability to provide round-the-clock neuroimaging (CT/MRI), monitoring of vital functions, laboratory control and assistance by specially trained personnel.
To determine treatment tactics, it is necessary to determine the type of stroke. The choice of therapy will depend on this: thrombolysis, anticoagulants, regulation of general hemodynamics, treatment for atrial fibrillation. General therapy is aimed at restoring the functions of the nervous and cardiovascular systems, normalizing water and electrolyte balance, controlling the metabolism of blood plasma glucose and body temperature.
Surgical intervention
For large cerebral infarctions, covering more than half of the middle cerebral artery and accompanied by edema and dislocation of the brain, conservative treatment methods are ineffective, and the mortality rate reaches 80%. In such cases, in order to avoid a critical increase in intracranial pressure, wide decompression craniotomy is used - hemicraniectomy. This can significantly reduce mortality and improve treatment results.
One of the most promising methods for treating acute ischemia has become endovascular interventions, when the operation is performed under X-ray or angiographic control. Several specific techniques have been developed: emergency angioplasty with stenting, mechanical destruction and/or removal of a blood clot - thrombectomy. The use of endovascular operations is limited to highly specialized centers where there are the necessary technical resources and qualified specialists - only under such conditions are these interventions safe.
You need to understand that the effectiveness of treatment depends on the area of brain damage and which areas were damaged. The treatment process is long and requires a lot of patience and effort, primarily from the patient himself and his loved ones. Proper rehabilitation after a stroke is extremely important to maximize the restoration of body functions and return the patient to as normal a lifestyle as possible.
Which doctors treat stroke?
Most patients with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke are subject to urgent hospitalization in a specialized neurovascular (stroke) department or center, or, in the absence of one, in a neurological department. In case of violation of vital functions, they are hospitalized in the intensive care unit, in case of epi-, sub-, intracerebral hematomas - in neurosurgery.
The leading doctors in the treatment will be neurologists, neurosurgeons and neurovascular specialists. In addition to them, doctors of instrumental and laboratory diagnostics, cardiologists, ophthalmologists, psychologists, speech therapists, endocrinologists, rehabilitation specialists and physiotherapists, and other specialists take part in the treatment process.
Cost of initial appointment, research, treatment
It is advisable to talk about the price of the initial appointment during a preventive examination, when there is no stroke as such, but the person has pathologies that increase the risk of its development. The cost of diagnostic procedures for stroke can be found in the corresponding table, but it must be taken into account that many studies are used repeatedly to monitor the treatment process.
It is quite difficult to determine even the approximate cost of stroke treatment in Moscow. Much depends on the type of stroke, the extent of brain damage, the patient's condition, the timeliness of medical care and other important factors. In any case, the cost of medical services will be justified - after all, we are talking about preserving life.
Treatment of patients in specialized stroke departments, cardiology centers - stroke units (IB) - reduces mortality and disability by 20%, reduces financial costs at all stages of treatment.
Advantages of treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
On the basis of a multidisciplinary medical center (academician Roitberg’s clinic) there is a cardiac rehabilitation center specially created for the treatment of strokes. How does IB differ from a regular neurological or therapeutic department:
- specializes in the treatment of patients with stroke, its staff is trained to care for this group of patients;
- the necessary diagnostic facilities - from computer and magnetic resonance imaging scanners to a laboratory with round-the-clock operation, an intensive care unit;
- work according to local protocols developed on the basis of domestic and international principles of stroke treatment;
- early mobilization and intensive rehabilitation.
multidisciplinary team:
- vascular neurologists;
- nurses are trained to care for stroke patients;
- rehabilitators who help restore physical capabilities and self-care skills;
- speech therapists – restore the ability to oral and written communication, correct swallowing disorders;
- neuropsychologists - working to restore cognitive functions.
In addition, in the cardiac rehabilitation center there is a constant opportunity to consult with doctors of various specialties: cardiologist, neurosurgeon, psychiatrist, urologist, endocrinologist, etc. In developed countries, hospitalization in stroke units has become the “gold standard”. In the UK and Germany, 9 out of 10 patients with stroke are treated in an IB, in Poland - 8 out of 10.