Alexandra Korostyshevskaya, Andrey Savelov, Irina Prikhodko, Yana Isaeva, Vasily Yarnykh “Science at First Hand” No. 3(88), 2020
Since childhood, we have heard that nerve cells do not recover. And although the question of the possibility of the formation of new neurons in the adult brain is still open, there is already evidence that the process of neurogenesis in humans continues into old age. Any disturbances in the development of nerve cells can lead to serious, sometimes irreversible pathologies. One of these disorders is defects in the protective insulating sheath (myelin) of nerve cell processes, which can form in a person even before birth. They are almost impossible to diagnose using traditional imaging methods.
About the authors
| Alexandra Mikhailovna Korostyshevskaya — Doctor of Medical Sciences, leading researcher at the laboratory of MRI technologies, head of the diagnostic department of the Institute “International Tomography Center” of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Author and co-author of more than 70 scientific papers. |
| Andrey Alexandrovich Savelov — Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, senior researcher at the laboratory of MRI technologies at the Institute of International Tomography Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Author and co-author of more than 90 scientific papers. |
| Irina Yurievna Prikhodko - software engineer at the laboratory of MRI technologies at the Institute of International Tomography Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Author and co-author of 3 scientific papers. |
| Yana Olegovna Isaeva - student at the Institute of Medicine and Psychology named after. V. Zelman Novosibirsk State University. |
| Vasily Leonidovich Yarnykh — Candidate of Chemical Sciences, head of the laboratory of the Department of Radiology, professor at the University of Washington (Seattle, USA) and Tomsk State University. Author and co-author of more than 70 scientific papers, including 5 patents. |
The average human brain contains about 100 billion neurons that receive, store, process and transmit information using electrical and chemical signals. Interaction between a neuron and other nerve cells and organs occurs through short ( dendrites)
) and long (
axon
) processes.
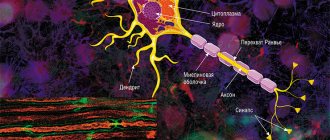
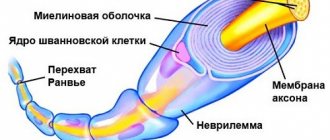
Each axon, like a wire, is covered with an insulating material - the myelin sheath.
, which provides a higher speed of nerve impulses and protects nerve fibers from damage. In addition, this shell has a supporting function, and also, according to the latest data, serves as a kind of “refueling station” for the axon, which needs a large amount of energy.
The axon is the main “cable” of a neuron, covered with a myelin sheath. It vaguely resembles a power line with a chain of insulators. The purpose of the shell, which is formed by special service cells (oligodendrocytes or Schwann cells), is to ensure the transmission of electrical impulses without loss and at maximum speed. © Servier Medical Art. Left
- axons of mouse sciatic nerves (
red
), wrapped in Schwann cells (
green
, nuclei -
blue
).
Photo by A. Alvarez-Prats and T. Balla. © Eunice Kennedy Shriver / National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
/ NIH
All damage to the myelin sheath or defects that occur during its formation lead to serious, sometimes incurable diseases. Among them, the most famous is multiple sclerosis.
is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects young people.
Myelin is also destroyed during strokes
, which occur not only in adults (primarily, as is commonly believed, in older people), but also in children, including the unborn.
Intrauterine stroke most often occurs after the 28th week of pregnancy, and in children - a month after birth. Stroke in a fetus leads to the development of brain defects, and in children it can cause cerebral palsy
at an early age.
At the same time, today we judge the “quality” of myelination of the brain of a particular person only by indirect clinical symptoms or magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI), which can usually detect myelin defects at a late, often irreversible stage.
In the brain, the myelin sheath is created by oligodendrocytes, in the peripheral nervous system - by Schwann cells. Each oligodendrocyte forms several “legs” that repeatedly “wrap” around part of an axon ( bottom
).
As a result, one oligodendrocyte is connected to several neurons. © Servier Medical Art. At the top
- oligodedrocytes in culture (
red
, nuclei -
lilac
). © jakeyoung64
Not everyone knows that myelin is many layers of cell membrane, “wound” many times around the axon. Myelin is formed by flat outgrowths of “service” glial cells, in which there is practically no cytoplasm. The myelin sheath is not continuous, but discrete, with gaps (nodes of Ranvier). Therefore, the axon has faster saltatory conduction: the speed of signal transmission along fibers with and without myelin can differ hundreds of times. As for the molecular composition of the “insulator,” it, like all cell membranes, consists primarily of lipids and proteins.
Neural insulation defects
Fetal brain development is a complex process in which rapid changes in the morphology and microstructure of nervous tissue occur. In some areas of the brain, the process of myelin formation begins as early as 18–20 weeks of pregnancy, and continues until approximately the age of ten.
It is myelination disorders that often underlie delays in the physical and mental development of a child, and also cause the formation of a number of neurological and psychiatric pathologies. In addition to diseases such as stroke, delays in fetal brain development with impaired myelination are sometimes observed in multiple pregnancies. At the same time, desynchronization in the development of the brain of twins is quite difficult to assess “by eye”.
But how to identify myelin defects during fetal development? Currently, obstetricians and gynecologists use only biometric indicators (for example, brain size), but these are highly variable and do not provide a complete picture. In pediatrics, even in the presence of obvious functional abnormalities in the child’s brain activity, traditional MRI or neurosonography
(ultrasound examinations of the brain of newborns) often do not show structural abnormalities.
Therefore, the search for accurate quantitative criteria for assessing myelin formation during pregnancy is an urgent task, which also needs to be solved using non-invasive diagnostic methods that have already been tested in obstetrics. Specialists from the Novosibirsk International Tomography Center SB RAS proposed using for these purposes a new method of quantitative neuroimaging, already adapted for prenatal ( prenatal)
) research.
A neurologist explained how nerve cells can be restored
Scientists have found a way to restore nerve cells. As “Doctor Peter” writes, Gleb Makshakov, head of the rehabilitation department of the Multiple Sclerosis Center of City Hospital No. 31, told how this happens.
According to American scientists, in patients after strokes, brain injuries and diseases such as multiple sclerosis, regeneration of nerve cells is possible with the help of physical exercise. The tests were carried out on mice in which the symptoms caused by the destruction of the myelin sheaths surrounding nerve fibers and the nerves themselves, which are responsible for transmitting impulses from the brain to the organs and back, disappeared forever.
As Makshakov noted, it’s a little more difficult with people. However, with physical activity in patients with multiple sclerosis, the brain is restored - functional studies have long shown this.
“Why this happens is also already clear: physical activity, including aerobic activity, reduces the level of inflammation in the head, which has a destructive effect on nervous tissue - the less inflammation, the better the myelin sheath and neurons feel. And if a person leads a sedentary lifestyle, smokes, or suffers from diabetes, then his inflammation is more pronounced,” the doctor said. — With functional restoration it is more difficult: the brain is built according to, so to speak, a network characteristic. One nerve center is more or less responsible for a specific function, such as the movement of an arm or leg. He needs other centers to work. The main center is associated with them in the process of mastering human motor (motor) skills. That is, one area of the cortex is connected to different areas of the brain. When a person whose structural connections have been destroyed undergoes physical rehabilitation, they are restored, so he feels better. But the symptoms can go away completely only in those whose disease is caught in time, when the neural connections still have sufficient reserve.”
The neurologist added that to achieve a recovery effect, physical activity should be selected depending on the degree of loss of function of the patient.
“If he is young and has no motor limitations, then physical activity should be like that of a healthy person. Aerobic - 10 thousand steps per day (fast walking, running) - daily. Intense physical activity - 2-3 times a week for 30-45 minutes (so as not to get too tired): in the gym, on the sports ground, if it’s difficult on your own, with a trainer. Even weight training and strength training are possible, if your condition allows. You can organize it in different ways, for example, after work, walk or climb the stairs without an elevator, get a dog and walk with it. If the patient is disabled (more than 4 points on the EDSS scale), he walks little or is confined to a wheelchair, he needs to be recommended physical activity by a qualified rehabilitation specialist (physical therapist, occupational therapist or exercise therapy instructor). These should be special adapted exercises that the patient can perform at home,” Makshakov noted.
The doctor emphasized that physical activity is important for any person, and especially for those suffering from multiple sclerosis - if he does not move, his condition will worsen.
“The main rule of the brain: you either use a function, or it gradually atrophies,” the doctor added.
On a regular tomograph
Any pathology of the fetal brain that doctors suspect during an ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman is usually an indication for an MRI; Similar studies have been carried out at the ITC SB RAS for more than ten years. MRI results can confirm, clarify, refute, or even change the preliminary diagnosis and, accordingly, pregnancy management tactics.
The fact is that the amount of myelin and the size of individual brain structures in the embryo are so small that any measurements are very complex and time-consuming. In addition, the fetus is constantly moving, which makes it very difficult to obtain high-quality images and reliable quantitative data. Therefore, we need technology that allows us to obtain images quickly and with high resolution even on small objects.
This is exactly what the method for fast mapping of the macromolecular proton fraction
(MPF) is a biophysical parameter that describes the proportion of protons in tissue macromolecules involved in the formation of the MRI signal, whereas the signal source is usually protons contained in water (Yarnykh, 2012; Yarnykh et al., 2015).
The macromolecular proton fraction (MPF) method is based on the magnetization transfer effect, when protons of free water “exchange” magnetization with protons of low-mobility macromolecules, such as proteins. The speed of this process affects the magnitude of the detected MRI signal and depends on the area of interaction between the macromolecular fraction and water
The method is based on a specialized procedure for mathematical processing of MRI images, which makes it possible to isolate signal components associated with the MPF of cell membranes. And in the brain of humans and animals, the main part of them is contained in myelin. MPF maps are reconstructed based on initial data, which can be obtained on almost any clinical tomograph.
To reconstruct the MPF maps, four source images obtained by various traditional MRI methods are used. The correctness of this approach was confirmed by the results of its testing on laboratory animals at Tomsk State University: in mice that were injected with a solution that causes myelin destruction, the results of MPF mapping coincided with the data of histological examination of tissues (Khodanovich et al., 2017).
Multiple sclerosis: drugs for remyelination
Roche has acquired Inception 5, a biotech startup focused on regenerative therapies for multiple sclerosis. The company emerged from the Inception Sciences incubator, with which the Swiss pharmaceutical giant entered into an agreement in June 2014, receiving the right to purchase if it achieves certain successes.
The focus of Inception 5 is the screening and development of low-molecular medicinal compounds that provide remyelination of nerve fiber sheaths damaged as a result of the progression of multiple sclerosis. The company's know-how is based on proprietary technology from the University of California San Francisco (UCSF), designed for high-throughput analysis of potential drug candidates. It was used to screen Roche's extensive library of molecules.
Current approaches to the management of multiple sclerosis profess the principles of preventing attacks from the immune system and neutralizing their consequences - no drugs have yet been invented that restore myelin sheaths, the disruption of which leads to a deterioration in critical signal conduction. Part of the problem is the lack of a technique that would confirm that a particular compound performs the task of remyelination. First, neurons are not easy to make grow in a laboratory setting. Second, oligodendrocytes, which produce myelin, wrap it around axons in a manner that is difficult to measure.
Researchers have come up with tiny cones of silicon that stimulate oligodendrocytes to wrap myelin around them. In other words, the result was axons made of pure glass. When these cones, called micropillars, are arranged in an array on a test plate, it becomes easy to measure myelin thickness. It is appropriate to draw an analogy with determining the age of a tree by rings in the cross section of the trunk.
Conical fused silica micropillars on a bottomless 96-well plate. Image: Nature Medicine, vol. 20, pp. 954–960 (2014).
The micropillar array concept allows for simple measurement of myelination with an inverted confocal microscope. Image: Nature Medicine, vol. 20, pp. 954–960 (2014).
Oligodendroglia: arrows indicate oligodendrocyte precursor cells interacting with individual micropillars; triangles indicate oligodendrocytes associated with them. Image: Nature Medicine, vol. 20, pp. 954–960 (2014).
An oligodendrocyte wrapped around a micropillar: showing multiple concentric layers of myelin. Image: Nature Medicine, vol. 20, pp. 954–960 (2014).
It should be understood, however, that despite the effectiveness of this approach, we are talking about a synthetic system that only approximately allows us to understand how myelin wraps around real axons. In the real world, this would be hampered by factors such as inflammation in the microenvironment of neurons affected by multiple sclerosis.
Inception 5 and Roche have not disclosed what exactly they are working on, but it is believed that the partners are testing clusters of ϰ-opioid receptor (KOR) agonists. It has been established that the latter is a positive regulator of oligodendroglial differentiation, promoting the process of remyelination. In preclinical testing, human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cells were targeted with (±)U-50488, the most potent KOR agonist discovered. As a result, it had a significant effect on accelerating differentiation into mature oligodendrocytes. All that remains is to modify the molecule so that it does not carry side effects such as analgesia, dysphoria and sedation characteristic of KOR activators.
Meanwhile, Biogen is developing the monoclonal antibody opicinumab, a leucine-rich repeat immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 1 (LINGO-1) antagonist designed to prevent further progression of demyelination. The mechanism of action is based on blocking this protein, which, being on the membrane of oligodendrocyte precursor cells, suppresses their differentiation, axonal regeneration and myelination. Despite the virtual failure of the SYNERGY phase II clinical trial, Biogen did not give up and launched the AFFINITY phase II clinical trial, increasing the dose and changing the patient population.
Acorda Therapeutics has rHIgM22, a stimulator of oligodendrocyte remyelination that targets integrin αVβ3 and is a recombinant version of an autoantibody isolated from the serum of a patient with Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.
"Mosmedpreparaty"
AbbVie is studying elezanumab (ABT-555) against repulsive guidance molecule a (RGMa), an inhibitor of axonal regeneration and remyelination.
Drug compounds with remyelination effects and their targets. Image: Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, vol. 16, pp. 617–634 (2017).
Roche is testing the cholesterol-like neuroregenerator and neuroprotector olesoxime, obtained through its acquisition of Trophos in January 2015 for an upfront €120 million plus €350 million as the project reaches certain development milestones.
The French MedDay is testing MD1003 - biotin (vitamin B7, vitamin H) in a high dose: it is a coenzyme of carboxylases involved in the metabolism and synthesis of fatty acids, which are part of high-lipid myelin.
During the screening of already approved medications with a proven safety profile, those that provide myelination in vitro and remyelination in vivo were identified, for example:
- antiallergic "Tavegyl" (Tavegyl, clemastine), a blocker of histamine H1 receptors;
- antipsychotic "Seroquel" (Seroquel, quetiapine), dopamine, serotonin and adrenergic antagonist with antihistamine and anticholinergic properties;
- antiemetic and prokinetic “Motilium” (domperidone), a blocker of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors;
- hypotensive "Wytensin" (guanabenz), an alpha2-adrenergic receptor agonist;
- thyroid "Cytomel" (Cytomel, liothyronine), a synthetic version of triiodothyronine;
- antifungal "Monistat" (Monistat, miconazole), inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol in the membrane and plasma membranes of fungi;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory "Indocid" (Indocid, indomethacin), inhibitor of cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (COX1 and COX2).
This mechanism of action is a side effect. Thus, since antagonism of the acetylcholine muscarinic receptor M1 (cholinergic receptor) improves myelination, and clemastine and quetiapine have a certain affinity for it, their use in the treatment of multiple sclerosis seems promising. Domperidone increases prolactin levels, thereby enhancing remyelination through the prolactin receptor (PRLR). Miconazole stimulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway and the activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1 and ERK2). Indomethacin modulates Wnt signaling and beta-catenin phosphorylation.
In general, the industry is actively immersed in the study of drug compounds that promote the repopulation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, accelerate their differentiation and/or maturation into myelinating oligodendrocytes, and counteract negative factors in the lesion microenvironment. These molecules can be used along with immunomodulators to control the damaging effects of inflammation. Because remyelination is neuroprotective, such drugs, if approved, would be appropriate for chronic use. In addition, restoration of myelin should mitigate the transition to progressive forms of multiple sclerosis as the disease progresses.