body .attr-article__date{ background: none; padding: 0; }
NEAD EAD SEAD South Administrative District South-Western Administrative District CJSC Central Administrative District SZAO Northern Administrative District 01 02 03 05 06 07 08 09 1 0 1 1 1 2 14 18 15 16 17 Babushkinskaya Prospekt Mira Pervomaiskaya Baumanskaya Paveletskaya Teply Stan Shipilovskaya Prague Academic University Barrikadnaya River Station Oktyabrskoye Bratislava Taganskaya Academician Yangelya October Field
The call center is open 24 hours a day
Ambulance 24/7
Date of publication: 04/19/2017
until October 31
We're giving away RUR 1,000 for all services per visit in October More details All promotions
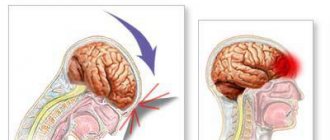
Symptoms of a concussion
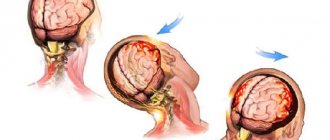
A concussion occurs when an external impact or force causes a sudden movement of the head. In this case, the brain is displaced inside the skull, and brain tissue “impacts” against its walls, which leads to the development of concussion symptoms.
The most common symptoms of a concussion
:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- confusion;
- deterioration of concentration and memory;
- memory loss;
- irritability, personality changes;
- increased sensitivity to light and sounds;
- sleep disturbance;
- decreased mood;
- disturbances of smell and taste.
A concussion is not always accompanied by loss of consciousness!
Only less than 10% of people lose consciousness with a concussion.
You don't have to hit your head!
Damage to other parts of the body, as well as sudden acceleration or deceleration of movement, can also lead to a concussion.
All cases of concussions require seeking medical help!
Recommendations for a speedy recovery
Complete rest is the key to recovery.
Avoid any mental or physical activity that may make your condition worse.
Avoid physical overexertion, which can worsen symptoms
:
- Sport
- Any vigorous activity
Limit mental stress or activities that involve high concentration as this may worsen your condition:
- video games
- watching TV
- reading
- correspondence
- using a computer
- school lessons
Do not take medications containing ibuprofen or aspirin for headaches caused by concussions.
because these drugs may increase the risk of bleeding. Acetaminophen-based medications can be used.
Do not resume sports activities
before your doctor allows you to do so.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Make an appointment
Symptoms of a concussion
It is important to understand that a concussion can occur even when the severity of the injury is relatively minor. Therefore, it is very important to be attentive to the condition of the victim and not to miss the first signs of a concussion.
So, the first signs of a concussion are as follows:
- Confusion that disappears after a short time.
- Dizziness – the patient’s head is dizzy even at rest, but when the body moves or the head tilts, it intensifies. Such symptoms of a concussion are associated with impaired blood circulation in the vestibular apparatus.
- Throbbing headache.
- Feeling of tinnitus.
- Feeling weak.
- Nausea, vomiting, occurring once.
- Noise in ears.
- Confusion, lethargy, incoherent speech.
- Double vision. Even a mild concussion can cause a person's eyes to hurt when trying to read.
- Photophobia . Even the usual level of light can cause discomfort. Increased sensitivity to sounds is similarly manifested.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
In many situations, after an injury, it is very important to find out whether a person has a concussion. There is a very simple method for determining a concussion at home. To do this, the victim must close his eyes, stand, raise his arms to the sides, and then try to touch the tip of his nose with his index finger. Even if signs of a mild condition appear, this will be difficult to do.
Another option is used to help you understand at home that you have a concussion. The victim should close his eyes, raise his arms and walk in a straight line, placing one foot after the other. But someone must monitor this, since the victim risks falling due to disorientation.
Symptoms of concussion in adults after injury can vary in severity. As a rule, pronounced signs of a concussion in adults persist for 1-3 days after a blow or other injury.
As for whether there can be a temperature in this condition, it must be taken into account that such a manifestation occurs often. After a concussion, there may be a temperature - it rises to low-grade levels.
Sometimes victims exhibit neurological symptoms. However, in some cases they are absent. As a rule, victims experience changes in pulse rate and blood pressure, lethargy, and memory deterioration.
It is important to understand that people with a concussion may not exhibit all of the symptoms described. But in any case, if you suspect a concussion, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor.
Symptoms of a concussion in a child
If you can check the condition of an adult using the methods described above, then recognizing the signs of such a condition in an infant or in a child 2-3 years old is more difficult. This condition manifests differently in children than in adults. Diagnosis is complicated by the fact that it is not always possible to trace the connection between symptoms and the disease. In addition, the signs are often nonspecific.
How to determine this condition in a baby? Typically, an infant who has suffered a concussion will exhibit the following symptoms:
- regurgitation during feeding;
- vomit;
- rapid heartbeat;
- decreased blood pressure;
- manifestation of anxiety, which is soon replaced by severe lethargy;
- crying for no reason.
The first signs of a concussion in children may include severe pale skin. Consciousness may not be impaired.
Signs of a concussion in a child 1 year of age and older manifest themselves with the same symptoms as in adults. Such babies, as well as children 2 years of age and older, may experience loss of consciousness. Sometimes the baby feels nauseous, is bothered by vomiting, has a headache, and the baby complains of tinnitus and dizziness. The child may not sleep well or sweat a lot. In some cases, children experience temporary post-traumatic blindness. Sometimes there is a so-called period of “imaginary well-being”, when immediately after the injury the baby feels normal. But later the condition worsens.
If a child has a brain or spinal cord injury, you should see a doctor immediately.
Stages
During the course of the disease, it is customary to distinguish 3 basic stages (periods):
- The acute period, lasting from the moment of traumatic influence with the development of characteristic symptoms until the patient’s condition is stabilized, in adults, on average, from 1 to 2 weeks.
- Intermediate – the time from stabilization of impaired functions of the body in general and the brain in particular, to their compensation or normalization, its duration is usually 1-2 months.
- The long-term (residual) period in which the patient recovers or the emergence or progression of newly emerging neurological diseases caused by a previous injury (lasts 1.5–2.5 years, although in the case of progressive formation of characteristic symptoms, its duration may be unlimited).
In the acute period, the rate of metabolic processes (the so-called metabolic fire) in damaged tissues increases significantly, and autoimmune reactions are triggered in relation to neurons and companion cells. Intensification of metabolism quickly leads to the formation of energy deficiency and the development of secondary disorders of brain functions.
Mortality in cases of concussion is not recorded; active symptoms resolve safely within 2-3 weeks, after which the patient returns to his usual mode of work and social activity.
The intermediate period is characterized by the restoration of homeostasis either in a stable mode, which is a prerequisite for complete clinical recovery, or due to excessive stress, which creates the likelihood of the formation of new pathological conditions.
Long-term well-being is purely individual and is determined by the reserve capabilities of the central nervous system, the presence of pre-traumatic neurological pathology, immunological characteristics, the presence of concomitant diseases and other factors.
How to get a concussion
Knockout in boxing
The easiest way is to call a boxer friend with a good knockout punch.
A concussion usually occurs during a swing, less often during a direct blow, and even less often during an uppercut to the chin.
However, if someone wields a knockout uppercut, such a blow will almost certainly cause a concussion, since the design of the head is not naturally designed to withstand blows from below.
When using an uppercut, you need to put on a mouthguard - otherwise you can split your teeth. But such boxers are rare; it will be easier for him to hit a direct or side blow to the cheekbone. There are good side strikes with the “teisho” plane - the base of the palm. They are more likely to cause a concussion than a fist, but few people wield them.
It is advisable to avoid blows to the temple - without gloves, a 3-4 mm thick bone can be broken even with a not very strong blow. Ask your partner to hit the cheekbone. For a good blow, he will need to stand for several seconds. It is useless to hit him in the forehead - the blow will be absorbed; the design of the head resists such blows best of all. In other parts of the head from above, in the back of the head - just as dangerous as in the temple.
Punch in the face
The safest thing is a blow to the face, but there is a risk of not only getting a concussion, but also a fracture of the upper or lower jaw.
On the other hand, a hematoma on the face will be evidence that a concussion was received.
A blow to the nose will also bring nothing but bleeding and a broken nose.
The second way is to get a concussion at home from a fall.
The problem is that a person will reflexively stop himself from falling and hitting his head on the floor.
Therefore, you will also need a partner. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Free up space in front of you on the floor near a wall or cabinet - God forbid you get caught with some dumbbell or metal nut on the floor.
- The floor must be wooden - otherwise there is a risk of serious damage.
- You need to squat down near the wall and prepare a thick, wide scarf or belt.
- Take twenty to thirty deep breaths.
- Stand suddenly near the wall - the partner immediately takes a thick scarf and presses his neck against the wall.
- Consciousness will begin to disappear.
- Until the legs completely give way and the body slides smoothly down, the partner must jerk the body around, put on the step and forcefully throw the back of his head on the floor.
- There will be no pain when falling; consciousness, if everything is in order, should return in a minute.
In this case, the situation is safer than with a punch to the back of the head, since the blow falls over a larger area.
Dangerous ways:
- Jumping from a height onto your feet, which are spread slightly wider than your shoulders onto the asphalt, can seriously damage your knees.
- A blow with a heavy object, a stack of books, a plastic bottle with water or a piece of wood - the force of the blow is unpredictable; if hit with full force, the pain can even split the skull.
The stupidest thing you can do is to tell the military registration and enlistment office with a satisfied smile that you got a concussion on purpose so as not to serve in the army. According to the law of the Russian Federation, evasion of military duty by self-mutilation is punishable by imprisonment for up to 8 years.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a concussion is difficult due to the paucity of objective data, the lack of specific signs and is based mainly on the patient’s complaints.
One of the main diagnostic criteria for the disease is regression of symptoms within 3–7 days.
In the structure of neurotrauma, concussion accounts for 70 to 90% of all cases.
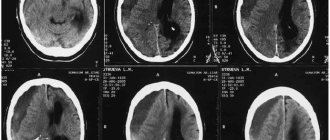
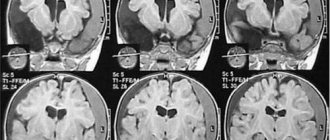
In order to differentiate a possible brain contusion, the following instrumental studies are carried out:
- radiography of the skull bones (no fractures);
- electroencephalography (diffuse cerebral changes in bioelectrical activity);
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (no changes in the density of gray and white matter of the brain and the structure of the cerebrospinal fluid containing intracranial spaces).
Carrying out a lumbar puncture in cases of suspected brain injury is contraindicated due to lack of information and a threat to the patient’s health due to possible dislocation of the brain stem; the only indication for it is the suspicion of the development of post-traumatic meningitis.
Expression of trauma
What is SGM? As a result of a blow, bruise or sudden movement, contact between the bones of the skull and the substance of the brain occurs. This is fraught with the following:
- Changes in a number of chemical or physical properties of neurons (the cells that make up the brain). This may lead to a change in the spatial organization of protein molecules.
- Pathological effects on the entire mass of brain matter.
- Temporary disconnection of signal transmission, as well as the relationship between the synapses of cellular neurons and parts of the brain. Synapses are the locations of contact between a pair of neurons. Or between the neuron and the effector cell receiving the signal. This is the cause of various functional disorders.
Cognitive problems
In most cases, patients have truly mild or moderate brain damage. After an accident, cognitive problems such as memory and concentration problems are noted. The effects of these mild forms of brain damage can affect work, family and social life. Over time, problems such as personality changes, increased irritability and decreased social behavior may also appear. “It is not uncommon for patients to show a good recovery at first glance, but over time they develop difficulties at work and in home situations,” explains Van der Naalt. At the same time, the majority of these patients resume their work activities within two months after the injury. Ultimately, 80% of them return to their old working level within six months, the rest have to change their type of activity or reduce the number of working hours. They still have residual symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, and problems with memory and concentration. Van der Naalt: “To return to the old level of functioning, they need to put in significantly more effort. Another problem they may face later is the inability to do several things at once. It's stressful."