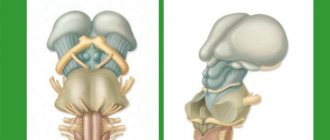
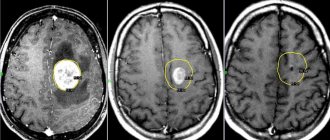
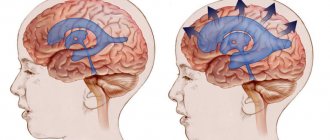
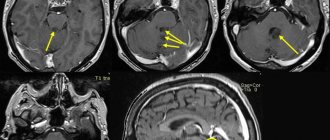
Tumors of the posterior cranial fossa are pathological neoplasms localized in the region of such parts of the brain as the cerebellum, medulla oblongata, lateral cistern, vermis, and fourth ventricle. In these parts of the central nervous system, various neoplasms can develop, originating from cells of the nervous tissue. Thus, among tumors of the posterior cranial fossa one can find meningiomas, acoustic neuromas, hemangioblastomas, medulloblastomas, astrocytomas, and gliomas. In most cases, neoplasms of this localization are detected in early childhood. Most of them are benign in nature and are characterized by slow growth. Cases of malignancy of neoplasms of this type are rare. In elderly patients, neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa, as a rule, are foci of secondary metastatic growth.
Symptoms of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa
The clinical picture of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa is determined by the degree of damage to the part of the brain that is involved in the pathological process. Most often, patients with this diagnosis develop the following pathological symptoms:
- causeless nausea and vomiting;
- painful headaches that cannot be relieved by taking painkillers;
- hearing loss;
- visual impairment;
- numbness or pain in the face and neck;
- paresis of the area of innervation of the cranial nerves;
- weakness of facial muscles;
- dizziness;
- gait disturbance;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- facial asymmetry;
- swallowing disorder.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Services of the clinic “Childhood Neurosurgery” of the Federal State Institution RNHI named after. prof. A.L. Polenova
In children, among pathological processes of a tumor nature, brain tumors are the most common after oncohematological diseases.
Moreover, in childhood, in 2/3 of cases we are talking about tumors of the posterior cranial fossa. Unfortunately, the prevalence of this disease remains very high and amounts to 3-5 cases per 100 thousand newborns. In some regions and countries this figure is two or three times higher. In the cavity of the posterior cranial fossa (subtentorial cavity) the brainstem, cerebellum, and 4th ventricle are located and, accordingly, the tumor process affects precisely these brain structures. By their histological nature, neoplasms of subtentorial localization are very diverse, but pediatric patients have certain features. The most common are astrocytomas (60%) and medulloblastomas (30%). The remaining 10% are ependymomas, oligodendrogliomas, angioreticulomas, choroid papillomas, dermoid tumors, etc. Symptoms of the disease consist of signs of damage to the cerebellum, stem structures and hydrocephalus. The brain stem (midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata) contains nuclei that regulate the movement of the eyes, facial muscles, tongue, larynx, but above all, cardiovascular and respiratory activity. Nerve conductors also pass through the brain stem to the muscles of the arms and legs. Therefore, damage to the brain stem by the blastomatous process is the most dangerous and severe. In this case, patients experience strabismus, facial asymmetry, paralysis of the limbs of varying degrees, impaired swallowing and voice, and in severe cases, disturbances of consciousness, breathing and cardiac activity appear. Dysfunction of the cerebellum consists of impaired gait and coordination of movements, dizziness, and impaired handwriting. With severe manifestations of cerebellar ataxia, children stop walking and cannot even sit; twitching of the eyeballs is noted - nystagmus. The occurrence of hydrocephalus is due to the fact that cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) passes through the 4th ventricle and when it is compressed by a tumor, the free flow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted. For this reason, there is a gradual accumulation of fluid above the 4th ventricle, which leads to the development of hydrocephalus (see Hydrocephalus). In most cases, the manifestations of hydrocephalus are the beginning of the disease, and subsequently signs of damage to the cerebellum and brain stem appear. Thus, the signs of the onset of the disease are most often headaches; young children become very moody and restless. Intensification of headaches is typical at night and in the morning, most often it is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and in young children - regurgitation, sometimes with a fountain. A brain tumor, including that of the posterior cranial fossa, can manifest itself in young children as delays in mental, speech and motor development. If up to a certain age the child developed according to his age and then his development stopped, this may also be the initial manifestation of the disease. One of the symptoms of a tumor of the posterior cranial fossa may also be an incorrect position of the head, tilting to the side or back. It is necessary to pay attention to the eyes, because... in some cases, a tumor of the posterior cranial fossa may manifest itself as strabismus, drooping eyelids, and asymmetry in the size of the pupils. With careful observation, you can notice that the baby uses only one hand when playing. As the disease develops, children, as a rule, spend less time than usual in games and get tired quickly. If any of the above symptoms appear, immediate consultation with a pediatric neurologist or neurosurgeon is necessary to exclude a blastomatous process in the posterior cranial fossa. The most informative method of diagnosis, in this case, is computer or magnetic resonance imaging, and in children under one year of age, also neurosonography (ultrasound) of the brain. Treatment is complex - surgery, radiation, chemotherapy. Indications for the use of a particular method and their sequence are strictly individual. First of all, it is necessary to remove the tumor surgically, and the result of treatment and prognosis depend on the completeness of removal of the tumor tissue. For a more successful operation, it is necessary to have modern microinstruments, a surgical microscope, and an ultrasonic resector. If the tumor is of low quality or has not been completely removed, radiation treatment or chemotherapy is necessary after surgery. For children under 3 years of age, radiation therapy is not advisable, since exposure to radiation can have a detrimental effect on the overall development of the child’s brain and body as a whole. In such cases, chemotherapy is widely used, as well as specific antitumor immunotherapy and photodynamic therapy, which are widely used in our institute. Brain abscess Malformations of the skull bones. Intracranial cyst Hydrocephalus. Hyperkinesis Cerebral palsy Craniovertebral anomalies Neuromas Tumors of the cerebellum Tumors of the 4th ventricle Tumors of the lateral ventricles of the brain Tumors of the cerebral hemispheres. Tumors of the posterior cranial fossa in children Tumors of the skull bones Tumors of the spinal cord Tumors of the brain stem Damage to individual peripheral nerves Post-traumatic hydrocephalus Birth hemorrhages of newborns TRAUMATIC INJURIES OF THE SKULL AND BRAIN Spina bifida Post -traumatic epilepsy Epilepsy arterial aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations
Diagnosis of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa in Israel
A qualitative examination of patients with signs of brain tumors is necessary to make a correct diagnosis, determine the location and characteristics of tumor growth, as well as determine the tactics of its treatment. To obtain the most complete information about such neoplasms as PCF tumors, advanced diagnostic technologies are used.
- X-ray – a simple X-ray examination makes it possible to determine the presence of signs of damage to the bone tissue of the skull.
- CT is a modern X-ray examination that allows highly accurate visualization of neoplasms of the central nervous system.
- MRI – performing this diagnostic procedure makes it possible to obtain the maximum amount of information about the nature of pathological changes in soft tissues.
- Spinal tap - this procedure is aimed at obtaining samples of cerebrospinal fluid. Laboratory study of cerebrospinal fluid makes it possible to assess the state of the central nervous system and determine the extent of the pathological process.
- EEG - electroencephalographic study is performed to assess the functional state of the central nervous system.
- Audiometry – used to examine patients with signs of acoustic neuroma.
- Genetic testing is performed if the patient has signs of a hereditary disease such as neurofibromatosis.
- Biopsy - in some cases, histological examination of tumor tissue samples is required to make a diagnosis and determine the extent of the pathological process. For this purpose, a surgical procedure is performed to obtain samples of tumor tissue.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Treatment of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa in Israel
Treatment of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa is best left to experienced neurosurgeons. The use of modern surgical techniques and the experience of a specialist makes it possible to completely remove the tumor without damaging the brain tissue.
- Surgical treatment - the only radical method of combating neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa is surgery. Today, Israeli neurosurgeons use modern technologies for neuronavigation and removal of tumors of the central nervous system, which make surgical treatment as safe as possible. Thanks to microsurgical instruments and special optical systems, the surgeon performs all actions with maximum precision. This allows you to avoid damage to healthy brain tissue and the development of dangerous complications.
- Radiation therapy - ionizing radiation energy can be used to combat neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa before and after surgery. In the preoperative period, radiation therapy helps prepare the tumor for surgical removal and reduce its size. In the postoperative period, radiation therapy sessions are used to reduce the likelihood of disease relapses.
- A modern type of radiation therapy is a technique called radiosurgery. This method of fighting tumors is based on the use of targeted energy of ionizing radiation, acting precisely on the tumor tissue. Thanks to the precise determination of the coordinates of the location of the tumor, a large number of radioactive rays are directed precisely at the tumor, without damaging healthy brain tissue. Radiosurgery is used to combat small tumors, while eliminating the need for surgical treatment.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Diagnosis and treatment
Treatment of a tumor of the posterior cranial fossa both at the Burdenko Research Institute and at Medsi is carried out after patients have been prescribed a high-quality examination. The following types of studies will help make a diagnosis:
- An X-ray that can reveal, at a minimum, the presence of damage to the integrity of the skull.
- Computed tomography is an important part of the examination, which can detect a tumor even in its early stages.
- Magnetic resonance imaging will give the maximum insight into the nature of the tumor.
- Puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid, which makes it possible to assess the state of the central nervous system and understand how much the disease has spread.
If necessary, specialists can prescribe other studies that will help more correctly localize the disease and this will help perform the operation even more effectively. By the way, the only radical solution to the problem is surgery for a tumor of the posterior cranial fossa. In this case, treatment should be carried out comprehensively, and recovery, in addition to surgery, is also facilitated by radiation therapy, which is recommended before and after surgery. Patients and their relatives are naturally concerned about the prognosis when diagnosed with a tumor of the posterior cranial fossa, but everything in this case depends on the histological structure of the tumor. Constant postoperative examination will help to avoid serious consequences in the form of tumor growth.
Advantages of the Israeli Oncology Center
Treatment of neoplasms of the posterior cranial fossa in Israeli clinics is highly effective for the following reasons:
- consultation with experienced specialists in the field of oncological diseases of the central nervous system;
- conducting a high-quality survey using advanced technologies;
- individual approach when leaving the therapy program;
- modern radiation therapy;
- safe and effective surgical treatment.
Tumors of the posterior cranial fossa require timely and high-quality treatment. The best solution when making such a diagnosis would be to contact highly qualified Israeli specialists.
↑ Top | Applying for treatment ↓
Reasons for appearance
A congenital (true) arachnoid cyst forms in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. The embryo does not have a placenta. Viral and bacterial infections are stopped by the maternal immune system, but intoxication can affect the developing nerve cells of the brain.
As a result, there is a disturbance in the formation of the brain: underdevelopment of the choroid and nerve endings. The resulting cavities turn into cysts.
Alcohol, cigarette smoke, and medications (antibiotics, steroids, aspirin) have a similar effect on the brain of the unborn child.
Cyst surgery on the coccyx
Surgery to remove a coccyx cyst is the most effective way to get rid of the disease.
The causes of secondary arachnoid cyst of the posterior cranial fossa are:
- infection with pathogenic microorganisms during TBI, epidemics of meningitis, from foci of chronic infection;
- concussion ;
- radioactive exposure;
- cerebral hemorrhage
Bacterial meningitis
The inflammatory process in the arachnoid membrane can be caused by meningococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, viruses and fungi.
Infection occurs by airborne droplets (meningococcus), through open wounds on the head due to injury or surgery.
Meningococcal cerebrospinal meningitis is a highly contagious disease. Affects children under 5 years of age and men (mainly). Other forms of purulent inflammation of the arachnoid membrane arise due to damage to the dura mater.
Concussion
With a traumatic brain injury, the integrity of the internal membranes, especially the arachnoid, is disrupted. For a cyst to grow, a necessary prerequisite is its presence in a dormant state.
Hematogenous infection
The foci of streptococcal and staphylococcal infections are chronic diseases of the nasopharynx. Dissemination (penetration) of the pathogen occurs through the circulatory system.
Exposure to X-rays
Gamma rays have a negative effect on the entire body, including the brain. The functional ability of the brain is impaired, which leads to pathological changes in its structure (the formation of cysts).
Violation of the soft shell
Rupture of the choroid due to high pressure leads to hemorrhage in the arachnoid region. The circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, an inflammatory process begins, as a result of which a cavity is formed.