Drooping eyelid or ptosis is a condition that can be congenital or acquired. The main danger is that drooping eyelids can be not only an unpleasant cosmetic defect, but also be a symptom of a serious illness.
Normally, the edge of the upper eyelid overlaps the eyeball and iris by about 1/3. But this is not so important for determining the presence of ptosis, since drooping of the eyelid, as a rule, is immediately noticeable to both the patient and others, in comparison with a healthy eye.
A condition such as drooping of the upper eyelid can limit visibility due to a narrowing of the palpebral fissure, thus leading to excessive stress on the organs of vision, “overstraining” them. For this reason, prolapse is considered to be an ophthalmological pathology, which can cause visual impairment. However, a visit to a neurologist would not be a bad idea; more on that below.
Causes of drooping eyelids
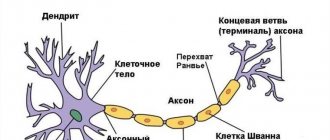
The upper eyelid is more than just a flap of skin. The eyelid consists of a muscle that attaches to the cartilage in the eye socket. The muscle (it is called the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid) is located in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat.
The main causes of the pathology:
- a congenital disease that is associated with insufficient development of the muscle designed to lift the upper eyelid;
- injury to the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid;
- damage to the oculomotor nerve;
- stretching of the tendon of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid (this condition is typical for old age);
- damage to the cervical sympathetic plexus (the so-called Horner's syndrome, expressed in ptosis, constriction of the pupil and “retraction” of the eyeball);
- diabetes mellitus as a cause of metabolic damage to muscles and nerves;
- acute cerebrovascular accident (in this case, drooping eyelid is accompanied by a number of other symptoms);
- tumor of the brain, spinal cord, or neck area;
- disturbance of neuromuscular transmission (myasthenia gravis or myasthenic syndrome);
- damage to the oculomotor nerve as part of polyneuropathy (in combination with damage to a number of other peripheral nerves);
- complication of botulinum toxin administration for cosmetic or medicinal purposes;
- botulism.
Considering the many factors that lead to drooping eyelids, consultation with a doctor is mandatory.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,500
Make an appointment
What is Horner's syndrome?
Horner's syndrome is a specific set of symptoms caused by pathological changes in the structures of the sympathetic part of the nervous system. The symptom was first described by the Swiss ophthalmologist J. Horner.
Horner's syndrome is not a separate disease, but occurs as a result of many pathological processes. As a result of damage to the sympathetic fibers of the lateral horns of the spinal cord C8-T1, the axons of sympathetic neurons or the sympathetic cervical ganglia, the innervation of the ocular muscle, which dilates the pupil, the muscle fibers of the retrobulbar zone and the muscle that dilates the palpebral fissure, is disrupted. All manifestations of Horner's syndrome occur on the side of the lesion of the sympathetic structures of the nervous system. There are cases of congenital Horner's syndrome.
Neurological diseases leading to ptosis
- Myasthenia gravis is a serious disease in which the transmission of impulses from nerve to muscle is disrupted. Myasthenia gravis is characterized by increased muscle fatigue. The disease affects all muscles, but the greatest manifestations can affect only the eye muscles, causing ptosis, double vision, and decreased focus. For the initial diagnosis of myasthenia gravis, a neurologist conducts a test with the introduction of proserin and examines the nerves and muscles using ENMG (electroneuromyography).
- Myopathy, in which double vision and drooping of both eyelids are also observed, while the performance of the muscle that lifts the eyelid is weakened, but present. Myopathies are of different types according to their origin. The examination uses needle EMG and a number of laboratory tests.
- Palpebromandibular synkinesis is involuntary concomitant movements that accompany chewing, abduction and opening of the lower jaw. For example, when you open your mouth, the prolapse can suddenly disappear, but after closing the mouth, it can be restored. This condition can be either an independent disease or the result of improper restoration of the motor fibers of the facial nerve after its damage.
- Bernard-Horner syndrome (expressed by a combination of drooping of the upper eyelid, narrowing of the pupil and “recession” of the eyeball). It is a manifestation of the pathology of the cervical sympathetic plexus. Sometimes the pathology is detected against the background of increased sweating on the face and incomplete paralysis of the brachial nerves on the affected side.
Drooping eyelid after botulinum toxin injection
According to statistics, after injections of botulinum toxin (Botox and other drugs containing it) into the eye area, drooping of the eyelid occurs in 20% of complicated cases, but this is almost always associated with errors during the procedure or is associated with the individual characteristics of the person.
Drooping of the eyelid after Botox injection is unpleasant, but, fortunately, it cannot be considered a serious pathology, since without additional therapy, signs of drooping completely disappear within 3-4 weeks after the injection of the drug.
Diagnostic techniques
In addition to a direct visual examination of the patient, in order to identify obvious symptoms, as well as compiling a detailed history, there are certain diagnostic techniques, the purpose of which is to unambiguously determine the disease:
- Instillation of an M-anticholinergic solution into the eyes. With such manipulations, Horner's syndrome can be unambiguously determined, since the action of this solution causes dilation of the pupils of the eye. If the pupil does not respond, then there is a syndrome or another reason.
- Determination of eye retention time - as already noted in the symptoms, in the presence of eye syndrome, the eyes have a reduced adaptive ability to changes in light intensity. As a result, knowing the adequate adaptation time, it is possible to determine the adaptation time of the patient's eye by measuring the time.
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging allows you to identify the formations that caused the occurrence of Horner's syndrome.
Treatment of drooping eyelid
If the cause of drooping eyelid is a neurological disease, such as myasthenia gravis or neuropathy, then the underlying disease is treated first. Since ptosis is a symptom, it also goes away when the underlying disease is cured.
However, in some cases, complete recovery is impossible, and then surgical treatment is carried out for cosmetic purposes or, if ptosis leads to significant disruption of life due to deterioration of vision, then for therapeutic purposes.
Children undergo this operation no earlier than 3 years of age, but it should be done as soon as possible to prevent decreased vision and the development of strabismus.
In order to eliminate a cosmetic defect (when vision is not impaired), the operation is recommended to be performed after puberty, when the bony facial skeleton is finally formed.
If the prolapse is caused by injury, the operation can be performed directly during the initial treatment of the wound surface by the surgeon, or after healing, that is, after 6-12 months.
One way or another, the doctor makes a decision on the timing of the operation depending on the specific case.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of this syndrome:
- the presence of benign or malignant tumors that affect the respiratory organs, brain, thyroid gland;
- dysfunction of blood vessels - varicose veins, pathological structure of the carotid artery;
- traumatic brain injuries and neck injuries (may occur during surgery);
- inflammatory diseases – otitis media, sinusitis;
- presence of systematic diseases;
- goiter, pathologies of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- any type of intoxication.
Horner's disease has a neurological etiology. Accompanied by complete damage to the neurons that lead to the optic nerve. Pathological lesions lead to disruption of the transmission of impulses to nerve fibers. In addition, this syndrome leads to heart damage, impaired sweating function, and increased blood pressure. It is difficult for a person to adapt to the environment.
The etiology of the syndrome can be determined only after examination by several specialized doctors. Initially, the reasons that led to such consequences should be eliminated. Then the doctor prescribes therapy to eliminate the symptoms of this pathology.
Preventing the development of drooping eyelids
An important point in the prevention of eyelid drooping is the timely treatment of any diseases that can provoke this pathology. For example, neuritis of the facial nerves must be immediately treated by a neurologist, and the possibility of drooping eyelids after Botox injections should be discussed with the specialist performing the manipulation.
If you notice weakness of the eyelids associated with age-related changes, then cosmetics and folk remedies can help you. Prevention methods include the use of tightening masks, oils and massage treatments.
Massage of the skin of the eyelids should be carried out with drooping eyelids. Before the procedure, the eyelids can be wiped with lotion to remove sebaceous scales and open the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands. Massage using a cotton swab or disk soaked in an antiseptic solution or special ointment. Use stroking with light pressure, making circular and linear movements, moving from the inner corner of the eye to the outer corner. You can lightly tap your eyelids with your fingertips.
There are special gymnastics for weakness of the eye muscles.
Starting position – standing, sitting or lying down.
- We look up, without raising our heads, then sharply down. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We look up and to the right, then diagonally down and to the left. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We look up and to the left, then down and to the right. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We look as far as possible to the left, then as far as possible to the right. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We stretch our arm forward and keep it straight. We look at the tip of the index finger and gradually bring it closer, without stopping looking until the picture begins to “double.” We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- Place your index finger on the bridge of your nose. We look at the finger alternately with the right and left eyes. Repeat 10-12 times.
- We move our eyes in a circle to the right and left. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We blink quickly for 15 seconds. Repeat blinking up to 4 times.
- We close our eyes tightly for 5 seconds, then sharply open our eyes for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
- Close your eyes and massage your eyelids with your finger in a circle for 1 minute.
- We shift our gaze from the nearest point to the far one and vice versa.
Movements of the eyeball during exercises should be as wide as possible, but not to the point of pain. The motor tempo can be made more difficult over time. The duration of such prophylaxis is at least 3 months.
It is worth noting that in case of myasthenia gravis and myopathy, such exercises are contraindicated, as they contribute to the worsening of drooping eyelids due to “exhaustion” of the muscle. Therefore, before engaging in any treatment, you must consult a specialist.
Causes
There are many causes of Horner's syndrome, ranging from damage to the nervous system to congenital defects and pathologies.
Let's look at them in more detail:
- Physical impact directly on the thoracic or cervical circuits of the sympathetic system. This can be either compression or direct damage. Often symptoms occur on the side where the impact was made.
- With damage to brain tissue due to lateral medullary syndrome.
- The cause of the syndrome may be cluster headache. These are very severe headaches that are felt on the walls of the skull. The pain is so severe that there are frequent cases of suicide in order to get rid of such pain.
- Traumatic cause associated with severe bruising directly to the base of the neck. Surgical trauma is also possible.
- Due to various tumors. In particular, this is a Pancoast tumor.
- Manifestation of an aneurysm. Very often, Horner's syndrome occurs after an aortic aneurysm.
- Inflammatory processes in the middle ear area.
- The cause may also be direct dissection of the aneurysm.
- Tumor of the thyroid gland.
- The occurrence of this syndrome may be associated with an autoimmune disease, such as multiple sclerosis.
- Tension of the stellate nerve due to the presence of an additional cervical rib.
- The cause may also be a blockage of nerve centers.
- In case of a cut in the sympathetic nerve of the neck.
- The cause may be an inherited disease that can cause tumors throughout the body. This is the so-called neurofibromatosis type 1.
Rapid destruction of the meninges or serous meningitis in children - treatment and prevention of the disease.
A particularly dangerous cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the brain, the treatment of which can only be done surgically, has its own characteristics of diagnosis and symptoms.
Our doctors
Pankov Alexander Rostislavovich
Neurologist
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Novikova Larisa Vaganovna
Neuropathologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Forecast of drooping eyelid
As a rule, ptosis requires either treatment of the disease that caused it, or purely cosmetic correction, or both.
When treated for cosmetic purposes, the prognosis is favorable. If surgical treatment was performed on a child, then he is monitored periodically throughout his growth period. For myasthenia gravis, the selection of adequate therapy or complete cure for myasthenia gravis can eliminate ptosis. With the exception of cases where, due to prolonged drooping of the eyelid, overstretching of the muscle tendon has occurred, then the defect becomes purely cosmetic and is eliminated surgically.
In all other cases of neurological pathology (syncinesia, neuropathy, facial nerve paralysis, myopathy), the prognosis depends entirely on the initial disease and the prognosis for its treatment.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Preventive measures
The specificity of Horner's syndrome is that it does not have special courses of treatment and prevention.
After all, it is often a symptom of a more complex and systemic disease, which already has direct methods of treatment and prevention.
The presence of the syndrome is very often determined only for the sake of exclusion or detection of a possible more serious disease that can threaten the patient’s life.
Bernard Horner syndrome is a specific disease associated with complications in the functioning of the sympathetic nerves , or their damage.
It has a number of specific symptoms, as well as methods of treatment and diagnosis of the disease. As a separate disease, it does not threaten the patient’s life, but only causes cosmetic and physical discomfort.
If the syndrome is caused by another, more serious disease, it can already pose a threat to a person’s life.
Treatment of this syndrome is carried out by stimulating the affected tissues or eliminating the cause of its occurrence. When treating this disease, it is important to consult a specialist in time to prevent truly dangerous complications.