In medical practice, special postures are used when diagnosing diseases and identifying pathologies. In neurology, the Romberg pose is widely used, which allows you to analyze and determine deviations in the functioning of the nervous system.
Thanks to a quick and fairly simple diagnostic method, specialists can identify neurological diseases and begin treatment faster. In addition, this research technique allows you to detect deviations during a simple examination without resorting to analyzes and additional studies.
Putting the body in order
First of all, this is necessary for city residents who need mental and physical training to improve the general condition of the body and increase performance. Physical training brings into play previously dormant corners of the whole body, revitalizing them and improving biochemical processes. Breathing becomes more uniform and, as a result, gas exchange normalizes.
A properly designed set of physical exercises improves physical, biochemical and even nervous processes in the body. If they work harmoniously, then the body responds faster to impulses sent by muscles, joints, vestibular apparatus and other body systems. Therefore, one can talk about the benefits of therapeutic and preventive gymnastics for hours.
How to test
The Romberg test is a simple diagnostic that identifies disorders of organs involved in maintaining balance - the vestibular apparatus (cerebellum, inner ear), proprioception (deep sensitivity), and higher cerebral functions of the cerebral cortex. The following steps are used:
- the patient stands, moves his legs tightly;
- closes eyes;
- extends his arms forward;
- sometimes it can be arms lowered along the body or legs placed in one line.
To reduce the risk of misdiagnosis when a person falls or staggers, the doctor looks at the patient's kneecaps. If he is healthy, they do not move. In the patient, they look up because the sufferer is trying to stand by tensing the muscles of his legs. This Romberg indicator is included in the mandatory neurological examination and is a minimal method of monitoring the patient and screening for identifying vestibular disorders.
Stainless steel railings with glass. Own production in Moscow. Low prices.
In many ways, balance testing depends on what kind of deviation is being diagnosed. In order for the patient to take the correct position, he needs to stand straight, with his legs pressed tightly against each other.
Next, the patient should stretch his arms in front of him and close his eyes. But test variants are possible when the eyes are closed, but the arms remain in a lowered position along the body. In this situation, the doctor must support the patient, preventing falls and injuries.
If we talk about the sphere of neurological abnormalities, then with this position any staggering is taken into account and the main task of checking the Romberg symptom is to determine the degree of stability. Time intervals are also taken into account, which are also important for correct diagnosis.
A more difficult version of the test involves placing your legs so that they are on the same line. This happens as follows: the patient places his feet so that the heel (for example, the right foot) is in contact with the toes (of the left foot) and they are on the same line.
In this position, the patient should extend his arms in front of him and close his eyes. An option is possible in which the head is thrown back.
The patient being examined stands up so that his legs are pressed tightly against each other. Then the subject stretches his arms forward and closes his eyes. An option is possible when the upper limbs are located along the body.
The complicated Romberg pose is performed so that the subject’s feet are on the same line, for example, when the toes of the left foot are adjacent to the heel of the right and vice versa. The subject stretches his arms forward, sometimes throwing his head back.
The neurologist observing the patient perform the test must protect him from accidental falls due to staggering.
A positive Romberg test may mean alcohol or drug intoxication, the effect of psychotropic drugs, mental illness or malingering, or inappropriate behavior of the person being tested.
First, the pose is performed in a simplified version, i.e. when the arms are along the body and the legs are together, and the patient’s eyes are closed. If this is successful, the test becomes more complicated, the legs are placed toe to heel of opposite legs, the arms are extended forward.
This test is easy to perform and can be used at home. However, if the subject already has cerebellar signs (unsteadiness of gait, incoordination of motor acts, nystagmus, tremor), it is necessary to carefully monitor the person so that he does not fall.
The inability to stand evenly, steadily and without swaying with a straight spine and closed eyes is called Romberg's symptom or pose; it is unstable in those who have problems with the nervous system.
The legs should be tightly pressed together, the spine line should be extended upward, the shoulders and chest should be open, and the arms should be straight out in front of the body, the hands should be located no lower than the line of the shoulder joints.
With their eyes closed, some people cannot maintain a stable position: they begin to sway, their hands may begin to shake, and they may feel like they are leaning back. In some cases, instability in the Romberg position is additionally checked by asking the person being tested to place one foot in front of the other so that the heel of the front foot touches the toes of the back foot.
Romberg test, how are the results assessed?
The results of the Romberg test can be assessed independently. But only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, based on the results of several examinations. Here's the simplest interpretation:
- If a person stands calmly and confidently, this is the norm. If there is swaying, it is important to note how long after it began.
- It is also necessary to note in which direction the patient is being “taken” - forward, backward, left or right.
- Does ataxia (that is, staggering) become stronger if the subject closes his eyes.
- Do your eyelids, your toes or hands, or your torso itself tremble?
If a person was able to stand quietly without these symptoms for the allotted time, then we can assume that he does not have functional disorders of the nervous system. Since he passed the Romberg test successfully. If the “alarm bells” described above appear, then this means only one thing - you need to consult a doctor.
Only he will be able to correctly interpret the results from a medical point of view. And determine the order of further important actions.
Children who do not play any sports have different standards for maintaining a calm state. Here are the standards in seconds of the Romberg test for time for children of different ages:
- child 7 years old – 16 seconds;
- children 8 years old – 21 seconds;
- for a child 9 years old – 24 seconds;
- for children 10 years old – 28 seconds;
- children 11 years old – 30 seconds;
- for children 12 years old – 36 seconds;
- children 13 years old – 44 seconds;
- for teenagers 14 years old – 48 seconds;
- teenagers 15 years old – 50 seconds;
- for boys and girls from 16 to 18 years old - from 51 to 53 seconds, respectively.
Symptoms of cerebellar dysfunction
If the use of the Romberg pose does not give a clear positive or negative answer, then the patient is asked to complicate it. To do this, place your feet along a straight line, so that the toe of one foot is pressed tightly against the heel of the other. If, in such a position, swaying or pushing of the body in different directions is already noticeable, then this is a consequence of the development of ataxia.
Symptoms according to Romberg appear if there are disturbances in the functioning of the cerebellum, as well as its relationship with other parts of the brain and in case of a disorder of the vestibular apparatus, impaired sensitivity due to damage to the spinal cord, or with polyneuritis. It is important to determine the direction in which the patient is staggering, since most often this has diagnostic significance. If there is a disease of the cerebellum, then the patient leans towards the affected hemisphere.
It is important to note that it is impossible to speak unequivocally about a disease of the central nervous system just by relying on this study. Since the Romberg pose is the simplest method that can only suggest diseases of the central nervous system in the early stages. If deviations are observed when performing this method, then it is worth conducting an additional full medical examination.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that rocking in the Romberg position indicates not only neurological diseases, it may indicate the presence of neuroses.
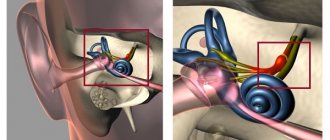
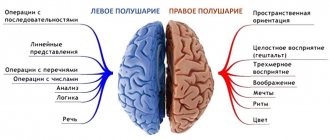
The cerebellum in the human body is responsible for orientation in space. Its neurons instantly respond to sent impulses that are responsible for changes in the environment or changing tasks. If cerebellar damage occurs at an early age, when the child has not learned motor skills, then learning movements will be extremely difficult.
If the defeat occurs when the necessary motor skills have been acquired, then the performance of already known exercises will occur with significant impairments. Deviations may be observed in relation to the trunk, as well as the limbs. The Romberg pose is suitable for identifying these violations. Ataxia is a consequence of a violation of the proper functioning of the cerebellum.
The main indicator of cerebellar dysfunction is the development of symptoms such as:
- cerebellar ataxia;
- muscle atony;
- asynergy.
Cerebellar ataxia is deviations from the correct execution of any movements and decreased coordination. From the outside, such movements may be regarded as unstable, clumsy or sloppy. They seem completely unrelated. In this case, ataxia can affect absolutely any part of the body.
The vestibular test in the Romberg position helps to identify ataxia. These disorders are accompanied by severe dizziness, vomiting and nausea.
With muscle atony, the patient's range of joint motion increases, the muscles become flabby and sluggish, and because of this, it is difficult for the patient to perform any physical exercises, and sometimes even just move.
When coordination of various muscle groups involved in individual movements is impaired, a symptom such as asynergia develops. For example, with normal movement of the limbs, the patient cannot crawl on all fours, because he does not understand how to coordinate the alternate movement of arms and legs.
Symptoms
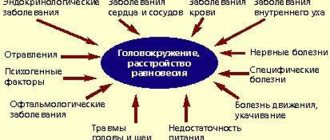
Such studies are resorted to when:
- dizziness (this symptom can be a sign of various pathologies, for example, with damage to the labyrinth, patients can often describe in detail the nature of dizziness, including indicating the exact direction of rotation of objects, position of the head and body, etc.);
- vegetative symptoms (in addition to dizziness, the subjects complain of nausea, which can be replaced by vomiting, increased sweating, pale skin, changes in pulse rates, etc.);
- spontaneous nystagmus (one of the most important symptoms, represents oscillatory movements of the eyeballs, which can be fast or slow, develops due to a disruption of impulses coming from the labyrinths to the nerves).
Along with this, typical markers of dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus are imbalance and unsteady gait.
If the posture is unstable: what does this mean?
Immediately make sure that the entire procedure is carried out in a calm environment, without external stimuli, and if there is staggering in the Romberg position, loss of orientation in space, or even a fall within a short period of time (less than eight seconds), then you need to sound the alarm: along with the untrained vestibular apparatus Most likely, the posterior nerve roots of the spinal column, which are responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses, are damaged, multiple atherosclerosis is possible (especially if maintaining a posture is impossible even with open eyes), although perhaps this is just a tendency to neurasthenia, neuroses and inability to control functions bodies.
If the cerebellum is affected, the patient will deviate towards the affected side, because the cerebellum is responsible for the coordination of movements, which a person comprehends in childhood. If the Romberg position is held, but not for long, then most likely there is only a tendency to atrophy of the skeletal muscles: this can be corrected if you practice this position every day until a stable result is obtained.
What does the Romberg test show?
- Carrying out such testing is aimed at determining the quality and correct functioning of the organs that provide a state of balance for a person. These are, first of all, the vestibular apparatus, the ability to sense your body as a whole and each of the organs and parts - relative to others, the full and uninterrupted functioning of the brain.
- Such testing is very helpful in diagnosing many diseases related to the nervous system. The doctor takes into account any staggering, determining the degree of stability, and also takes into account the periods of time during which the patient does or does not maintain balance.
- As a rule, the Romberg pose if there is a suspicion that the functions of the cerebellum or the central nervous system are impaired, if the spinal cord is affected. In addition, similar testing is used in case of suspected pathology of the inner ear; on the inflammatory intracranial process and in some other cases.
- The Romberg test can detect diseases such as neurosis or hysteria, indicate the presence of traumatic brain injury or ataxia. It is effective against meningitis and encephalitis, as well as Meniere's disease.
Test
- The patient is asked to take the Romberg position if there is a suspicion of static or vestibular ataxia, neuroses, when the work is disrupted or there are diseases of the cerebellum, parts of the nervous system or cerebral hemispheres are affected. This test is also carried out in the presence of impaired coordination of movements and obvious instability of the patient.
- The Romberg position used when detecting a state of alcohol or drug intoxication.
What are the benefits of Romberg pose? Why do it?
If you try to regularly perform the Romberg pose, the body, learning to stretch and correct the maintenance of balance in space, will use different and varied neural circuits, thus maintaining the central nervous system in a healthy state.
The main options are the classic and complicated Romberg pose. The first thing you need to do is a classic test; if it goes well, you need to do a more complicated test as a supplement.
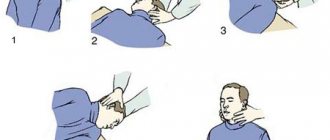
The classic (simple) version is done like this:
- The patient’s starting position is standing straight with support on two legs. The heels of the feet should be together, the toes slightly apart.
- The patient closes his eyes, extends both arms forward and spreads his fingers to the sides.
- The doctor must observe the patient’s balance, record the absence or presence of tremors in the body and limbs. They also pay attention to the leg muscles: if they are tense, or alternately tense (doing active work), it is difficult for the patient to stand straight, and he makes an effort to do this.
Classic Romberg pose
If there are no deviations (the fingers do not tremble, the patient stands straight, without swaying, without deviating the body), an addition is applied - the patient is asked to touch the tip of the nose with the index finger of one (and then the other) hand with his eyes closed. If in this case there is no instability and the limbs do not tremble, the test is considered passed.
What does swaying in the Romberg pose reveal?
The patient's inability to maintain stability in this position indicates disturbances in certain areas of the brain. The neurology of such deviations can be different. That is, swaying and loss of balance can be caused by the following neurological reasons:
- hysteria;
- Meniere's disease and inflammatory diseases of the inner ear;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- meningitis (bacterial inflammation of areas of the spinal cord and brain);
- neuroses;
- encephalitis;
- consequences of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- cervicogenic dizziness (one of the causes of salt deposition in the cervical spine);
- lesions (infectious and traumatic inclusive) of the spinal cord.
- psychiatric illnesses.
Carrying out the test for children makes it possible to identify nervous system problems at their early stages.
Training with Romberg pose
Romberg pose - what is it for a healthy person? This is an indicator of the condition of the entire organism as a whole. Correct positioning in this pose is a state that a normal, healthy body should have.
This is exactly the posture that any person should have in his youth, when his muscles are still in good shape. Unfortunately, after a hard day at work, as well as with age, it becomes more difficult for the muscles to keep the body in the correct position, and this requires some effort. In order to help the body cope with the load placed on it, it is necessary to constantly train it.
Yogic version
In the arsenal of yoga poses there is a similar position: Tadasana is a mountain pose, in some schools of yoga it is called Samastitihi, which means “to stand straight and calm.” This is the basic position from which the lesson begins, a test for the stability of the mind and the body’s reaction to it. Some beginners consider this pose uninteresting and insignificant due to its apparent simplicity, and only over the years they understand its real taste and importance, because yoga is not a beautiful or spectacular body position, like legs behind the head, but the ability to keep your mind in check ( “Yuj”, the word from which the term “yoga” comes from, translated from Sanskrit means bridle, harness), remaining even and calm in any situation.
In the arsenal of yoga poses there is a similar position: Tadasana is a mountain pose, in some schools of yoga it is called Samastitihi, which means “to stand straight and calm.” This is the basic position from which the lesson begins, a test for the stability of the mind and the body’s reaction to it. Some beginners consider this pose uninteresting and insignificant due to its apparent simplicity, and only over the years they understand its real taste and importance, because yoga is not a beautiful or spectacular body position, like legs behind the head, but the ability to keep your mind in check ( “Yuj”, the word from which the term “yoga” comes from, translated from Sanskrit means bridle, harness), remaining even and calm in any situation.
What is the diagnosis?
The main objective of the Romberg test is to determine dysfunctions of the organs that are responsible for balance. The systems that are responsible for human balance include:
- vestibular apparatus;
- proprioception system;
- brain functions.
Diagnostics makes it possible to determine whether there are abnormalities in the nervous system, possible disturbances in the functioning of the spinal cord, or whether there are disturbances in the functions of the vestibular apparatus.
Initially, there was only one version of the Romberg pose; now different versions are used. Stopwatches are also used in diagnostics, which allow you to obtain a quantitative assessment of the result.
With this technique, the patient closes his eyes, which allows him to determine how great the influence of vision is in maintaining balance, and how well other organs cope with this function.
What deviations can the sample reveal?
There are quite a few diseases for which this diagnostic technique is used. Depending on the complexity of the disease or possible pathology, different posture options may be used.
Quite often, after using a simple pose, a more complicated version of the Romberg test can be used, which will provide more information for making a diagnosis.
The pose is used for the following diagnostic purposes:
- if cerebellar dysfunction is possible;
- for possible pathologies of the inner ear;
- if there is a suspicion of disorders of the central nervous system;
- in cases of spinal cord damage;
- if there are disorders of deep sensitivity;
- other neurological diseases are possible;
- possible intracranial inflammatory processes.
How to achieve sustainability?
Try to practice this position for at least five minutes every day, after first checking the correctness of the Romberg pose with the photo above. It is very convenient to do this in front of a mirror, positioning yourself sideways to it, to make sure that the spine is straight and the arms are positioned correctly.
You should try to stretch the crown of your head upward, keeping your spine in one straight line. Pay more attention to the internal tone in the pelvic area: this is where the stability of the entire position comes from, while the pose should not be overly tense and compressed like a spring, it is rather easy composure and concentration.
At first, perhaps, the pose will be difficult and there will be no long-term fixation, or the body will sway or tremble in some areas, but as you get used to it and experience in practice, everything will definitely work out!
Romberg Pose - Results
The Romberg pose in neurology, in addition to determining dysfunction of the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres, gives an assessment of a person’s physical fitness (there are tables and photos):
- if the pose is maintained for more than 15 seconds without tremor, the person is healthy, this is the norm for stability;
- there is a staggering of the body - the indicator is satisfactory;
- holding a pose for less than 15 seconds – unsatisfactory stability;
- the presence of tremor in the patient’s limbs is an indicator of body disorders.
The Romberg test is divided into simple and complex, and in each exercise the results will differ from the previous ones.
The first execution option is for the subject to stand with full support on two legs, with eyes closed and arms outstretched with fingers slightly apart. During research, attention is paid to the duration of stay in a given state, as well as any swaying or voluntary movements of the person.
The second method is more complicated. Involves placing your feet in line with the heel of the first foot touching the toe of the other. The person is with his eyes closed and his arms extended forward.
Read: The role and responsibilities of the midwife in the maternity hospital and at home
The doctor, observing the patient, evaluates the following characteristics of the test:
- stability - the patient stands confidently or staggers, if swaying appears - after what period of time this happened;
- the direction of the patient’s deviation in case of instability - it matters in which direction the person “falls”: to the right, left or back;
- does ataxia (staggering) worsen when closing the eyes;
- whether there is tremor of the fingers, arms, legs or torso, or trembling of the eyelids.
When staggering occurs, the test is considered positive. If the doctor interprets the result as a “negative Romberg test,” this means that no pathology has been identified.
| Age, years | Duration of maintaining balance, seconds |
| 7 | 16 |
| 8 | 21 |
| 9 | 24 |
| 10 | 28 |
| 11 | 30 |
| 12 | 36 |
| 13 | 44 |
| 14 | 48 |
| 15 | 50 |
| 16 | 51 |
| 17 | 52 |
| 18 | 53 |
Unsteadiness in the Romberg position or the presence of tremor may indicate the presence of some disease, therefore, if deviations from the norm are detected, a thorough further examination is required.
We recommend
List of medications for the treatment of epilepsy
The lower test is carried out using two techniques: lying on your back and lying on your stomach. This method is also carried out with eyes closed. The specialist asks the patient to raise his legs 50 degrees from the ground and hold them in this position. Here it is important to determine either the weakness of one leg or the general weakness of both legs, as well as the inability to hold the legs at all.
For complete differentiation, you can help the patient by holding his legs with his hand. The leg that is paretic will put more pressure on the arm.
The upper Barre test is carried out as follows: the patient should extend his arms forward, palms. After such movements, he closes his eyes and holds his hands for thirty to forty seconds.
With minor deviations, a weak hand may simply be slightly off. With more significant paresis, the affected arm bends at the elbow.
Read: What functions do the colorless organelles leukoplasts perform and their structural features
While watching a patient perform the Romberg test, an outside physician must evaluate several important parameters.
- Stability in the Romberg pose - how confidently a person stands, after what time swaying appears.
- The doctor must notice where the patient’s body deviates, back or forward, to the right or to the left, the diagnostic result depends on this.
- It is assessed what happens when the patient closes his eyes, whether instability increases. Do the patient’s fingers, toes, or eyelids tremble while performing the exercise?
What does stagger mean?
Different parts of the nervous system are responsible for how much a person is able to maintain balance in a given position. If, when checking the Romberg pose, loss of balance, staggering, swaying or deviation to the side is observed, then this means that a neurological disease is present.
Situations are possible when the patient loses his balance during the diagnostic process and leans to one side. Such a deviation may indicate a possible lesion of the cerebellar hemisphere, and the side on which the patient fell is taken into account, which indicates precisely the side of the lesion.
Situations are also possible when a person leans back or falls; such a manifestation may indicate possible mental illnesses. But simulation by the patient is also possible, since such behavior is more related to the mental state.
In order to avoid misdiagnosis, doctors who conduct diagnostics pay attention to the patellar muscles.
The difference between a healthy and a sick patient is that when a fall occurs in the presence of a disease, the patient tries to stand, thereby straining the muscles and the kneecaps rise. In cases where simulation occurs, the patient does not tense his muscles, as he does not show any attempts to stand.