What is MRI of the brain based on?
The diagnostic effect of brain MRI is based on nuclear magnetic resonance. In response to the powerful radiation created by the generator, the hydrogen atomic nuclei contained in the tissues line up along the electromagnetic field lines and begin to vibrate. Each atom becomes like a spinning mini-spinning top, emitting energy waves.
Different structures emit different amounts of energy - some give it out more intensely, while others less so. The difference is recorded by a device that takes pictures (slices) in different projections.
To do this, the patient is placed inside a tomograph in which generators maintain a high-frequency electromagnetic field. Special radio emitters generate pulses, and coils record the energy sent by vibrating atoms.
The resulting slice images are combined into a three-dimensional matrix using a special computer program, in which dark or light unhealthy areas are visualized against a gray background.
Features of research in primary school and preschool age
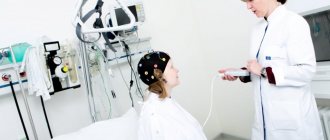
When a child needs an MRI, parents and medical staff may face a number of challenges. It is completely impossible to explain to infants that they should lie quietly for a few minutes, and patients of preschool and primary school age may simply be afraid of the procedure. The feeling of discomfort will be reinforced by the need to remain motionless throughout the entire diagnostic procedure (it takes from 15 to 45 minutes) and the noise caused by the operation of the tomograph. There are several options for how brain MRI is done for children.
The most problematic is MRI of the brain or other organs in newborns. It is not possible to establish verbal contact with such a child, and the slightest separation from parents can be accompanied by a whole storm of emotions. It would be safest to wait until the patient falls asleep, and while he is resting, perform an MRI of the child’s head or other area being examined. However, even special headphones designed to suppress the noise of the device do not always cope with their task. The presence of the mother next to the child during the procedure also does not always help to calm the child. The most effective method is the use of medicated sleep or anesthesia, but under the age of 4 years, the risk of such a procedure is not always comparable to the importance of the information received.
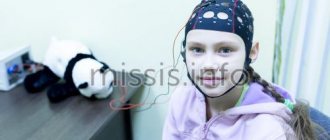
Carrying out an MRI for children aged 5 to 7 years is somewhat simpler. Here the psychological preparation of the child for the procedure comes to the fore. The little patient needs to be explained what will happen to him, why this is all necessary and that there is no pain or danger in the procedure. You should communicate with a child in such a situation as with an adult, only if something is unclear, explain it in a simple, playful way. Medication aids are used only in cases where a small patient is prone to emotional reactions, is overly excited or does not cooperate, and diagnostics are indispensable. In our center, children undergo MRI without anesthesia; we allow parents to be present during the entire procedure to make it easier for the child to cope with stress.
There is practically no difference between how brain MRI is done for children over 8 years of age and for adults. The situation is similar with studies of other organs and systems. At this stage of development, the psyche is already sufficiently formed and does not require special approaches.
Is it worth using anesthesia?
Drug anesthesia is a condition in which the interaction of the nervous system with the environment is suppressed using special drugs. This procedure is necessary during surgical interventions, since it ensures complete elimination of pain. Anesthesia is quite difficult to tolerate even by adults due to nausea and a feeling of dizziness after coming out of it. The development of complications from the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is quite rare, but they should always be remembered in children with diseases of the liver, kidneys and central nervous system. Since the use of anesthesia is associated with certain risks, when it is used during an MRI in children, an anesthesiologist is always present to provide emergency care. The decision about whether children can undergo MRI under anesthesia should be made taking into account all possible risks and benefits derived from the diagnostic procedure.
Medication-induced sleep is somewhat safer. Here the little patient is not put under anesthesia, but simply falls into a deep sleep under the influence of sedatives. The main problem is that most sleeping pills are contraindicated for children under 3 or 6 years of age, and selecting their dosage is somewhat more difficult than the dosage of drugs for the same anesthesia.
Any auxiliary medications should be used only in cases where vital research is impossible without them. If an MRI is required over the age of 5 years, then first of all you should try to come to an agreement with the child. Also, whether anesthesia will be used largely depends on where the MRI is done for children - qualified specialists prefer to avoid any unnecessary impact on the growing body.
Advantages of magnetic resonance imaging over other methods
An MRI examination gives results much more accurately than x-rays, echoencephalography (EchoEG), ultrasound and other diagnostic options. It allows you to obtain maximum data about existing tumors, diseases, post-traumatic and post-stroke changes. Unlike CT and X-rays, in this case the body is not irradiated.
Only soft tissues are visualized in the finished images. The bones of the skull are not visible, so they do not interfere with analysis and decoding.
The contrast agent used in MRI diagnostics is much less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to X-ray contrast agents used for radiography.
Price
Dear patients, on October 9 and 10 there is a 20% discount on MRI!
| Description | Price | Until October 12 | From 21:00-2:00 7:00-9:00 |
| MRI of the brain | RUB 5,400 | RUB 4,590 | RUB 4,050 |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (angiography) | RUB 5,400 | RUB 4,590 | RUB 4,050 |
| Brain MRI with contrast | RUR 11,000 | RUB 10,250 | — |
| Issue of film with photograph | 500 rub.r. | 400 rub.r. | 400 rub.r. |
| Recording a photo on flash | RUR 1,000 | RUR 650 | 600 rub. rub. |
All MRI prices >>>
How does the procedure work?
The patient removes all metal jewelry and takes out removable dentures containing metal.
The patient is placed on a movable table and secured with special belts. This measure is necessary because you will have to lie inside the tomograph, remaining motionless, for a long time.
A device equipped with wires that transmit and receive radio signals is placed on the head. The equipment is quite noisy and tires with constant clicks and whistles. Therefore, the patient’s ears are protected with earplugs. After this, the table slides into the device, and the specialist sits down at the computer, in which the transmitted data is analyzed and processed.
The technique takes pictures, the quality of which depends on the characteristics of a particular MRI scanner. The thinner the visual slices the equipment makes, the more accurate the final images will be. The duration of diagnosis is 20-30 minutes, and when contrast is used - up to an hour.
After MRI diagnostics, you can immediately return to your normal life. No side effects subsequently or during the MRI examination occur, with the exception of an extremely rare allergy to gadolinium salts.
Finished photographs are handed out printed or recorded on a magnetic medium - disk or flash card. It can be sent to email with SMS notification.
- Standard - done without the introduction of contrasting solutions, but at the same time provides a sufficient amount of information.
- With contrast, before which drugs containing gadolinium salts are injected into the vein - gadopentetic and gadoteric acids, Omniscan, Magnevist, etc. These solutions penetrate into the bloodstream and, once in the rays of the MRI scanner, highlight the resulting “picture”. At the same time, the changed areas become better visible, which simplifies decoding. The technique is most often used to detect vascular abnormalities, multiple sclerosis and tumor formations. The dose of contrast agent is selected individually, taking into account weight.
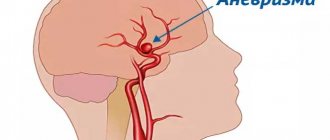
- MR angiography – is performed to assess the condition of blood vessels in atherosclerosis, aneurysms, blood clots and pre-stroke conditions. It is done with gadolinium contrast to show blood flow problems in detail.
- MR imaging of the pituitary gland, an appendage that is an endocrine gland. The pituitary gland secretes hormones responsible for reproductive function, tissue metabolism and the regulation of human growth. An examination is prescribed if an adenoma is suspected - a benign tumor that causes migraine-like pain, hormonal imbalances, gigantism, infertility, obesity and sexual dysfunction. The same method is used to identify malignant pituitary formations that have similar symptoms and are accompanied by a pronounced deterioration in health.
Is it possible to do an MRI with contrast for a child?
Enhanced MRI: benign cyst at the cerebellopontine angle (arrow)
Chelated gadolinium paramagnetic improves imaging capabilities. Children's age is a relative limitation to contrast: if there is a threat to life, the decision to perform an enhanced MRI is made by a council of doctors. Gadolinium allows you to get an idea of the tumors (borders, exact localization, distant metastasis, the presumable nature of the tumor - benign, malignant, growth prospects), features of the blood supply to organs (ischemia, stenosis, vascular malformations, aneurysms, etc.). The dye accumulates in the affected tissues, making the images as clear as possible. General contraindications to the administration of a contrast agent are:
- renal failure with a decrease in glomerular filtration rate less than 30 ml/min;
- polyvalent allergies, including gadolinium intolerance.
For ethical reasons, studies examining the side effects of paramagnetic administration to children have not been conducted. Preparations containing gadolinium are not recommended for use in children under two years of age due to insufficient safety data.
Indications for general anesthesia for MRI
Intravenous or inhalational sedation is only necessary for patients who are unable to hold their body still for long periods of time. Main indications for general anesthesia:
- Claustrophobia is the fear of closed spaces. Such patients, while inside the device, experience panic, which negatively affects their health and makes MRI diagnostics impossible.
- Mental disorders accompanied by unpredictability of behavior and high excitability.
- Uncontrollable involuntary head movements (swaying, shaking, tics).
- Epilepsy and other types of convulsive readiness and seizures - anesthesia is given only intravenously due to the risk of provoking a seizure attack.
- Early childhood. Small children cannot lie still for a long time in an MRI scanner, so light mask anesthesia is indicated for them.
- Severe pain syndrome, in which prolonged stay in one position causes discomfort, cramps, pain and spasms.
Is it safe?
At the beginning of the use of MRI diagnostics in medicine, due to a lack of information, the study was prescribed for health reasons. More than thirty years of experience in the use of magnetic resonance scans has shown that there is no danger to a growing organism: under the influence of the field induced by the device, no biochemical reactions occur, there is no effect on the immune, reproductive systems, brain functions, etc.
There are certain risks associated with anesthesia to ensure the baby's medicated sleep, so electrocardiography (ECG) is first performed, test results and general condition are assessed. During the procedure, the doctor monitors pulse, blood pressure, oxygen saturation and other vital signs.
At the Magnit Center in St. Petersburg, a child over 5 years old will be tested on a doctor’s referral or upon self-referral. It is possible to undergo an MRI of any area of the body at night; discounts will be a pleasant bonus. Diagnostics are carried out using an expert-class Siemens scanner with a field strength of 1.5 Tesla. You can sign up in person, through the contact form on the website or by phone. Late diagnosis of a serious pathological process in a child is life-threatening. Come - we are waiting for you!
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
- Neoplasms or their metastases. Diagnosis is prescribed for persistent migraine-like pain, sudden loss of vision and hearing, auditory, olfactory and visual hallucinations, attacks of confusion, sudden reading and writing disorders, often accompanying cancer pathologies.
- Epilepsy and other diseases manifested by fainting, confusion and convulsions.
- Suspicion of single or multiple cystic cavities filled with fluid, bloody or other contents.
- Possible presence of parasites (cysticercus and echinococci) carried through the vascular bed with the bloodstream into the head.
- Inflammations – meningitis, encephalitis, arachnoiditis, myelitis. Lesions caused by infections - measles, herpes, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, tick-borne encephalitis.
- Rehabilitation after stroke, traumatic brain injury and surgery. Using magnetic resonance diagnostics, the doctor evaluates the effectiveness of the treatment and predicts long-term results.
- The likelihood of developing multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and other degenerative processes.
- Children are examined for congenital pathologies and hydrocephalus.
With all these diseases, life and health directly depend on a timely diagnosis. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of brain disorders in yourself or your child, you need to come to the clinic and be examined.
What the results show
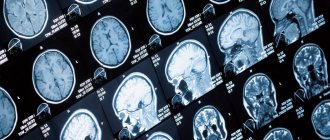
MRI studies, especially those performed with contrast, reveal numerous pathological processes. In the sections, compactions, cystic cavities, and hematomas (collections of blood) are visible in detail. Scars, parasites and their cysts, foci of degeneration, sclerosis and inflammation are identified.
Vascular changes are diagnosed, manifested by impaired patency, narrowing or dilation of blood vessels, the appearance of aneurysms (protrusion of walls) and thrombosis.
The degree of tissue damage in traumatic brain injuries, hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes is determined. The affected areas look lighter and are visible even if they are small in size and have sparse neurological symptoms.
Congenital defects are determined - underdevelopment and hypertrophy of the organ, small and incorrectly located gyri, cysts, holoprosencephaly - lack of division into hemispheres. Hydrocephalus is detected - accumulation of fluid in the ventricles, which with this anomaly are greatly enlarged.
Pathological areas and neoplasms appear as dark or lightish spots of various sizes and shapes, standing out against a grayish background. Oncological seals, especially malignant ones, have blurred, uneven edges and surrounding areas of necrosis.
MR diagnostics is recommended periodically for everyone who has been treated for oncological pathologies of any location. It detects metastases, which usually accompany cancer recurrence.
Contraindications
- Installed pacemakers and other electronic devices that are disrupted by the surrounding electromagnetic field.
- Fixed dentures with metal elements present in the mouth, crowns containing metal, braces and other orthodontic structures. The metal they contain is heated by a magnet and deteriorates, damaging surrounding tissue.
- Tattoos applied to the skin, made with metal-containing ink. Due to the heat caused by the electromagnets, burns may occur in these areas. In the absence of information about the pigment. used when applying a tattoo, it is better not to risk it and do a CT scan, ultrasound or x-ray. Examination is also prohibited for any metal piercing that cannot be removed.
- MRI examinations with contrast are not performed during pregnancy or if contrast agents are intolerant. Such an examination is not prescribed for severe kidney pathologies that make it difficult to eliminate gadolinium.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe and highly informative procedure that detects pathologies in the early stages. Therefore, in case of migraine-like phenomena, coordination problems, a sharp decrease in hearing and vision, fainting, or progressive memory deterioration, you must definitely go to the clinic and be examined. The price of MRI diagnostics is low and quite affordable for Muscovites and residents of Moscow Region.
Get an MRI of the brain >>>
How often can children have an MRI?
The doctor decides how often to diagnose the baby.
A native (non-contrast) study can be performed on a patient over 5 years of age an unlimited number of times - as required by the medical situation. Enhanced MR scanning is used in oncology practice as the main diagnostic tool for identifying early tumor relapse and assessing the effectiveness of treatment. The optimal interval between MRIs is 6 months.
For young patients for whom it is impossible to perform a magnetic resonance examination without anesthesia, it is preferable to choose ultrasound, neurosonography, etc. for dynamic monitoring.