Diagnostics
Suspicion of a lacunar infarction appears only if the patient suffers from arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus or diseases associated with cerebral vessels. Due to the difficulties caused by the specificity of symptoms, it often takes a very long time to make a final diagnosis. First, the neurologist conducts a survey, and then necessarily prescribes the following examinations:
- Laboratory blood tests;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
Modern medicine makes it possible to accurately and quickly identify any disturbances in the functioning of the body. However, in the case of lacunar stroke there are a number of problems:
- Consequences of the disease
- Classification
- Treatment of ischemic stroke of the brainstem and lacunar
- Rehabilitation period
- Treatment of lacunar stroke
- Treatment tactics
- Features of the development of lacunar stroke
- Danger and consequences
- Cerebral infarction (lacunar infarction)
- Clinical picture
- 5 Causes of lacunar stroke
- Forecast and consequences
If the cause of a stroke is an increase in blood pressure, then there may be cases where the deviation from the norm is so insignificant that doctors do not take it into account. Therefore, they begin to look for other reasons why the patient experiences certain symptoms
At this time, the patient’s condition may worsen, which, as it later turns out, was caused by circulatory disorders associated with increased blood pressure. The size of the gaps can be extremely small, which is why even modern equipment will not allow them to be noticed during the first study. This is why sometimes doctors have to perform a CT or MRI again. Gaps may not be identified immediately. This is due to the fact that on CT or MRI they appear in real form only a week after formation. Until this point, they are either visible in a much smaller and lower-density state than they actually are, or not visible at all. Symptoms appear gradually. Even after a serious circulatory disorder, the patient may not have any external signs of a stroke. The condition usually worsens over several days. For this reason, there are great risks of not identifying the disease at all until the patient’s health deteriorates critically. Angiography may not show any abnormalities that could indicate a problem with the blood vessels in the brain. There is no guarantee of their detection even with repeated studies.
All these problems make lacunar ischemic stroke a particularly dangerous phenomenon. Only the highest quality and responsible examination will identify violations in the first days. But even with the work of highly qualified doctors and the availability of modern equipment, there is no guarantee of a quick correct diagnosis.
Diagnosis of cerebral infarction
The doctor may suspect a lacunar cerebral infarction based on the patient’s complaints. But a complete picture of the disease can only be obtained using the following research methods:
- First of all, this is computed tomography, which allows you to obtain a virtual multi-level slice of the brain;
- General laboratory analysis of blood and urine, as well as analysis of blood biochemistry, the presence of glucose in it, determination of cholesterol levels, coagulation indicators;
- ECG to detect heart rhythm disturbances;
- Ultrasound duplex scanning allows you to analyze the condition of the vessel walls, the presence of cholesterol plaques on them, and congenital defects.
Consequences of the disease
Brain damage, the consequences of which can be very different, due to lacunae or ischemia, most often provokes a relapse of the disease. But most often, lacunae lead to disturbances in the patient’s mental state; the following are observed:
- loss of memory, most often partial, for the names of relatives and friends, etc.;
- nervousness, tearfulness and hysteria prevent a person from adapting to society;
- complete or partial disorientation in location and time, sometimes patients fall into childhood or youth.
Such people require constant monitoring and self-care, because... in this state they can easily die or injure themselves. Death from the disease itself is extremely rare, and most often occurs with repeated lacunar stroke.
This is caused by the lack of therapy and preventive measures. Despite the fact that the prognosis after this disease is most often positive, not a single doctor will say how long his patient will live.
And this is connected not only with how the patient will control his illness, but also with how the lacunae affected the cortical structure.
Preventive measures for lacunar stroke do not differ from those recommended for any other type of ischemia:
- Remove excess stress, both physical and mental, focus on feasible types of sports activities, giving preference to walking.
- Work on self-hypnosis, yoga classes. It has been proven that regular yoga classes lead to normalization of the entire body.
- Bringing weight to standard values, adjusted for age.
- Building a diet on a diet against sclerosis with a complete rejection of foods that provoke it.
- Strict control of blood pressure indicators.
- Timely detection of hypertension and its proper treatment.
- Completing a full course of rehabilitation if you have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- When the prothrombin index increases, use special drugs aimed at reducing it. It is imperative to control this process so as not to provoke health problems, which can be caused by excessive thinning of the blood.
- If you experience any symptoms that indicate problems with the brain, immediately consult a doctor for help.
- Rest. It must be regular and complete. You cannot burden yourself with either physical activities or mental stress. It is the latter that becomes the cause of all diseases, including lacunar stroke.
Therefore, it is so important to quickly respond to the signals that your body sends you. Due to the fact that the risk group is elderly people, their relatives should be as attentive as possible to them, monitor changes in their behavior and health
golovaum.ru
With lacunar cerebral infarction, the consequences are different. They depend on the following factors:
- areas of brain damage;
- size of the infarct area;
- timeliness of diagnosis and adequacy of care.
The most common consequences of lacunar stroke are:
- memory impairment;
- development of dementia;
- disruption of the process of defecation and urination;
- hypersalivation;
- stiffness of movements;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- speech disorder.
Often the mental state of the affected person changes. He becomes whiny and hysterical. All these changes, unlike a major stroke, do not pose a threat to life. However, the quality of life deteriorates significantly. It sometimes takes years to restore motor functions and speech.
Complications after a lacunar cerebral infarction can be very diverse. They will depend on the following range of factors:
- Areas of brain damage;
- Size of the damaged area;
- Timeliness of diagnostic measures and adequacy of treatment.
- The consequences of lacunar infarction can lead to such negative complications as:
- Coordination disorder;
- Intellectual impairment such as dementia;
- Decreased memory;
- Decreased ability to analyze.
- Problems with urination and defecation;
- Speech defects;
- Changes in a person's mental state. The patient is characterized by tearfulness, hysteria, and depression.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The clinical picture of lacunar cerebral infarction is typical of mild or transient symptoms.
Although 2/3 of lacunar infarctions occur without warning signs, warning signals are present in approximately 1/3 of cases. The following symptoms are typical for lacunar infarction:
- loss of muscle strength or sudden onset of awkward movements of a body part, especially unilaterally (on the face, upper or lower limb);
- numbness or other unusual sensations in some parts of the body, especially if it is on one side;
- bilateral or unilateral complete or partial loss of vision;
- inability to speak or understand speech;
- loss of balance, uncertainty when walking, unexpected fall;
- any other sudden temporary deterioration in health (dizziness, headache, difficulty swallowing, sudden memory loss);
- unusually severe, sudden headache;
- unexplained disturbance of consciousness, convulsions.
Later the disorder may manifest itself as psychological changes, mainly:
- slowing down of mental processes;
- decreased memory, especially in relation to fresh impressions (old memories are retained in memory);
- loss of interests;
- apathy;
- depression.
Diagnostics:
- taking anamnesis;
- physical examination;
- clinical picture;
- neurological examination;
- cardiac examination;
- CT, CT angiography;
- MRI;
- ECHO;
- Ultrasound of the carotid artery;
- EEG;
- fundus examination.
Classification
Clinical classification is based on clinical symptoms and is discussed in the section on symptoms of lacunar infarction.
In the development of the disease there are:
- the most acute period is the first 3 days;
- acute – 28 days;
- early recovery – the next 6 months after suffering a circulatory disorder;
- late recovery – for 2 years.
Due to mild symptoms and the absence of pronounced motor, speech and sensory disorders, it is very difficult to describe the features of each interval. Therefore, this division is of secondary importance.
Treatment of ischemic stroke of the brainstem and lacunar
The most common brain disease that leads to disability and death is stroke. Stroke is often caused by blockage of blood vessels. This is caused by elevated cholesterol levels. If you want to be healthy and not encounter this disease, watch what you eat.
Ischemic stroke treatment
Treatment in the acute period is the most important, then treatment of ischemic stroke proceeds as follows:
- normalize respiratory function normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system correct blood pressure antioxidants vitamins neuroprotectors
After the rehabilitation period, regular consultations and examinations with the attending physician and a visit to the sanatorium are prescribed.
Treatment of ischemic stroke of the brain is quite serious, since the flow of blood to the brain is stopped. The first thing they do is hospitalize the patient. They are already conducting a thermogram, which will help determine the degree of brain damage and the type of stroke, and based on this they make a prescription for stroke treatment.
After treatment and discharge, the patient continues to undergo rehabilitation, since it is necessary to eliminate the consequences of a stroke as much as possible, restore the functions of the brain and other affected parts of the body.
Ischemic stroke left side treatment
Each side of the brain is responsible for a specific area of human life.
Right hemisphere for:
Which hemisphere is affected, those abilities are distorted, speech and many other visible signs of a stroke are often affected.
Treatment of ischemic stroke drugs
Drug treatment of ischemic stroke:
- Anticoagulants - nadroparin, heparin, enoxyparin, daltoparin
- Neuroprotectors - glycine, piracetam, cerebrolysin, pentoxifylline, vinpocetine, calcium channel blockers and instenon
- Recovery - ginkgo biloba, vinpocetine, pentoxifylline, piracetam, phenotropil
In principle, these drugs are the standard treatment for ischemic stroke.
Drugs for the treatment of ischemic stroke:
Ischemic stroke treatment and recovery are interconnected, since after hospitalization the treatment does not end, there is also a course of physical therapy and massage.
Stem ischemic stroke treatment
A brain stem stroke is one that occurs in the brain stem.
Causes of brainstem stroke:
- hormonal contraceptives, taken for a long time
- control heart rate
Ischemic stroke symptoms, treatment, symptoms:
- pale skin or red face
- blood pressure increases
- breathing and blood circulation are impaired
Repeated ischemic stroke treatment prognosis In half of the cases the disease recurs, but in 70% it leads to death. You need to monitor your health before a relapse occurs.
Lacunar ischemic stroke treatment
Lacunar ischemic stroke provokes heart attacks.
Often in the evening I had a headache and high blood pressure, and in the morning the first symptoms appeared - fatigue, numbness, disorientation.
Lacunar ischemic stroke can be treated well; you need to start treatment on time and remember that lifestyle is the key to recovery.
Rehabilitation period
During the rehabilitation period, a whole range of measures is carried out, both medical and pedagogical, legal, social and psychological. All of them are aimed at restoring lost functions as a result of a lacunar stroke.
Principles of the rehabilitation program:
- If rehabilitation measures are started as early as possible, for example, from the first days of the onset of symptoms of the disease, recovery occurs much faster and more fruitfully. This is an excellent chance to avoid possible secondary complications, such as contractures, congestive pneumonia, thrombophlebitis and others.
- Rehabilitation should be carried out only under the supervision of specialists. If events are organized incorrectly, the chance of full recovery will be significantly less.
- Recovery requires the participation of a physical therapy methodologist, a neurologist, a physiotherapist, a psychotherapist, an occupational therapist and a speech therapist.
- The rehabilitation process involves the presence and support of the patient’s loved ones. It is best to entrust the patient with the most basic household chores on weekends or in the afternoon.
Rehabilitation after stroke
The consequences of lacunar stroke include both motor and psychological disorders, so the rehabilitation of such patients must be comprehensive. It needs to start as early as possible and be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
Motor rehabilitation is aimed at eliminating negative consequences from the musculoskeletal system. Its goal is to restore full range of motion. For this use:
- special physical exercises;
- electrical stimulation of the neuromuscular system;
- passive gymnastics;
- training on simulators.
The prognosis for early initiation of motor rehabilitation is positive. In most patients, the amount of motor activity in the affected limb increases.
Speech impairment is a common consequence of lacunar stroke. For the rehabilitation of such patients:
- conduct classes with a speech therapist;
- communicate with family.
The absence of speech isolation is the most important factor for positive rehabilitation. It significantly improves the prognosis and increases the likelihood of restoration of speech understanding and production.
Social rehabilitation is achieved by creating a favorable microclimate in the family, gradually involving the patient in household chores, and interesting hobbies.
Treatment of lacunar stroke
Patients with lacunar infarctions are treated in neurological departments. They are necessarily prescribed antihypertensive therapy, drugs to restore nervous tissue, and prevention of thrombosis and embolism.
Antihypertensive therapy includes the prescription of ACE inhibitors (enalapril, lisinopril), diuretics (indapamide, furosemide), vasodilators (nifedipine, diltiazem), etc.
Patients with lacunar stroke need constant monitoring of blood pressure levels, but it is important that it does not become too low
In cases of severe atherosclerotic damage to the carotid and vertebral arteries, as well as in patients over 75 years of age, the pressure should not be quickly reduced, as this can cause even greater disruption of blood flow in the brain.
Antithrombotic therapy is considered an important stage in the treatment of cerebral infarctions. Patients are shown aspirin, heparin, clopidogrel. With the cardioembolic mechanism of stroke, when the cause is blockage of the perforating arteries by fragments of blood clots or deposits on the heart valves, anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin) are necessarily prescribed.
To prevent subsequent lacunar strokes, which tend to recur, aspirin up to 325 mg is prescribed. If the patient does not tolerate aspirin well, then its dosage is reduced to 50 mg per day and treatment is supplemented with dipyridamole at a daily dose of 400 mg in two doses.
Aspirin is indicated in the presence of microangiopathy, a combination of brain pathology with cardiovascular lesions. With concomitant lipid metabolism disorders, diet and lipid-lowering drugs (statins) are prescribed.
To improve microcirculation in the brain tissue, nicergoline, vinpocetine, and nootropil are used. It is advisable to prescribe neuroprotectors (akatinol, magnesium sulfate), B vitamins. If depression develops, antidepressants (fluoxetine, amitriptyline) are indicated.
In addition to drug therapy, patients undergo rehabilitation courses to restore motor function, sensitivity, speech, etc. Massage, physiotherapy, special exercises for paresis, and speech training help. You can restore memory and intellectual abilities by solving problems, memorizing poems or short texts.
Patients with cardiovascular pathology predisposing to thrombosis and embolic complications are observed by a cardiologist, who always prescribes aspirin and, if necessary, anticoagulants. If atherosclerosis of the carotid and vertebral arteries is diagnosed, then surgery may be needed to improve blood flow.
After suffering a lacunar stroke, patients are prescribed maintenance therapy with neuroprotectors, vitamins, and vascular medications, which are prescribed in courses 1-2 times a year.
The prognosis after a lacunar infarction is considered favorable, since the resulting neurological disorders regress quite quickly, and a complete restoration of impaired functions is possible
At the same time, this pathology should be given due attention by a neurologist, since repeated heart attacks occur in at least every tenth patient, and in a third, after a few years, signs of vascular encephalopathy with intellectual deficit and mental disorders increase
According to some data, after 10 years only 30% of patients remain alive, most of whom have severe signs of dementia. To avoid such developments, you need to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and take measures to prevent circulatory disorders in the brain.
2012-2020 sosudinfo.ru
Display all posts with the tag:
Stroke
Go to section:
Diseases of the brain and blood vessels of the head, cerebrovascular diagnostics, anatomy, pharmacology
Recommendations to SosudInfo readers are given by professional doctors with higher education and specialized work experience.
One of the leading authors of the site will answer your question in the form below.
Treatment tactics
For adequate therapy and in the future for the purpose of preventing recurrent cerebrovascular accidents, patients are prescribed aspirin to reduce the aggregation of blood elements (sticking together and forming blood clots) and improve its fluidity. The most acceptable dose is considered to be 75 mg of acetylsalicylic acid, produced specifically for these purposes.
If it is impossible to take aspirin due to intolerance or side effects, it is possible to replace it with dipyridamole at a dose of 200 mg daily or 75 mg of clopidogrel. Dosages are specified and regulated by specialized specialists.
Normalization of blood circulation is achieved by prescribing drugs that improve microcirculation. The optimal choice is nicergoline, vinpocetine, pentoxifylline. First, a course of intravenous drips is carried out, followed by a transition to long-term use of tablet forms.
At the same time, neurotrophics are recommended - medications that optimize the supply of oxygen to the brain and stimulate recovery. These are Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, citicoline and ginkgo biloba preparations (memantine, tanakan, bilobil).
With the development of signs of dementia and the formation of a lacunar state, anticholinesterase drugs and precursors of acetylcholine, a biologically active substance involved in the conduction of impulses along nerve trunks, are prescribed. These are prozerin, neuromidin, galantamine in the required dosages.
With parkinsonism, the patient needs to take specific drugs to reduce tremors (cyclodol, amantadine).
To restore mental abilities and reduce the manifestations of dementia, it is necessary to use the patient’s intelligence as much as possible, forcing him to memorize poems, allowing him to solve simple mathematical problems.
Since the leading cause is hypertension, its adequate reduction can be considered as one of the links in the treatment process. The therapist and cardiologist select an adequate dose and combination of drugs. When prescribing a correction regimen, the patient’s age and the presence of significant concomitant diseases are taken into account: diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease.
Features of the development of lacunar stroke
Lacunar stroke is a type of ischemic brain injury that occurs in people suffering from arterial hypertension and related vascular changes. Elderly people are the main risk group. This type of stroke is characterized by pathological changes in small-caliber perforating arteries. A characteristic feature of a lacunar stroke is the formation of lacunae, that is, small cavities, in the depths of the brain.
Lacunae are round or irregular in shape and range from 1 to 20 mm in diameter, although formations larger than 15 mm are rare and are considered gigantic. Inside these cavities there is blood or plasma with fibrin. Their walls look like a bag, which can rupture when exposed to certain factors. Foci of necrosis are located deep in the gray matter; damage to the cerebral cortex does not occur even in the event of minor bleeding. A person can live with small gaps in the brain without even realizing it until histological analysis is carried out. All people associate stroke with severe neurological disorders, leading to paralysis and disruption of the patient’s usual life activities.
But there are types of pathology during which external symptoms do not appear, brain disorders are weak and characterized by regression. The person continues to live his usual life, unaware of the changes that have occurred. These types include lacunar ischemic stroke, which is called silent.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for lacunar cerebral infarction, in contrast to other forms of ischemic stroke, is most favorable. In a single case of the disease, almost complete restoration of all functional capabilities of the body occurs. Residual sensory or motor impairments bring some discomfort, but you can learn to live with it.
In case of relapses, a lacunar state of the brain can be diagnosed. This complication is observed in the majority of patients with vascular dementia. The patient often withdraws into himself and falls into a depressive state.
After an attack of illness, a person experiences problems with memory, often does not remember the address of residence, does not recognize relatives, is incapable of analyzing situations, and becomes sloppy.
Danger and consequences
When a patient is diagnosed with a single case of lacunar stroke, the prognosis for him is often favorable. In most cases, the victim completely recovers impaired brain functions, and only some patients may still experience partial impairments of sensitivity or motor function.
If a stroke relapse occurs, then certain negative consequences are possible, for example, a lacunar state of the brain (not uncommon in people with vascular dementia). In addition, the formation of lacunae in the area of the brain stem is especially dangerous, since this is where the respiratory and cardiovascular centers are localized.
If we talk about life prognosis, then the mortality rate as a result of lacunar stroke is only 2%, but this percentage increases with a second attack. However, it is quite difficult to say anything about life expectancy in this case. Much depends on the age of the person, the location of the pathological foci, the severity of concomitant ailments, as well as the timeliness of the assistance provided.
Consequences and prognosis
It was previously thought that lacunar infarction did not leave permanent damage to brain tissue, but recent studies show that 50% of people suffer from complications.
The consequences depend on the degree of damage to the brain tissue, i.e. on how quickly blood flow in the affected vessel can be restored. This ensures that the area of the brain that is not damaged is preserved.
Repeated lacunar infarction leads to the following consequences:
- Parkinson's syndrome;
- dementia, organic psychosyndrome (lacunar dementia);
- motor disorders.
The clinical spectrum of consequences varies from the person returning to normal life (without any disability) to coma, death. Less serious consequences include slight discomfort when moving one arm or leg, or loss of sensation. These disorders can be stopped or eliminated through rehabilitation.
Serious violations:
- plegia (complete paralysis) of one limb;
- hemiplegia (complete paralysis of the right or left half of the body);
- speech disorders (both the ability to speak and the ability to understand);
- inability to read, write;
- intellectual-mnestic disorders;
- various types of consciousness disorders.
If a patient develops consequences after a lacunar cerebral infarction, an important part of the therapeutic course is rehabilitation treatment under the guidance of a specialist. The goal of rehabilitation is to ensure the restoration of the greatest possible number of functions of the affected part of the brain.
There are various programs to improve speech, speech therapy, impulse rehabilitation; patients explore alternative movements that provide maximum self-sufficiency.
Cerebral infarction (lacunar infarction)
One of the types of cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke) is lacunar infarction, which is a small (up to 15 mm in diameter) brain damage that occurs when local blood circulation and gas exchange are disrupted. The reasons for this situation are varied and not fully understood, but most often it is blockage of supply vessels as a result of changes in their walls (atherosclerosis, inflammation), emboli (blood clots, fat droplets, bacterial colonies, etc.). Most of them are found in the periventricular region, basal ganglia, and thalamus - the central, deep structures of the brain. Lacunar infarctions account for 20-30% of all strokes.
Lacunar infarction can occur at any age, but the likelihood of its occurrence increases with age and reaches its maximum after 85 years. More often, cerebral circulatory disorders occur in men. The most significant risk factors for the occurrence of lacunar cerebral infarctions are:
- hypertonic disease,
- diabetes,
- chronic renal failure,
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis,
- abnormalities in the circulatory system and heart defects,
- rheumatism,
- cardiac arrhythmias,
- disorders of the blood coagulation system, blood diseases.
Clinical picture
Clinical symptoms of cerebral infarction may be insignificant or distinct, but short-lived. This depends on the location of the lesion in the central nervous system. More often it is represented by mono- or hemiparesis, disorders of statics and coordination of movements, syndrome of speech disorders and memory. General cerebral symptoms (lethargy, lethargy, confusion, headache, nausea and vomiting) are usually absent.
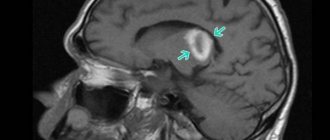
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most preferred method in determining the location, and most importantly, in assessing the stage of development of the ischemic process. In the acute phase, the most information is carried by diffusion-weighted images (abbreviated as DWI) - images obtained using a specialized pulse sequence provided in expert-class MRI scanners, which we use in the study of all patients without exception.
Using DWI, you can see a minimal change in the diffusion (speed of movement) of fluid in brain tissue at the molecular level, which is the first sign of ischemic brain damage. In addition, when examining the brain of a patient with suspected lacunar infarction (as in all other cases), we use the entire set of pulse sequences that comply with the international standard to identify possible associated changes.
The patient is 32 years old. After visiting a neurologist, she went to the MRI room to rule out systemic damage to the central nervous system with a preliminary diagnosis of transient ischemic attack.
When scanning the brain in several modes, a lacunar infarction with a diameter of 7 mm was discovered in the cortical parts of the left parietal lobe. An acute infarction is clearly visible on DWI (a pulse sequence available in expert-class tomographs), but is poorly visible in a mode with signal suppression from free fluid.
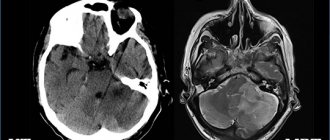
A correct and timely diagnosis, including taking into account cause-and-effect relationships in the development of the pathological process, which is significantly facilitated by the MRI examination method described above, will predetermine the tactics of treatment measures.
After treatment, the patient's condition improved. On MRI after 3 months, positive dynamics are noticeable.
Detection of such changes is possible only with high-field magnetic tomographs of 1.5 T or 3 T, and also requires sufficient research time.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic has a Philips Achieva 1.5T high-field tomograph, and we have an individual approach to each patient.
Registration for an MRI examination is carried out by specialists, and the examination lasts as long as necessary.
To sign up for the study, as well as find out more information about MRI, please call: 8 (495) 304-304-9.
Diseases that increase the risk of cerebral infarction
The following causes of lacunar cerebral infarction are distinguished:
- Constant high blood pressure, chronic hypertension. The disease can occur both against the background of arterial crises and with stable indicators.
- Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries. It can occur as a result of an improper diet containing animal fats. With this disease, plaques form on the vascular walls, obstructing the flow of blood.
- Diabetes.
- Tendency to form blood clots.
- Infection of brain tissue.
- Systemic vasculitis.
- Congenital features of brain tissue.
- Previous myocardial infarction.
Smoking, which causes spasm of blood vessels, as well as obesity are also risk factors.
Clinical picture
In most cases, the attack can be sudden, very quickly leading to blockage of the arteries, but it can last up to five days. Precursors may include ischemic attacks that cause disruption of cerebral circulation in small cerebral arteries.
During an attack, you may experience high blood pressure and an irregular heart rhythm. Single cysts - lacunae do not lead to paralysis of the body. Detection of the lacunar form of cerebral infarction is complicated by the implicit manifestation of symptoms:
- Impaired motor skills are expressed in the inability to move the limbs; they become less sensitive.
- Loss of coordination. The patient may complain that everything is floating before his eyes, there is an unsteady gait and disorientation.
- The lacunar form of the disease is characterized by neurological disorders, expressed in the deterioration of memory, the ability to analyze, there is no logic of reasoning, and other processes of the brain are disrupted.
To immediately contact a doctor, one of the following symptoms of a stroke is sufficient:
- A sharp manifestation of weakness in the legs, fainting, loss of consciousness;
- Distortion of the face, numbness of half the body, limbs, impaired skin sensitivity;
- Difficulty in speech and impairment of its perception;
- The patient begins to feel dizzy and finds it difficult to maintain coordination of movements;
- Severe pain in the head appears;
- Cramps, increased muscle tone.
The disease can occur in the form of a micro-stroke or without clinical manifestations at all. It can develop at any age. Cases of the disease have been described in patients who have just turned 25 years old.
Features of the pathology:
- stroke develops only against the background of hypertension;
- there are no headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, loss of consciousness or disturbances thereof;
- neural symptoms increase gradually over 2-48 hours (usually the patient’s disturbances develop during night sleep, and in the morning he wakes up with symptoms of a stroke);
- the prognosis for this disease is favorable; after an attack, complete or partial restoration of brain function is observed;
- examination of cerebral vessels using contrast agents does not show any abnormalities; computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can reveal small foci of low density, but not always, especially if the infarction is small.
Doctors describe about 20 clinical syndromes that can be observed with the development of lacunar stroke. The following are most often diagnosed:
- The isolated motor variant is the most common and occurs in 60% of patients. Lacunae form within the capsule and pons. The patient develops paralysis of one half of the body, usually the limbs, sometimes the face. Plegia is observed on the side opposite to the lacuna. No further neurological symptoms develop.
- The isolated sensitive variant is observed in almost 20% of patients. The lacunae in this case are localized in the ventral thalamic nerve ganglion. Disturbances of all types of sensitivity develop: temperature, nociceptive, tactile, muscle-articular. Manifestations of the disease can involve the head, arms, legs and torso. Typically, after what period sensitivity is fully or partially restored.
- Atactic hemiplegia develops when pathological foci appear in the capsule and pons of the brain. Occurs in 12% of patients. The patient experiences muscle hypotonia in the arms or legs, pyramidal disorders, and impaired coordination of movement on the side of the injury.
- Dysarthria and clumsiness of the hands when moving are observed in 6% of patients; pathological foci form in the pons of the brain. The patient has a speech impairment; on the one hand, paralysis of the limbs and head may develop.
The following syndromes are also often diagnosed:
- dyskinesia;
- false bulbar syndrome;
- parkinsonism syndrome;
- forced gait in small steps;
- urgency to urinate, incontinence;
- hemiparesis and loss of sensation of one half of the body.
With the development of a lacunar stroke, there is no disorder of consciousness or vision, systemic impairment of formed speech (aphasia), or other symptoms of damage to the cerebral cortex.