Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
Intracranial hypertension (ICH)
is a syndrome of increased intracranial pressure due to various causes. The condition can be life-threatening, so full diagnosis and treatment in the neurological department of the hospital is necessary.
Reasons for development
Due to the strength of the skull bones, any formation or fluid increases intracranial pressure.
The most common causes are the appearance of space-occupying lesions in the brain (tumor, abscess or hematoma). The condition threatens a person’s life, since the respiratory or vascular centers may be damaged as a result of compression. This will be fatal. Ischemia of cerebral vessels can cause a stroke.
An increase in brain volume due to tissue swelling or impaired fluid outflow also causes an increase in pressure. Insufficient oxygen supply to cells and their death due to hypoxia in various diseases is a possible cause of the development of ICH.
Changes in hormonal status, taking medications, especially antibiotics and hormones, and severe kidney disease can cause the development of ICH. It may result from complications after surgery or infections.
Intoxication of the body with heavy metals or traumatic brain injuries can also lead to the occurrence of this pathology.
Osteopathy as an auxiliary method in the treatment of intracranial hypertension
In most cases, the condition can be alleviated by treatment with an osteopath, who, using manual techniques, returns the vertebrae to their natural position and relieves bone tension, and with it the symptoms. As a result, blood flow in the vessels of the brain is restored, stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull is eliminated and tension in the skull is relieved.
The use of techniques acts similarly to drugs with a diuretic effect, excess cerebrospinal fluid is eliminated naturally and intracranial pressure, its symptoms are normalized.
The duration of treatment and the duration of sessions are set by the doctor depending on the patient’s condition and related factors. As a rule, symptoms disappear or become significantly weaker after just a few treatments.
The combination of osteopathic therapy with other treatment methods can achieve stable remission and significantly improve the quality of life.
Symptoms
Cephalgic syndrome: patients are bothered by a constant headache without clear localization, especially in the morning.
There may be dizziness, nausea, or vomiting. Often there is depression of consciousness up to coma. Ophthalmological syndrome: upon examination, the doctor discovers congestive changes in the fundus with hemorrhages. Papilledema is noted. Patients note loss of visual fields or the appearance of dark circles.
Focal symptoms include bilateral damage to the abducens nerves. Clinically, this is manifested by convergent strabismus. The progression of this condition is dangerous due to displacement of brain structures and herniation of the brainstem. This will cause breathing and heartbeat to stop.
Read also
Myelitis
Myelitis is a neurological pathology characterized by inflammation of the gray and white matter of the spinal cord, which leads to damage to myelin (the substance that forms the sheath of nerve fibers) and the axon (the process...
Read more
Weakness and numbness in the arm and leg
The appearance of general muscle weakness and numbness in the body, arm or leg is a very serious syndrome, and if it occurs, you should consult a neurologist as soon as possible. Connected…
More details
Rehabilitation after stroke
It is very important to begin rehabilitation after a stroke as early as possible, since further recovery and the ability to avoid disability depend on this. For rehabilitation after a stroke in the clinic “First...
More details
Intracranial hypertension on MRI
Intracranial hypertension is an increase in intracranial pressure. Normal intracranial pressure is 15 mm Hg. When blood pressure doubles, a stroke occurs. At a pressure of 50 mm Hg, the patient can...
More details
Pinched nerve
This morning you arrived at your country house. While taking out a heavy and large bag of tools from the trunk of your car, you suddenly felt a very strong, shooting pain in your lower back on the right side. Raise...
More details
Diagnostics
To begin with, a neurologist collects complaints and conducts an examination.
Based on its results, indications for instrumental diagnostic methods are determined. With their help, you can clearly see the cause of your symptoms and make a diagnosis. The diagnostic standard is a CT or MRI of the brain. This method allows you to see tumors, hematomas and other formations inside the skull that can cause ICH. You can also evaluate the condition of the optic nerves and ventricles of the brain. An ophthalmologist must examine such patients to identify changes in the fundus.
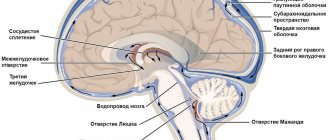
Intracranial pressure disorders
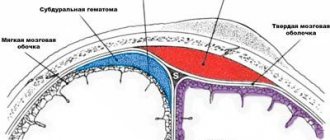
The relative closedness of the cranial cavity leads to the fact that a decrease or increase in the volume of its contents is accompanied, respectively, by intracranial hypotension or hypertension. With intracranial hypotension, the cerebrospinal fluid pressure is below 100 mm of water column, with hypertension – above 180–200 mm of water column.
1) Intracranial hypotension. It occurs for a number of reasons. The main one is the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, or liquorrhea (Latin liquor - liquid; Greek rheo - flow), with fractures of the skull bones.
Especially often, liquorrhea occurs with fractures of the ethmoid bone and the pyramid of the temporal bone, as well as the bones of the base of the skull, in which both layers of the dura mater are torn, followed by the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid through the nose. With a fracture of the ethmoid bone, liquorrhea from the nose is observed. When the pyramid of the temporal bone is fractured, cerebrospinal fluid penetrates into the tympanic cavity of the middle ear. If the eardrum is damaged, cerebrospinal fluid leaks from the ear. If it is intact, the cerebrospinal fluid enters the Eustachian (auditory) tube, which connects the middle ear cavity with the nasopharynx. From the auditory tube, the cerebrospinal fluid enters the nasopharynx, and is then released through the nose and partially swallowed.
Another cause of liquorrhea is medical manipulation: removal of a significant amount of cerebrospinal fluid during puncture of the ventricles of the brain or liquor tanks, as well as a technical error, that is, damage to the dura mater with a needle that is too thick. The danger of liquorrhea is that the risk of infection of the brain and its membranes increases significantly.
With intracranial hypotension, the state of the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain—the cerebrospinal fluid “cushion”—changes. In this case, a change in the tension of the vessels and nerves that perform the function of “anchor” formations occurs, as well as irritation of the meninges.
Clinical manifestations of liquor hypotension:
- persistent diffuse headache occurs, especially intense in the back of the head (“drainage” or “puncture” headache, if it is associated with cerebrospinal fluid sampling);
- headache intensifies with rapid turns of the head, walking (“every step hits the head”), moving from a horizontal to a vertical position;
- headache is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, unsystematic dizziness (uncertainty when standing, moving), and a feeling of “fog” before the eyes. If the patient lies in bed for some time with the leg raised, the headache decreases;
— lethargy, apathy, increased fatigue, impaired concentration, and a tendency to increase heart rate (up to 85–100 beats per minute) are also characteristic;
- mild signs of meningeal syndrome may be detected - “meningism” (the term indicates irritation of the meninges of non-inflammatory etiology).
Treatment of cerebrospinal fluid hypotension: bed rest, avoidance of physical activity, drinking plenty of fluids, elimination of the dural defect.
2) Liqueur hypertension. It occurs when the total volume of tissue located in the cranial cavity increases. This occurs for various reasons: cerebral edema, venous congestion, hydrocephalus, space-occupying processes (tumor, abscess, parasitic cyst, infectious granuloma, etc.), various damage to the brain and its membranes (meningitis, encephalitis, arachnoiditis, traumatic brain injury, eclampsia pregnant women, status epilepticus), hyponatremia with the flow of water from the blood into the brain tissue, hypoxia, intoxication. With craniostenosis and depressed fracture of the bones of the calvarium, a decrease in the volume of the cranium is observed.
There are two stages of development or existence of intracranial hypertension.
1. The compensated stage is a condition in which the increase in the total volume of intracranial tissue is compensated by a decrease in the amount of blood and cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, the blood moves from the vessels of the cranial cavity to the reserve vascular spaces, and the cerebrospinal fluid begins to be intensively absorbed and/or its secretion slows down. This stage does not manifest itself clinically.
2. When reserve capacity is depleted, the 2nd stage occurs - decompensation of intracranial hypertension with characteristic and increasing symptoms. Cerebral circulation is impaired, as perfusion pressure in the vessels of the brain drops (it is defined as the difference between mean arterial pressure and intracranial pressure). If the perfusion pressure is below 50 mm Hg. Art., the stage of decompensation begins - arterial blood flow becomes insufficient. When the difference becomes zero, it stops completely.
Clinical picture of intracranial hypertension (ICH):
— at the beginning of the development of ICH it is characterized mainly by paroxysmal headaches, which occur and are most intense more often in the mornings;
- then an increasing diffuse headache of a bursting nature joins. It intensifies with coughing, sneezing, physical stress, moving the head, flexing and straightening the neck, squeezing the veins in the neck;
- “cerebral” vomiting not associated with food intake is observed;
- swelling of the optic discs appears, fraught with secondary atrophy of the optic nerves and loss of vision;
— the most severe complication of intracranial hypertension is the displacement and herniation of brain structures into the cracks between the sheets of the dura mater.
Return to Contents
Benign intracranial hypertension (BIH)
This is one of the types of ICP, which can be attributed to a temporary phenomenon that is caused by a number of unfavorable factors. The condition of benign intracranial hypertension is reversible and does not pose a serious danger, since in this case the compression of the brain does not occur due to the influence of any foreign body.
The following factors can cause ADHD:
- Hyperparathyroidism;
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- Discontinuation of certain medications;
- Hypovitaminosis;
- Obesity;
- Pregnancy;
- Overdose of vitamin A, etc.
Benign intracranial hypertension is associated with impaired absorption or outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Patients complain of headaches that get worse with movement, and sometimes even with sneezing or coughing. The main difference between the disease and classic cerebral hypertension is that the patient does not show any signs of depression of consciousness, and the condition itself does not have any consequences and does not require special treatment.
Treatment of intracranial hypertension at the Yusupov Hospital
Intracranial hypertension is a pathological condition caused by diseases of the brain and not only. The pathology requires mandatory treatment to avoid the development of numerous and irreversible consequences. Do not delay going to the doctor for any manifestations of increased intracranial pressure.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in treating intracranial hypertension. The quality of services provided in the hospital is at the European level. All diagnostic and treatment procedures are performed using the latest medical equipment. The rooms are equipped with maximum comfort for patients. You can make an appointment with a doctor by phone.