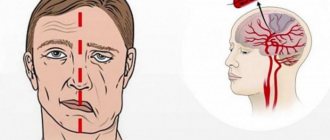
Symptoms
Among the symptoms of cerebral atherosclerosis are:
- Certain signs of cerebral atherosclerosis include the following symptomatic picture:
- Sleep problems: insomnia, disturbing dreams, difficulty getting up and problems falling asleep again;
- Loss of sensation in half of the body;
- Severe, frequently recurring headaches;
- Increased cholesterol levels in blood tests:
- Changes in gait and loss of coordination;
- Changes in vision, flickering of “spots” before the eyes, tinnitus;
- Emotional changes: irritability, depression, tearfulness and anxiety;
- Hot flashes and sweating of the face;
- Increased fatigue, constant weakness and absent-mindedness;
- Trembling of the chin and limbs;
- Memory impairment, problems with short-term memory;
- The appearance of facial asymmetry. Source: L.S. Bizhanova. Ischemic brain disease // Bulletin of KazNMU, No. 2, 2015, pp. 241-242 Shabir O.
Clinical signs do not appear immediately. This happens long after cholesterol has begun to be deposited. Symptoms appear after the lumen of the arteries and capillaries of the brain narrows so much that 15% or more less blood begins to flow to the organs.
Signs of the disease depend on the stage:
1. In the first stages, the disease makes itself felt only after physical or emotional stress and quickly passes when the patient goes into a state of rest. The main symptom is asthenia, accompanied by fatigue, weakness, decreased alertness, and general lethargy. Rarely, sleep is disturbed, insomnia or daytime sleepiness occurs. Mostly, patients complain of headaches, tinnitus, and memory impairment. In the latter case, patients remember the past well, but do not remember new information well.
2. As the disease progresses, anxiety, suspiciousness, depression, and mood swings appear. Memory impairments become more pronounced, to the point that the patient does not remember what happened to him today. There is a constant headache and noise in the ears, speech is persistently impaired - it becomes unclear, diction changes, patients feel dizzy and have unsteady gait. Hearing and vision also deteriorate, limbs and head shake, and a person stops thinking logically and clearly.
3. At the last stage of atherosclerosis, dementia develops; the patient may behave like a child or become aggressive and tearful. Most people completely or partially lose their memory and cease to be interested in the world around them and the events in it. The ability to navigate in time and space is lost, the patient needs constant care because he loses self-care skills in everyday life. This stage is irreversible.
What should you avoid?
- Butter. Even an elderly person should not be completely deprived of this product: butter contains vital vitamins and other organic substances. But it should be consumed in the smallest quantities - 10-15 g per day. The rest of the fats in the diet should be vegetable. Don't forget that there are also oils that are beneficial for blood vessels.
- Fatty fermented milk products. Full-fat whole milk is very difficult to find in the store. But fatty fermented milk products are in abundance. These are yellow cheeses, which indicates a high fat content, cream, sour cream in large quantities, too fatty cottage cheese (18%), etc. All these products also contain animal fats, which complicate digestion and provoke a narrowing of peripheral and cerebral vessels.
- Lard, fatty meat. Animal fats in lard, pork, lamb, fatty poultry, and offal are a source of large amounts of energy. But they are dangerous because they are poorly absorbed, and fat is deposited on the internal organs, causing the destruction of the walls of blood vessels, disrupting the possibility of their natural expansion.
- Strong meat broth. It contains concentrated fats and other substances that thicken the blood, preventing its normal flow and preventing the free expansion of blood vessels.
- Canned food. Canned fish contains a lot of fats, which provoke the appearance of “bad” cholesterol in the blood and reduce the elasticity of the arteries. Canned vegetables contain a lot of salt and preservatives
- Fried potatoes. Despite the fact that it is a vegetable, it is a starchy food that is difficult to digest. And when fried, it forms a large amount of carcinogens that clog the blood and blood vessels. In addition, it contains an unacceptably large amount of fat, as it absorbs any oil very well.
- Ready-made sauces. Soy sauce contains a huge amount of salt, which changes the composition of the blood and prevents blood vessels from relaxing. Mayonnaise and creamy sauces are bad because they contain a lot of salt, preservatives, and most importantly, unnecessary fats that increase the level of “bad” cholesterol, which is easily deposited on the walls of the arteries.
- Sweets and baked goods. Cakes, pastries, buns, cookies, candies and other sweets - almost everything that is produced industrially increases the level of sugar and fats in the blood, makes blood vessels brittle, permeable and inelastic, and prevents their normal expansion.
- Strong coffee, cocoa, tea. These are conditionally prohibited products, since they are harmful to blood vessels only if they are tightly brewed. For example, medium-strength coffee does not provoke spasms, but, on the contrary, prevents atherosclerosis, and therefore ultimately maintains the elasticity of the arteries. For more information about the effect of coffee on blood vessels, see a separate article.
- Alcohol abuse. Despite the fact that almost any alcohol-containing drinks dilate blood vessels, those diagnosed with hypertension should not use alcohol. Alcohol of any strength guarantees an increase in pressure and a decrease in the elasticity of the walls of the bloodstream. Alcohol-containing drinks can be used only for prevention or once, as a temporary measure, and in very limited quantities (50-150 for low-alcohol drinks, 30-70 for strong drinks).
Also check out the infographic:
What about alcohol?
Diagnostics
A neurologist deals with this disease. First, the doctor collects anamnesis, interviews the patient about complaints, and conducts a series of tests. So, the following factors indicate the presence of the disease:
- The patient cannot look up;
- Reflexes are weakened or excessively increased, most often asymmetrically;
- In a standing position, legs together, arms extended forward, the patient cannot maintain balance;
- When the patient stretches his arms forward, his fingers tremble and become weak;
- Closing his eyes, a person cannot bring his finger to the tip of his nose.
These are indirect signs that only allow us to make an assumption about the presence of atherosclerosis. Therefore, a comprehensive examination is then carried out with consultations of other doctors - ENT, ophthalmologist, etc., depending on the existing disorders. At the medical office, you can get advice from related specialists on any disease, including in cases of suspected cerebral atherosclerosis. Source: Berwick J, Francis SE. Neurovascular dysfunction in vascular dementia, Alzheimer's and atherosclerosis // BMC Neurosci. 2021 Oct 17;19(1):62. doi:10.1186/s12868-018-0465-5.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo a biochemical analysis of the blood lipid spectrum (cholesterol, triglycerides, etc.)
List of instrumental studies:
- REG – radioencephalogram;
- Angiography of cerebral vessels;
- Duplex head scanning;
- Ultrasound Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
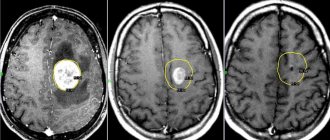
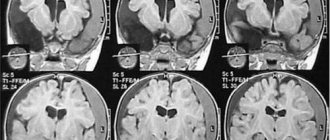
- MRI of cerebral vessels;
- CT – computed tomography;
- EEG – electroencephalogram.
The diagnostic capabilities of a medical doctor allow you to accurately diagnose atherosclerosis, the extent of the disease and choose an effective treatment regimen.
For what reasons does cerebrovascular accident occur?
- Birth trauma in children
- the problem can be a consequence of a cesarean section, when a sharp drop in pressure occurs, as well as oxygen starvation during intrauterine development. It is assumed that in the first three years of life the child’s central circulation is restored. But if this does not happen, cysts, epilepsy, and encephalopathy may form. Therapy is needed here, including medications to dilate blood vessels. - Changes in hormonal levels
- this occurs throughout almost the entire life of a person: during growing up, puberty, in women during pregnancy, during breastfeeding and menopause. Changing hormonal levels requires additional efforts from the circulatory system. - Emotional and physical stress
- the load on the blood flow gradually increases, which leads to general poor health, memory deterioration and tactile sensitivity. Impaired cerebral blood flow can lead to the development of serious diseases: osteochondrosis, tumors, acute thrombosis, etc. - Poor nutrition and lack of vitamins
- consumption of fatty and salty foods, strong coffee, smoking and addiction to alcoholic beverages leads to deterioration of nutrition and blood supply to the brain. This leads to the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels and chronic spasms of the cerebral choroid plexuses. - Infectious diseases
- pathologies such as meningitis and encephalitis negatively affect the functioning of the central nervous system. Treatment of the pathological condition requires complex measures and effective vascular drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain. - Old age
- with age, the human body weakens, the structure of the vascular wall of the brain changes, the blood becomes more viscous and metabolism is disrupted. All this leads to poor circulation, provokes the development of tumors, increases the risk of strokes, and leads to the development of atherosclerosis. Inflammatory processes and somatic pathologies provoke disruption of cerebral blood flow.
Types of cerebrovascular disorders
Experts distinguish two main forms: acute and chronic. Each of them is characterized by certain symptoms and is divided into separate subtypes. The acute form of the disorder develops within a few hours or minutes. This group includes strokes that occur as a result of hemorrhage in the brain tissue or due to oxygen starvation, which developed against the background of blocking the lumen of the feeding vessel.
The acute form of circulatory disorders can also include ischemic attacks and hypertensive crises. Quite often, such pathological phenomena occur as a result of injury. Symptoms such as numbness of a part of the body, impaired speech and vision (dark spots, colored circles), drowsiness, increased sweating, and stuffy ears are noted.
It takes years for chronic disorders to develop. The initial stages of the pathology do not have pronounced symptoms: the patient’s condition often indicates chronic fatigue syndrome. The patient notices drowsiness, headaches, absent-mindedness, and sudden mood swings. At the second stage, memory deteriorates significantly, attacks of aggression appear, the head is constantly dizzy, and efficiency disappears. And the third stage is characterized by almost complete personality degradation, dementia and impaired coordination of movements. Here an irreversible pathological process occurs.
Diagnosis of vascular disorders
When the first signs of cerebrovascular accident appear, you should consult a neurologist. He will conduct an examination and prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis, which will help determine the cause of the pathology:
- general blood analysis;
- blood for glucose;
- lipidogram - analysis of the lipid spectrum of the blood;
- magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral vessels;
- ultrasound examination of blood vessels;
- coagulogram for blood clotting;
- CT scan;
- neuropsychological testing;
- electroencephalography – performed for epilepsy or speech problems;
- genetic test if there is a suspicion of a hereditary factor.
Treating atherosclerosis
- Shishkin A.A.
- Volkov A.M.
- Kabirov A.V.
- Baranov V.S.
Shishkin Andrey Andreevich
Candidate of Medical Sciences. Surgeon, proctologist, phlebologist at SM-Clinic. Proficient in all modern methods of conservative and surgical treatment of diseases of the veins of the lower extremities (including sclerotherapy, EVLT - endovasal laser coagulation, traditional phlebectomy)
Read moreVolkov Anton Maksimovich
Phlebologist, surgeon at SM-Clinic. Performs operations with a modern proprietary method of treating varicose veins using a laser (modified endovenous laser coagulation. M-EVLC).
Surgical treatment of varicose veins of any complexity (phlebectomy, miniphlebectomy) More detailsKabirov Alexander Vitalievich
Cardiovascular surgeon at SM-Clinic. Candidate of Medical Sciences Proficient in all modern methods of conservative and surgical treatment of diseases of the veins of the lower extremities (including sclerotherapy, EVLT - endovasal laser coagulation, traditional phlebectomy)
More detailsBaranov Vladimir Sergeevich
Cardiovascular surgeon at SM-Clinic. Candidate of Medical Sciences Treats lower varicose veins using non-surgical and surgical methods (aesthetic sclerotherapy, ECHO sclerotherapy, stem sclerotherapy, phlebectomy, miniphlebectomy, EVLT).
More details
Treatment
The basis of treatment for this pathology is lifestyle adjustments. This means:
- lipid-restricted diet,
- rejection of bad habits,
- physical activity regimen,
- avoiding stress,
- treatment of chronic diseases.
The focus of drug therapy is the use of lipid-lowering drugs, antiplatelet, antihypertensive and antioxidant drugs, drugs to improve microcirculation and symptomatic therapy. Therapy, as a rule, takes a very long time and depends on the stage at which it was started.
In case of severe stenotic processes, surgical treatment is recommended for the patient. Most often, surgical intervention is performed on the internal carotid arteries. Source: E.A. Shirokov. Stenosing atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries: modern strategies for diagnosing and treating patients // Consilium Medicum, vol. 18, no. 9, 2021, pp. 37-42.
Treatment for this disease is aimed at ensuring that metabolic processes are restored, and harmful cholesterol no longer settles on the walls of blood vessels. At the same time, attention is also paid to restoring blood circulation and normalizing the nutrition of brain tissue.
Drug therapy
This is the most important part of the comprehensive treatment of atherosclerosis. Patients may be prescribed several groups of medications:
- Statins - reduce the size of cholesterol plaques, reduce the risk of narrowing of the main arteries of the brain, and stop the growth of plaques.
- Antiplatelet agents – reduce blood viscosity and prevent blood clots.
- Fibrates are similar in action to statins, but do not affect the size of plaques, but lower the triglyceride content in the blood.
- Means for restoring vascular function.
- Bile acid sequestrants prevent cholesterol from being absorbed from food.
- Nootropics and medications that improve metabolic processes in nervous tissue.
- Hypotensives that stabilize blood pressure and help prevent stroke.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes to improve the general condition of the body. They must contain vitamins A, C, group B and nicotinic acid.
Medicines are taken in long courses, and most of them are taken for life with periodic dosage adjustments.
Surgical treatment
Operation is a last resort, indications for it:
- narrowing of the lumen of the carotid artery by 70% or more;
- condition after a minor stroke;
- recurrent ischemic attacks.
Surgical options:
- bypass - the formation of a vessel bypassing the one affected by cholesterol deposits;
- endarterectomy - a procedure to remove cholesterol plaques along with a small amount of tissue that lines the vessel from the inside;
- stenting using endoscopic technology - an expanding structure impregnated with a composition that dissolves cholesterol is installed in the vessel.
Operations can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. An anesthesiologist is consulted before the operation. The length of hospital stay varies depending on the technique, as do recommendations for the recovery period. SM-Clinic doctors inform patients in detail about all the nuances and are ready to answer any questions related to treatment at the initial consultation. Consultation on the operation is free of charge.
You can find out more about discounts on preoperative examinations by following the link.
Diet
Changing your diet is also a way to improve your well-being and is a great help for other treatment methods. Atherosclerosis very often progresses precisely against the background of poor nutrition and lifestyle, so it is necessary
- follow a certain diet:
- reduce consumption of red and fatty meats and meat in general;
- limit the consumption of confectionery products and baked goods;
- eat as few egg yolks as possible;
- limit solid vegetable fats – margarine – in the diet;
- completely eliminate alcohol, sausages, fast food, and canned food.
Recommended products include vegetables (fresh, pickled, dried), cereals (rice, buckwheat, barley, millet, oats, flax, etc.), dried, fresh and dried fruits, turkey and chicken fillets, river and sea fish.
You need to eat at least 5 times a day at the same time in small portions. It is necessary to avoid fried foods and prepare food using the methods of boiling, steaming, stewing, and baking.
Possible risks associated with atherosclerosis
The most dangerous complication is a stroke. If at the same time the patient has poor eating habits, is overweight, moves little and is regularly exposed to stress, then with an 80% probability he will become disabled as a result, unable to care for himself. The mortality rate is also high.
Prevention
To prevent cerebral atherosclerosis, you need to avoid smoking, follow a diet, and keep yourself in good shape with moderate physical activity. It is very important to establish a psycho-emotional background, protect yourself from stress, and if this is not possible, then take courses of sedatives and amino acids, for example Glycine.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments* |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a cardiovascular surgeon, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1 750 | — |
| Program “Risk of atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease, predisposition to dyslipidemia” | 19 000 | — |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.
Vasodilator foods - Top 10 products
Many products, primarily of plant origin, have a certain effect on blood vessels. Knowledge of these properties will allow you to maintain blood pressure in a normal state, and the walls of the bloodstream - capable of easily expanding under the pressure of the blood flow. Below we briefly list products that dilate blood vessels.
- Vegetables. You need to make vegetables the basis of your entire diet. Beets, all types of cabbage, onions, garlic, pumpkin, tomatoes, zucchini, chili, cayenne and bell peppers, consumed daily, maintain normal vascular tone, allowing them to expand in their natural need.
- Bread. Without it, it is difficult to imagine the food of modern man. But in order for the arteries and veins to remain healthy, it must be whole grain. This vasodilator food contains large amounts of fiber, minerals and vitamins. This entire complex helps remove toxins from the body and prevents fat deposition.
- Cereals. For the reasons already indicated, they must also be present in the daily diet. B vitamins provide relief from stress and cramps. Porridges, casseroles and desserts are prepared from oats, buckwheat, millet, rice, barley, wheat, and corn, which improve metabolic processes and help lower blood pressure.
- Fresh or frozen sea fish, seafood and seaweed. All of these foods contain Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, which nourish the cardiovascular system. Without them, the normal functioning of arteries and veins is impossible. Laminaria helps the liver produce “correct” cholesterol and normalizes blood pressure.
- Lean poultry and beef. Animal protein is necessary for the body, but without excess fat.
- Fruits, dried fruits and berries. Pomegranate, apples, pears, apricots, strawberries, raspberries, viburnum, rowan, blueberries, raisins, dried apricots, figs help normalize cholesterol in the blood and reduce vascular tone in the brain due to the production of nitric oxide in the blood, which dilates the arteries.
- Greenery. Almost any greenery contains substances that are vital for the cardiovascular system.
- Unrefined vegetable oils, seeds, nuts. The kernels of seeds and nuts contain a large amount of substances that support arteries and veins in working condition. If you are prone to varicose veins of the legs, it is especially useful to eat walnuts and almonds.
- Green tea. Green tea is known to dilate blood vessels. This drink is a recognized remedy for lowering blood pressure and cleaning blood vessels that cannot dilate due to the presence of cholesterol deposits on their mucous membrane.
- Medicinal herbs. Collections for dilating blood vessels may include such useful herbal remedies as motherwort, mistletoe, fireweed, valerian, birch buds, chamomile, hazel, and hawthorn.
To calculate the required amount of vegetables, berries, fruits, herbs and make them the basis of the diet with narrowed blood vessels, you need to get used to eating about a kilogram of plant foods (not counting cereals!) per day, distributed evenly. For example, with five meals a day, you need to consume 200 g of plant food at a time. These can be baked, boiled, stewed or pickled vegetables for breakfast, lunch and dinner, and fresh vegetables in pieces, fruits, berries or salads from them for second breakfast and afternoon snack.