Our clinic specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the nervous system, incl. non-surgical treatment of increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus. You will also find help in treating the consequences of intracranial hypertension: depression and nervous exhaustion, vegetative-vascular dystonia, headaches, visual disorders and others. We will be happy to help you!
- Increased intracranial pressure: treatment at the Echinacea clinic with and without medications
- Make a diagnosis
- Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
- Causes and consequences of increased intracranial pressure
- What is intracranial pressure
- What is hydrocephalus of the brain
Increased intracranial pressure: treatment at the Echinacea clinic with and without medications
We actively use methods to normalize intracranial pressure, both classically and without drugs. Some simple measures may be enough to get you back to good health. The effect is usually noticeable already in the first week of treatment.
1. Unloading the venous bed of the head using special methods of soft manual therapy and osteopathy;
Normalization of intracranial pressure: for treatment, sometimes it is enough to eliminate the infringement of blood vessels by the vertebrae
2. Special gymnastics to reduce intracranial pressure (used by the patient independently, developed by the doctor after examining muscle tone); 3. Individual drinking/eating regimen.
Living with increased intracranial pressure is both unpleasant and harmful. The human brain cannot work normally under the influence of excess pressure ; moreover, slow atrophy of the brain substance , this leads to a decrease in intellectual abilities, disruption of the nervous regulation of internal organs (hormonal disorders, arterial hypertension, etc.). Therefore, we will take measures to normalize intracranial pressure as soon as possible.
In the treatment of increased intracranial pressure, it is important to reduce the release and increase the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. Traditionally, it is customary to prescribe for this purpose drugs that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid and improve venous outflow (evacuation of venous blood from the cranial cavity). Often it is enough to take the medicine 1-2 times a week.
But still, we strive to free our patients from constant medication use. There are two ways to do this:
- If possible, eliminate the cause of increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus;
- Use more non-drug methods for treating cerebral hydrocephalus.
What to do in very severe cases
In very severe cases (for example, cerebrospinal fluid block after neurosurgical operations or congenital cerebrospinal fluid block), surgical treatment is used. For example, a technology has been developed to implant tubes (shunts) to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid.
How to measure ICP in a child
The condition of persistent increase in intracranial pressure is most dangerous for children, especially when their age does not exceed 3 years. During childhood, brain structures grow and develop rapidly, and neural connections progress. If during this period the brain is compressed, this will affect nutrition, the progression of brain structures, and in severe cases can cause direct damage to the brain structures as a result of compression. The result can be both reversible (in case of timely assistance) and irreversible consequences - developmental delays, neuropathies, pathological reflexes, etc.
Signs that should alert parents and serve as a reason for an emergency examination by a neurologist: constant restlessness of the child, frequent crying, irritability, poor appetite, divergence of cranial sutures, and in infants - bulging of open fontanelles. Older children may complain of pain behind the eyes and in the frontal lobe, which may radiate to the ears and back of the head. A common symptom is blurred vision, visual abnormalities in the form of flashes of light in front of the eyes, dark spots or bands. In the later stages, symptoms of exophthalmos are observed, Graefe's symptom is the presence of a white strip of sclera between the upper edge of the iris and the upper eyelid, as well as spontaneous movements of the eyeball.
It is somewhat easier to check whether the level of pressure inside the skull in children corresponds to the age norm than in adults, due to the large number of cartilaginous elements in the skull, but this is impossible to do at home due to the need to use special devices.
The process of measuring pressure inside the closed space of the skull is complex; it is impossible to measure ICP at home.
Which doctor can diagnose? Neurologist. To do this, resort to the following methods:
- neurosonography - ultrasound of the skull and brain structures, which is suitable for children with an open fontanel. The method allows you to determine the state of the midline structures of the brain, its ventricles filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and their displacement depending on the force of pressure. Then, based on the presence of displacement of certain structures, using special algorithms, a conclusion is made about the value of intracranial pressure;
- Doppler sonography - allows you to visualize blood circulation in the vessels of the patient’s brain, with its help you can evaluate all the rheological properties of blood - from thickness to flow rate. Using the resulting data, the pressure in the cranium is determined by calculation;
- otoacoustic method - after measuring the amount of outward displacement of the eardrum, the measurement result is interpreted into the value of intracranial pressure.
In addition, CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) results can be used to measure ICP.
Make a diagnosis
Intracranial pressure can be directly measured only by inserting a special needle with a pressure gauge connected to it into the fluid cavities of the skull or spinal canal. Therefore, we do not use direct measurement of intracranial pressure.
On the left is an MRI scan of a normal brain. The brain matter is shown in gray, the cerebrospinal fluid is in white. Normal size of the fluid spaces of the brain (they are slit-like). The ventricles are visible inside the brain. The subarachnoid spaces are the white border around the brain.
In the center there is internal hydrocephalus. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid inside the brain in the form of a butterfly is visible. On the right is external hydrocephalus. External hydrocephalus is also an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid outside the brain in the form of a wide white border. The volume of the brain matter is reduced - brain atrophy from fluid pressure
We can confidently judge the increase in intracranial pressure based on the following data:
- Dilation and tortuosity of the fundus veins is an indirect but reliable sign of increased intracranial pressure;
- Expansion of the fluid cavities of the brain (internal hydrocephalus of the brain, external hydrocephalus) and external hydrocephalus (rarefaction of the medulla) along the edge of the ventricles of the brain, clearly visible on computed x-ray tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Violation of the outflow of venous blood from the cranial cavity, established using ultrasound vascular studies.
How much the brain suffers from increased intracranial pressure can be judged from EEG data. The gold standard for instrumental examination of patients in our clinic is an assessment of symptoms, brain tomography , fundus images and EEG .
Good optics helps us see the subtle nuances of the fundus vessels
Echoencephalography (Echo-EG) provides indirect and not always reliable data on increased intracranial pressure; it is less reliable than CT and MRI, so we do not use this method.
Symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of intracranial pressure
Change in pupil reaction;- Swelling of the optic nerve;
- Problems with vision (peripheral vision is impaired first, and then central vision). Acuity decreases, diplopia occurs;
- Reduced hearing threshold;
- Dyspeptic syndrome consisting of nausea and vomiting;
- Severe headache that lasts for a long period of time, a feeling of constant fatigue and drowsiness;
- Pain when turning the head, as well as when sneezing and coughing;
- Sudden hyperhidrosis (production of a large amount of sweat), a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- Irritability, nervousness, decreased ability to work;
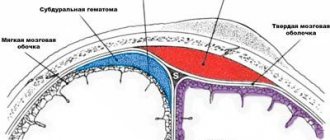
- The occurrence of hematomas in the periorbital area;
- Pain in the cervical vertebra and spinal cord;
How to treat increased intracranial pressure?
It is necessary to understand that the condition in question is not an independent nosological unit, but a symptom of some disease that affects the human nervous system. Only after the pathology, the presence of which leads to an increase in intracranial pressure, has been identified, will it be possible to draw any conclusions. After all, it is reliably known that treatment of intracranial pressure (increased), equally as treatment of any other somatic pathology, can only be effective if its root cause is determined for the purpose of further elimination, and nothing else.
It is in order to correctly identify the root cause of the pathology that it is necessary not only to conduct a number of laboratory and instrumental studies, but also to consult a competent specialist who can interpret the results obtained, compare them with indicators of the objective condition, and then draw appropriate conclusions and select the correct treatment that will will relieve the symptoms discussed above.
If you notice signs of increased intracranial pressure, do not delay your visit to the doctor, this will need to be done as soon as possible, since what matters here is when exactly the necessary treatment will be prescribed.
The most experienced and competent neurologist in Tushino conducts an appointment in our clinic. Hurry up to sign up, because if treatment is started on time, it will be much easier to get rid of the pathological condition before the disease manifests itself and does not lead to undesirable consequences.
Get advice on visiting a neurologist. Consultation on the service does not oblige you to anything.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
Increased pressure on the brain substance can disrupt the functioning of the central nervous system. Hence the characteristic symptoms:
- Heaviness in the head or headaches that increase in the morning or in the second half of the night;
- In severe cases, nausea and/or vomiting in the morning may occur;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia (sweating, a drop or increase in blood pressure, palpitations, lightheadedness, etc.) is an almost obligatory symptom;
- Fatigue, “dullness”, easy exhaustion during work or study loads;
- Nervousness;
- “Bruises” under gases (if you stretch the skin under the eyes in the area of the “bruise”, dilated small veins are visible);
- Possible decrease in sexual desire and potency;
- If the human body is in a horizontal position, cerebrospinal fluid is released more actively and absorbed more slowly, so intracranial pressure and its symptoms tend to peak in the second half of the night or in the morning;
- The lower the atmospheric pressure, the higher the intracranial pressure, so the deterioration of the condition is associated with changes in weather.
Rules for measuring pressure
Many parents are interested in how to measure intracranial pressure in a child. Measuring a person’s ICP must be performed according to certain rules, under sterile conditions, since this is a very important and responsible procedure. A trepanation hole should be made in the skull, into which anesthetics are injected, then it is shaved and thoroughly treated with antiseptic solutions.
Blood pressure is measured using local or general anesthesia; doctors prescribe mild painkillers to eliminate some of the symptoms of the disease. They try to avoid the use of potent drugs, since during the procedure they additionally check indicators of brain functioning.
Increased pressure inside the skull is a quantitative indicator that accurately reflects the degree of influence of cerebrospinal fluid on the state of brain tissue, so it is impossible to establish this yourself, without the use of appropriate equipment.
But the patient can independently detect an increase in pressure based on certain clinical symptoms. Dizziness, heat in the temples, increased weakness, loss of consciousness, headache, attacks of suffocation, and blurred vision should alert you. These signs may indicate histological damage to the neural tissues of the brain.
The doctor needs not only to perform a thorough examination of the patient, but also to correctly interpret all the data and finally make a diagnosis in order to prescribe appropriate therapy. Experts believe that an increase in pressure can be objectively assessed and identified after intracranial surgery is performed on a patient by assessing the average pressure readings.
Causes and consequences of increased intracranial pressure
The reasons we find most often:
- disruption of the outflow of venous blood from the cranial cavity
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation)
- suffered a traumatic brain injury (even a very old one, up to birth trauma)
- meningitis or encephalitis
- congenital structural features of the central nervous system (Arnold-Chiari anomaly, congenital intracranial hypertension, etc.);
- poisoning with brain damage.
Consequences As a result of the disease, brain cells are gradually destroyed, and their place is filled with fluid. The functions of systems controlled by the brain become disordered, and complete or partial loss of vision, hearing, memory, potency, miscarriage, depression, nervous exhaustion and other health problems may occur.
On the left is a normal brain, the liquid (cerebrospinal fluid) is indicated in white. On the right is untreated internal hydrocephalus: brain atrophy, almost the entire cranial cavity is occupied by fluid.
Physiotherapy
After it has become clear that it is impossible to measure intracranial pressure at home, we should talk about how to normalize it and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. During the treatment process, you can use physiotherapeutic methods (electrophoresis with medicinal substances, applying a magnet to the collar area on the neck), physical therapy, massage of the spine, back of the head, base of the skull, circular shower and acupuncture. Basically, these techniques are used in uncomplicated cases of increased ICP, in the absence of a threat to normal life.
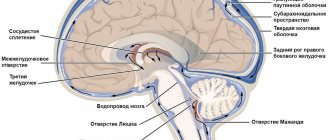
What is intracranial pressure
Wise nature placed the human brain in a protective liquid environment ( subarachnoid fluid spaces ) and provided it with internal fluid cavities ( ventricles ). Thus, the brain is actually suspended in a special fluid - cerebrospinal fluid (also known as cerebrospinal fluid or CSF ). The cerebrospinal fluid is in the cranial cavity under a certain pressure. It is the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid on the brain that is called intracranial pressure .
A normal level of intracranial pressure is very important for the proper functioning of the brain and all processes subordinate to it. We often see a total improvement in the well-being of our patients as intracranial pressure normalizes.
What is increased intracranial pressure? All fluid spaces and ventricles are interconnected by ducts. The liquor is constantly circulating. In some parts of the brain it is released, and then flows through the cerebrospinal fluid ducts to other parts of the brain, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Complete renewal of the cerebrospinal fluid occurs on average 7 times a day. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid causes an increase in its pressure on the brain substance. This is called increased intracranial pressure (intracranial hypertension).
Three common causes of chronic increased intracranial pressure:
- too much cerebrospinal fluid is released;
- the cerebrospinal fluid is not absorbed fully enough;
- the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation pathways is impaired.
A little anatomy
This disease is associated with the cerebrospinal fluid that washes the brain and the brain itself. Liquor is an important intracranial fluid, the entire volume of which regulates pressure on the human brain.
If the volume of fluid is much higher than normal, this may cause an increase in pressure. That is, it can be noted that an increase in intracranial pressure is a set of symptoms, but not a disease as such. Read more about the symptoms and treatment of intracranial pressure below.
What is hydrocephalus of the brain, external hydrocephalus
If intracranial pressure is increased significantly and for a long enough time, the fluid cavities of the brain may expand; this expansion is called internal or external hydrocephalus. Since the cranial cavity is a closed space, the expansion of the fluid cavities of the brain occurs due to a decrease in the mass of the brain matter itself. To protect you from the death of working brain tissue, we will offer you a course of medications, in combination with a set of exercises to reduce intracranial pressure and, if necessary, osteopathic correction.
External hydrocephalus (brain) - expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain (subarachnoid spaces).
Internal hydrocephalus (brain) - expansion of the internal liquor cavities of the brain (ventricles).
Our clinic pays great attention to finding the root causes of such a condition as increased intracranial pressure. In this case, treatment can be kept to a minimum, and our assistance to patients will be reliable.
Methods for reducing pressure
If ICP increases due to an existing secondary process, the primary disease must initially be eradicated, for example, hormonal imbalance, atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis or hypertension. But symptomatic treatment of this disease is also very important.
The patient can independently determine the symptoms, and treatment for intracranial pressure is prescribed by a specialist. It will be as follows:
- Conservative: taking medications to enhance the outflow of excess blood from the brain, reducing the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid as much as possible. Doctors mostly prescribe diuretics. If a tumor or meningitis is detected, steroid-type anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce swelling. Doctors also recommend using potassium supplements and agents to improve venous blood flow. Nootropic drugs will be ineffective for this disease.
- Surgical. The most commonly used type of surgery is bypass surgery. A special tube is inserted through which excess fluid is pumped from the ventricles of the brain into the peritoneum. But there are also some disadvantages - the catheter can unexpectedly break, bend or become clogged. There are also a number of specific complications of this procedure.
To reduce intracranial pressure, tinctures of mint, hawthorn, medicinal valerian, eucalyptus or motherwort are used. These herbs eliminate vascular spasms, providing a mild calming effect on the patient.