How to treat intercostal neuralgia on the right or left?
Intercostal neuralgia is a reflex pain syndrome that occurs when the intercostal nerves are compressed, irritated or inflamed. Otherwise it is also called thoracalgia. This phenomenon is unpleasant, as it is accompanied by intense pain.
Clinical manifestations are very similar to the symptoms of a number of diseases of internal organs, in particular the heart. That is why many patients, frightened by an attack of intercostal neuralgia, turn to a cardiologist or begin to self-medicate by taking heart medications. The latter, along with the lack of correct diagnosis and adequate treatment, does not bring relief, but only aggravates the patient’s condition.
Since thoracalgia is quite common among older and older adults, being fully aware of it will ensure health and well-being during these stages of life.
Causes and risk factors
Intercostal neuralgia is not inherently an independent disease. From a medical point of view, this is a complication caused by the underlying disease or pathological process occurring in the body.
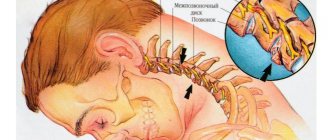
The human chest has twelve pairs of ribs, which are attached to the thoracic vertebrae of the spinal column at the back. The thoracic nerves, exiting through the intervertebral (foraminal) foramina and branching, are located between the ribs.
The mechanism of occurrence of intercostal neuralgia is simple. Seizures can be caused by:
- pinching or inflammation of nerve endings in the intercostal space;
- pinching of the roots of the thoracic spinal nerves at the point of their exit from the spinal canal.
The most common causes of neuralgia of the intercostal nerves are:
- osteochondrosis, spondylitis, ankylosing spondylitis and other diseases of the thoracic spine;
- excessive physical activity;
- tumors of the thoracic spinal cord;
- chest injury;
- sudden unsuccessful movement;
- general hypothermia of the body, hypothermia of the chest and back;
- pathologies of the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- forced awkward body position;
- herpetic infection.
The contributing factors are:
- age-related changes in blood vessels;
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus);
- diseases of the nervous system;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- immunodeficiency;
- intoxication of the body;
- uncomfortable workplace.
In women, intercostal neuralgia can be caused by wearing tight underwear, as well as being underweight. In children and adolescents, intercostal neuralgia can occur during a period of intensive growth of the bone skeleton.
Causes of neuralgia
The human nervous system is a “communication system” in the human body, designed to ensure the transmission of impulses from each organ to the brain and back. The main “transport channels” are nerve fibers; they extend from the spinal cord, to which they are attached with the help of roots and are directed to all organs along the intercostal spaces. The nerves themselves are heterogeneous - they are a bundle consisting of fibers that are divided into three types: sensory, motor and autonomic.
Editorial: How long does the human brain live after death?
In addition to nerve fibers, ligaments and muscles are located in the intercostal space, and the nerve roots come into contact with cartilage and bone. Since the fibers themselves are receptors, their slightest compression or pinching causes severe pain, which intensifies even more with the slightest movement of the body. In addition, changes can occur in the structure of the nerves themselves.
Among the reasons for changes, compression or infringement will be:
External factors
In the presence of hypothermia, muscle spasms may occur, which will irritate the nerve fibers. In case of too much physical activity, small microtraumas of muscle and nerve fibers occur, which in turn causes compression. Injuries cause swelling of the muscle mass, which causes a pain response in the nerve fibers.
Spinal disease
In diseases of the spine, which include all types of spinal curvature, intervertebral hernias, osteochondrosis, radiculitis, most often there is a shift of the vertebral discs, an unusual arrangement of the vertebrae, an increase in the volume of cartilage or, conversely, their abrasion (in osteoporosis). All this infringes on the nerve roots, leads to their tears, inflammation and causes neuralgia.
Among the causes of thoracic neuralgia, diseases associated with spinal problems account for 80%.
Infectious diseases
Infections can cause the disease. Here, an important role in the occurrence of symptoms is played by the penetration into the body of toxins secreted by viruses and bacteria, which will irritate the nerve endings, causing attacks of acute pain.
Poisoning
Poisoning with heavy metals, such as lead, toxins and a number of other substances affecting the nervous system, can cause intercostal neuralgia.
- These same reasons include alcoholism, which also results in general poisoning of the body.
- Long-term use of a large number of medications can also cause general poisoning of the body and, as a result, neuralgia.
Immune system dysfunction
In diseases associated with a malfunction of the immune system, intercostal neuralgia occurs due to damage to nerve fibers and the myelin sheath of the nerves.
- Diabetes mellitus causes changes in the functioning of blood vessels and the nervous system.
- Multiple sclerosis destroys the myelin sheath of nerves.
- Menopause in women disrupts the overall hormonal balance.
Nervous system disorders
Stress and other nervous overloads affect the functioning of the entire nervous system and can manifest themselves as pain in the form of intercostal neuralgia.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia
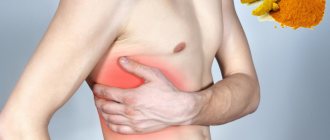
The main symptom of intercostal neuralgia is pain along the intercostal space. The intensity of pain can vary: from sharp, acute, severe, shooting (more often) to constant, medium intensity. The pain intensifies when the patient moves, when coughing and sneezing, and even when breathing. Often a person takes a forced position: leans towards the affected side in order to minimize the range of movements in it. Some patients, when coughing, laughing or sneezing, press their palm firmly against the affected intercostal space for the same purpose: to reduce the range of movements in this area so that it hurts less.
When the intercostal nerve on the left is damaged, the pain often imitates the sensations of angina pectoris: patients evaluate the pain as burning, with irradiation (spread) to the left arm, scapula, and spine. However, angina pain still does not depend on movements, coughing, laughter, etc., and, moreover, decreases after the patient takes nitroglycerin tablets or its analogues. However, in order not to miss such an important cardiac pathology, in doubtful cases the doctor prescribes an ECG for the patient. It is important not to confuse intercostal neuralgia with myocardial infarction, because the pain with it is also not reduced by nitroglycerin. Therefore, if pain suddenly arises in the heart area, you should not tempt fate, hoping for the best, but you need to play it safe: call an ambulance and undergo an electrocardiogram.
Differential diagnosis based on clinical manifestations is an important step in the treatment of patients. First of all, it is necessary to exclude heart pathology, since the treatment of intercostal neuralgia and heart diseases require different methods of therapy, and incorrect diagnosis and lost time in case of cardiac pathology can be decisive for the patient’s condition. The differences are primarily that:
- with neuralgia, chest pain persists for a long time, both day and night;
- the pain intensifies when changing the position of the body in space, coughing and sneezing, deep inhalation and exhalation, sudden movements, when palpating or squeezing the chest.
In case of heart disease, in particular angina pectoris, the resulting pain quickly passes after 5-10 minutes or is relieved by taking nitroglycerin. Movements and changes in body position, coughing and deep breathing do not cause increased heart pain, but may be accompanied by disturbances in heart rhythm and changes in blood pressure. To exclude the possibility of cardiac pathology in the presence of pain in the chest or under the left shoulder blade, it is necessary to urgently perform an electrocardiogram, and sometimes an x-ray.
Serious life-threatening symptoms
Severe, debilitating pain can make breathing very difficult. Pain can also occur for life-threatening reasons, such as a heart attack. You should seek help if any of these symptoms appear:
- Chest pain that may spread to the jaw, shoulder, left arm, or back.
- Pressure in the chest, cramps and a feeling of rupture.
- Cough with yellow-green mucus
- Cardiopalmus.
- Breathing problems, such as severe shortness of breath and inability to breathe deeply.
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Severe chest pain when breathing and coughing.
- Confusion, dizziness, fainting.
Localization of pain
- Referred pain. Referred pain, as a rule, is a consequence of the development of a pathological process in the internal organs (diseases of the retroperitoneum, aortic aneurysm, pathology of the digestive tract, coronary artery disease).
- Radiating pain. The mechanism of development of this pain has not been fully studied to date. According to experts, parts of the nervous system may misinterpret the source of pain due to the presence of common pathways through which both visceral and somatic pain are carried out. Referring pain, resulting from stretching, irritation or compression of a somatic nerve or nerve root, is more intense. With physical activity, sneezing or coughing, the pain may intensify, and can often spread to the affected area of the body.
- Local pain. Its cause can be any pathological process aimed at pain receptors of various tissues, muscles, ligaments, skin, tendons, bones, joints, etc. In this case, pain develops directly in the area of damage.
Causes of rib pain
Pain on the left or right under the ribs can have a different nature, as well as the reasons that cause it. It can be strong and almost imperceptible, aching or sharp, occurring at certain moments or continuous. In almost every case, the cause of pain may be a disease that develops in the chest area.
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic - 4,500
Make an appointment
Chest injuries
Chest injuries usually include fractures or bruises of the ribs. Fractures are characterized by ruptures of bone tissue and cartilaginous joints of one or more ribs. Depending on the injury, pain symptoms may be constant, aching, or acute and intense.
Bruises are characterized by mild pain, which is accompanied by swelling and the appearance of a hematoma in the area of injury. As a rule, pain symptoms disappear after seven to ten days. Fractures require mandatory diagnosis in order to exclude the possibility of injury to the soft tissues of the lung or other internal organs. Depending on the side of the injury, the pain can be localized on the right or left under the ribs or between them. Its intensity and duration depend on how severe the injury was.
Intercostal neuralgia
Pain between the ribs along the nerves can occur due to the following diseases:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine;
- vertebral protrusion;
- intervertebral hernia.
Attacks in the form of shooting pain, similar to an electric shock, occur due to pinched or irritated nerve roots, and their appearance can be triggered by the following factors:
- hypothermia;
- penetration of infection;
- exercise stress;
- getting a back injury.
The pain becomes stronger with strong inhalations/exhalations or attempts to change body position.
Costochondritis
Costochondritis (or, as it is also called, Tietze's syndrome) is a disease in which thickening of the cartilage tissue of the ribs occurs, leading to their pain. Pain is not localized in one place and can spread to the entire sternum. They can be quite strong and appear brighter with sudden movements, deep inhalations/exhalations or coughing. Pain may be accompanied by:
- local edema;
- an increase in temperature in the area of the pathological process.
It appears suddenly and in its manifestations is comparable to an angina attack.
Angina pectoris
Angina is characterized by constant, pressing pain behind the sternum and sometimes between the ribs. It is localized in the retrosternal region and can spread to the left side of the neck, left arm and left side of the chest and may be accompanied by:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- feeling of fear.
Other reasons
In addition, pain in the ribs can occur with the following diseases:
- malignant neoplasms (in particular, osteosarcoma of the ribs) are characterized by dull pain at the beginning of the disease, which becomes more and more pronounced as it develops;
- fibromyalgia - pain occurs when trying to raise your arms or turn your torso;
- pleurisy - pain symptoms manifest themselves with coughing and deep inhalations/exhalations;
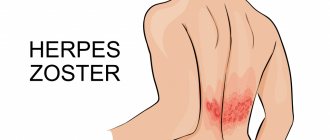
- herpes zoster - characterized by intense pain under the ribs in the right or left side, which is accompanied by itching or burning.
Another reason is hypertonicity of the pectoral muscles, which occurs as a result of intense physical activity. The pain in this case increases and is localized in the intercostal space.
More about fibromyalgia
Diagnostics
After the doctor has collected the patient’s complaints and history of the development of the disease, additional examinations must be carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
The most informative and used of them:
- Chest X-ray - reveals disturbances in the structure of bone tissue, as the main cause of the development of neuralgia;
- Bacteriological blood test - if the cause of thoracalgia is an infection, it reveals the causative agent of the disease, in other cases the analysis remains unchanged;
- Complete blood count - normal values are typical, or a slight increase in leukocytes in the case of an inflammatory reaction in the nerve area;
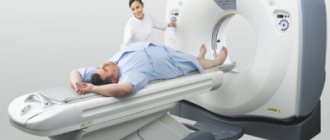
- Magnetic resonance imaging - determines bone and cartilage changes, swelling, pinching or inflammation of the intercostal nerve;
- Computed tomography is a more accurate method compared to x-rays; it reveals smaller abnormalities in the structure of bone tissue;
- Ultrasound – used to differentiate neuralgia from other pathologies, with thoracalgia it remains unchanged;
- Electrospondylography – determines the pathology of the intervertebral discs and spine;
- Myelography - the spinal cord and intercostal nerves are examined using a contrast agent on an X-ray machine, and allows you to identify changes in the nervous tissue;
- Electromyography - determines abnormalities in muscle fibers along the affected nerve.
Drug treatment
For neuralgic pain, drug treatment at home is the main thing. Typically, the following drugs are prescribed for neuralgia:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: piroxicam, diclofenac, indomethacin, ibuprofen and voltaren. These medications are used externally in the form of ointments, and internally in the form of capsules, tablets and injections.
- Medicines that relieve the main symptom – pain: spasgan, sedalgin or analgin.
- Muscle relaxants sirdalud, baclofen, clonazepam (relieve one of the causes of neuralgia - muscle spasm).
- Medicines such as viperalgin, vipratox, apizartron and virapin, containing bee and snake venom, significantly alleviate the condition of patients.
- Anesthetics (lidocaine and novocaine), which are used to perform blockades in acute conditions, injecting them intramuscularly.
- B vitamins, the deficiency of which negatively affects the nervous system and provokes intercostal neuralgia.
- Sedatives are prescribed for insomnia caused by excruciating neuralgic pain.
Treatment
In the fight against left-sided thoracalgia, complex treatment is used, which is aimed at solving the following problems:
- relief of pain;
- relieving inflammation;
- elimination of the disease that caused neuralgia.
During the acute period of thoracalgia, the patient is recommended to adhere to bed rest and exclude all possible movements. To get rid of pain and improve the general condition, methods such as are prescribed: taking medications (analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, vitamins); physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis, laser therapy, acupuncture).
For a patient suffering from intercostal neuralgia, during an exacerbation it is recommended:
- adhere to bed rest, using a flat and hard surface;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages;
- avoid severe stressful situations.
After getting rid of severe pain, it is necessary to establish the cause that provoked the attack of thoracalgia and proceed directly to the treatment of this disease.
If the development of pathology occurs against the background of deformities of the spinal column, then treatment is applied, including:
- exercise therapy;
- special massage;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- osteopathy.
Learn more about the treatment methods for intercostal neuralgia:
- To find out how dangerous intercostal neuralgia is for pregnant women, follow the link
- How and with what help is intercostal neuralgia treated at home?
- Find out more about the treatment of intercostal neuralgia using ointments and injections on the page
- A list of names of tablets for intercostal neuralgia and their descriptions are here
Drugs
Did you know that...
Next fact
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia on the left side with medical means includes taking medications from the following pharmacological groups::
| Group | Action | Names |
| Analgesics | Relieve pain syndrome |
|
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Eliminate inflammation, reduce pain |
|
| Muscle relaxants | Helps relax muscles and relieve spasms |
|
| B vitamins | Regenerate nerve tissue |
|
| Anesthetics | Relieves acute pain |
|
| Sedatives | Fight stress and insomnia |
|
| Diuretics | Relieves puffiness |
|
Surgical method
The use of surgical intervention for left-sided thoracalgia is possible if conservative therapy is ineffective . The surgical method can be aimed at treating osteochondrosis and spinal disc herniation, which caused neuralgia. The operation is indicated for large formations in the area of the spinal column that cause compression of the nerve roots and cause pain.
Exercise therapy and massage
Physical therapy exercises and massage sessions are more effective in treating intercostal neuralgia on the left and help:
If intercostal neuralgia occurs as a result of muscle spasm, then massage will help relieve tension and release a pinched nerve and speed up blood circulation;- increase the speed of metabolic processes;
- relax muscles and eliminate spasms;
- strengthen the muscle corset;
- reduce pain;
- improve overall well-being;
- prevent re-development of neuralgia.
To enhance the relaxing effect of the massage, it is recommended to use a warming cream . The procedure is carried out in a sitting position and involves rubbing and stroking the intercostal spaces and spinal muscles.
The set of exercises, intensity and duration of training for each patient is selected exclusively by a specialist in this field. When performing special gymnastics, sudden movements of the body and lifting weights should be avoided. Exercise therapy can be done either under the supervision of a professional or independently at home.
Home medicine
In the fight against intercostal neuralgia, along with traditional treatment methods, folk remedies are successfully used to relieve pain and eliminate inflammation.
To make you feel better, use the following recipes::
| Ingredients: | Preparation |
| Flaxseeds | The grains of the plant are wrapped in gauze and steamed, and then applied in the form of applications on the left side |
| Horseradish root | Squeeze the juice from this part of the plant and apply it to the affected area. |
| Wormwood, sea buckthorn oil | Steam the wormwood and combine with oil. Apply the resulting mixture to the left side of the chest. |
| Alcohol, pepper patch | Treat the affected area with alcohol and wipe dry, then apply a patch to the skin. |
| Salt or sand | Apply bags of warm salt or sand to the problem area |
| 4 tbsp sage, 100 g sea salt, 0.25 l boiling water | Brew sage in water, leave for an hour, then strain. Add salt and broth to the bath, lie down for 15-20 minutes |
| 0.1 l milk, 1 tbsp honey, 5 drops eucalyptus and lavender oil | Combine all components and pour into the bath. Immerse yourself in water for 10-15 minutes; there is no need to rinse the skin after the procedure. Repeat sessions 1 time every 2 days |
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of thoracalgia on the left side, as well as to avoid relapses of the disease, you should follow simple recommendations:
- monitor general health;
- sleep at least 8 hours;
- eat well;
- eat foods containing B vitamins;
- exercise daily;
- maintain correct posture;
- avoid excessive loads;
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- do not abuse alcoholic beverages;
- quit smoking.
Non-drug therapy
Intercostal neuralgia can be treated without the use of medications using the following methods:
- Using massage movements of the hands with a warming ointment or cream applied to them, deep warming and relaxation of the muscles that create a protective “corset” (or, conversely, leading to compression of the intercostal nerve) is achieved. It is performed in a sitting position with rubbing and stroking the intercostal spaces with the fingertips and subsequent kneading of all the spinal muscles.
- Unlike the previous method, acupressure applies pressure to the physiologically and bioenergetically massaged chest points associated with the diseased organ, leading to pain relief, relaxation and a quick effect by stimulating the body’s own defense mechanisms.
- Similar physiologically and bioenergetically justified effects are the methods of acupuncture (acupuncture), cauterization, and laser therapy, which make it possible to quickly neutralize muscle imbalance in the deep back muscles with the elimination of pain.
- Treatment of intercostal neuralgia by placing massage cups on the back pursues the same goals, being a simple and harmless technique for the body (provided there are no contraindications to its use).
- Manual techniques are resorted to after the end of the acute period. They consist in returning to their proper places the bone structures and muscles and ligaments that serve them that have been displaced during the disease and are carried out exclusively after manual diagnosis. As a result of the impact, the diameter of the narrowed tunnels (bone-tendon and musculoskeletal) returns to normal and the function of the pinched nerve is restored.
Like all the above methods, physiotherapeutic methods using:
- magnetic or electromagnetic field;
- ultrasonic, ultraviolet and infrared radiation;
- electro- and iontophoresis, with a dose of the drug substance that is minimal for the risk of the fetus.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia using traditional methods
There are many folk recipes that can be used to treat intercostal neuralgia at home. However, I would like to note that since the reasons causing it are quite serious, you should not self-medicate and check whether the disease can go away on its own. Secondly, it is necessary to accurately confirm the diagnosis, excluding pathologies of the cardiovascular system and other disorders. Otherwise, the underlying disease can be triggered.
- Sage baths with sea salt help relieve tension and reduce pain.
- Rubbing with tincture of valerian or infusion of birch buds is effective - their effect is in no way inferior to industrially produced ointments. However, it is better not to apply alcohol compresses at night - prolonged exposure to alcohol can lead to burns.
- Warming up also helps, but the thermal effect for intercostal neuralgia should not be direct, that is, do not apply a heating pad, hot potato or egg, but wrap yourself in a downy scarf or knitted woolen item. If you heat the painful area too much, the pain will go away for a short time and then such an effect will only increase the swelling of the soft tissues and bring even greater pain.
- For topical application to affected areas, use black radish juice or horseradish juice. Compresses based on steamed flax seeds help a lot.
To prevent chronic neuralgia, it is important to eliminate the effects of harmful concomitant factors, such as psycho-emotional stress, heavy physical activity, alcohol abuse, and also to treat existing diseases of the nervous system, systems and organs, etc.
Exercises
Physical therapy (physical therapy) is an effective way to treat neuralgia due to the anatomical structure of the human body. The nerves are located in the grooves of the ribs, which are covered by muscles. Spasmed muscles put pressure on nerve trunks, which causes pain. Exercises relax the muscles of the back and chest, improve blood circulation, and as a result the pain goes away. Gymnastics are prescribed only after acute pain has been relieved.
When performing physical exercises, you must consider some rules:
- Classes begin with a light warm-up - the body should be warmed up.
- The load must be increased gradually.
- You can't exercise through pain.
- Movements should be careful and smooth.
- Exercises should be aimed at strengthening the back muscles and stretching the spine.
- When performing exercises, you need to relax your back muscles as much as possible.
- You need to study every day, without skipping.
Gymnastics using the method of Dr. Bubnovsky is very effective. The essence of his technique: no medications, the medicine will be exercises, including those performed on special simulators. These exercises increase blood circulation and relax the deepest muscles.
Prevention
Specific prevention of neuralgia of the intercostal nerves has not been developed; general strengthening measures will help prevent the development of pathology. Recommended:
- avoiding hypothermia;
- hardening of the body;
- a healthy lifestyle, including regular moderate physical activity and a rational, balanced diet;
- measures to help prevent spinal curvature or treat an existing curvature;
- timely treatment of spinal diseases, chest injuries, pathologies of internal organs;
- work in comfortable conditions, with prolonged forced body positions, take breaks for a short warm-up.
Consequences
Intercostal neuralgia on the left side does not pose a particular threat to the patient’s health, but it can cause a lot of discomfort, cause sleep disturbances, hypertensive crisis and other negative consequences. The main danger of thoracalgia is that its symptoms are similar to the manifestations of diseases of the internal organs, so neuralgia is often confused, for example, with cardiac disorders. At the same time, the disease can be caused by serious hidden pathologies, such as intervertebral hernia, diabetes mellitus, tumor .
Video: “Intercostal neuralgia: symptoms, treatment”