MRI for traumatic brain injury Concussion is the most common type of traumatic brain injury (TBI). The organ does not undergo anatomical changes, and the neurological symptoms go away on their own. The diagnostic process includes questioning, examination and the use of instrumental methods. Performing magnetic resonance imaging if a concussion is suspected is unreasonable in the acute period. This is due to the fact that the considered variant of TBI is not accompanied by structural changes. An MRI after a suspected concussion will most reliably show the condition of the nervous tissue and promptly identify the presence of serious problems several weeks and even months after the injury. In the acute period, diagnosis does not make sense.
A concussion is considered a minor injury, accompanied only by disruption of brain function. A person may experience certain symptoms after an injury, including:
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- short-term amnesia (memory loss);
- sleep disturbance;
- headache, etc.
Loss of consciousness lasts from seconds to 5 minutes. The patient may not remember events that preceded the traumatic exposure (retro-) or occurred immediately after it (anterograde amnesia). However, all symptoms will go away in no more than 7 days. The main task of doctors in such a situation is not to miss dangerous injuries.
A brain contusion is a more severe injury. In this variant of TBI, morphological changes occur, cells are damaged and the connections of their processes (axons) may be disrupted, intracranial vessels rupture with the formation of hemorrhages and hematomas. When physical force is applied to the head, the nervous tissue receives two blows: the first - directly at the site of impact, the second - on the opposite side. The described phenomenon occurs due to the fact that the brain is injured from the inside by its own skull. The recovery period for a bruise may take more than one month, but a computed tomography scan will show the presence of this type of injury and will allow treatment to begin, and an MRI will reveal the consequences of a severe head injury after a while, helping to choose the right method of rehabilitation.
Subdural hematoma due to traumatic brain injury
Table of contents
- In what cases is a CT scan prescribed, and in which MRI?
- Contraindications
- Advantages of each type of tomography
- Technical specifications
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Computed tomography
is a type of study in which a layer-by-layer scan of the patient’s organ is performed. A multislice computed tomograph is used to carry out the procedure. The principle of its operation is based on the reflection of X-ray radiation from tissues and bones. The result of the study is presented as a 3D image on the doctor’s monitor and can be recorded on disk.
The CT machine is a circle around a table with movable sensors, which, rotating during the examination, take pictures from different angles.
Since using this method the patient receives a certain dose of radiation, the study is not recommended to be done frequently.
Magnetic resonance imaging
is an examination based on the effect of magnetic resonance, which is reflected differently from more or less dense tissues.
A tomograph is also used for this, but of a different, often closed type. It is equipped with a retractable table on which the patient is placed, and a tube-shaped apparatus into which this table is pushed.
This is a fairly safe examination method, although there are a number of limitations in its use, mainly related to the presence of metal implants in the body.
Should a concussion be treated?
Definitely a must! First aid for the victim is rest and a cold compress on the site of the injury. Harvesting the summer harvest, renovating the apartment and any other important work can wait. It’s better to lie down and call an ambulance or go to the emergency room (just don’t drive). You should also not take medications, as they can mask the symptoms and blur the clinical picture.
The victim must obtain a doctor's prescription. These can be mild sedatives, diuretics (to prevent edema). And in severe cases, neurosurgery may be necessary to eliminate intracranial hemorrhage.
In what cases is a CT scan prescribed, and in which MRI?
Because both types of examination rely on different physical and chemical phenomena, the effectiveness of each varies depending on the tissue being analyzed.
When a doctor prescribes a brain MRI or CT scan, he is guided by what exactly needs to be examined. Thus, CT is considered more effective in examining hard tissues, skull bones and their disorders, and MRI is considered more effective for analyzing soft tissues.
Main indications for CT scanning
The study is prescribed in the following cases:
- The patient suffered a traumatic brain injury
- Constant headaches after a stroke
- Pathological change in the bone tissue of the head
- Concussion diagnosed
- It is necessary to confirm or deny the presence of hemorrhage
- Brain structures have shifted
- There is a possibility of a foreign body
Main indications for MRI
Such a study is prescribed in the following cases:
- Suspicion of a tumor
- Regular headaches, dizziness, fainting
- The patient suffered a stroke
- Lost hearing or vision
- Injuries, hematomas and swelling
- Memory loss, problems concentrating
- Inability to perform CT
MRI is also prescribed to evaluate:
- Correctness of treatment
- State of the brain after detection of a malignant tumor
- Pre- and postoperative condition
Magnetic resonance imaging is recommended for a child if:
- He had pathologies during intrauterine development
- He lags behind his peers in various indicators
- The child suffers from convulsions, dizziness, loss of consciousness
- He stutters or has other speech problems
Physiological manifestations of concussion
Pathology arises, as mentioned earlier, as a result of trauma, which can be of a different nature and affect any part of the patient’s skull. In this case, a lightning-fast increase in intracranial pressure develops, which is considered a direct etiological factor causing further functional disorders - loss of intercellular connections of brain structures, disruption of cellular nutrition, physicochemical transformations.
After a concussion, MRI is also performed to identify more serious consequences, including rupture of intracranial vessels and irreversible traumatic changes in areas of the brain. It is this type of research that is most informative regarding morphological and structural changes.
Contraindications
Computed tomography is not performed
in the following cases:
- When the patient is pregnant
- With a large body weight (more than 130 kg) of the patient
It should be used with caution for nursing mothers, and if the procedure is completed, the baby should not be breastfed for another day.
If the study is carried out with a contrast agent, there are more contraindications:
- Allergy to iodine
- Diabetes
- Endocrine diseases
- Problems with the liver and kidneys
MRI should not be performed in patients who:
- There are metal prostheses made from materials that interact with a magnetic field
- Heart valves and pacemakers
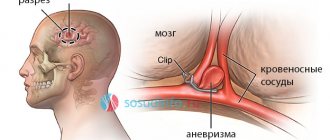
- Metal clips on vessels with aneurysm
- Hearing Aids
- Fixed dentures made of steel and similar materials
The study is applicable with limitations when:
- The patient is in the first trimester of pregnancy
- The patient suffers from a fear of enclosed spaces
- The patient has crowns, braces
Also, an obstacle to both studies may be the patient’s inability to lie still for the required time due to severe back pain.
If the patient knows about the presence of any limitation (pregnancy, previously diagnosed diabetes, metal implants, etc.), he must inform the doctor in advance.
What are we complaining about?
Typical symptoms of a concussion: temporary fainting, headache, blurred vision, double vision, nausea, vomiting. But even if the victim understands the speech addressed to him, clearly answers questions and does not complain about anything at all, then there is no point in rejoicing that he successfully fell from a tree or from a stepladder. If after some time drowsiness, weakness appear, blood pressure rises, temperature rises, or the condition changes in any other way, then you need to undergo diagnostics.
It is better to play it safe than to later face manifestations of post-concussion syndrome or complications. And this can be either memory impairment or attacks of aggression, or a stroke. Moreover, such consequences are not at all uncommon. According to statistics, after a mild head injury, almost 10% of cases develop a stroke within five years.
Advantages of each type of tomography
To decide between a brain MRI or a CT scan, you need to consider their purpose and benefits for a particular diagnosis, and also take into account the types of tissue that need to be studied.
Benefits of CT
Computed tomography is one of the most accurate ways to study disorders associated with the state of the brain. It is especially effective if it is necessary to identify abnormalities resulting from traumatic brain injury, as well as other problems with the bones and dense tissues of the skull.
This happens because X-rays are reflected in a special way from dense bone tissue. However, the radiation dose that the patient receives is much lower compared to other x-ray studies. In this way, various diseases can be diagnosed without the use of invasive methods, which makes the procedure painless.
Using CT, you can diagnose a stroke, arterial disorders due to atherosclerosis, changes in the structure of the cerebral cortex and lesions of the facial bones. It allows us to examine such disorders in great detail and identify the causes of diseases.
The procedure takes no more than fifteen minutes. There is no risk of distorting the result if the patient accidentally moves.
Patients suffering from claustrophobia can easily tolerate a CT scan because an open machine is used, in which only the head is immersed, and not the whole body.
It is important that the CT result can be seen immediately, although in some cases the image may not have enough contrast.
Benefits of MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is no less accurate than CT, but its scope is somewhat different. It allows you to diagnose diseases of the soft tissues of the brain and shows results in three planes:
- Axial (horizontal projection)
- Frontal (direct projection)
- Sagittal (lateral projection)
MRI allows you to very clearly see problems with soft tissues: benign and malignant (cancer) neoplasms (their shape, location and volume), dysfunction of the pituitary gland, nerve and muscle fibers. You can see and measure the volume of edema, tumors of the nervous system, and more. The bones will be displayed indirectly.
This method is safe, so it can be used to diagnose pregnant patients, but only in the second and third trimesters. It is also allowed to be used for diagnosing children from the age of three. It is necessary to explain to the child how the study will take place so that he is not afraid and tries not to move.
MRI can be done several times over a short period of time.
The procedure lasts about half an hour. During this period, the patient is required to lie still. Otherwise, the image may be distorted and the result may be unreliable or inaccurate.
For patients with a fear of closed spaces, the study can be carried out in a state of medicated sleep.
Symptoms of concussion and skull injuries:
- damage that is visible to the naked eye;
- headache;
- vomiting reflex;
- nausea;
- loss of consciousness;
- nose bleed;
- pale skin;
- temperature increase;
- decreased performance;
- slow reaction;
- poor appetite.
Technical specifications
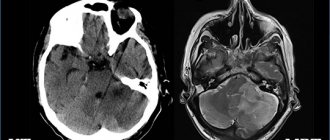
MRI provides extremely clear images (excluding bones) in the form of projections from different angles; CT scan provides a less clear picture, but the structure of the bones is clearly visible, and the image is presented on the monitor in the form of a 3D model.
Another important point is the amount of time you need to spend in the device. For CT it ranges from 5 to 15 minutes, for MRI – about half an hour. The patient should remain as still as possible. But it is not so critical for the results of a computed tomography scan if the patient moves a little. Such movement can introduce serious distortion into magnetic resonance imaging data.
CT can help make an urgent diagnosis if the patient is seriously injured and has symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage.
To choose the most effective examination method (brain MRI or CT), you need to pay attention to many factors. Only a qualified doctor can do this. The patient is obliged to provide all information that will help in this.
Concussion Screening
Why do you need a concussion evaluation? To promptly notice and treat possible dangerous conditions that often accompany a concussion:
- The release of blood into the membranes and substance of the brain;
- Fractures of the bones of the skull, orbits, face, cervical vertebrae;
- Hemorrhage in the orbital tissue and eyeball;
- Inner ear injury;
- Foci of death of brain matter.
MRI and X-ray computed tomography of the brain will show brain swelling, hemorrhage, traumatic changes in the brain, damage to the bones of the brain and facial skull.
To assess the mobility of the vertebrae after injury, an x-ray of the cervical spine with the head tilted forward and backward (fractures, dislocations and subluxations of the vertebrae are clearly visible).
Evoked potentials of the brain are the most accurate research method today, providing information about disturbances in the conduction of impulses in various parts of the brain (visual, auditory, sensory, motor pathways of the nervous system).
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- MEDSI clinical diagnostic centers have modern equipment, which allows you to obtain the most accurate results
- Radiologists, oncologists, surgeons and other professionals take on the most complex and rare cases
- It’s easy to sign up for a consultation and find out more details – all you need is one phone call at + 7 (495) 7-800-500
- MEDSI will help you choose the right examination, treatment and rehabilitation measures (if necessary)