Russian scientists warn that the pathogen that causes Wuhan pneumonia is capable of penetrating the blood-brain barrier and directly destroying brain tissue. Descriptions of clinical cases have already appeared in which COVID-19 caused necrotizing encephalopathy in those infected - a critical lesion of the main organ of the central nervous system. However, coronavirus can cause neurological complications without damaging the lungs at all. Brain dysfunction is indicated, in particular, by a symptom such as loss of smell. The pathogen can also have a negative effect on the cardiovascular system.
“Up to 50% are asymptomatic, and they can spread the virus”
Professor Sergei Netosov - about what will help Russia win the fight against COVID-19
Attack on the brain
Some patients with COVID-19 develop serious brain damage, doctors warn. In addition to the high temperature, fever, cough and difficulty breathing that traditionally accompany coronavirus pneumonia, some infected people experience mental changes caused by neurological disorders. Professor of the Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, head of research in the field of molecular virology and oncology Andrei Kozlov told Izvestia that influenza and herpes viruses can lead to the death of entire areas of the brain. A similar picture is observed with the new coronavirus.
— Several articles noted that some patients did not have pulmonary dysfunction, but experienced absent-mindedness or epileptic symptoms. Together with the previously noted loss of taste and smell, such symptoms may indicate infection of brain tissue by coronavirus, the expert believes.
Photo: de
Double infection: patients with both influenza and COVID-19 are especially dangerous
In this case, test systems may not detect coronavirus
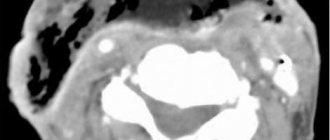
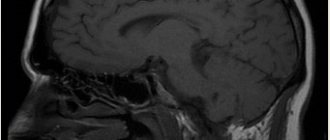
At the end of March, doctors from Detroit described a case of necrotizing encephalopathy in an employee of one of the American airlines. A woman in her 50s was hospitalized with a fever and cough. In addition, she experienced confusion.
Doctors conducted a series of tests for influenza, chicken pox and West Nile fever, but all of them were negative. A swab taken from the nasopharynx confirmed the diagnosis of COVID-19. However, due to symptoms atypical for coronavirus, it was decided to undergo a CT and MRI scan for the woman. The resulting images showed focal lesions in various areas of the brain, in particular, the temporal lobes, whose functions are associated with the perception, analysis and synthesis of speech, as well as the ability to sense tastes and smells, were damaged. Doctors diagnosed the patient with acute necrotizing encephalopathy, a rare disease that develops against the background of viral infections, most often influenza.
Lifelong misadventure: COVID-19 may become a chronic disease
Experts are studying cases of coronavirus re-infection
Main types of pathology
Experts divide the disease according to etiological factors, represented by:
- Ischemic damage - a heart attack at the cellular level develops as a consequence of blockage of blood vessels with air and blood plaques. The problem occurs with spasms of the arteries, increased tension of organs against the background of oxygen starvation. A heart attack damages the tissue of the kidneys, spleen, heart muscle, and brain.
- Traumatic – formed as a response to the direct impact of individual factors on tissue. The source of necrosis is increased or decreased temperature, the influence of radiation and electric current.
- Trophoneurotic – formed in disorders or diseases associated with the nervous system.
- Toxigenic - pathological process is preceded by the penetration of bacterial or non-bacterial toxins. Sometimes there is the development of toxic necrosis during fetal development, associated with the influence of pathogens or medications.
Necrosis occurs:
- traumatic and toxic (divided according to the mechanism of formation) - direct type;
- ischemic, allergic or trophoneurotic - indirect type.
Additional division allows specialists to choose a therapy suitable for the body.
Cytokine storm
Encephalopathy (dystrophic damage to brain tissue) can develop due to the fact that the cells of the immune system of a person infected with coronavirus begin to actively release cytokines into the blood. This class of substances includes about a hundred complex proteins involved in many immune and inflammatory processes in the human body, Nikolai Karpov, an employee of the Institute of Biology of Tyumen State University, told Izvestia. The increase in the concentration of such proteins is called a “cytokine storm.”
“In excess, these substances can damage the walls of blood vessels and cause hemorrhages in the brain, which leads to the development of certain neurological symptoms (depending on the affected area),” the expert said. “It is also possible that the virus can penetrate the blood-brain barrier directly into the brain tissue.
Electron microscopic image of coronavirus reproduction
Photo: REUTERS/US NIAID-RML
According to the scientist, not only coronavirus, but also influenza, as well as other acute respiratory viral infections, can cause encephalopathy, but this complication is rare. In general, science knows dozens of viral diseases, which in a certain percentage of cases cause neurological complications. For example, the viruses of tick-borne encephalitis, measles, herpes types 1 and 2 and West Nile fever, almost all alphaviruses, including the Karelian fever virus (an acute infection believed to be carried by mosquitoes of the genus Culex. - Izvestia) and a lot others.
Corona pressure: hypertension has become the most common companion of COVID-19
At the same time, stress and panic can worsen the course of cardiovascular diseases, Russian scientists believe
6.4. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis (lat. osteoporosis) is a disease of bone tissue due to metabolic disorders, manifested by changes in the structure and thinning of the bone, leading to deformation and fractures. The main changes characteristic of osteoporosis and determined by special studies are expressed in a decrease in the number of load-bearing trabeculae and bone mass per unit area.
The formation of the skeleton, as a rule, by the age of 24-25 provides a peak in bone mass, then, with increasing age, the bones thin out and become less strong and elastic. This can be partly explained by the fact that after about 35 years of age, calcium leaching from bones occurs more rapidly than transport and deposition into bone tissue. This, as a rule, is inherent in everyone, but in some people, with certain changes in metabolic processes, bone tissue proteins are lost, the balance of microelements is disturbed and leaching becomes excessive, which ultimately leads to osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis affects the entire skeleton, but most often the hips, forearms and vertebrae. If we look at the average graphical picture of changes in bone density in accordance with age, we will see a period of low bone density in a growing and developing organism, when metabolic processes are represented mainly by bone formation and its slight resorption. This is typical for childhood and adolescence. At 25 years of age, when maximum bone mineral density is reached and the metabolic processes of bone formation and resorption (resorption) are balanced, bone density is maintained. After 50 years, when, due to certain shifts in metabolic processes and endocrine changes, resorption prevails over bone formation, a mechanism is formed in the body for loss of bone density by an average of 3-5% per year.
Biochemical parameters in patients with osteoporosis indicate not only a decrease in the content of calcium, mainly the ionized form, and phosphorus in the blood, but also an increase in the content of alkaline phosphates and a decrease in the level of calcium in the urine. The total amount of calcium in the body is 1.2-1.5 kg, the presence of other inorganic substances - phosphorus, sodium, potassium, magnesium - is necessary to maintain metabolic processes, absorption of calcium by the intestines and transport by proteins, as well as for the reabsorption of calcium by nephron tubules. Bone tissue contains predominantly 25-30% water and 70-75% inorganic and organic substances.
Inorganic substances contain 60-70% calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate (approximately 700 g), of which 99% is found in bone tissue. Phosphorus in bones is approximately 440 g. Of organic substances, the content of ossein is 20-40%. The organic components of bone form a network structure that gives bone strength and withstands various stresses. Research results confirm that inorganic substances allow bone to withstand compression, and organic collagen fibers allow it to withstand tension.
Bone, being an ideal structural material, plays the role of support and leverage, has high strength and low weight. Some researchers believe that bone is much stronger than granite, and its density is much less than that of steel and granite. Bone has the greatest resistance to compression in the longitudinal direction, and when stretched, it is easily damaged, so the placement of trabeculae depends on the load-bearing capacity of the bone.
The distribution of stress in bone under load depends on the shape and structure of the bone itself. Bone's ability to withstand prolonged stress and fatigue is limited. Bone is very sensitive to physiological stimulation by tension: the greater the force of tension, the greater the trabeculae and bone density.
Radiographs of osteoporosis indicate that trabeculae in cancellous bone thicken and decrease in number, and cortical bone becomes thinner and takes on a layered appearance. Often there is an expansion of the epiphyseal line, and in childhood brush-like formations form on the metaphysis.
Osteoporosis can be accompanied by metabolic diseases of the skeleton: softened bone fluorosis, renal osteodystrophy, hyperparathyroidism, calcium assimilation disorders, nutritional osteodystrophies. Multifactorial changes in the body under certain conditions contribute to the formation of osteoporosis with obligate changes in the structure of the femoral head and the development of ANFH.
Osteoporosis, which causes changes in the structure of the femoral head and leads to compression obstruction of the microvasculature, creates ischemia and conditions for the development of aseptic necrosis. Considering the pathogenetic connection of osteoporosis and aseptic necrosis, it is very important for each doctor and patient to use the principle of individual diagnosis and prevention of osteoporosis with examinations of increasingly younger people, up to children and adolescents, to assess their rate of bone mass gain.
Treatment of dry necrosis
There are two ways to stop the destruction of cells in tissues:
- surgical intervention;
- apply local treatment.
Local treatment, the most gentle, consists of the following measures: treating the area around the affected area with an antiseptic; applying a bandage soaked in ethyl alcohol or other disinfectant (boric acid, chlorhexidine), etc. But it is not always possible to do without the intervention of surgeons, since necrosis is a rather complex disease. Conservative therapy can improve blood circulation in the affected area (intimothrombectomy, bypass surgery). It is not recommended to treat this disease on your own. It is best to contact a specialist who will prescribe treatment. The process of stopping tissue cell death is quite complex. To achieve restoration of the body, it is necessary to take radical measures. In such cases, the work is carried out by several doctors specializing in different fields of medicine. The results of treatment may depend on several factors, including the location of the lesion, the size of the area with necrosis and the general condition of the patient. Tissue destruction can have a toxic effect on the patient’s body due to the emergence of microbes in the affected area. That is why the first actions are aimed at disinfecting this area. Experts recommend visiting doctors as often as possible to check the condition of your body. Such procedures can help identify the disease at the primary stage, which will significantly facilitate further treatment.