Neurosis of the stomach and intestines often occurs due to stress and poor lifestyle. This means that most modern people are at risk. Delayed diagnosis will lead to progression of the disease and increased damage to health. The consequences can be serious weight gain, ulcers, chronic intestinal diseases and much more.
In this article we will talk about the symptoms and treatment of gastric neurosis. We will also try to find out what causes the disease and how to prevent it.
What is gastric neurosis?
All systems of the human body have nerve endings, so neurosis can occur in any organ.
There are especially many of them in the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore gastric neurosis occurs quite often. Psychosomatic causes usually do not cause severe pathologies of the stomach. But pain during the development of this pathology is felt quite strongly, which is why the quality of life of the sick person is significantly reduced. Feeling severe pain, people often do not want to believe that the cause of their occurrence is psychological. However, it is important to take into account that a prolonged depressed state causes a general decrease in immunity, and failures of the immune system can provoke the development of various infectious diseases.
Psychiatrist consultation
treatment of neuroses at home and in the clinic
rehabilitation until complete recovery
We work around the clock
Call a doctor at home Leave a request and we will call you back in 1 minute
8
Or call
Not defeat, but irritation!
Not only poor nutrition and physical inactivity are dangerous for the intestines. In 80% of cases, functional disorders of this organ arise due to stress. It is not for nothing that a disorder such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is also called intestinal neurosis. In this case, no dangerous organic lesions occur, but this does not make it any easier for patients.
Related article Medicinal plants: 45 recipes for a healthy stomach and liver Gastrointestinal disorders that develop with IBS can be explained by a disruption in the interaction between the digestive and nervous systems. The work of the intestines is controlled by the brain, it sends signals for emptying, and the intestines clearly follow the order. But under stress, the brain receives incorrect signals, to which the completely confused intestines respond with pain and other unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, it is not surprising that people who are emotional, have high anxiety and low resistance to stress and, by the way, high intelligence, more often suffer from stomach problems. By the way, women are diagnosed with IBS 4 times more often than men, because they, as a rule, perceive everything that happens more acutely. In total, from 15 to 48% of the population suffer from this disaster.
Diagnosis of gastroneurosis
Many signs and symptoms of gastric neurosis are identical to those that develop with gastritis.
Therefore, to correctly diagnose this disease, it is important to pay attention to the presence of psychological symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat, headaches, overexcitation, insomnia, panic attacks, phobia, hypochondria, etc. Characteristic signs of gastric neurosis in children are nervous vomiting, not accompanied by nausea. In adults, this disease often manifests itself in the form of anorexia (complete lack of appetite) or bulimia (a condition in which a person eats too much food). Both of these pathologies are dangerous and can ultimately even lead to death.
Evening concert
There are a number of signs that are typical of IBS. This is pain, rumbling and cramping in the abdomen, problems with stool (diarrhea or constipation, and more often their alternation), increased gas formation (flatulence). Sometimes atypical complaints arise, for example, headaches and frequent urination.
Article on the topic
Bear disease. What diseases can be hidden behind common diarrhea? Most often, the concert plays out in the stomach in the evenings, and especially after eating gas-forming foods (fresh vegetables and fruits, black bread). Symptoms usually subside after a bowel movement. Emotional shocks, anxieties and worries often lead to aggravation. And finally, an important point - by the morning the pain and discomfort usually disappear.
If the stomach aches in the morning no less than in the evening, then this is atypical and, most likely, does not indicate IBS, but some more serious diagnosis. By the way, under no circumstances should you tolerate severe abdominal pain that cannot be treated with antispasmodics. Indeed, such a sign may hide a life-threatening surgical pathology that requires urgent surgery (for example, acute appendicitis, cholecystitis or pancreatitis). In such a situation, you need to call an ambulance.
Therefore, a diagnosis of IBS can only be made after an examination that shows that there is nothing more dangerous. If there are no changes in the mucous membrane, and the discomfort in the intestines persists for longer than three months, and the stomach grips at least three times a week, then the doctor has the right to talk about the presence of this very syndrome.
Click to enlarge
Treatment options
The main therapeutic method used to treat gastric neurosis, as well as all other neurotic disorders, is psychotherapy.
Therapy involves group and individual personality-oriented sessions. During these sessions, the specialist helps the patient to discover the psychological conflict that caused the development of gastric neurosis in order to rebuild the personal relationships that caused the development of the pathology. The main task in this case for the psychotherapist is to switch the patient’s attention from the symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases to resolving the internal psychological conflict. Gastroenterological drugs are also used for treatment. They are prescribed to improve metabolic processes, eliminate spasms, normalize the secretion of gastric juice, and protect the gastric mucosa. Medicines are also prescribed to the patient for psychotherapeutic purposes - to give him confidence that treatment is being carried out. In advanced cases, the treatment regimen may also include tranquilizers and antidepressants.
Reasons for development
The immediate cause is autonomic dysfunction, which is provoked by the following factors:
- Prolonged stress . Constant overload, conflicts and negative experiences affect the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Constant exposure to the above circumstances leads to disruptions in autonomic regulation.
- Other neuroses . Symptoms of the disease can be observed with neurasthenia, hysterical neurosis, phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder. A combination with eating disorders - bulimia and anorexia - is often found.
- Personal characteristics . People who are irritable, hot-tempered, or insecure and have difficulty accepting criticism are prone to gastroneurosis. The disease is more often diagnosed in anxious individuals who are overly concerned about their own health.
These circumstances are aggravated by the habit of eating on the go, while watching TV or surfing the Internet, and the tendency to have irregular snacks. Risk factors include smoking, drug use, and abuse of drugs with psychotropic effects. An unfavorable predisposing background is created in the presence of severe neurological and somatic pathologies that aggravate disorders of autonomic regulation.
Our offers
Our clinic treats mental disorders in Moscow.
If you have symptoms of stomach neurosis, contact us. We employ experienced psychiatrists. They specialize in the treatment of psychosomatic diseases of various internal organs caused by psychological reasons. Our doctor will examine you, perform the necessary tests, after which he will make an accurate diagnosis and provide appropriate treatment. If necessary, a psychiatrist can visit your home.
Call by phone
Diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome
The first thing to do is to rule out diseases with identical symptoms. To do this, it is enough to take tests (including a blood test for celiac disease), conduct an ultrasound of the internal organs, and examine the gastrointestinal tract using one of the endoscopy methods.
In addition, you can do a CT scan (computed tomography) of the abdominal organs and undergo an X-ray examination.
If none of the examinations yielded results, you should focus all your attention on the nervous system, because with 99% probability the cause of the disease lies here.
How is the nervous system diagnosed in IBS? A neurologist must conduct an initial examination, collect the patient’s complaints and, based on them, determine further actions. At the Clinical Center for Autonomic Neurology, we conduct a study of heart rate variability - extremely effective for making a primary diagnosis.
At this stage, disturbances in the functioning of the sympathetic or parasympathetic division of the ANS may be detected.
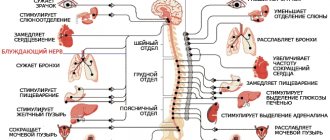
With sympathicotonia, the clinical picture of the disease will be a decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the stomach and intestines, spasm of the sphincters, which is expressed by severe heaviness in the abdomen, even after a small amount of food eaten, constipation, and bloating. With parasympathicotonia, on the contrary, it is insufficient work of the sphincters and increased peristalsis, which is manifested by belching air, flatulence, and frequent diarrhea. Pain can occur in both conditions. And often not isolated manifestations are observed, but their combinations (both sympathicotonia and parasympathicotonia).
The next stage of diagnostics is thermal imaging diagnostics. This method of examining the ANS is unique for our country and is available only in highly specialized neurological medical centers in a number of countries in Europe and Asia. Therefore, we are proud to be able to offer our patients this valuable diagnostic. The thermal imager has high accuracy in determining thermoregulation disorders on the body surface. By comparing foci of pathological thermoregulation with autonomic nerve centers, the doctor determines which nerve centers are impaired and prescribes local physical, neural and placental therapy.
In a patient with IBS, a thermal imager usually reveals a functional deviation in the functioning of the nerve centers of the thoracic and lumbar back, as well as the centers of the abdomen - the celiac (solar) plexus, the superior and inferior mesenteric, the superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses.
Extraintestinal symptoms
Temperature increase
Fever can be a symptom of infectious and inflammatory bowel diseases if it is accompanied by increased bowel movements, abdominal pain, and false urge to defecate (tenesmus).
Unreasonable weight loss or weight gain
Noticeable weight loss without using a weight loss diet or significant increase in physical activity may be a sign of an unhealthy gut. Inflammatory processes in the intestines during various diseases cause disruption of the absorption of nutrients necessary for the body and lead to weight loss. It can also be caused by bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine.
Weight gain may be caused by insulin resistance or a tendency to overeat, which may be due to, among other things, an imbalance of the intestinal microflora. Studies examining the gut microbiota of thin and obese people have found that overweight people are more likely to have an imbalance of gut bacteria. Also, certain types of bacteria can affect weight gain because they produce metabolite substances that increase the absorption of carbohydrates and fats, which leads to an increased intake of calories into the body and determines weight gain.
Decreased immunity
Intestinal dysfunction leads to serious problems with the immune system, facilitating the penetration of bacteria and viruses into the human body. Due to inflammatory processes in the intestines, not only the local protection of its mucous membrane from the penetration of foreign bacteria and viruses deteriorates, but also disruptions occur in the functioning of the general protective mechanism of the entire body.
An imbalance of intestinal microflora leads to the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and viruses in the intestines.
Increased fatigue, loss of strength
Research shows that people with chronic fatigue syndrome have abnormal levels of certain types of gut bacteria. In fact, the link between an unhealthy gut and chronic fatigue is so strong that one study estimates that 80% of people with chronic fatigue can be diagnosed simply by examining their gut flora.
An unhealthy gut can also negatively impact your circadian rhythm, which can disrupt sleep and make you feel overly tired during the day.
Unexplained low mood, anxiety, depression
Gut microflora plays an important role in mental health and a person's response to stress. While the exact mechanisms behind this phenomenon are not entirely clear, there is evidence that certain hormones produced in the gut, called gut peptides, control signaling between the gut and the brain (and vice versa). Hormonal imbalance can contribute to the development of anxiety and other psycho-emotional disorders.
Insulin resistance
The mechanisms that cause insulin resistance - a decrease in the sensitivity of tissues (muscle, fat and liver) to the action of insulin - are not completely known, but along with increasing age, dyslipidemia, excess weight, and the distribution of fat in the body, disturbances in the composition of the intestinal microflora play an important role. Scientific research has proven that microflora bacteria not only participate in metabolism in the body, but can also affect tissue sensitivity to insulin.
Skin problems
For eczema, psoriasis, acne and other inflammatory skin diseases, topical skin care products are often recommended, but you should be aware that some skin diseases can be combined with intestinal diseases. For example, celiac disease, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease have extraintestinal manifestations, sometimes directly related to the activity of the underlying disease, which determines treatment tactics.
Dysbiosis of intestinal microflora and impaired intestinal permeability that accompany intestinal diseases can cause the development of inflammatory reactions that worsen the condition of the skin. Read more about skin manifestations of gastrointestinal diseases
Vitamin and mineral deficiency
Celiac disease, lactase deficiency, infectious and parasitic intestinal diseases cause impaired absorption of vitamins and minerals in the intestine with the development of their deficiency.