Anonymously
Around the clock
Attention! The material contains information about substances, the use of which can cause serious harm to your health!
In the first weeks of quitting smoking, tobacco withdrawal occurs, which often causes relapses. A person who has firmly decided to quit a bad habit must know how to survive nicotine withdrawal and minimize poor health.
- What is nicotine withdrawal?
- Signs of withdrawal syndrome when quitting smoking
- Consequences of quitting smoking
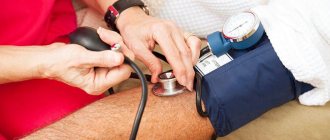
- Quit smoking - blood pressure went down
- Quit smoking - headache, dizziness, drowsiness
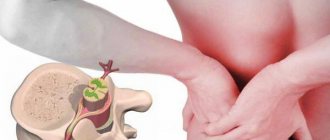
- Quit smoking - back hurts
- Nasal congestion
- Depression when quitting smoking
- Sore throat, lump in throat, pain
- Panic attacks when quitting smoking
- Lost appetite, loss of strength
- I quit smoking and have chest pain
- How long does smoking cessation last?
- How to fight the urge to smoke
- Methods to combat smoking withdrawal syndrome
- Drug therapy for tobacco withdrawal
- Relieve withdrawal symptoms at home
- FAQ
- If you quit smoking, how can you not start drinking more?
- Quit smoking, but no cough. Why?
- I haven’t smoked for a month, but I still crave it. What to do?
- Treatment of nicotine addiction at the Zdravnitsa clinic in Moscow
We will select an individual treatment plan
Free consultation 8-800-200-27-23
Nicotine is a legal drug
It's hard to wrap your head around it, but nicotine is a drug. Cigarettes are sold everywhere, and only in recent years have restrictions on the sale of tobacco products been tightened: it has become more difficult for teenagers to buy them; in stores, packs of cigarettes are hidden from prying eyes in special locked cabinets. Naturally, it is hard to believe that the drug can be sold in the open.
The method of drug use also plays an important role in the frivolous perception of tobacco addiction. The cigarette is easy to smoke. Even a Spartan meal for alcoholics requires minimal preparation, and you don’t need company to smoke a cigarette; you can even ask the first person you meet for a lighter. And the process itself seems harmless and safe. True, for the time being.
Withdrawal syndrome when quitting smoking
After a certain period of regular tobacco smoking, a person suddenly discovers that he has become dependent on this process.
When quitting smoking, he begins to experience obvious inconveniences. They are primarily expressed in psychological discomfort. Smokers describe this condition in different ways, but, as a rule, it is an inability to concentrate and irritability. There are also physiological manifestations that accompany nicotine withdrawal.
This whole set of unpleasant and painful symptoms is called withdrawal syndrome. It is a sign that the smoker has developed a persistent physical dependence on tobacco, or more precisely on its psychoactive component - nicotine.
How does nicotine affect the body?
When smoking cigarettes, nicotine acts on the central nervous system of a person, which is where the feeling of a surge of strength, vigor, and lifting the mood arises. The psychoactive substance affects the acetylcholine receptors of the brain, which provokes an unnatural release of adrenaline.
This is how a conditioned reflex arises; a connection is formed in the psyche between smoking a cigarette and receiving pleasure. Later, when the addict wants to get rid of the disease, it will be very difficult to break it.
In the case of smoking, this reflex arc causes harm to the body. However, it is worth remembering that all rewarding reflexes are formed in this way, and this can be used not only for harm, but also for good. In the case of sports activities, the body itself rewards us with the release of joy hormones. But we can give them to ourselves consciously with the help of natural pleasures. Thus, knowledge about the formation of reflexes makes it possible to control and shape your life according to your own rules.
But in the case of smoking tobacco, the opposite happens. The release of hormones is provoked by force; the body does not receive any real benefit or pleasure. But the deceived brain still adds smoking to the list of useful and pleasant actions that bring satisfaction. This is a stable psychological dependence on a drug.
How does a person feel when quitting smoking?
When a dependent person begins to smoke regularly, a physical craving for nicotine is added to the psychological dependence.
During the period of quitting smoking, the patient experiences a strong desire to smoke, psychological discomfort is expressed in anxiety, irritability, and excessive psychological stress. The addict becomes depressed, he can be aggressive and unrestrained, it is difficult for him to concentrate on anything because thoughts about smoking constantly creep into his head.
Withdrawal syndrome when quitting smoking is an unpleasant condition from a psychological point of view, however, this is not all the tests that a smoker faces.
Substitution
We are talking about vapes, smoking mixtures, electronic cigarettes, tobacco heating systems and other devices. When smoking, nicotine addiction develops, and it is because of this that it is difficult to quit smoking. Nicotine affects the functioning of the central nervous system. When you try to quit smoking, withdrawal begins, which manifests itself mainly in neurological problems. Among them are difficulties in concentration, anxiety, irritability, aggression, increasing discomfort, and constant thoughts about smoking. If a person switches from regular cigarettes to devices or mixtures that replace them, in fact, he does not give up nicotine, and the addiction continues. Only the method of obtaining nicotine changes. At the same time, when using new devices, it can be more difficult to control the dosage, and they themselves are positioned as safer. Because of this, the amount of nicotine consumed may even increase, and the addiction may intensify.
Have questions? Get a free specialist consultation by phone:
+7
Physiological manifestations of withdrawal syndrome
Let's not forget that nicotine is a real poison. It poisons the human body and causes great harm to it.
During the period of nicotine withdrawal, the body also has a hard time. A smoker develops severe headaches and may develop seizures. A classic symptom of abstinence, characteristic of many addictions, hand tremors, also awaits a nicotine addict.
The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is abnormal. On the one hand, there is an increase in appetite, on the other hand, the smoker suffers from nausea. Sometimes the patient may experience constipation. A rapid heartbeat is accompanied by sharp changes in blood pressure, shortness of breath appears, as if the person does not have enough air when breathing. A state of general weakness and weakness complements this bouquet of symptoms.
And the method of using the drug itself harms the respiratory system, so when you quit smoking, a strong cough occurs, and ulcers may appear in the mouth. During the period of withdrawal syndrome, a smoker's overall level of immunity decreases. The immune system decides that it is possible to “relax”, because so many poisons no longer enter the body. Together with the damage caused by smoking to the respiratory organs, this leads to bronchitis, laryngitis, and rhinitis. When a person smokes, his bronchioles are in a state of prolonged spasm; accordingly, during the period of withdrawal syndrome, they expand, and infections penetrate through them more easily.
Main signs of nicotine addiction
- An irresistible craving to take a substance.
- Difficulties in controlling one’s own behavior in conditions where it is impossible to obtain this substance in a timely manner.
- The development of withdrawal syndrome, a state of withdrawal (withdrawal) in situations when the substance stops entering the body.
- The appearance of signs of tolerance, that is, the need to constantly increase the dose of the substance.
- Narrowing the range of interests, the ability to refuse other pleasures and events if during them there is no opportunity to use a psychoactive substance.
- Continued use of the substance even when severe physical or mental health disorders appear.
All these signs are present in nicotine addiction, so smoking is considered not just a bad habit, as previously thought, but a chronic disease.
The average duration of nicotine withdrawal syndrome lasts about a month.
Many heavy smokers, hoping to reduce the discomfort that occurs when quitting smoking, switch to using electronic cigarettes. But modern gadgets, although less harmful to health, since they do not contain tar and acrid smoke, still contain nicotine, which continues to support addiction.
Nicotine withdrawal is a combination of various symptoms that have varying degrees of severity and cause psychophysical discomfort.
Nicotine withdrawal syndrome is characterized by a whole complex of symptoms:
- insomnia;
- muscle pain;
- mood swings;
- thirst, feeling of dry mouth;
- increased cough, shortness of breath;
- increased appetite;
- psycho-emotional lability: anxiety, irritability, short temper, aggression, apathy, depression;
- disruption of intestinal function: alternation of diarrhea, constipation;
- hand tremors;
- decreased performance;
- headache;
- instability of blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances (tachy- and bradyarrhythmias);
- mental dependence.
According to statistics, 70-80% of all smokers tried to give up this bad habit at least once, but were unable to cope with the consequences of withdrawal symptoms.
Treatment of nicotine withdrawal syndrome
We have described a number of physical and psychological symptoms that accompany smoking cessation. This is how the body adjusts to a normal mode of operation without the use of nicotine. This is a lot of stress for a person, for his body and psyche. Therefore, few people can go through the pangs of nicotine withdrawal on their own. The best thing to do in this case is to consult a doctor.
After all, it can be a shame when a patient, having endured the most painful first days or weeks of nicotine withdrawal, then smokes a cigarette again. So he dooms himself to walking in circles.
Modern narcology offers many ways to combat nicotine addiction, varied and effective. Why not make it easier for yourself to quit smoking?
Lifestyle
Tobacco addiction quickly becomes part of the lifestyle and begins to affect it. A person gets used to smoking after eating or immediately after waking up; he needs frequent breaks from work and smoke breaks. Smoking accompanies communication, hard work, and relaxation. It also limits opportunities for exercise and affects appetite and activity levels. Trying to quit smoking without changing your lifestyle is a common mistake: in this case, the smoker is deprived of his usual rituals, receiving nothing in return and acutely feeling the lack of a cigarette. If you start changing your lifestyle and only then move on to quitting smoking, it will be easier to get rid of nicotine addiction. There are several basic recommendations:
- change your diet. It is good if it is fractional: it is advisable to eat more often and in small portions, but at the same time try not to smoke after or before meals. The diet should be balanced and varied: this will improve your overall health and help you cope with withdrawal symptoms faster;
- bad habits. As you prepare to quit smoking, you should also limit your alcohol consumption. Alcohol can become a provoking factor: many people smoke while intoxicated, when control is weakened;
- physical activity. It is worth spending more time on the move, playing sports, being outside more often;
- sleep and rest mode. It is important to normalize it: the duration of night sleep should be at least 7-8 hours, the person should get enough rest. This will improve the functioning of the central nervous system, reducing associated symptoms during withdrawal.
It is worth changing your lifestyle in such a way as to eliminate situations that provoke a breakdown immediately after quitting smoking:
- It is undesirable to go to places or companies where people smoke;
- you need to limit your stress level, choose a “quiet” period to quit smoking: vacation, long weekends or holidays;
- It is worth changing your smoking habits in advance (for example, a cigarette immediately after waking up, with the first cup of coffee, after a meal, on the way to work, while driving).
Why is treatment for nicotine addiction necessary?
When smoking, nicotine interferes with the body's metabolic processes and becomes an integral part of metabolism. Every cell of the body, even indirectly, experiences its impact. First of all, of course, nicotine addiction has an effect on the central and peripheral nervous systems of a person.
Nicotine acts on brain receptors, unnaturally stimulating nerve cells, stimulating the endocrine glands, in particular the pituitary gland. Subtle and complex metabolic processes are stimulated excessively, the body gets used to this state, and it becomes normal for it.
In fact, a smoker who has developed a persistent addiction does not smoke for pleasure, but to return to his “normal” state.
Naturally, such deep attachment is not easily overcome. Withdrawal syndrome when quitting smoking can break anyone, so the body needs to be helped to get through this difficult period, especially since there are plenty of funds for this today.
Possible reasons
Nicotine not only affects the psyche, causing addiction and a special psychological state, but also affects the human autonomic system, the blood vessels of the brain and other internal organs, causing appropriate reactions.
There may be several causes of headaches in former smokers:
Nervous tension and stress - psychologists have long proven the direct connection between smoking and a person’s internal problems, fears and complexes. By smoking a cigarette, the smoker simultaneously calms himself with a familiar ritual of actions, stupefies the brain with a mild narcotic substance, helping the body cope with stress or workload. Doctors compare an adult who has given up smoking to a baby whose pacifier was taken away: it became unclear what to do and how to calm himself down. It will take several weeks until the brain gets used to the absence of the “pacifier” and this period is characterized by headaches due to nervous tension and constant stress;
Changes in vascular tone - nicotine, entering the blood, causes a narrowing of blood vessels in the brain and other organs; when you quit smoking, small vessels begin to dilate, this can cause dizziness, a drop in blood pressure and even fainting;
After just 12 hours without smoking, carbon monoxide and other harmful volatile compounds are completely eliminated from the body, the level of oxygen in the blood increases, and an unexpected oversaturation of brain cells with it can also cause headaches and dizziness in the first days of quitting cigarettes;
Another common cause of headaches when quitting smoking is a decrease in the reactivity of cerebral vessels, a change in the gas composition of the blood and an increase in the amount of oxygen in it affects the receptors located in the walls of blood vessels and slows down the response of blood vessels to external and internal stimuli. In practice, this leads to the fact that the vessels “do not have time” to narrow or expand in time if necessary, and delayed reactions become the cause of migraine-like headaches or severe autonomic reactions;
Unfortunately, quitting smoking, accompanied by all of the above changes, in rare cases provokes the occurrence of serious pathologies in the brain - sudden changes in pressure in the vessels can cause a transient ischemic attack of brain cells.
Treatment with drugs
When treating nicotine addiction, specialists quite often turn to medicinal treatment methods. It should be noted that in essence these methods are coding for smoking.
By themselves, they cannot cure addiction, but they give the patient the opportunity to live without cigarettes and appreciate the benefits of a healthy lifestyle. Secondly, drug blocking of addiction in combination with psychotherapeutic treatment methods can cure the disease completely. In addition, medications alleviate or relieve withdrawal symptoms when quitting smoking, and a person goes through the period of adaptation to life without cigarettes more easily.
What medications are used to relieve nicotine addiction? They can be divided into two types of drugs. Some are replacement therapy and simulate the flow of nicotine into the body. The most common of these products is the anti-nicotine patch.
The person who uses the patch does not experience withdrawal symptoms. If the remedy is chosen correctly, then the body is easy to deceive; the body does not even suspect that you no longer smoke. What does it mean to choose correctly? It is important to consider how strong cigarettes you smoke, in what quantity and how often. In other words, the patch should imitate your smoking regimen as accurately as possible.
It is best to select an anti-nicotine patch with the help of a doctor, because this very convenient and effective remedy may not help you only because of the wrong dosage. In addition to the patch, there are also sprays, chewing gums, and mouth rinses that have a similar effect. Their disadvantage is that you can violate the regimen and forget to use them, which will negate the effect of the treatment. In this regard, the patch is the most convenient solution.
There are drugs that block receptors in the brain, those that respond to nicotine entering the body. Thus, the smoker does not experience any sensations from the smoking process, which makes it meaningless.
A fairly large group of drugs works to reduce cravings for tobacco. In fact, these medications relieve the unpleasant psychological manifestations of withdrawal symptoms, which will allow the patient to control their behavior.
Please note that many drugs have side effects. In addition, for the correct choice of medication, it is necessary to take into account the specific medical history of the disease. That is why the choice of treatment for smoking should be entrusted to a professional so that it brings benefit to your health and not additional harm.
How to quit smoking correctly
A necessary condition for any method of treating tobacco addiction is a person’s strong, conscious desire to quit smoking. All other methods: medicinal, psychotherapeutic are additional, allowing to reduce the manifestations of physical dependence on tobacco.
Smoking cessation products are divided into several groups:
Nicotine replacement therapy – chewing gum, transdermal patches, inhalers, sublingual tablets. These drugs contain a minimal amount of nicotine, which, when introduced into the body, will reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms. These are auxiliary methods of quitting smoking and, if used rationally, without increasing doses, they will help to endure nicotine withdrawal.
According to the WHO, there is no evidence base for the effectiveness of the use of e-cigarettes in replacement therapy for smoking cessation.
Nicotinic receptor agonists: Champix, Cytisine blocks the effect of nicotine on brain receptors, so a person, even smoking one cigarette after another, does not receive the expected satisfaction, and the craving for smoking gradually decreases.
Symptomatic drugs: sedatives (seduxen, phenazepam, tinctures of valerian and motherwort), stimulants (phenamine, meridil, extracts of ginseng, eleutherococcus, zamanikha).
Aversive therapy is the use of drugs that cause aversion to nicotine: silver nitrate, tannin suspension, glycerin are used to irrigate the oral cavity. These drugs, interacting with tobacco smoke, cause a person to become disgusted with the smell and taste of tobacco.
Non-medicinal methods: reflexology, electrical neurostimulation, laser therapy.
Psychotherapy. To reduce cravings for tobacco, psychotherapists teach methods of relaxation, meditation, and autogenic training in classes.
Combined method: drug support, antidepressants, psychotherapy methods.
The question of how best to quit smoking - abruptly or gradually - does not have a clear answer. Doctors believe that the process of quitting smoking should occur individually.
As a result of the studies, no proven advantages - for or against - one or another method of smoking cessation have been identified.
The choice of a plan for getting rid of a bad habit is determined by several factors:
- smoking experience;
- number of cigarettes smoked;
- age;
- health status;
- characterological characteristics of a person’s personality (willpower, suggestibility);
- social status.
The method of abruptly quitting smoking is recommended for young people with little smoking experience, smoking less than one pack of cigarettes per day.
Recommendations:
- A specific day for complete smoking cessation is assigned.
- First, all items reminiscent of smoking are removed from the home and place of work: lighters, ashtrays.
- Avoidance of smoking companies.
- Emotional support from family and friends.
- Switch to a balanced diet.
- If you have a strong desire to smoke, slowly drink a glass of water or juice.
- Intensification of physical activity.
Abrupt cessation of smoking causes temporary psychological discomfort, a period of nicotine withdrawal and a short-term deterioration in well-being associated with the restructuring of the body.
With this method of quitting cigarettes, the most difficult 3-5 days, then your physical well-being will gradually improve. But psychological discomfort persists for a long time - and when an emotionally unstable situation arises (trouble at work, family squabbles, alcohol), the person breaks down and starts smoking again.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
If a person wants to get rid of the very root of the disease, from internal psychological causes, a psychotherapist or psychologist will help him with this. This process may take several weeks or months, but it is worth it.
With the guidance of a professional, you will understand what exactly pushed you down the path of addiction and you will be able to get rid of bad habits of thinking and attitudes. A specialist will help you get used to life without the use of artificial stimulants, using psychotherapeutic techniques for treatment.
Treatment of nicotine addiction in
You can receive treatment for nicotine addiction in our drug treatment center. The advantage of this choice is that we cooperate with the best clinics in Russia and can offer a large number of methods for quitting smoking. As you have already noticed, an individual approach in treating this addiction is extremely important.
Most smokers delay seeing a doctor, either postponing solving the problem for an indefinite period of time, or making numerous fruitless attempts to get rid of the disease on their own. This, of course, is the right of every person, it is even spelled out in the laws of the Russian Federation. But your body suffers irreversible damage. I wouldn’t want to scare anyone, however, during this time you may develop some serious disease, sometimes incurable.
Therefore, there is no need to take risks; now treatment for addiction can be carried out gently and painlessly if you use the qualified help of a narcologist. You can learn more about the treatment of nicotine addiction from our consultants at any time. The toll-free call center number is listed on the page, call and ask your questions, because this does not oblige you to anything.