General information
Lasegue's symptom from the group of violations of the tension of the roots is also called “pathology of straight leg raising” and is characteristic of neuropathy of the femoral nerve and spinal roots, Guillain-Barr syndrome , etc.
The symptom is named after the French physician Ernest Charles Lasegue, famous for lecturing on the mentally ill in Paris in the 19th century. Being a representative of traditional medicine, he preferred the observational technique of treating patients over the experimental one. The symptom he discovered plays a very important diagnostic role in neurology.
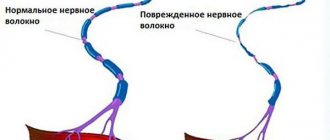
Diagram of the connection between the sciatic nerve and the spinal cord
Method for identifying Lasegue's symptom
During the examination, the doctor places the patient on his back on the couch and begins to smoothly lift the subject's leg, bending it at the hip joint and holding the knee. The leg is raised to a maximum of 90° or until pain occurs along the sciatic nerve. At this stage, it is important that the patient clearly determines at what angle the pain occurs. The true Lasegue symptom in neurology is an important indicator for tracking the dynamics of the disease.
At the next stage, the medical worker must bend the leg at the knee and if the pain stops, then Lasegue’s symptom is considered positive; when returning to the starting position - straightening the leg, the pain should resume. Otherwise - if the acute pain has not stopped, then the origin of the pain is different - it is not caused by the tension of the affected spinal root.
Symptoms
The clinical picture will manifest itself due to disruption of the spinal roots and nerve endings in the sacral plexus.
Depending on the degree of tension, the symptoms are manifested by the following condition. The syndrome will be considered positive when, with the straight leg extended upward at a certain angle, intense pain is felt in the thigh or lower leg. As a result of the next phase, they pass or the severity decreases significantly.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
The peculiarity of this condition is that the sensation of pain disappears when performing flexion movements of the hip or knee joint. This is explained by the fact that as a result of a decrease in tension, the roots begin to relax.
In medical practice, the following signs are identified that will indicate the presence of Lasègue syndrome in a patient:
- raising the lower limb will always be accompanied by severe pain;
- during the test, the skin in the thigh area on the outside numb
- when lifting the uninjured leg, pain will appear in the injured limb; this condition is called cross symptom;
- As a result of flexion of the joints, subside .
In the case when the pain does not disappear, they speak of a negative syndrome. In this case, there is a need to further identify the cause leading to unpleasant sensations.
Pathogenesis
The so-called “position” and “tension” symptoms are based on myofixation of the affected movable segment - reflexive or subconscious, which occurs as a result of irritation of the receptors present in the deformed tissues. This may increase intradiscal pressure. Normally, nerves have a reserve of length, although limited. They are able to move in relation to nearby tissues in the fascial bed, so there is almost no tension on the nerve. However, if for one reason or another pathological changes develop in nearby structures - their fibrous growth, deformation - then this can lead to excessive overstretching of the nerve.
When lifting a leg in people, depending on the angle (usually 70-90°), pain occurs in the lumbosacral region and the back surface of the limb, more often in the area of the lower leg, popliteal fossa, thighs and buttocks, because they act in such a situation as one whole, while the lumbar lordosis is straightened, the iliopsoas muscles are activated, the remaining parts of the spine are brought closer together, which causes injury to the affected tissues or excessive tension of the sciatic nerve roots.
What is lumbar osteochondrosis?
The most common pathologies associated with the musculoskeletal system include osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. This disease is characterized by the appearance of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the area of bones and joints. Despite the fact that pain due to osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is localized in a clearly defined area, it can spread to other organs and disrupt a person’s usual way of life. Also, degenerative changes can limit the function of the lower extremities.
Do not try to treat lumbar osteochondrosis on your own. This can cause serious complications in the body and significantly worsen the condition of the spine. In this article we will tell you in detail how to treat lumbosacral osteochondrosis.
Classification
Depending on the severity of the manifestations, the positive Lasegue symptom is of 3 types:
- the first type - which is characterized by a mild manifestation of low-intensity pain that occurs when the patient raises his leg no higher than an angle of 60°, and a protective reaction occurs in the form of a moderate contraction of the muscles of the back and pelvis, as well as the abdominal wall;
- the second type is characterized by moderately severe pain when lifting the leg at an angle of no more than 45°, which causes a moderate autonomic reaction and protective contraction of individual muscle groups;
- the third type is manifested by pronounced pain when lifting the leg at an angle of up to 30° against the background of generalized protective muscle contractions and a sharp autonomic reaction; such a disorder is considered articular, since when lifting by so many degrees, tension on the root does not occur.
Determination of the leg elevation angle when testing for Lasegue's symptom
Important! Elderly people with weak hamstring muscles may experience a pseudo-positive Lasegue sign, which usually manifests itself as soreness in the thigh muscles.
Modification of Lasegue's symptom can be used for expert cases:
- to identify pain when lowering the leg on the edge of the couch in patients lying on their stomach;
- conducting a study of Lasegue's symptom in patients in a standing position;
- the use of Vengerov's maneuver, in which the abdominal muscles contract during the study of Lasegue's symptom, which requires additional preliminary distraction;
- study of the cross Lasegue symptom with ankylosing spondylitis, which causes pain in patients in the “sick” leg using the Lasegue method on the healthy side.
Evaluation of the results obtained
The occurrence of pain when raising the leg at an angle of 60 degrees cannot indicate a positive Lasègue symptom; this is due to the fact that at this angle the nerve reaches its maximum stretch.
Bending the limb at an angle of 40-60 degrees also causes maximum stretching of the nerve; painful sensations may not be associated with a symptom of tension, but indicate that the length of the nerve has reached its limit.
Only bending the leg at an angle of up to 30 degrees indicates a true Lasègue symptom.
The manifestation of Lasegue's syndrome may indicate the development of certain diseases of the lower spine, but is not a prerequisite for establishing a final diagnosis. To accurately determine the disease, methods for identifying other symptoms of tension, fluoroscopy and MRI are used.
Causes
The cause of Lasegue's symptom quite often is damage to the nerves of the lumbosacral plexus, for example, as a result of lumbar osteochondrosis , hernia , hematoma , abscess , ankylosing spondylitis , radiculitis , neoplasms, piriformis syndrome , heavy fetus in late pregnancy. Such changes are very dangerous, as they can lead to pinched sciatic nerve , paralysis and disability.
Sciatica when raising the leg can also occur as a result of organic lesions of the sciatic nerve caused by diabetes mellitus , infections or intoxications .
What it is
Lasegue's symptom is an informative diagnostic method often used in practice in the field of neurology. Another name for it is tension symptom.
Lasègue's symptom identifies damage to the lumbar spine.
It is performed in a lying position, while the straight leg is raised 40 degrees, which is accompanied by painful sensations.
When bending the leg, the pain immediately disappears. This test, in combination with other signs of lower back damage, helps to correctly identify spinal pathology and, if necessary, conduct a more detailed examination.
This kind of study is carried out for people who may have problems with the spine, nerve endings and other diseases that are largely associated with osteochondrosis, as well as other pathologies.
Tension symptoms are not specific to radicular syndrome, but can be used to assess the severity and dynamics of pain.
If, when checking Lasegue's symptom, pain appears when raising the leg above 70 degrees, most likely it is not associated with compression of the root.If the pain does not stop when bending the leg at the knee joint, it may be caused by problems with the hip joint, and may also be psychogenic in nature.
Neurologist
Pershina Natalia Sergeevna
8 years of experience
The syndrome acts as one of the signs indicating the presence of sciatic nerve neuritis or radiculitis. It can be identified using the following exercise:
- Starting position : lying down, face up.
- The patient's straight leg is raised 40 degrees. At the same time, it should be extended in the area of the knee and hip joints. This pose will usually be accompanied by painful sensations.
- The moment the limb is bent, the pain disappears.
The syndrome includes several signs of tension. In normal condition, the sciatic nerve can stretch by 15 millimeters. Against the background of the presence of infringement, its length decreases.
In theory, a similar phenomenon is possible for its entire length. However, in many cases, nerve fiber pinching occurs precisely in the buttocks or spine. As a result of the fact that the pinched nerve roots begin to stretch, severe pain occurs at the site of the lesion.
Diet for Lasegue's symptom
Rejuvenating diet against aging of the body
- Efficacy: no data
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1600-1700 rubles. in Week
The cause of disruption of the nervous system can be an inadequate and unbalanced diet, so it is very important that a person daily consumes all the nutrients necessary for life and the full amount of calories corresponding to his height, weight, gender and lifestyle. To improve your condition, nutritionists recommend:
- limit consumption of animal fats and salt;
- drink up to 2 liters of pure mineral water;
- regularly consume fresh vegetables, fruits and berries, raw seeds and nuts;
- introduce lean porridges and soups into the diet;
- give up coffee and alcohol, and drink lactic acid drinks, compotes, fruit drinks, juices and herbal teas;
- add healthy vegetable oils to your food and don’t forget about seafood;
- When preparing meat, give preference to boiling, steaming or grilling.
Consequences and complications
Tension of the sciatic nerve can lead to certain consequences. First of all, this is explained by the fact that as a result of its pinching or shortening, the cause of which is an intervertebral hernia, there is a possibility of the onset of destructive processes of nerve connections.
Against the background of this phenomenon, the development of paralysis cannot be ruled out.
Identification of a positive Lasègue symptom provides an initial comprehensive assessment of the patient’s general condition. Thanks to it, it is possible to identify developing pathological processes and determine the source of the lesion, which facilitates timely treatment.
Osteochondrosis
This is one of the most common causes of pain. Lasegue's symptom for osteochondrosis is characterized by acute pain that spreads over the entire surface of the thigh. Its range is wide: from the buttocks to the very foot. In such cases, the patient is prescribed drug therapy. Treatment of osteochondrosis involves taking drugs that belong to four groups:
- Medicines containing vitamin D. It improves the absorption of calcium. Contraindication: increased content of this element in the patient’s blood. Side effects include the formation of kidney stones.
- Drugs whose action is aimed at reducing the release of calcium from the bones and reducing pain. For example, "Alostin" and "Calcitrin". In rare cases, the body reacts negatively to their intake: nausea, vomiting, and hypertension develops.
- Therapy aimed at treating osteoporosis. This includes drugs such as Bivalos, Fosamax, Bonviva. They block the process of bone tissue resorption.
- Female hormones are estrogens. Among their functions is the prevention of increased bone fragility. The most popular are “Proginova”, “Klimonorm” or “Estron”.
In addition to medications, the patient is prescribed physical therapy and other necessary procedures.
Treatment
For people far from medicine, we explain when treatment is prescribed. Symptoms and syndromes, which are a set of symptoms, do not require therapeutic measures. The basis of recovery is always considered to be the elimination of the cause of the disease. The concept of “symptomatic treatment” does not imply the exclusion of measures aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease. It is the relief of the causes that leads to the disappearance of symptoms, including the positive Lasegue symptom.
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the diseases that caused its appearance. For osteochondrosis, as well as other serious diseases, the patient is prescribed non-steroidal drugs to relieve pain, muscle relaxants, as well as vitamin complexes, in particular B vitamins.
After successful therapy, the patient may be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, massages, acupuncture, and therapeutic exercises. In some cases, to eliminate the cause of the disease, patients are recommended to undergo neurosurgical treatment. It is prescribed if conservative measures are ineffective.
Radiculitis
The reasons for the appearance of Lasegue's symptom also originate from this disease. In addition to it, the patient also has other symptoms: Neri - the connection between bending the head and pain in the lower back, Bakhretev-Fayerstein - the affected limb begins to hurt when raising the healthy leg. The patient is prescribed the following medications:
- Non-steroidal drugs that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects: Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Flurbiprofen, Indomethacin, etc. They help quickly eliminate the main symptom of radiculitis - pain.
- Muscle relaxants relieve skeletal muscle spasms. Despite many side effects, they are able to eliminate compression of nerve fibers. For example, “Tubocurarine”, “Doxacurium”, “Rapakuronium”. By the way, they are also prescribed for the treatment of osteoporosis.
In addition, in order to eliminate Lasègue’s symptoms of radiculitis, the patient is prescribed narcotic analgesics. But this is only in critical cases, when the pain is simply unbearable and cannot be relieved by other medications. The patient is also recommended to take antidepressants and vitamins.
Mechanism of occurrence
Lasègue's symptom belongs to the group of tension symptoms. It occurs when the sciatic nerve is damaged. Moreover, this can be both at the level of the roots that form from the spinal nerves, and at the stage of the nerve passing through muscle, ligamentous or bone formations.
It is widely believed that this phenomenon is caused by limited stretching of the nerve and its roots. Indeed, hernia and bone deformities of the vertebrae lead to irritation of the nerve roots. The path of their exit through the spinal foramina is also lengthened. Displacement during movements of the bones of the spine, pelvis and muscle work lead to an impact on the initial areas of the sciatic nerve. Normally this is a painless process.
But a number of studies have made it possible to clarify that a significant role belongs to muscle-tendon changes. Back in 1971, F.F. Ogienko spoke about the occurrence of reflex stretching of biarticular muscles, affecting the work of two segments of one limb.
With pathology of the sciatic nerve, neuroosteofibrosis occurs in the buttocks, the posterior group of thigh muscles and partially in the lumbosacral muscles. These are reflex changes in tissues affecting tendons and muscle attachments. The tissues become dense and do not stretch well. This leads to rapid irritation of the receptors in them during diagnostic tests.
Therefore, according to modern views, Lasegue’s symptom occurs due to stretching of the sciatic nerve (with interference in its path) and the reaction of altered muscles and ligaments.
Symptom assessment
Checking this symptom allows you to translate the patient’s subjective pain sensations into quantitative expression.
Carrying out the test over time helps to track the effectiveness of the therapy. And differentiation between a positive and a false-positive result provides information about the probable cause of pain. The result of the Lasègue test is recorded as positive or negative. If positive, the angle of leg elevation at which the pain occurred is recorded in degrees. The sharper the angle (smaller numerical expression), the stronger the severity of the pain syndrome.
If there is a suspicion of malingering on the part of the patient, the doctor examines the occurrence of autonomic reactions to pain. The tension of the abdominal muscles during pain is also discreetly checked. It is possible to modify this tension symptom when the straightened leg in the supine position is lowered from the edge of the couch.
Complemented by checking for other signs of tension.
- For example, the Neri test is performed - intense flexion of the neck with the chin brought to the chest, which causes pain in the area of the affected nerve root.
- The Bonnet test allows you to differentiate the level of damage to the sciatic nerve , revealing increased tone of the piriformis muscle, which compresses the nerve as it exits the pelvis.
What does a positive result mean?
Lasègue's symptom can be positive when:
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine, with bone growths along the edges of the vertebrae, narrowing of the lumen of the intervertebral foramina, displacement of the vertebrae.
- Herniated intervertebral discs that protrude to the side and change the course of the nerve roots.
- The presence of space-occupying formations near the nerve roots (tumor, abscess, hematoma).
- Injuries to the lumbosacral region, both due to damage to bones, joints and soft tissues, and due to the resulting swelling.
- During long periods of pregnancy, when the fetus puts pressure on all structures inside the pelvis.
- Piriformis syndrome, in which a spasmed muscle in the obturator foramen of the pelvis presses on a nerve.
- For overwork of paravertebral muscles, myositis and secondary muscular-tonic syndromes.
- Damage to the sciatic nerve itself (due to infections, intoxications, diabetes mellitus).
In case of pathology at the level of the roots, the area of predominantly the 4th and 5th lumbar segments is involved.
Positive is most often detected with complaints of pain in the hip, lower back or deep in the buttock. Pain along the sciatic nerve is called ischalgia . This is a syndrome that requires mandatory clarification of its etiology.
Identifying a positive result requires a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition and checking for other signs. This is necessary to establish the exact location of the lesion and identify the most likely cause of this pathology.
What is Lasègue syndrome?
Every 4 people in Russia suffer from severe dorsalgia. If pain radiates to other areas of the body, this may also indicate a herniated disc (HMD). But research shows that GMD are often clearly visible on X-rays and MRI images, but are not always the cause of symptoms. Only in 20% of cases, GMD causes severe pain syndromes that require conservative measures or surgical correction. Many patients are unaware of GMD because the disease is asymptomatic. Quick and timely detection of various diseases of the spinal column helps prevent serious consequences. If you have any symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
How is Lasegue syndrome diagnosed?
This disease should be determined by a neuropathologist who examines the patient with characteristic complaints - back pain, inability to perform movements, severe spasm of the muscles of the lumbar region, buttocks, back of the thigh and lower leg, weakness occurring in these parts of the limb, numbness of the skin on the legs
Particular attention should be paid to detecting this sign when a unilateral lesion is detected - identifying Lasegue's symptom most likely indicates the development of radiculitis (sciatica, inflammation of the sciatic nerve) on the affected side
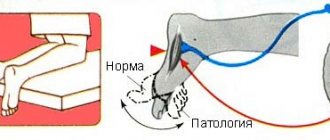
To detect this sign, the patient must lie down on a hard, flat surface, and from this position, under the supervision of a physician, try to raise the lower limb being examined. At that moment, when the person is still lying motionless, there is no pain or any discomfort in the area of distribution of the sciatic nerve roots.
No discomfort or pain occurs when a person lying on his back raises his leg, which is bent at the knee joint at a right angle - the roots (fibers) of the spinal nerve are not stretched.
How is Lasègue Tension Syndrome Diagnosed?
If pain occurs only at the moment of raising the straightened leg, then the doctor can confidently say that the patient has a positive symptom of Lasegue tension. The severity of pain progressively increases until the lower limb is raised to less than 60° - it is at this angle of flexion that the maximum degree of stretching of the sciatic nerve fibers is achieved.
Long-term studies have proven that the degree of nerve overstretch has a clear dependence on the angle of elevation of the lower limb at which this symptom will be detected. The smaller the angle at which pain occurs, the more pronounced the pathological changes in the tissues of the spinal column. If unpleasant sensations occur at a greater angle of elevation of the lower limb, then they indicate, rather, overstretching of the ischiofemoral muscles with a general decreased flexibility of the musculoskeletal system.
Simultaneously with identifying Lasègue's symptom, the neurologist may try to identify other symptoms of damage to the nervous system - signs of involuntary contraction of the abdominal muscles, gluteal and lumbar muscles, increased back pain when coughing - a neurological examination of the patient is always a complex, multi-stage event.