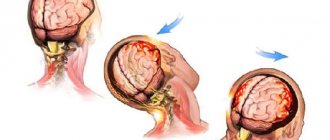
Concussion is the most common pathological condition among the consequences of traumatic effects on the skull and brain tissue. This pathology is considered a relatively mild and reversible disorder of brain function, however, insufficient diagnosis of the consequences of injury can cause severe disturbances in its further activity.
In this regard, MRI for concussion, which is performed painlessly and does not pose a risk to the patient’s health, serves as a reliable technique that allows us to fully assess the traumatic consequences.
Physiological manifestations of concussion
Pathology arises, as mentioned earlier, as a result of trauma, which can be of a different nature and affect any part of the patient’s skull. In this case, a lightning-fast increase in intracranial pressure develops, which is considered a direct etiological factor causing further functional disorders - loss of intercellular connections of brain structures, disruption of cellular nutrition, physicochemical transformations.
After a concussion, MRI is also performed to identify more serious consequences, including rupture of intracranial vessels and irreversible traumatic changes in areas of the brain. It is this type of research that is most informative regarding morphological and structural changes.
Main factors causing brain contusion
The main sources of occurrence include:
- Car collisions.
- Professional factor.
- Domestic conflicts.
- Criminal damage.
- Sports injuries.
In children under 7 years of age, UGM can occur as a result of a fall. The disorder occurs in the event of a sharp fall during epileptic seizures or failure of the muscular parts of the lower extremities. Typically, a bruise causes fractures of the skull, and in 50% of situations - intracranial hemorrhages (formation of subdural or intracerebral hematomas).
Pathophysiology is of two types:
- Primary - damage is caused by trauma, which provokes a displacement of the brain, its hemispheres and a hydrodynamic source. The victim develops anatomical disturbances of neurons and cells, rupture of synaptic connections, vascular abnormalities and the formation of blood clots. The affected areas are represented by multiple and single nature, which are located at the point of impact and the counter-impact area.
- Secondary - begins due to destructive metabolic processes caused by the primary type. In place X, inflammation and swelling of aseptic origin progress, failure of the circulatory system and metabolism of neural elements. These factors cause the damage boundaries to expand.
As a result, the patient in both cases experiences necrosis of neural areas, which subsequently causes neurological deficits.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a concussion are pronounced and characteristic. In the first minutes after injury, the following clinical picture develops:
- vomit;
- pronounced increase in breathing;
- disturbances in the rhythm of the pulse (slowing or, on the contrary, increasing);
- partial or complete loss of memories of immediate events preceding the injury.
Most often, the patient’s recovery period is not accompanied by deviations from the norm in body temperature and blood pressure, but the following characteristic symptom complex of the rehabilitation period is observed:
- severe, varied headaches;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- general weakness;
- inhibition of cognitive processes;
- noise in ears;
- sweating
It should be noted that all of the above symptoms are characteristic exclusively for patients of the young and middle age groups, while newborns and elderly people demonstrate a slightly different clinical picture. The fundamental difference here is the absence of a symptom of loss of consciousness.
After injury, young children exhibit frequent regurgitation, weakness and drowsiness, while older people report impaired coordination of movements and disorders of mental activity, including memory. Due to the uncharacteristic clinical picture and the vulnerability of the body, patients in this age group first of all need tomography for a concussion.
What tests are needed to check for a brain contusion?
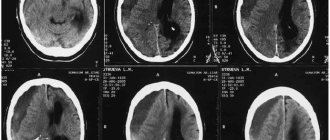
A mandatory medical method for checking a person’s condition is the use of a computer tomograph, which checks the brain. The clinical picture on the scan depends on the severity of the damage:
- In the case of the first form, the ability to detect violations is up to 50%. At the site of the impact, the diagnosis can notice the formation of edema and petechial bleeding. Edema can affect the entire area of the brain or the entire hemisphere, which will lead to a narrowing of the space of the cerebrospinal fluid compartment.
- In case of moderate brain contusion, the appearance of inflammatory zones with a reduced level of density is noted on the tomogram. Hemorrhagic impregnation has a high density.
- The severe stage of dysfunction is visualized on images in the form of lesions with increased/decreased secretion. The first option indicates the presence of blood clots, and the second indicates the area of progression and formation of swelling. Sometimes destruction can penetrate into the cerebral regions and go into the subcortical structures.
During treatment therapy, a computer examination is required to monitor effectiveness. The first and second forms of the anomaly and their consequences disappear completely over time, and the third shows a decrease in the perimeter of the areas of destruction, then the formation of cysts or atrophy zones begins.
Does an MRI show a concussion?
Since a concussion is usually not accompanied by morphological disorders, conducting research is most important in order to exclude the development of complications. It is worth conducting an MRI in case of a concussion first of all to exclude a dangerous pathology - brain contusion. Doctors recommend resorting to this technique in case of danger of intracranial hemorrhages, severe traumatic brain injuries and ischemic conditions. Due to the fact that the magnetic resonance imaging technique is extremely informative, it is always useful to conduct an MRI if the patient has hit his head.
The examination will take about 15 minutes, during which the patient remains under the influence of the electromagnetic field of the tomograph - it is completely safe and painless. At this time, the doctor receives three-dimensional images of the skull bones and brain tissue.
The feasibility of MRI for head injuries has been confirmed by leading world research and is explained by the information content of this modern diagnostic method.
Consequences of cerebral concussion
The consequences of brain contusion are extensive and depend on the severity. But even with a mild form with a fairly quick rehabilitation period, complications in the form of disturbances in the emotional sphere (irritability, psychosis) and the periodic occurrence of migraines cannot be excluded.
Post-traumatic syndrome after concussion may be delayed. Signs may take many months to appear, and sometimes begin during the early rehabilitation period.
Complications:
- Paralysis or paresis - the central gyri on the left side are damaged;
- Speech impairment – the source of damage is located in the frontal or temporal part;
- Hemorrhage;
- Hearing and vision impairment.
The consequences of a bruise inevitably occur after severe injuries. The person has difficulty restoring social adaptation, and psychosis or mental illness often develops.
Autonomic disorders persist for a long period (sweating, blood pressure, lethargy), migraine attacks cause irritability, and with excitement, a disturbance of the speech center may appear (in the form of stuttering). Phobias and epileptic seizures develop quite often.
Severe forms of bruises rarely lead to complete recovery and more often the victims become disabled. According to statistics, this form has high mortality rates.
Clinic of subdural hematomas
Clinical manifestations of subdural hematomas are presented in two large groups, which can be found in our table below:
| Group of symptoms | Clinical manifestations |
| General cerebral symptoms of hematomas |
|
| Focal symptoms of hematomas |
|
Magnetic resonance imaging of a cerebral cyst
A small brain cyst does not pose a danger if located outside the functional centers. Morphologically, the formation looks like a cavity with liquid internal contents. The bubble can remain inside the white or gray matter for life. If it forms after an injury and increases in size, dynamic control of the cavity is required.
Inflammatory cysts are formed by bacteria and parasites (echinococcus, alveococcus). After the infection is suppressed, the formations subside.
Autoimmune cysts gradually progress. Dynamic MRI helps monitor the condition of the bladder. With a growing formation, surgical treatment will be required. The absolute norm against the background of autoimmune damage to brain tissue requires repeated magnetic resonance imaging no later than 1 year.
The formation of antibodies to brain neurons and blood tests for infections are additional ways to verify pathological changes. After an MRI of the aneurysm, laboratory evaluation of cholesterol and blood clotting will be required.
Periodic rises in pressure are dangerous by rupture of cerebral arteries with the development of hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke. Classical MR angiography helps to obtain maximum information about the pathology.
Treatment of subdural hematomas
The treatment tactics for subdural hematomas are based on the results of diagnostic studies and the individual indications of the patient. It may involve the use of conservative or surgical techniques.
| Hematoma treatment methods | What are they? |
| Conservative | Indicated for patients who have not lost clarity of consciousness with hematomas up to 10 mm thick, accompanied by a displacement of structures by no more than 3 mm. They are also used if the patient is in a deeply depressed state of consciousness or in a coma, provided that the volume of the hematoma does not exceed forty milliliters and the intracranial pressure is not lower than 25 mm. rt. Art. Conservative treatment involves the use of drugs to prevent cerebral edema, relieve pain, vomiting and convulsions. |
| Neurosurgical | Surgical intervention is practiced for hematomas with symptoms of brain compression, focal manifestations, or in case of increased intracarnial pressure syndrome. Removal can be carried out using endoscopic techniques through a specially created opening. In addition, craniotomy is used, aimed at removing not only the hematoma, but also the areas of crush injury. |
The Department of Neurology at CELT sees neurologists and neurosurgeons with many years of experience in scientific and practical work. You can make an appointment with them online on our website or by contacting our operators: +7 (495) 788 33 88.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions