general information
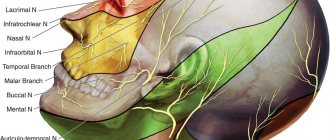
The trigeminal nerve consists of sensory and motor fibers. It originates in the structures of the brain and is divided into three branches:
- ophthalmic: responsible for the eye, forehead and upper eyelid;
- maxillary: innervates the area from the lower eyelid to the upper lip;
- mandibular: involves the chin, lower jaw, lips and gums.
With neuralgia, one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected, which determines the main symptoms of the pathology. People over 45 years of age are most susceptible to the disease, and women get sick more often than men.
Make an appointment
Painkillers do not cure. Find and eliminate the source of nerve irritation
Finlepsin and painkillers can reduce pain, but do not affect the cause of trigeminal neuralgia. avoid lifelong use of Finlepsin and painkillers if you eliminate the source of pain itself, which irritates the nerve and causes pain impulses. This is exactly how treatment will be structured in our clinic. We will examine you, find the cause of neuralgia and do everything to help you.
The exit of the filling material beyond the apex of the tooth caused severe pain in the second branch of the trigeminal nerve in the man. Side view:
tooth, a free fragment of filling material that conflicts with the trigeminal nerve is circled. Neuralgia appeared several months after a visit to the dentist. | Shooting pain in all three branches was a consequence of poor circulation in the cerebral parts of the trigeminal nerve in an elderly woman. The area of the brain affected by blockage of one of the brain vessels is circled. Check the blood vessels of the head and neck | A young woman had trigeminal neuralgia due to pressure from one of the cerebral arteries on the trigeminal nerve root. The MRI scan shows the intersection of the trigeminal nerve (runs vertically) with the artery (runs horizontally). The artery put pressure on the trigeminal nerve as it exited the brain stem. |
avoid lifelong use of Finlepsin and painkillers if you eliminate the source of pain itself, which irritates the nerve and causes pain impulses. This is exactly how treatment will be structured in our clinic. We will examine you, find the cause of neuralgia and do everything to help you.
What sources of trigeminal nerve irritation do we find most often:
- Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve by viruses (herpes and postherpetic neuropathy of the trigeminal nerve);
- Problems in the area of the tooth root - filling material leaving the tooth root, inflammatory process (pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- Traumatic tooth extraction, unsuccessful dental anesthesia;
- Facial trauma and its consequences;
- Inflammatory process of the nose and paranasal sinuses, cysts of the maxillary sinuses.
Causes
The causes of trigeminal neuralgia can be of different nature:
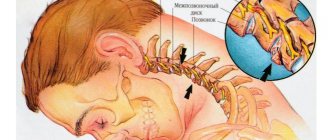
- compression of the entire trigeminal nerve or its branches against the background of: enlargement of the arteries or veins of the brain (aneurysms, atherosclerosis, strokes, increased intracranial pressure due to osteochondrosis, congenital developmental features);
- tumors of the brain or facial tissues in close proximity to nerve fibers;
- congenital anomalies of bone structure, narrowed openings through which nerve branches pass;
- injuries of the skull, facial area: bone fractures, post-traumatic scars of soft tissues;
- proliferation of scar tissue after injury, surgery, inflammation;
The risk of developing trigeminal neuralgia increases significantly:
- over the age of 50;
- against the background of mental disorders;
- with regular hypothermia;
- with insufficient intake of nutrients and vitamins into the body (anorexia, bulimia, malabsorption, etc.);
- with regular overwork, stress;
- for helminthic infestations and other helminthiases;
- for acute infections: malaria, syphilis, botulism, etc.;
- for chronic inflammation in the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, abscesses, etc.);
- against the background of autoimmune lesions;
- with excessive exposure to allergies;
- for metabolic disorders.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Damage to the trigeminal nerve can be caused by both trauma (fractures, tissue ruptures, unprofessional conduction anesthesia) and destruction of the myelin sheath of the nerve itself (a typical problem for patients with multiple sclerosis).
But more often we are talking about the inflammatory nature of the pathology.
The most common causes leading to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- inflammation of the membranes of the brain or spinal cord (meningitis),
- diseases of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis),
- malocclusion,
- herpes transmitted to the ganglia (nodes) of the trigeminal nerve,
- hypothermia: everyone knows the phrase: “I got a cold on my nerve.” In fact, a person’s tissues become overcooled, and then the nerve becomes inflamed.
- bacterial infection of the upper respiratory tract, throat.
Symptoms
The main characteristic symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is paroxysmal pain. It comes suddenly and in its intensity and speed of spread resembles an electric shock. Typically, intense pain forces the patient to freeze in place, waiting for relief. The attack can last from a few seconds to 2-3 minutes, after which there is a period of calm. The next wave of pain may come within hours, days, weeks or months.
Over time, the duration of each attack of neuralgia increases, and periods of calm are reduced until a continuous aching pain develops.
The provoking factor is irritation of trigger points:
- lips;
- wings of the nose;
- eyebrow area;
- middle part of the chin;
- cheeks;
- area of the external auditory canal;
- oral cavity;
- temporomandibular joint.
A person often provokes an attack when performing hygiene procedures (combing hair, caring for the oral cavity), chewing, laughing, talking, yawning, etc.
Depending on the location of the lesion, the pain takes over:
- the upper half of the head, temple, orbit or nose if the ophthalmic branch of the nerve is affected;
- cheeks, lips, upper jaw – if the maxillary branch is affected;
- chin, lower jaw, as well as the area in front of the ear - with neuralgia of the mandibular branch.
If the lesion affects all three branches or the nerve itself before it is divided, the pain spreads to the entire corresponding half of the face.
Painful sensations are accompanied by other sensory disturbances: numbness, tingling or crawling sensations. Hyperacusis (increased hearing sensitivity) may be observed on the affected side.
Since the trigeminal nerve contains not only sensory, but also motor pathways for the transmission of impulses, with neuralgia the corresponding symptoms are observed:
- twitching of facial muscles;
- spasms of the muscles of the eyelids, masticatory muscles;
The third group of manifestations of neuralgia are trophic disorders. They are associated with a sharp deterioration in blood circulation and lymph outflow. The skin becomes dry, begins to peel, and wrinkles appear. Local graying and even hair loss in the affected area is observed. Not only the scalp suffers, but also the eyebrows and eyelashes. Impaired blood supply to the gums leads to the development of periodontal disease. At the time of the attack, the patient notes lacrimation and drooling, swelling of the facial tissues.
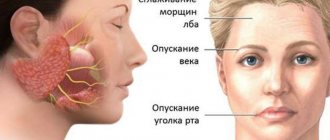
Constant spasms of muscle fibers on the diseased side lead to facial asymmetry: narrowing of the palpebral fissure, drooping of the upper eyelid and eyebrow, upward movement of the corner of the mouth on the healthy side or drooping on the diseased side.
The patient himself gradually becomes nervous and irritable, and often limits himself to food, since chewing can cause another attack.
Neuritis of the facial nerve - massage and rehabilitation
When diagnosed with facial neuritis, treatment should begin as early as possible - preferably within the first hours after the onset of symptoms. In this case, the success of treatment will be maximum and in 75-80% of cases will completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Massage for damage to the facial nerve is one of the main stages of treatment.
Objectives of massage for neuritis of the facial nerve:
- Improve blood and lymph circulation in the face (especially on the affected side), as well as the neck and collar area;
- Stimulate paretic muscles on the affected side;
- Restore impaired functions of facial muscles;
- Prevent the formation of contractures.
Areas for massage in case of damage to the facial nerve:
- Neck area;
- Collar area;
- Face area.
Symptoms of facial nerve damage:
Neuritis of the facial nerve is an inflammatory lesion of the nerve innervating the facial muscles of one half of the face. As a result, weakness develops in these muscles, leading to a decrease or complete absence of facial movements and the appearance of facial asymmetry.
Typically, neuritis of the facial nerve develops gradually. Initially, pain may occur behind the ear and only after 1-2 days the first symptoms appear:
- Facial asymmetry becomes noticeable;
- On the side of the affected nerve, the nasolabial fold is smoothed out, the corner of the mouth is lowered and the face is skewed towards the healthy side;
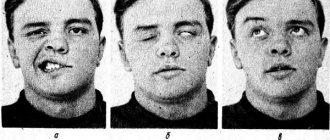
- Weakness of facial muscles, which makes it impossible to move them: smile, bare teeth, frown or raise an eyebrow, etc.
- Slurred speech.
The clinical picture of neuritis of the facial nerve is so vivid that it almost never raises doubts. However, before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to undergo an examination, including an examination by a neurologist, otolaryngologist, and ophthalmologist. Additional examination methods (CT or MRI of the brain) are prescribed to exclude the secondary nature of neuritis, such as tumor or inflammatory processes.
In the first days of the disease, it is not allowed to massage the affected side. Only positional treatment, massage of the healthy side of the face, collar area and therapeutic exercises! We add massage to half of the lesion only after a week.
The massage begins with the collar area and neck according to the method used for hypertension or hypotension, depending on blood pressure indicators. Then they begin to massage the face on the affected side using a tonic technique.
Massage techniques for neuritis of the facial nerve: stroking, kneading (very light), very gentle vibration (point). On the healthy side, massage using a sedative system.
We massage the facial nerve 1 cm below the ear canal, at the stylomastoid process, using short-term vibration. When the severity of the process subsides, do not influence the nerve!!! Finally, all areas of the face are stroked.
Treatment by position for neuritis of the facial nerve:
- Sleeping on your side is on the affected side;
- Chew food on the affected and healthy side;
- Putting a scarf on your head, tie it, pulling the muscles from the healthy side towards the affected side (from bottom to top), trying to restore the symmetry of the face;
- To eliminate facial asymmetry, adhesive tape is applied from the healthy side to the affected side. The technique is directed against the pull of the muscles of the healthy side and is carried out by firmly fixing the other free end of the patch to a special helmet-mask.
Exercises for facial muscles (physical therapy) after massage:
- Raise your eyebrows;
- Close your eyes;
- Smile with your mouth closed;
- Squint;
- Lower your head down, inhale and, as you exhale, snort – vibrate your lips;
- Whistle;
- Expand your nostrils;
- Smile with your mouth open;
- Extinguish the match with a sharp exhalation;
- Puff out your cheeks;
- Retract your cheeks with your mouth closed;
- Take water into your mouth, close your mouth and rinse, trying not to throw out the water;
- Move air from one half of the mouth to the other alternately;
- Follow with your eyes the finger moving in a circle;
Exercises to improve articulation:
- Pronounce the sounds o, i, u;
- Pronounce the sounds p, f, v, bringing the lower lip and upper teeth in;
- Then pronounce a combination of these sounds: oh, fu, fi, etc.
Massage and exercise therapy are prescribed daily for 2-3 weeks until complete recovery, and if there is no effect, the massage is interrupted for 10 days, while prolonging the gymnastics.
DO YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS? GET ANSWER:
Physiotherapist, osteopath, rehabilitation specialist Karasenko V.P.
Diagnostics
A neurologist diagnoses trigeminal neuralgia. During the first visit, he carefully interviews the patient to find out:
- complaints: nature of pain, its intensity and localization, conditions and frequency of attacks, their duration;
- medical history: when pain attacks first appeared, how they changed over time, etc.;
- life history: the presence of chronic diseases, previous injuries and operations is clarified, special attention is paid to dental diseases and interventions.
A basic examination includes assessing the condition of the skin and muscles, identifying asymmetry and other characteristic signs, checking the quality of reflexes and skin sensitivity.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- MRI of the brain and spinal cord with or without contrast: allows you to identify tumors, consequences of injuries, vascular disorders; sometimes the study is replaced by computed tomography (CT), but it is not as informative;
- electroneurography: study of the speed of nerve impulse transmission through fibers; allows you to identify the fact of nerve damage, assess the level of the defect and its features;
- electroneuromyography: not only the speed of impulse passage along the nerve bundle is studied, but also the reaction of muscle fibers to it; allows you to assess nerve damage, as well as determine the sensitivity threshold of trigger zones;
- electroencephalography (EEG): assessment of the bioelectrical activity of the brain.
Laboratory diagnostics includes only general studies to exclude other causes of painful attacks, as well as to assess the condition of the body as a whole (usually a general blood and urine test is prescribed, as well as a standard set of biochemical blood tests). If the infectious nature of the disease is suspected, tests are carried out to identify specific pathogens or antibodies to them.
Additionally, consultations with specialized specialists are prescribed: ENT specialist (if there are signs of nasopharynx pathology), a neurosurgeon (if there are signs of a tumor or injury), and a dentist.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
Treatment is aimed at:
- to eliminate the cause of damage;
- to alleviate the patient's condition;
- to stimulate the restoration of nerve structures;
- to reduce the excitability of trigger zones.
Properly selected treatment can reduce the frequency, intensity and duration of pain waves, and ideally achieve stable remission.
Drug treatment
Trigeminal neuralgia requires complex treatment using drugs from several groups:
- anticonvulsants (carbamazepine and analogues): reduce the excitability of nerve fibers;
- muscle relaxants (baclofen, mydocalm): reduce muscle spasms, improve blood circulation, reduce pain;
- B vitamins (neuromultivit, milgamma): stimulate the restoration of nerve fibers, have an antidepressant effect;
- antihistamines (diphenhydramine): enhance the effect of anticonvulsants;
- sedatives and antidepressants (glycine, aminazine): stabilize the patient’s emotional state.
For severe pain, narcotic analgesics may be prescribed. Previously, drug blockades (injecting the problem area with anesthetics) were actively used, but today this method of treatment is almost never used. It contributes to additional damage to nerve fibers.
Treatment of the root cause of the disease is mandatory: elimination of dental problems, taking medications to improve cerebral circulation, etc.
Physiotherapy and other non-drug methods
Non-drug methods complement drug therapy well and help stabilize patients’ condition. Depending on the condition and concomitant diseases, the following may be prescribed:
- ultraviolet irradiation: inhibits the passage of impulses along nerve fibers, providing an analgesic effect;
- laser therapy: reduces pain;
- UHF therapy: improves microcirculation and prevents muscle atrophy;
- electrophoresis with analgesics or antispasmodics to relieve pain and relax muscles;
- diadynamic currents: reduce the conductivity of nerve fibers, significantly increase the intervals between attacks;
- massage of the face, head, cervical-collar area: improves blood circulation and lymph outflow, improving tissue nutrition; must be carried out with caution so as not to touch trigger zones and provoke an attack; the course is carried out only during the period of remission;
- acupuncture: helps relieve pain.
Surgery
The help of surgeons is indispensable when it is necessary to eliminate nerve compression. If indicated, the following is carried out:
- removal of tumors;
- displacement or removal of dilated vessels pressing on the nerve (microvascular decompression);
- expansion of the bone canals in which the branches of the nerve pass.
A number of operations are aimed at reducing nerve fiber conductivity:
- exposure to a gamma knife or cyber knife;
- balloon compression of the trigeminal node: compression of the node using an air-filled balloon installed in close proximity to it, followed by death of the nerve fibers; surgery often leads to partial loss of sensation and decreased muscle movement;
- resection of the trigeminal node: rarely performed due to the complexity and large number of complications.
Make an appointment
How is the treatment carried out?
At East Clinic we combine several non-drug methods:
Component No. 1 - acupuncture
What's the point? Along the nerves from the point of needle insertion, impulses travel to the brain, activating its areas responsible for certain organs. Depending on the technique of needle insertion, organs increase or slow down their work. For trigeminal neuralgia, acupuncture helps normalize the functioning of the nervous system as a whole and eliminate the symptoms of the disease. How is the session going? The specialist determines a set of points for acupuncture, and after that, places the needles in a certain way, at certain points, for a certain time. There are several acupuncture techniques. With the first, only distant points are used, for example, on the limbs. In the second case, the points are on the healthy side of the face. With the third - on his sore side. Most often, all three methods are combined simultaneously.
Component No. 2 - acupressure of the cervical-collar area
Helps relax superficial and deep muscles, eliminate blood stagnation, remove muscle spasms, improve blood circulation in the area of “competence” of the trigeminal nerve, reduce inflammation, stimulate the processes of tissue repair and regeneration. In addition to physical pain relief, massage affects the emotional state. Tension and anxiety go away, mood and sleep improve, vigor and desire to live appear. The choice of points and methods of influencing them during massage of the cervical-collar area depends on the severity of the process, the general condition of the patient and concomitant diseases. For trigeminal neuralgia, massage complements and enhances the effect of acupuncture.
Component No. 3 - warming up (moxotherapy)
Special wormwood cigars are used and certain areas are heated with them. Thermal exposure leads to a local increase in skin temperature to 43-45 degrees Celsius, this is comfortable and safe - there will be no burns. Warming up improves blood supply and releases biologically active substances that reduce pain, spasms and inflammation.
Complications
Without treatment, trigeminal neuralgia gradually progresses. Over time, a pathological pain focus forms in one of the parts of the brain. As a result, the pain covers the entire face, is provoked by any minor irritant and even the memory of an attack, and subsequently becomes permanent. Vegetative-trophic disorders progress:
- irreversible atrophy of the facial muscles is formed;
- teeth become loose and begin to fall out due to advanced periodontal disease;
- baldness is increasing.
Due to constant pain, the patient's sleep is disturbed and severe depression develops. In severe cases, patients may commit suicide.
Prevention
Prevention of trigeminal neuralgia is a set of simple measures that significantly reduce the risk of developing pathology. Doctors recommend:
- undergo regular preventive examinations;
- at the first signs of the disease, seek help (the sooner treatment is started, the greater its effect will be);
- eat right, get the required amount of vitamins, minerals, unsaturated fatty acids;
- regularly engage in light sports and gymnastics;
- get enough sleep and rest;
- minimize stress and physical overload;
- avoid hypothermia and harden yourself;
- to refuse from bad habits.
Myofascial pain syndrome of the face and temporomandibular joint
Very often, muscle pain in the face is mistakenly interpreted as trigeminal neuralgia. In such cases, taking Finlepsin (Carbamazepine) and conventional treatment for trigeminal neuralgia does not help. This pain is not associated with a nerve, but with constant excessive tension in the muscles of the face and some neck muscles. This pain is called “Myofascial pain syndrome of the face.”
Possible reasons:
- Malocclusion and improper closure of teeth;
- Involuntary muscle tension due to nervous exhaustion and depression (pain can be very severe);
- Previous trauma to the temporomandibular joint (blow to the jaw), previous fracture of the jaw.
Rupture or displacement of the articular disc of the temporomandibular joint may mimic trigeminal neuralgia
Facial muscle pain responds well and quickly to treatment.
As a last resort, you can use a fail-safe remedy for painful muscle tension - Botox . We inject Botox using a syringe with a microneedle directly into the painful muscle, and after 2-3 days the muscle loses its tone and stops causing pain. The effect lasts up to 6 months; This time is usually enough to eliminate the cause of muscle pain in the face.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If you or your relative are bothered by severe pain in one or another part of the face, the neurologists of the Health Energy clinic will come to the rescue. We will conduct a full diagnosis to identify the causes of the pathology and prescribe comprehensive treatment. At your service:
- modern drug regimens to reduce the frequency and intensity of attacks;
- physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, laser therapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, etc.;
- delicate therapeutic massage;
- acupuncture;
- help from a psychologist if necessary.
Advantages of the Health Energy Clinic
The Health Energy Clinic is a multidisciplinary medical center where every patient has access to:
- screening diagnostic programs aimed at early detection of diseases and pathologies;
- targeted diagnostics using modern equipment and laboratory tests;
- consultations with experienced specialists, including foreign ones;
- modern and effective comprehensive treatment;
- necessary certificates and extracts;
- documents and appointments for spa treatment.
Trigeminal neuralgia is a serious pathology that can seriously disrupt a person’s normal lifestyle. Don't let pain and fear take over your thoughts, get treatment at Health Energy.
Why choose East Clinic?
Firstly, the effectiveness of treatment
Thanks to an integrated approach, we achieve results, and after just a few sessions, pain decreases and attacks occur less frequently. After the first course, the positive effect of treatment is achieved in the vast majority of cases.
Secondly, this is the qualification of specialists
Our doctors worked in leading medical institutions in the city, public and private clinics. All of them passed the qualifying exam and received the right to work with patients. Many of them have more than 25 years of experience and continue to improve. We chose those whom we ourselves would trust with our health.
Thirdly, it saves time and money
We provide acupuncture, massage and heating sessions on the same day. So in 1-2 weeks you can already see the difference and spend less time on therapy. Plus, if you pay for the course right away, you get a 10% discount.
Fourth, it's about caring for patients.
We select a convenient time for you, schedule sessions, and provide complete information about your condition in an accessible form. The doctor tries to perform all manipulations extremely carefully and accurately, so that if you have trigeminal neuralgia, treatment does not cause you additional discomfort. Our task is to relieve you of painful feelings in a comfortable, friendly environment.
Fifthly, it is monitoring the results of treatment
The clinic's management carefully monitors the effectiveness of each patient's treatment, and the doctor adjusts the treatment regimen depending on how he feels. If the desired result is not achieved, the patient is consulted by another doctor, or a consultation is held. Our goal is to relieve you of pain using the knowledge and experience of our specialists.
We understand that pain rules your life. Don't despair, there is a treatment for trigeminal neuralgia. Give it a try. Call and make an appointment at 8 (495) 153-52-14 with a doctor of traditional Chinese medicine at the East Clinic.