Indications for the study
The presence of a retrocerebellar cyst can be suspected by some characteristic symptoms:
- Severe headaches that do not go away even after taking painkillers;
- Unreasonable loss of consciousness or fainting state;
- Sensation of squeezing and pulsation in the head;
- Deterioration of hearing or vision;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Numbness of the limbs;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Epileptic seizures.
Magnetic resonance imaging is required if surgical intervention in the brain area is necessary.
Note that the clinical picture and severity of symptoms depend on the exact location and size of the retrocerebellar cyst.
What is an ovarian cyst?
This pathology consists of the appearance in the ovary of a benign neoplasm, consisting of a clearly defined membrane filled with liquid or porridge-like contents. Depending on the reasons for their appearance, the following types of cysts are distinguished:
- Functional. Such a cyst is formed in women of childbearing age (less commonly, menopause) from ovarian follicles when the ovulation process is disrupted (for example, due to hormonal imbalance). In this case, the egg sac does not dissolve, giving rise to a mature egg, but is preserved and increases in volume. A functional cyst in most cases only causes discomfort and does not threaten a woman’s health. Over the course of about 2-3 menstrual cycles, it independently decreases in size, resolves and disappears.
- Organic. A cyst of this type no longer goes away on its own and is a full-fledged pathology. It differs from the functional one by a denser wall and different types of contents. The only way to treat it is a careful operation to remove the ovarian cyst while preserving intact organ tissue (as far as possible).
The mechanism of appearance of an organic cyst can be different, which also determines the difference in the structure of its subtypes - for example:
- dermoid variety (teratoma) is formed due to a disruption in the process of embryogenesis in the ovary and is a capsule containing tissues atypical for this organ - hair, skin, teeth, bones, sometimes even the rudiments of full-fledged organs;
- an endometrioid cyst is formed due to the introduction of uterine endometrial cells into the ovaries; its cavity contains a characteristic dark brown thick liquid consisting of old menstrual blood;
- a parovarian cyst is formed from the tissues of the ligamentous apparatus of the ovaries; it can be located near the ovaries themselves or closer to the fallopian tubes.
The causes of ovarian cysts can be:
- accidental or violent injuries, careless surgery, etc.;
- hormonal imbalances caused by taking medical hormones, contraceptives, eating disorders, various diseases, stress;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs caused by infectious pathogens, exposure to negative environmental factors (for example, cold);
- various metabolic disorders - in particular diabetes mellitus.
In the vast majority of cases, the cyst is a benign formation that does not threaten the woman’s life. However, if left untreated, it can cause the following complications:
- Cyst rupture. This is a violation of the integrity of the membrane, due to which its contents enter the abdominal cavity. Depending on the type of tumor, its size and other factors, rupture can be accompanied by either minor pain or severe shock.
- Twisting of the cyst. In this case, the tumor does not burst, but the ligament that connects the affected ovary to the uterus is twisted. Because of this, the blood supply to the organ is disrupted, which leads to its atrophy and, as a consequence, impaired reproductive function.
- Malignization. This is the transformation of a cyst from benign to malignant. Malignization occurs quite rarely and depends on the type of tumor, its size and other factors. Most often, a mucinous cyst, characterized by a high growth rate, degenerates into a malignant tumor.
- Impact on surrounding organs. Increasing in size, the ovarian cyst affects the fallopian tubes and uterus, bladder, and intestines. This often leads to discomfort, pain, disturbances in urination, defecation, and reproductive function.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Obviously, pathology that can potentially lead to such complications must be treated. Curing a functional cyst is quite simple: it either goes away on its own or with the help of medications. With an organic cyst, the situation is more complicated - as a rule, drug therapy in this case is ineffective. The only way to remove it is surgical treatment.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is safe for the body only if all contraindications are excluded.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended in the following cases:
Very often, to obtain more informative images, doctors prescribe additional contrast. In this case, you must ensure that there are no following contraindications:
- Pregnancy of any stage.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Kidney failure.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Allergic reaction to components included in contrast agents.
Preparation rules
During a routine examination, doctors recommend following a few simple recommendations:
- If it is necessary to administer contrast, you must come to the clinic on an empty stomach, that is, do not eat food for 7-8 hours.
- If you are afraid of research or confined spaces, be sure to consult with a specialist. Your doctor may prescribe you sedatives to make the examination process more comfortable.
- Do not bring any metal products inside the tomograph. For this reason, doctors recommend removing metal accessories in advance.
- Prepare a change of clothes that do not have metal or metal-containing accessories.
- The duration of the diagnostic test is about 40 minutes. Empty your bladder in advance to avoid discomfort during the procedure.
How is an MRI performed?
To ensure that the procedure is as informative as possible and that the images are clear, experts recommend performing magnetic resonance imaging in closed-type tomographs. Before starting the study, the patient must change into clothes without metal structures, take off his shoes and lie down on a retractable table. If the doctor has prescribed additional contrast enhancement, a special drug is injected into a vein, which is distributed throughout the circulatory system in just a few minutes. Then the table moves inside the tomograph, where the research process takes place.
Maintaining immobility is the main requirement for the patient! Remember that even minimal movements can lead to a decrease in the information content of the procedure.
It is also worth noting that when performing magnetic resonance imaging, a specific loud noise is observed. If this scares you, you can use earplugs.
Patients generally tolerate MRI well. Inside the tomograph there is good lighting and ventilation, there is a loudspeaker, as well as a panic button for emergency stop of the study.
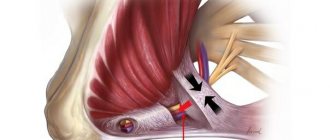
Methods for removing ovarian cysts
To remove an ovarian cyst, it is necessary to carefully separate the tumor from healthy tissue and remove it from the abdominal cavity. The methods used can be divided into 2 categories:
- Classic cystectomy. This operation is performed through an incision in the wall of the abdominal cavity under the direct visual control of the doctor over the tumor and surrounding tissues. Classic cystectomy does not require the use of special instruments and is generally easier to perform. However, the open incision can become infected and cause irritation, and the operation leaves a fairly large and noticeable scar on the body.
- Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cyst . This minimally invasive method involves excision of the tumor using an endoscopic device (laparoscope) inserted through a small puncture in the abdominal wall. This somewhat complicates the operation itself and increases the requirements for the qualifications of the specialist performing it. But after it there is no open incision, which reduces the risk of infection, and there are practically no unaesthetic scars left.
Today, laparoscopic cystectomy is the preferred method for removing ovarian cysts. Classic surgery through an incision is performed only in extreme cases or in the absence of appropriate specialists and instruments. Therefore, laparoscopic cystectomy will be discussed in detail below.
MRI with contrast
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed with contrast, especially if any neoplasm is suspected. This makes it possible to examine the tumor in detail and distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one.
The contrast agent clearly highlights the vessels, which allows you to see any tissue pathologies. Don't worry, contrast agents are safe for the human body. Most patients tolerate this procedure well. You must first consult a doctor and exclude all possible contraindications.
Efficiency and safety of ovarian cyst removal
The invasive and minimally invasive methods of surgical removal of ovarian cysts used today show fairly high efficiency and a low level of risk associated with complications. However, they do happen sometimes and you need to be aware of them:
- Pain syndrome. It occurs most often due to the accumulation of carbon dioxide residues in the abdominal cavity. They act on large clusters of nerves, causing them to become irritated. This does not pose a threat to life, but it causes discomfort that passes over time.
- Adhesive process. Occurs due to scarring of tissue in places where surgical instruments impact them. Adhesions after removal of an ovarian cyst occur quite rarely, but can lead to disruption of the anatomical structure of the reproductive organs and, as a result, to infertility.
- Subcutaneous emphysema. Also a non-life-threatening complication caused by the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the upper layer of subcutaneous fat. It occurs when the surgical technique is violated, but goes away on its own.
- Bleeding. This complication already poses a real threat to the patient’s life. It occurs due to a violation of the surgical technique, poor diagnostics, or for other reasons. Internal bleeding leads to the accumulation of blood in the abdominal cavity, causing acute peritonitis to develop in it.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
The cost of surgery to remove an ovarian cyst using a classical or laparoscopic technique is today affordable for the vast majority of patients of reproductive age. The price may vary depending on the chosen method of surgical intervention, size, type, position of the cyst, and other complicating factors. In most cases, this procedure provides a high chance of complete recovery from this pathology.
Decoding the results
A retrocerebellar cyst is located in the brain behind the cerebellum, in the posterior cranial fossa. During magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to clarify the exact location and size of the formation.
The report will contain all the information, but the MRI specialist cannot make a diagnosis - this must be done by your attending physician. If the diagnosis of retrocerebellar cyst is confirmed, the doctor will determine treatment tactics. For benign tumors, it is often possible to do without surgical interventions - they are required only in cases of large tumors or rapid growth. To avoid serious consequences, consult a doctor at the first alarming symptoms. Be healthy!
How is surgical removal of an ovarian cyst performed?
Although laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure, it is performed only by a suitably qualified specialist in a hospital setting. The operation is performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia) with tracheal intubation or the use of a mask. This method of pain relief allows for better control over the quality of anesthesia.
The patient is positioned on the operating table, the head of which is tilted down at an angle of 30 degrees. Thanks to this, the intestines move towards the diaphragm and free access to the ovaries. To further improve visibility and provide the instruments with the necessary freedom of action, carbon dioxide is released into the abdominal cavity through a puncture in the navel through a tube, which inflates the abdomen and increases its internal volume. The operation then proceeds as follows:
- A laparoscope, a tubular instrument with a miniature camera and a light source, is inserted into a puncture made in the navel. With its help, the doctor establishes visual control over the operated organ and the surrounding area, assesses the size and shape of the cyst, and its condition. Based on this examination, a conclusion is made about the need for further use of laparoscopy or classical cystectomy.
- Through lateral punctures in the abdomen, the doctor inserts additional instruments into the abdominal cavity. With their help, under visual observation through a laparoscope, he peels out the inner surface of the cavity and sucks out its contents. In some cases, the doctor performs partial or complete removal of the ovary with a cyst in women with a strong spread of the pathological process in its tissue.
- At the final stage, the doctor examines the operated organ and surrounding tissues for bleeding or other injuries. If there are none, the instruments are removed from the patient’s body, the gas is sucked out from the abdominal cavity, the punctures are sutured and covered with bandages. The anesthesia tube is removed from the patient's trachea, she is brought to consciousness and transferred to a regular ward.
The postoperative period after laparoscopy lasts an average of 14 days. The patient is discharged from the ward after 3-5 days, the stitches from the punctures are removed after 7-10 days. If complications arise during the operation, the rehabilitation period can be increased depending on their severity.