Due to the structural features of the skull, the human brain is well protected from external influences. Everyday blows to the head usually do not lead to injury to the organ and are not accompanied by the appearance of alarming signs or discomfort. If you experience nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or loss of consciousness after blunt trauma to the skull, seek medical advice. Such symptoms may indicate a concussion, one of the mildest forms of TBI, which can still cause complications if left untreated. The clinical picture characteristic of the condition in most cases does not require calling an ambulance. It is important to understand which doctor to contact in case of a concussion so as not to waste valuable time.
You need to know which doctor to see so as not to waste precious time.
Features and signs of concussion
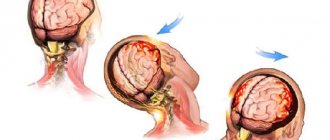
A concussion is a type of closed traumatic brain injury. Most often, the phenomenon occurs against the background of a blow to the head with a blunt object or a collision of the skull with a hard surface. A concussion can also develop when there is a sudden change in the position of the head in relation to the body, for example, when a car suddenly stops. If a person is influenced by one of the listed factors, it is recommended to calm him down and question him for complaints.
If signs of deterioration in health appear, the victim should be laid on his side on a hard surface.
He needs to place something soft but dense under his head to straighten his neck and give his body the most comfortable position.
Characteristic and indirect symptoms of a concussion:
- loss of consciousness – rarely observed in children and elderly patients. Depending on the severity of the condition, it lasts from 5 seconds to several hours. After the victim comes to his senses, he develops other signs characteristic of this form of TBI;
- headache – intense, obsessive, can have a different character and localization, intensifies with physical activity or trying to move the eyes;
- dizziness, unsteadiness of gait, poor balance;
- confusion of consciousness, which manifests itself in inhibition of reactions, the patient’s lack of understanding of what is happening, loss of orientation in space and time;
- ringing in the ears, blurred vision or double vision, difficulty concentrating on a specific object;
- nausea followed by single vomiting or without it;
- pallor or redness of the skin, increased sweating;
- changes in the quality and frequency of pulse and breathing;
- amnesia – the patient does not remember the fact of injury or the events preceding it;
- general weakness, lethargy, loss of interest in the outside world, desire to sleep;
- Indirect manifestations include speech disorders, increased sensitivity of the patient to light, smells, loud sounds, and irritability.
An indirect symptom of injury is tinnitus.
When assessing the signs, it is important to remember that each concussion case is different. Vague symptoms that do not lead to a noticeable deterioration in the victim’s well-being also cannot be ignored. The clinical picture may become more vivid some time after the injury. Don't wait for this to happen. The sooner the patient receives help, the lower the risk of developing negative consequences.
Concussion, traumatic brain injury
Head injuries very often result in serious brain problems for a person. All traumatic brain injuries are divided into open and closed. As a result of the former, a serious wound is formed on the head, which can sometimes even be accompanied by a fracture of the skull bones. Closed injuries are a little less dangerous, but still unpleasant. They are not visible from the outside, but this does not mean that everything is in order inside. Such injuries are divided into concussion, contusion and compression.
Among all head injuries, concussion ranks first. Moreover, according to the observations of traumatologists, it occurs more often in women. Although it may be that they simply seek professional help more often than men.
A concussion can occur as a result of blows, bruises and sudden movements: acceleration or deceleration, such as a fall. The causes of concussions are usually road traffic accidents, domestic, sports and work-related injuries, as well as injuries received as a result of street fights.
As a result of a concussion, certain problems arise with the functioning of nerve cells in the brain. At the same time, their nutrition may deteriorate, a slight displacement of the layers of brain tissue may appear, and the connection between some brain centers may be disrupted. A severe concussion can rupture blood vessels and seriously injure certain areas of the brain.
The main danger with traumatic brain injuries is intracranial bleeding, since the leaked blood can compress the brain structures. In addition, brain injury can lead to a real disaster - brain swelling.
When a patient gets a shock after a head injury, his life hangs by a thread. Especially if the lower parts of the brain responsible for breathing and blood pressure are damaged.
After an injury, a person often loses consciousness. This can last from a few seconds to several minutes. The time spent in this state may be one indicator of the severity of the concussion. The extreme degree of loss of consciousness is coma.
When a concussion occurs, a person often does not understand where he is, what happened, and has difficulty recognizing the people around him. Another important indicator by which one can judge the severity of brain damage is memory loss: whether a person remembers the moment of injury, and if not, how much of the time before the injury has disappeared from his memory. The greater the memory loss, the more serious the injury!
When the victim comes to, he may feel sick. He often turns pale, feels dizzy and has a headache, there is noise in his ears, it is difficult for him to focus his eyes, his breathing becomes rapid, and his pulse jumps.
In the first hours after a concussion, the victim’s pupils are dilated or constricted - a traumatic brain injury of any severity leads to disruption of the nerve pathways responsible for the functioning of the eyes.
If you suspect a concussion, you must provide first aid to the victim.
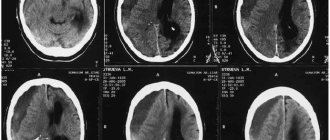
If you have a concussion, you should consult a traumatologist. He will examine and interview the patient, check reflexes, prescribe an X-ray of the skull, and if more complex brain damage is suspected, refer him for a consultation with a neurologist. Which will conduct a series of studies using: electroencephalography (EEG), echoencephalography, computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, Dopplerography of cerebral vessels. To rule out problems with the spine, a magnetic resonance imaging scan of the spine or even a spinal tap may be required.
If you have a concussion, which doctor should you contact?
After collecting complaints, he checks the patient’s pulse and breathing, measures his blood pressure, and assesses the condition of his pupils. Doctors do all this to assess the general condition of the victim and exclude a number of other pathologies and emergency events. After this, the patient will in any case need to consult a specialized specialist - a traumatologist or neurologist. If the victim is in serious condition, both may need to intervene.
A person will definitely need to consult a specialized neurologist.
Traumatologist or neurologist?
Although a neurologist deals with various pathologies of the central nervous system, which doctor to contact if you suspect a concussion depends on the characteristics of the case. In case of a traumatic brain injury, which is accompanied by bleeding, disruption of the integrity of the bones of the skull or skin, it is better to consult a traumatologist. The same option is relevant for cases where head damage is complemented by injuries to other parts of the body. Confusion, deep fainting, and the general serious condition of the victim are also indications for intervention by a traumatologist.
If the victim has already come to his senses, his condition is satisfactory, he reacts to those around him, you can get by with a consultation with a neurologist. This scheme of action is suitable for cases when the patient, apart from a head injury, is not bothered by anything, there are no visible consequences of the blow or are reduced to a hematoma or dissection. The specialist can only make a final diagnosis and determine the severity of the injury, which is proven using basic diagnostic techniques.
Treatment of concussion
After diagnostic measures are completed in the hospital, therapy is prescribed in accordance with the condition of the victim. The hospital also determines which doctor treats a concussion - a traumatologist or a neurologist. For minor injuries that are not complicated by other bodily injuries, it is enough to remain in bed and limit physical activity. A recovery period of about two weeks is required.
Drug treatment:
- During the rehabilitation period, drugs are prescribed to improve blood circulation in the brain: Cavinton, Stugeron.
- Memory restoration is facilitated by nootropic drugs: Noopept, Piracetam, Lucetam, Aniracetam, prescribed by a neurologist after a traumatic brain injury.
- Organic drugs such as Cerebrolysin and Cortexin speed up recovery and reduce neurological symptoms.
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid agonists, Aminalon, Picamilon, calm the overexcited cerebral cortex.
- Glycine is an amino acid that inhibits excessive activity of the central nervous system.
- Actovegin or Solcoseryl reduce the intensity of pathological vascular reactions after traumatic brain injury.
- For the treatment of convulsive syndrome, anticonvulsants are prescribed: Carbamazepine, Ethosuximide.
- Diuretic drugs Furosemide, Veroshpiron, Orthosiphon stamen eliminate post-traumatic edema.
- Eliminate headaches with non-narcotic analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Analgin, Tempalgin, Aspirin, Paracetamol, Citramon.
Why does your head hurt after hitting your head: causes and consequences.
Note to parents! Head injuries in children: what to do to avoid them.
Important: how spinal cord damage manifests itself in spinal trauma.
Normal rest is the most important condition for the recovery of patients after traumatic brain injuries. For this, the patient needs full sleep, the absence of bright light sources in the room or ward, since photosensitivity is initially increased. The victim should be protected from sharp sounds, which can provoke headaches and convulsions.
During the recovery period, it is prohibited to consume alcoholic drinks, energy drinks, and foods that stimulate the nervous system - chocolate, coffee, glutamic acid. Salty food provokes swelling, increased headaches, and increased intracranial pressure, so it is necessary to limit its consumption. To relieve nausea, tea with lemon, lemon balm infusion, and sour caramel are recommended.
Diagnosis of concussion
Contrary to popular belief, even a mild concussion can lead to dangerous complications. You should not think that in a situation where a TBI is not accompanied by obvious external damage, it is enough to undergo an examination and interview with a neurologist. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture and the age of the patient, he is prescribed magnetic resonance imaging or CT, EEG, X-ray, and vascular ultrasound. Additionally, laboratory tests and Glasgow scale tests are performed. Using all these approaches, doctors check the degree of brain damage and exclude the possibility of additional negative factors affecting the central nervous system.
Depending on the symptoms, the patient may be prescribed an EEG.
Do they put you in hospital?
The decision on the need for hospitalization is made based on the results of the examination, laboratory test data and computer diagnostics.
This allows you to verify the correctness of the diagnosis, accustom the patient to a regimen and diet, and minimize the negative consequences of a concussion. The hospital also determines the optimal treatment option for a particular patient. Depending on the severity of the injury, hospitalization lasts on average from 3 days to a month.
Hospitalization of a patient lasts on average from 3 days to a month.
Where to go if you have a concussion
Mild and moderate concussions are usually accompanied by symptoms that do not prevent the victim from being taken to a medical facility. This could be a clinic, hospital, emergency room. The doctor on duty will examine the patient and then decide on further action. In a situation where a brain injury is accompanied by impaired consciousness, the patient’s inability to move, and a risk of spinal injury, it is better to call an ambulance by phone.
While the team is on the move, it is recommended that a person with a suspected concussion receive basic first aid. If there is bleeding, it must be stopped using bandages or a clean cloth. If a hematoma forms, cold can be applied to the site of impact. The patient is placed on his right side, with his right arm and leg bent at a right angle, and his head slightly raised. If there is a risk of spinal injury, the victim is left on his back, but when vomiting, the head should be placed on the side.
Any traumatic brain injury is a reason to seek medical help. It is not so important which doctor you contact in case of a concussion, the main thing is that this must be done quickly. If possible, it is better not to risk the victim’s health at all, but to immediately call an ambulance, whose employees will understand the situation.
Traumatologist or neurologist?
Which doctor to contact for a concussion, a neurologist or a traumatologist, depends on the severity of the condition. In any case, if you experience nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or impaired consciousness, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Sometimes a traumatic brain injury is accompanied by other bodily injuries: fractures, dislocations, bleeding, burns. In such cases, you should contact the trauma department. Bleeding often requires emergency surgery, so such patients are sent from the emergency room to the general surgery department.
Which doctor should you go to if you have a concussion? If the victim’s condition is satisfactory, a visit to a neurologist is sufficient. However, it is necessary to exclude all dangerous injuries, including hematomas.