Any head injury that leads to the appearance of signs of damage to the central nervous system poses a danger to the health and life of the victim. For some diseases, short-term conservative therapy is sufficient, while others require surgical intervention. Experts distinguish two forms of closed-type TBI, which follow a similar scenario, but at the same time have important differences. These are brain contusion and concussion - conditions that just a few years ago were considered different degrees of injury of the same type. The speed and correctness of diagnosis in such cases determines the patient’s prognosis and chances of recovery.
Any head injury threatens the life of the victim.
Symptoms and signs of brain contusion
By brain contusion we mean a closed-type TBI, which entails damage to organ structures. The pathology is a consequence of domestic, criminal, industrial, road transport sports or childhood injuries.
The condition is characterized by the formation of areas of necrosis in the tissues of the central nervous system.
The stimulator of negative processes is a change in the position of brain formations, a hydrodynamic shock to tissues, and displacement of an organ.
Symptoms of brain contusion depending on the severity:
- mild degree – loss of consciousness, which occurs in 100% of cases and lasts at least 2 minutes. Also, a mild bruise is accompanied by headache, amnesia, vomiting, dizziness, and a slight increase in temperature. Upon examination, a slight disturbance in cardiac and respiratory rhythm, nystagmus, and different pupil sizes become apparent. Often the picture is supplemented by meningeal symptoms in the form of stiff neck and failure of a number of reflexes;
- moderate degree - loss of consciousness for at least 10 minutes, signs of deep stupor and lethargy, deeper amnesia, headache, repeated vomiting. Respiratory and heart rhythm disturbances are pronounced, but may have a different clinical picture. Depending on the characteristics of the case, tachycardia and a noticeable increase in blood pressure or slowing of the pulse are possible. Neurological symptoms are pronounced and are accompanied by low-grade fever;
- severe degree - loss of consciousness lasts for hours and even days. Coma gives way to stupor. This degree of brain damage is accompanied by damage to the cardiovascular center, which is manifested by a serious disturbance in heart rhythm. Obviously pathological breathing, temperature rise to critical levels. The basic neurological picture is accompanied by a bilateral change in the shape of the pupils, signs of impaired sensitivity, motor activity, and reflexes.
In severe cases, loss of consciousness lasts for hours or even days.
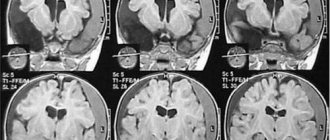
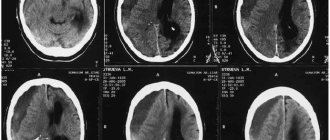
Early diagnosis of brain contusion is the key to a favorable outcome of the injury. Even with a blurred clinical picture, pathology can be accompanied by phenomena that are dangerous to the health and life of the patient. TBIs of this type often occur with cerebral edema, focal hemorrhages, damage to the meninges, and the initiation of inflammatory and destructive processes in tissues.
Bruise or concussion. How to recognize?
October 31, 2016
It is very difficult to distinguish a brain contusion from a concussion. How not to get confused and provide the necessary assistance in a timely manner?
Anything can happen in life, so it is important to be ready to provide first aid to your loved ones or strangers. But how to do this if, when you hit your head, it is very difficult to immediately determine the injury received: a concussion or a bruise? A brain contusion and a concussion are different things; a brain contusion is a much more severe injury than a concussion. The most common form of injury after an impact is a concussion. Common consequences of a concussion are vomiting, short-term memory loss, amnesia and lasts on average about two days. A brain contusion differs from a concussion in terms of skull injuries, breathing problems, increased anxiety, loss of consciousness and attacks of aggression. The best way to determine the nature of the injury is undoubtedly a computed tomography scan, however, first aid must be provided to the victim in any case. Firstly, call an ambulance, even at the slightest sign of injury, then ask the doctor in the control room whether you can give the patient citramon or analgin, secondly, the victim must be laid on his side and this position secured. This is necessary, first of all, to prevent tongue retraction. The arm located below must be bent at the elbow, and the one on top must be placed under the head. There are many differences in symptoms between a concussion and a bruise. Let's try to figure it out. The first thing that distinguishes these two injuries is the presence of macrostructural damage, such as swelling, hemorrhage, and open injuries. A concussion does not cause fractures of the skull bones. With a concussion, loss of consciousness lasts no more than five minutes, while with a bruise it can last up to several weeks (in severe forms). Disturbances in cardiac and respiratory rhythm during concussions are absent at all, while during a bruise they occur quite often and can be a serious threat to the health of the victim. Also, with a bruise, the body temperature rises noticeably, which is not observed with a concussion. Regardless of the severity of brain damage, the victim requires urgent hospitalization. If, in the case of a concussion, a person can be cured with simple bed rest and medications, then bruises are more difficult to treat, including surgical intervention. It is also important to remember that repeated concussions double the severity of symptoms, so it is important to immediately provide quality medical care to such a person. Every injury has its own consequences, especially traumatic brain injuries. And each such injury leads to various pathological processes - tissue necrosis, traumatic edema and much more. Such injuries also lead to regenerative processes, that is, to the restoration of damaged tissue. All this leads to certain consequences for the body. Ischemic lesions, intracranial aneurysms, nerve lesions, cranial defects and many other diseases can remain with you for many years after injury. Therefore, be careful, take care of yourself, your health and the health of other people.
Tags:
- Injuries
- Brain
To leave a comment you must be an authorized user
Symptoms and manifestations of concussion
The brain, placed in the cranial cavity, is suspended in the cerebrospinal fluid. This protects it from collision with surrounding bones and prevents tissue irritation. A concussion that occurs as a result of an impact or a sharp displacement of the head relative to the axis of the body is accompanied by a hydrodynamic shock to the brain matter. In severe cases, this is complemented by a mechanical effect on the central nervous system due to its collision with the bones of the skull. In any case, this form of TBI occurs without damage to the structures of nervous tissues; everything is limited to a transient disruption of connections between neurons. Symptoms characteristic of a concussion:
- loss of consciousness – does not always develop, lasts from 5 seconds to several hours;
- intense headache;
- nausea, possible single vomiting;
- dizziness, problems with coordination and orientation in space, lethargy;
- memory loss is short-term or affects a short period of time, often the gaps are filled thanks to specialized therapy;
- slight change in heart rate, breathing;
- pallor or redness of the skin;
- slight increase in temperature in rare cases;
- ringing or buzzing in the ears, transient blurred vision;
- trembling of the eyeballs, changes in the size of the pupils or their asymmetry.
Nausea often occurs with BGM.
The clinical picture that occurs as a result of a concussion is in many ways reminiscent of a mild organ bruise. This complicates the process of diagnosing the condition for people not related to medicine. For this reason, the appearance of symptoms of damage to the central nervous system after a head injury is an indication for immediate seeking professional help.
Classification of traumatic brain injuries
Depending on the damage to the skin of the head: Closed craniocerebral injury Occurs as a result of damage inflicted through the soft tissues and bones of the skull, in which the integrity of the skin of the head is not compromised. There are no conditions for infection of the brain and its membranes.
Open traumatic brain injury Characterized by damage to the skin of the head and bones of the skull.
- Non-penetrating. The integrity of the dura mater is preserved;
- Penetrating. The dura mater is damaged. Conditions arise for primary or secondary infection of brain tissue.
What are the signs to distinguish a bruise from a concussion?
Technically, a bruise and a concussion are two completely different conditions.
In the first case, macrostructural damage is obligatory and obvious, and there is also a high probability of violating the integrity of the skull bones. A concussion leads to a transient disruption of intercellular connections in the nervous tissue, so the clinical picture is not so bright. Most often, its most severe consequence is a hematoma, and a bruise can cause traumatic swelling, hemorrhage, tissue crushing and massive death of neurons. The differences between a concussion and a bruise are given in the comparative table:
| Symptom | Brain concussion | Brain contusion |
| Loss of consciousness | Usually just a few minutes | Can last for hours, days, weeks |
| State of consciousness | Clear, although with signs of inhibition | From moderate stun to deep coma |
| Amnesia | Short term | May be long lasting |
| Vomit | One-time | Usually multiple |
| Cephalgia | Obsessive, moderate | Intense, persistent |
| Hyperthermia | Temperature is normal or low-grade | The rise in temperature dominates in all cases, the indicator can reach extreme levels |
| Heart rate disturbance | Within 60-90 beats per minute | From minor deviations to severe tachycardia or bradycardia |
| Breathing problems | Missing or not obvious | Obvious dysfunction of the respiratory system |
| Neurological signs | Nystagmus, skin and tendon reflexes are slightly impaired | Marked changes in muscle tone, reflexes, signs of meningeal syndrome, limb dysfunction |
The statistics of traumatic brain injuries are characterized by the predominance of concussion. Despite this, when symptoms characteristic of this form of TBI appear, doctors insist on conducting a full diagnosis in order to exclude contusion of a central nervous system organ.
With a bruise, severe tachycardia or bradycardia may appear.
Treatment of head injury due to concussion and contusion
Depending on the severity of the manifestations and causes of the headache symptom, focal disturbances in the neurological status, and the level of consciousness disorder in the patient, with a diagnosis of concussion and brain contusion confirmed by the attending physician, the following therapeutic actions are possible:
- bed rest
- drug therapy (NSAIDs, analgesics, hormones)
- blockades - injections of anesthetics into the attachment points of the posterior cervical muscles
- lumbar puncture
- manual therapy
- physiotherapy (UHF, SMT, etc.)
- physiotherapy
- acupuncture
- surgical treatment
Lumbar puncture (LP) is performed to measure cerebrospinal fluid pressure, study the patency of the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord, and determine the color, transparency and composition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Lumbar puncture is used for accelerated sanitation of cerebrospinal fluid and restoration of cerebrospinal fluid flow, including after surgery. In such cases, in the absence of contraindications, up to 10-20 ml of cerebrospinal fluid or more are removed.
Attention! If you have complaints of long-term or chronic, as well as acute headache, you should contact a neurologist or neurosurgeon for advice first. A very common mistake is made by relatives of a patient with traumatic brain injury (TBI), when self-diagnosis begins with tomography, ultrasound, EEG, etc. At the same time, there is no hint of an attempt to consult a neurotrauma specialist in person.
Doctors' advice
Basic first aid for closed head injury is universal, but diagnosis and further treatment must be entrusted to professionals. The specialist, independently or using special approaches, will determine exactly whether you are dealing with a concussion or bruise and will draw up a suitable treatment regimen. Only in this case will the victim’s recovery be as fast as possible, and the negative consequences after the injury will be minimal.
Knowing the signs, symptoms, and distinctive features of a bruise and concussion, you can independently understand the situation. In any case, the actions of the victim, his relatives or eyewitnesses must be the same - it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance so that professionals can take care of the patient.
With head injuries, a person, especially a child, receives various bruises and abrasions. But if the bruise is too severe, it can also lead to a concussion. How to distinguish a regular bruise from a concussion?
Nature has safely hidden our brain in the skull, where it is protected by bones and intracranial fluid, which absorbs shock. If the bruise is too severe, the brain may shift relative to its normal position and hit the skull from the inside. Does this almost always result in a concussion?
Signs of a concussion:
- severe dizziness after a blow,
- noise in ears,
- weakness and feeling of apathy,
- headache,
- There may be a short-term loss of consciousness.
In addition to these common symptoms, there may also be dangers such as stupefaction or confusion, as well as retrograde amnesia - in this condition, a person forgets events that happened before or during the injury. It has been noticed that the longer the period of “forgotten”, the more severe the condition.
Along with the listed symptoms, respiratory and cardiac problems may also occur, which is manifested by an uneven pulse and rapid breathing. Such symptoms indicate damage to the medulla oblongata, which is responsible for the basic functions of the body - breathing and heart rate.
If a person has suffered a severe head injury and is experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned, he should be seen by a doctor. Since the brain is a very delicate organ, disruption of its functioning can affect the entire body, and only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment
.
An encephalogram, computed tomography, and MRI are used to diagnose a concussion.
If the doctor has diagnosed a concussion, the patient is prescribed strict bed rest for 1-2 weeks and medications that stimulate cerebral circulation.
First aid for concussion
— Apply ice or a cloth soaked in cold water to the bruise if there is no blood.
- Rinse the wound with clean water and apply a gauze pad.
— If there is a suspicion of a severe head or spinal injury, the patient should not be moved until the ambulance arrives.
ethnoscience
also offers his own methods for alleviating concussion.
1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of horsetail into a glass of boiling water, leave and drink ¼ cup 4 times a day.
Pour a glass of boiling water over arnica flowers (1 tablespoon) and leave for 2 hours. Take 2 tbsp. spoons 3 times a day before meals.
St. John's wort (2 tablespoons) pour a glass of water and bring to a boil. Strain the resulting broth and drink 2 glasses a day for a week.