Possible symptoms of a concussion
- Brief confusion or loss of consciousness. With a strong blow, the moment of injury disappears from memory.
- Dizziness even at rest, and when turning, bending or other changes in body position, the symptom intensifies.
- Severe headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Double vision, inability to concentrate on one point.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sounds.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Reaction inhibition - the victim gives an answer to the question after some time.
- Pale skin, weakness, sweating.
Important! A concussion is not always accompanied by visible head injuries, so the absence of wounds does not exclude brain injury.
Mechanism, classification
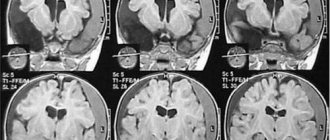
Brain contusion is classified as a type of TBI and is called concussion. With it, damage to brain tissue always occurs, which causes the formation of foci of destructive changes in the brain matter, often accompanied by the appearance of bruising or pinpoint hemorrhages. It is impossible to restore destroyed tissue after a concussion. According to the ICD, bruise is included in the section of intracranial injuries and has code S06.
Mechanism of development of bruise
The pathogenesis of injury is associated with mechanical impact on the brain from the outside. It causes the formation of a zone of increased pressure at the point of physical contact, where damage occurs to soft tissues, nerve cells with endings, and blood vessels. In the opposite part of the head, an area with low pressure is formed, within which disturbances also appear. Sometimes the damage in the second zone may be greater than in the first.
When struck, the cerebral hemispheres are displaced along with the cortex, which is why the internal parts stop receiving all signals. This phenomenon causes problems with the reticular formation, which causes loss of consciousness. Also, at the moment of impact, the cerebrospinal fluid moves sharply. This leads to the appearance of microscopic hemorrhages. The final element in the mechanism of injury is the formation of edema in damaged areas, accompanied by impaired circulation.
With very severe bruises, the injury is combined with subarachnoid hemorrhage, fractures, and hematomas that appear inside the skull, which can form even several days after the concussion.
Classification
A bruise can vary according to several criteria. To do this, doctors identify certain stages and degrees of severity. They help to anticipate all sorts of risks and make the right decision about treatment. All this is determined at the diagnostic stage in the hospital.
The division of trauma into stages determines differences in the duration of manifestation and severity of symptoms. There are three in total:
- Acute stage. This period lasts from 3 to 8 weeks, depending on the severity of the injury. It is characterized by the most vivid symptoms. If you start treatment at this stage, the risk of complications will be low.
- Intermediate stage. It can take from 2 to 6 months, depending on the degree of brain damage. Symptoms during this period are less pronounced, but continue to torment the person.
- Stage of long-term consequences. It proceeds quite gently, but sometimes unpleasant sensations may appear. Occasionally, complications begin to develop during this period. The stage lasts about 2 years, but can become chronic.
The bruise is also characterized by the severity of brain damage, which is of great importance for treatment and urgency of hospitalization. The following degrees are distinguished:
- Easy. Damage at this level is minor and does not pose a serious danger. In rare cases, hemorrhage may occur with skull fractures. A victim of a mild bruise loses consciousness for a short period of time, he may vomit, which manifests itself against a background of severe dizziness. Sometimes tachycardia occurs.
- Average. With second-degree brain damage, the victim loses consciousness for several hours. After he comes to his senses, a headache will appear, combined with vomiting, partial memory loss, rapid breathing, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, mental disorders, and nervous system disruptions.
- Heavy. A third-degree contusion is clinically characterized by serious brain damage. It is expressed in the severing of connections with soft membranes, the formation of detritus and hemorrhage. Sometimes there is significant compression of the entire brain. A person loses consciousness for a long time, sometimes falls into a coma. In this case, blood circulation is impaired, body temperature increases, swallowing function fails, eyeballs begin to move involuntarily, and epileptic seizures occur.
Any degree of injury causes serious health problems, resulting in dangerous symptoms that cannot be ignored. At the first signs of concussion, you should definitely call an ambulance.
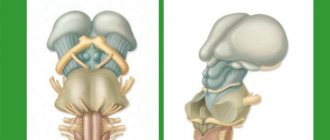
Often a bruise is combined with a cervical spinal cord injury, which significantly complicates the treatment procedure and recovery.
First aid for concussion
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
Types of traumatic head injuries
Brain injuries can come in a variety of forms. They can be divided into two main groups:
- open;
- closed.
The second group is not characterized by the development of external bleeding. In appearance, it does not look as scary as the first one, but this is a deceptive phenomenon. The blow can cause traumatic swelling or contusion of the brain. Even with a brain injury, a fracture of the vault or at the base of the skull may occur. These conditions cannot be determined if the victim has a closed form of injury. If the victim is not provided with emergency assistance in a timely manner, the swelling may lead to the death of the patient.
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
Causes, symptoms, complications
In the diagnosis of contusion, not only the symptoms of the injury, but also its causes are of great importance. They are a determining factor in how severe the brain damage can be. Therefore, doctors attach special importance to them.
Causes
Traumatic brain injury is always caused by strong physical contact with a hard object in the form of a blow. The severity of the injury depends on its strength. Knowing the cause allows you to predict in advance how serious the damage is.
Main reasons:
- Domestic injuries. Carelessness when performing housework, as well as accidental falls from furniture.
- Industrial injuries. Violation of safety regulations at work, lack of protective uniform.
- Sports injuries. Bumps or falls while playing sports, lack of sports protective equipment.
- Game injuries. Careless play by children, accidental bumps or falls on hard surfaces.
- Criminal injuries. Intentional injury to the skull, blunt force trauma, or falling onto hard surfaces.
- Road accident. Accidents of various types while inside a vehicle or in contact with it.
- Epilepsy attacks. Falling onto a hard surface caused by an epileptic seizure.
The variety of causes makes injury very common. It is especially common for young children and people whose work is associated with increased danger.
Symptoms
Almost always, victims have a mild brain contusion, characterized by mild symptoms and reduced risks. Higher degrees of damage are characterized by increased pain, which may result in additional signs of injury.
What symptoms do victims exhibit:
- Loss of consciousness. This is the main symptom that occurs in almost all victims. Consciousness may be absent from 1 hour to several days.
- Impaired consciousness. The person acts very slowly, feels dazed, drowsy, and disoriented. The third degree of contusion causes stupor or coma.
- Damage to the nervous system. Uncontrolled eye movements, asymmetric changes in pupil size, impaired coordination and speech, decreased sensitivity, and uncontrolled urination may appear.
- Increase in body temperature. As a rule, it appears only in severe cases of damage. Temperatures may rise to 41°C.
- Heart rhythm failure. In almost all victims, the heartbeat accelerates, but sometimes it may decrease. This is often accompanied by increased blood pressure.
- Breathing problems. A person breathes quickly, and with the third degree of severity of a bruise, breathing may become shallow and unstable.
- Memory loss. Most often, the victim does not remember the events before the injury, but sometimes memory can be lost completely.
- Cephalgia, dizziness. The headaches are bright, concentrated in one area, and the victim suffers from dizziness. They are often accompanied by weakness.
- Vomit. The onset of the symptom is sudden and there is no feeling of nausea before vomiting. It can be one-time or multiple.
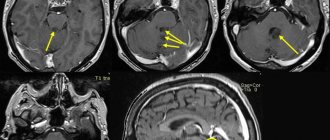
- Hemorrhage, fractures, hematomas. With severe injuries to the skull, open fractures may appear, accompanied by bleeding. Hematoma formation is also common.
Such symptoms should raise serious concerns for the life of the victim. Therefore, it is extremely important to provide first aid in a timely manner and call an ambulance.
Complications
Even with a mild injury there is a risk of complications. They can have an extremely negative impact on health, and some of them can be fatal. That is why you should pay special attention to them, without stopping treatment without a doctor’s recommendation.
What can the patient expect:
- Brain atrophy;
- Impaired blood flow from the brain;
- Formation of cysts, hematomas;
- Development of hydrocephalus;
- Decrease in intelligence and cognitive functions;
- Mental disorders;
- Asthenia;
- Vegetovascular dystonia;
- Deterioration or morning vision;
- Subdural type of hygroma;
- Arachnoiditis;
- Parkinson's or Alzheimer's disease;
- Epilepsy;
- Paresis;
- Paralysis of the whole body.
Most often, patients experience ischemic complications, which have a significant impact on their health. In especially severe cases, coma is possible, and in the absence of treatment, death is possible.
The presence of alcohol in the blood often has a complicating effect. The victim’s body will be more vulnerable, while those who drink most often refuse the help of a doctor, which causes even more problems.
Treatment
The prognosis is most often positive. Even with severe contusions, with proper treatment, there is a high probability of recovery and return to a full lifestyle. Therapy is carried out only in a hospital, because The patient needs to be monitored and cared for. It includes two types of treatment: medication and surgery. The latter is used only in particularly dangerous cases.
Medication
The main influence on the problem is the medication method. With its help you can overcome a bruise of the first or second severity. It is also used for severe contusions, but in conjunction with surgical procedures.
The doctor prescribes the following medications to the patient:
- Analgesics and diuretics (“Ibuprofen”, “Analgin”, “Mannitol”);
- Antihistamines and antiemetics (“Suprastin”, “Domperidone”);
- Metabolic and nootropics (“Piracetam”, “Nootropil”);
- Hemostatic or blood stimulating (“Ditsinon”, “Sermion”);
- Sedatives and vitamins (“Phenazepam”, “Neurovitan”).
They may also prescribe other medications that improve the condition of the brain stem and also strengthen the entire body.
Surgical
Sometimes surgery may be required. The cause is compression of the brain, as well as a significant displacement of brain structures or a large area of damage.
To improve the condition, craniotomy is used. To do this, a small hole is made in it through which damaged tissue is removed. There are 2 types of trepanation:
- Osteoplastic. Doctors cut out a large piece of the skull to gain access to the brain and remove the affected areas.
- Decompression. A small hole is made in the patient's temporal lobe, which is then covered with muscle.
The second type of surgery can be performed without removing damaged brain structures. It depends on the severity of the injury.
In case of serious brain damage and complications, the patient is assigned a disability group that corresponds to the degree of loss of ability to work.