Choking and lack of air is an extremely unpleasant and frightening sensation, especially when it wakes you up in the middle of the night. In addition, night suffocation is always a sign of some serious disease that must be treated.
In this article we:
Let's name the possible reasons why a person suffocates in his sleep;
We'll tell you what to do when you suddenly wake up at night from lack of air;
We will recommend which doctor to see.
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA) is the most common cause of shortness of breath at night.
This is how typical patients describe their condition. Compare the sensations with your own; perhaps you will recognize yourself immediately.
Valery:
“I didn’t know that I was suffocating in my sleep,” my wife said. For many years I just snored, but lately my breathing has also been interrupted. She often wakes me up, because sometimes I don’t breathe for a minute... In general, I sleep restlessly, I sweat a lot at night, and I often get up to go to the toilet. In general, I’m not happy with my sleep at all, or with my overall well-being. Drowsiness during the day, headache in the morning, high blood pressure...”
Kirill:
“A neighbor in a compartment on a train once told me that I suffocate in my sleep. Previously, I didn’t attach any importance to sleep at all, but after this incident I began to pay attention - and it’s true, there are problems. Sometimes I doze off in the evening and suddenly wake up abruptly, breathing quickly - as if there is not enough air. Or I wake up at night because I start snoring. Or I sleep restlessly, wake up and cough, and I also need to breathe before I fall asleep again. The Internet says it’s sleep apnea.”
So, the signs of obstructive sleep apnea:
- The sleeping person snores.
- In his sleep he suffocates. Stopping breathing occurs more than 5 times per hour and lasts 10 seconds or longer. The longest cessation of breathing recorded by the staff of our Sleep Medicine Center in a patient with apnea syndrome was 3.5 minutes.
- Often such pauses in breathing are observed by relatives and others. The patient himself, even with severe breathing problems, may not remember anything about the attacks of suffocation!
- In addition to snoring and respiratory arrest, there may be other symptoms: restless sleep, night sweats, heartburn (especially at night), frequent urination at night, daytime sleepiness, involuntary falling asleep during the day, morning headache, etc.
Look at the characteristic signs of breathing at night in a person with obstructive apnea in the video presented.
Typically, people who suffocate in their sleep due to obstructive sleep apnea are overweight men 40-60 years of age and older. Many have hypertension and heart disease. Apnea also occurs in other people (young people, women, children), but less frequently.
Sleep apnea is a serious condition. If left untreated, it can cause myocardial infarction, stroke, and sudden death in sleep.
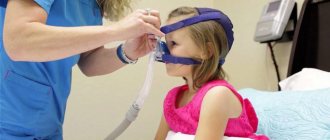
If you suspect you have sleep apnea, consult a sleep specialist. You will undergo a polysomnography (overnight sleep study), an accurate diagnosis will be made, and the cause (or causes) and severity of the disease will be determined. After this, effective treatment will be recommended. The CPAP therapy method allows you to quickly stop suffocation during sleep, eliminate symptoms and reduce risks.
Who should I contact if I don't have enough air?
There may be several reasons for feeling unwell. And it is not always clear which doctor to contact with a particular ailment. Our expert will help you navigate. In order to get a complete answer, in the comments to this article you need to:
- briefly outline the main symptoms;
- make the question as specific as possible;
- write a question in the comments under this article.
You will find answers to your questions in the next issue of the section “What kind of doctor do I need?”
Question: I constantly have some kind of shortness of breath, as if I don’t have enough air or oxygen, but when I take a cardiogram, they say everything is fine. Here's how to figure it out... I actually don't have enough oxygen.
The feeling of lack of air - inspiratory shortness of breath - is difficulty breathing during inspiration with a feeling of insufficient oxygen supply to the body. In healthy people, difficulty in breathing may be associated with a discrepancy between the volume of air inhaled and the need for oxygen, for example, when performing physical activity, during training, or when climbing a mountain. Wearing tight clothing and belts can contribute to a feeling of lack of oxygen. Also, such a respiratory disorder in women can be associated with pregnancy, especially in the second and third trimesters.
A feeling of lack of oxygen can also occur in pathological conditions:
- lung diseases of various etiologies;
- diseases of the larynx;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- chest and lung injuries;
- foreign bodies entering the respiratory tract;
- neurotic disorders.
To exclude pathological changes in the body and to determine the cause of shortness of breath, an examination by a general practitioner is necessary, who, taking into account the medical history, will prescribe the necessary amount of laboratory and instrumental studies (x-ray examination, study of the function of external respiration, determination of the gas composition of the blood, etc.), as well as consultation with specialized specialists (pulmonologist, otolaryngologist, etc.).
_____________________________________________________________________
Question: I always want to sleep and have no strength. I used to have a lot of energy, but now, as soon as I have free time, I try to lie down. Around the same time, a strange cough appeared that did not go away. I've already tried a bunch of drugs, but nothing helps. I also began to sweat and began to lose weight. I don’t know if these symptoms are related, but I would like to understand which doctor to go to.
Drowsiness, decreased performance, weight loss, sweating and coughing are a symptom complex that may be characteristic of thyroid pathology. The cough in this situation is reflexive in nature and does not bring relief to the patient; it is often dry and persistent. At the same time, the cough treatment that we use for colds does not have an effect.
Other causes of increased fatigue and drowsiness may include:
- deficiency conditions (anemic syndrome, vitamin D deficiency, B vitamin deficiency);
- long-term stressful conditions;
- sedentary lifestyle or, conversely, physical fatigue;
- various diseases: chronic infections, systemic diseases, diseases of the lungs and cardiovascular system, other endocrine diseases;
- sleep disturbance.
If you have the above complaints, you must contact a general practitioner so that, based on the collection of complaints, examination and anamnesis, he will prescribe the necessary laboratory and instrumental tests and, based on their results, refer you to specialized specialists (endocrinologist, neurologist, etc.).
occupational therapist, head of the hospital “Clinics for the whole family 1 + 1”
answered your questions Photo depositphotos.com The author’s opinion may not coincide with the opinion of the editors
Heart failure
Specific description of the complaint.
Valentina:
“I have had heart problems for a long time, hypertension, 10 years ago I had a heart attack. I take pills... A couple of weeks ago it got worse. I can’t walk as much as before – I’m out of breath. When I go to bed at night, I’m also out of breath! I noticed that if you sleep on a high pillow or even half-sitting, it’s easier to breathe.”
Signs:
- A person suffocates not only in his sleep, but also simply in a lying position with a low headboard;
- Shortness of breath appears or worsens on exertion;
- A patient is a person with heart disease.
Patients with heart failure (chronic circulatory failure) may experience breathing problems at night. This is a sign of deterioration (decompensation). If you have heart failure, shortness of breath appears or worsens, and you begin to choke while lying down, be sure (urgently!) to consult a cardiologist.
What are the causes of shortness of breath?
Difficulty breathing, or a feeling of lack of air in a person, is popularly called shortness of breath. The medical name for this phenomenon is dyspnea. This phenomenon has many different causes, which are associated with both the respiratory system and the heart. Shortness of breath may be normal. In this case, it does not harm the human body in any way and does not indicate the presence of pathologies. Normally, difficulty breathing in a person usually occurs during heavy physical exertion, especially when he is not in good physical shape.
Lack of air in the body
You should pay attention to this phenomenon if difficulty breathing occurs in a person for no apparent reason when he is at rest.
If your breathing is noisy, and the depth of inhalations and exhalations is constantly different, you should definitely understand the reason for this phenomenon.
Bronchial asthma
Alyona:
“A week ago, I woke up suddenly in the middle of the night with tightness in my chest. I realized that I was suffocating. It was hard to breathe, harder when exhaling than when inhaling. I had to stand up and put my hands on the windowsill to feel at least a little easier. About 15 minutes passed. I was examined and was diagnosed with asthma.”
Choking in classic bronchial asthma is difficult to confuse with something else.
- The attack develops quite quickly;
- During suffocation, it is more difficult for a person to exhale than to inhale;
- The body position with a forward bend and support of the hands (on the knees, window sill) helps to breathe;
- The attack lasts up to 20 minutes;
- Choking quickly resolves with the use of specific drugs (for example, salbutamol);
- Not only nighttime, but also similar daytime attacks are possible.
If you find yourself short of breath in your sleep and have symptoms similar to asthma, contact your physician or pulmonologist.
Causes of shortness of breath
When talking about the causes of shortness of breath, you should not mention physical activity, stuffy rooms, or conditions caused by stress. All these reasons can be easily eliminated by changing the environment around a person, and do not indicate the presence of possible pathologies in the body.
Shortness of breath at rest may indicate cardiovascular and bronchopulmonary pathologies that can threaten a person’s life. That is why you should pay close attention to such symptoms. Chest injuries also need to be evaluated and treated as they are another cause of this symptom.
The main reasons for lack of air are:
- Pneumothorax. A condition in which air accumulates in the pleural cavity of the lungs, causing the lung itself to not function fully.
- Bronchial asthma. With this disease, the airways become very narrow in size, which leads to a lack of air.
- Injuries. If the injury causes damage to the lung, the person may experience shortness of breath.
- Heart failure. A concomitant pathology may be pulmonary edema.
- Lack of air due to a sharp increase in blood pressure.
- Pneumothorax, pulmonary edema, and mechanical injuries are conditions in which a person needs urgent medical attention.
- Also, one of the common causes of lack of air is anemia - iron deficiency anemia. With this disease, the amount of blood in the body is greatly reduced, due to which organ tissues are not supplied with oxygen, since oxygen transfer is the main function of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
All of the above situations require diagnosis and proper treatment. If any of these conditions are left unattended, it can lead to very serious consequences in the future. Therefore, if shortness of breath occurs, you should immediately consult a physician.
A person suffocates in his sleep - other reasons
Perhaps the reasons why you suffocate in your sleep are still unclear to you. You may not have the combination of symptoms that we listed above when describing different diseases.
The feeling of suffocation can manifest not only physical, but also psychological problems - for example, nocturnal panic attacks. If you do not understand why you are suffocating in your sleep, contact a somnologist. A specialist will identify your problem and help you.
To make an appointment with a somnologist, call 85 or leave your contact details and we will call you back.
If you want to make an appointment with a doctor yourself, all contacts are listed here.