Forehead bruise: symptoms, treatment, characteristics of injury in children
An active lifestyle and inattention cannot do without bruises to the frontal part of the head. Most often, small children suffer from bumps; in 90% of cases, when a child falls, he will hit his head. A forehead bruise can be completely harmless, or it can cause serious traumatic brain injury.
Types of hematoma
A hematoma forms after a strong blow, as a result of which blood vessels rupture and blood collects under the skin. The victim may feel slight pain, swelling and a blue-violet hue in the bruised area.
A hematoma can be:
- Subcutaneous. Occurs when the forehead is bruised without damaging the surface of the epidermis. Hemorrhage after an impact occurs under the skin.
- Intramuscular. It is formed in the head muscles themselves after an injury.
When examining a hematoma, you can assess the condition of the victim. If only soft tissues are injured, then there is no need for medical assistance. A cause for concern is a dissection at the site of the bruise or visual changes in the frontal bone, which indicates a fracture. In this case, an urgent appointment with a traumatologist is necessary.
Causes of bumps on forehead
For a bump to appear on the forehead, it is enough to fall from a height close to a person’s height. There are many vessels on the head, and even a minor blow to the frontal part of the head, especially in children, will lead to the formation of a hematoma.
Bumps on the forehead appear when soft tissues are compressed, they occur especially often in children
A lump may also appear due to prolonged compression of soft tissues. In this case, a stationary, dense, slightly painful formation of a reddish tint is formed. Gradually, the traumatic area turns pale and becomes pale yellow.
Symptoms of hematoma
The most common symptoms of a hematoma are the appearance of a lump and redness of the bruised area. They do not pose a threat to life, pass quickly, and do not require special hospital treatment.
Alarming symptoms of a hematoma are:
- nausea, vomiting;
- Strong headache;
- dizziness;
- violation of movement coordination;
- difficulty speaking;
- change in pupil size;
- There are circles and spots in front of my eyes.
If alarming symptoms are noticed, the victim should be immediately shown to a doctor. A forehead bruise may be accompanied by a concussion or intracranial, internal cerebral hemorrhage. In this case, to obtain accurate and detailed information, it is best to undergo an MRI of the brain.
Medicinal ointments
The following ointments help to cope well with the consequences of hemorrhage:
- "Troxevasin".
- "Lyoton."
- Hepatrin ointment.
- Homeopathic remedy – “Traumel S”.
Medicinal ointments must be applied to the site of the injury several times a day. You can also get rid of the bump using traditional medicine.
ethnoscience
You can speed up the process of resorption of a lump on the forehead using the following time-tested methods:
- Apply finely chopped or beaten plantain leaves to the cone for 10 minutes.
- Combine water and alcohol in equal quantities, wet gauze and apply to the bump for 15 minutes. It is recommended to use this compress 2 days after injury.
- Apply a compress of raw potatoes, grated on a fine grater, to the bump for half an hour in the morning and evening.
- Chop the cabbage leaf and boil it in milk. Cool slightly until warm, wrap in a napkin and apply for an hour 2 times a day.
- An iodine mesh will help quickly eliminate a bump on the forehead.
For a bruised forehead, a compress of raw potatoes, grated on a fine grater, helps a lot.
You can prepare ice cubes with parsley in advance; they will help relieve swelling if your forehead is severely bruised. To do this, pour the leaves of the plant with water, freeze and use as needed.
Features of treatment in children
Even a minor bruise will cause a bruise and bump on the child’s forehead.
But injuries under 3 years of age can be dangerous, because the child’s skull is not yet strong and cannot protect the brain from a concussion. After an injury, you need to closely monitor your baby.
If he loses consciousness, disturbances in his coordination of movements are noticed, vomiting, or a severe headache are observed, then you need to call an ambulance.
If the injury does not bring great discomfort to the child, then apply cold to the bruise and, if necessary, give an anesthetic (Panadol, Ibufen). There is no reason to worry when the baby is still cheerful and active.
Fibroma
Description
Benign tumor of epithelial cells. Initially, the bumps on the gums above the tooth are small in size and do not hurt. However, mechanical stress and other negative factors can lead to the transformation of fibroma into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out surgically. The doctor excises the tumor, applies stitches, and prescribes rinses. Further follow-up visits may be required to monitor the recovery process.
A lump appeared: ambulance
The first task after a bruise is to relieve pain. It will become much easier if you apply something cold to the injury. Pre-treatment with iodine or alcohol tincture is effective.
- Ice from the freezer, wrapped in a scarf or bag. Within 10-15 minutes after contact, the pain will begin to go away and the swelling will decrease.
- A handkerchief or napkin soaked in cold water. They are periodically moistened, preventing complete drying.
- Special gel pillow.
- A piece of frozen meat wrapped in a towel.
- A bottle of cold water.
- A rubber bladder half filled with ice. The air is removed from it and the lid is screwed on tightly. Apply by covering the device with a towel.
The larger the size of the lump, the longer the time of contact with a cold object. To prevent hypothermia, do
If you have a head injury, it is recommended to use a cold compress.
breaks. An excessive decrease in temperature is fraught with complications.
Vegetable oil will provide effective help. Cotton wool or gauze soaked in it is applied to the bruise for 30-35 minutes. The product removes redness and swelling.
The next day, exposure to heat is effective. The bruise site is heated with herbal compresses. Heat will relieve swelling and reduce swelling. The neoplasm will resolve.
Heated salt does not cool down for a long time. It is wrapped in loose fabric and applied to the injury. A freshly boiled egg is used for the same purpose.
The first aid when a lump appears is a cold compress.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after delivering the victim to a medical facility, external examination, palpation, and history taking.
When diagnosing, an important component is the ability not to miss not only hematomas and lumps, but also possible collateral, even more complex, injuries. The neurologist’s task is to check the neurological status for the level of consciousness, contact, orientation, muscle tone, balance, memory and tendon reflexes
The neurologist’s task is to check the neurological status for the level of consciousness, contact, orientation, muscle tone, balance, memory and tendon reflexes.
The traumatologist prescribes:
- x-ray of the skull to exclude bone fractures;
- spinal puncture to determine an increased number of red blood cells;
- computed tomography to determine the exact location of the injury, the amount of edema and ischemia.
Only on the basis of a complete examination can specialized treatment be prescribed.
Why bumps appear on the head: reasons
Often people suffer soft tissue injuries or are exposed to a variety of diseases. This may cause a lump to form on the back of the head or another area of the head. In most cases, a hard or soft ball under the skin is a consequence of a bruise, an insect bite, or a benign tumor. To avoid health problems in the future, you should inquire in advance about the symptoms of bumps on the back of the head of various origins.
A bite of an insect
If a lump on the head hurts when pressed, itches, itches, then this is the result of an insect bite. To get rid of the tumor, you can use special antihistamine medications. An antiseptic, wound-healing agent will also cope well with this problem. If the swelling does not go away for a long time, it is better to consult a doctor.
Injury
One of the most common causes of a lump on the back of the head is a blow, bruise, or any other soft tissue injury. You can fall unsuccessfully and get injured on the left or right. In this situation, swelling and growth appear. Sometimes when pressed, painful sensations occur. As a rule, such skin damage goes away on its own, but you can speed up healing by using a regular cold compress.
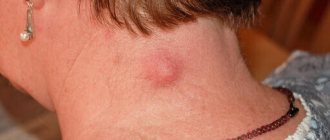
Atheroma
A lump on the head under the skin is sometimes an atheroma - a hard formation that forms due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Such a tumor does not cause pain, but can grow quickly and become inflamed due to infection. The result is a painful tumor. To eliminate a tumor on the head in the form of a lump, you need to visit a doctor who will prescribe treatment (laser therapy or standard surgery).
From the editor: Symptoms, causes and treatment of dysarthria in children
Hemangioma
When the lump on the back of the head is red and round in shape, it is probably a hemangioma - a benign vascular tumor (as in the photo). Often it is formed due to failures in the development of blood vessels. This growth is very painful when injured and can bleed. It is recommended to remove the hemangioma, otherwise there will be a risk of a number of complications. A tumor on the back of the head is eliminated using various methods: surgery, laser surgery, cryodestruction.
Lipoma
A mobile, soft lump on the head of an adult without a bruise is a lipoma (fat). This tumor refers to benign connective tissue formations that form under the skin. In most cases, this bump does not threaten the health and life of the owner. The wen increases in size very slowly and does not cause discomfort. However, it is worth undergoing a medical examination.
Fibroma on the head
A hard or soft lump in the occipital region, which may have a stalk - fibroma. This neoplasm consists of fibrous and connective tissue. Sometimes such a noticeable growth under the skin causes pain if it is accidentally touched or injured. Fibroma is always eliminated; this happens through cryodestruction, laser therapy, electrocoagulation and other techniques.
Wart
A type of bump that can pop up under the hair, on the top of the head, at the back of the head - a small “pea” called a wart. This subcutaneous formation appears due to infection with HPV infection (papillomavirus). The dermatologist prescribes one of several treatment options, which depends on the type and size of the wart (from taking medications to surgical removal).
Types of hygroma
There are different types of hand hygromas:
Mucous cysts - hygromas occur against the background of deforming arthrosis of the joints. Most often they form at the distal interphalangeal joint - in this case, hygroma occurs in the area of the nail phalanx, at the base of the nail. Hygroma on the finger develops when osteophytes, present in deforming arthrosis, begin to irritate the skin, underlying tissues and capsular ligamentous apparatus. Because of this, a hygroma occurs - a formation that is hollow inside, in a transparent capsule, with transparent, jelly-like contents.
When a hygroma appears on the nail phalanx, it begins to put pressure on the growth zone of the nail and deform it.
Treatment of hand hygroma
Treatment boils down to excision of the cyst. Due to the fact that with mucosal cysts the skin over the lump on the hand becomes weak, the formation is excised along with the changed skin. After the operation, plastic surgery is performed - both with free skin grafts and with complex skin reconstructions.
A tendon ganglion is a cyst that is formed from the tendon sheaths and the walls of the tendon sheaths. Such hygroma of the hand can cause not only pain, but also limitation of motor functions.
Treatment of a tendon ganglion involves removing the formation - this does not pose any technical difficulty. After operations there are practically no relapses or side effects.
Synovial cysts in the area of the wrist joint (hand hygroma) are the most common type of hygroma.
First aid and subsequent treatment
Every child can fall and bump, and the most important thing after that is to provide him with first aid in order to alleviate the condition and prevent complications from occurring.
If a lump forms on a child's forehead, apply a cold compress. Ice should not be applied to bare skin; it should be wrapped in some cloth. If there is no ice, you can use any product from the refrigerator or even a cloth soaked in cold water. The compress should be kept on the bruised area for about ten minutes and the procedure should be repeated during the first day. Thanks to the cold, spasm of the blood vessels on the forehead occurs, which leads to a reduction in pain and stops subcutaneous hemorrhage. If the hematoma grows quickly and does not go away after a few days, you should show the child to the pediatrician. If there is a bleeding abrasion, you should treat the bruise site with a cotton swab dipped in hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine. There is no need to cover the wound with a band-aid or smear it with brilliant green. The main thing is to watch that the child does not put his hands in there. If a crust forms during the healing process, you cannot rip it off, otherwise a small scar will remain. If there is a large cut or if the bleeding does not stop, you need to urgently call a children's emergency room; you may need to cauterize the vessel and apply sutures. If after hitting the head the child does not have any visible injuries, then you should monitor the behavior and general condition of the baby
It is necessary to take into account any actions that are unusual for the child. For example, if he is always playful, then parents should be wary of his calmness and vice versa
Refusal to eat, drowsiness, as well as physiological disturbances, for example, vomiting, fainting, convulsions, should be a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
If everything is fine at first glance, you need to calm the child down, put him in bed, tell him a story, talk to him, but you should not let him sleep for several hours after receiving the injury. The child should be awake, this will help assess his condition and see dangerous symptoms that may not appear immediately. You also need to wake up the baby on the first night after the injury in order to check if everything is fine with his coordination. If after a couple of days the child’s condition remains good, it means that the damage was minor and you can calm down, the bump on the forehead will soon go away.
Treatment of a hematoma on a child’s forehead should consist of cold compresses on the first day and warm compresses on subsequent days. You can also use pharmaceutical products that dissolve the bruise and help the lump go away faster. Among these drugs, ointments can be used for children:
- Traumeel;
- Rescuer;
- Aibolit;
- Bruise Off.
These ointments have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects and are approved for use in pediatrics. As a folk remedy, you can apply a cabbage leaf or a burdock leaf to the bump, and then secure it with a bandage. Such sheets should be changed as they heat up. Quiet walks in the fresh air will help a little patient recover faster and forget about the injury.
Dangers of a blow to the head
Most soft bumps on the head of children and adults do not cause complications, but it is important to know the risks of injury to get the full picture and make the right decisions. The most serious consequences of head contusions are cerebral edema and cranial bleeding.
Brain swelling usually forms within 24 hours. Cases where there is no unconsciousness are usually underestimated. A treacherous sense of security also occurs when a person responds well after unconsciousness has subsided.
The brain, skin and soft tissues of the head after injury behave similarly to other bruised parts of the body. For example, a lump on a sprained ankle appears the next day. But unlike the ankle, there is no room for swelling in the brain. There is a maximum of 0.5 cm between it and the wall of the skull, and the cerebrospinal fluid is almost not compressed. Therefore, the swelling expands at the expense of the brain, thereby damaging it.
The same applies to intracranial bleeding, which can accompany bumps on the back of the head in children and adults. A person is threatened not by blood loss, but by its penetration into the confined space of the skull. When there is bleeding into the skull and brain, symptoms appear almost immediately, the most typical of which are loss of consciousness and uneven pupil width.
Immediately after an injury, you cannot even rely on an x-ray image - swelling may not be visible on it. The severity of the condition can only be assessed after several days or even weeks.
If a bump appears on your head after a blow, what should you do and how to prevent possible complications? Despite the good post-traumatic condition of the patient, the absence of these symptoms, amnesia, he should not be left unattended for the next 24 hours. First of all, it is necessary to treat the wound. It should be anointed with an antibacterial agent (it is recommended to smear it periodically, in accordance with the recommendations on the ointment packaging), if necessary, cover the affected side of the scalp with a bandage.
After treating the wound, the victim should rest (as a rule, a person who has hit his head feels tired). Be careful, in newborns and small children sleep can be confused with loss of consciousness. Therefore, periodically awaken the victim and monitor his condition.
Hematoma
Description
If there is a swollen lump on the gum filled with blood, most likely it is a hematoma. This tumor occurs as a result of an incorrectly removed tooth or injury. Such a lump on the gum above the tooth, as a rule, does not hurt.
Treatment
Dissolves on its own. But if the lump hurts, consult your dentist for advice. The doctor will prescribe painkillers.
Causes
Hematomas can occur even if a person feels completely normal and is not aware of the development of diseases. But most often they are associated with a traumatic brain injury, and the fact of a concussion does not play any role. This may result from a fall, a car accident, a blow during a fight, or an accidental injury.
There are other reasons:
- vascular pathologies leading to rupture of an aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation, hemorrhagic diathesis;
- bleeding due to vascular destruction due to tumors, hypertension, rheumatism or atherosclerosis;
- changes in blood due to diseases, including liver pathologies, disorders of its coagulation;
- toxic damage to the body, consequences of bypass operations performed by surgeons.
Elderly people are at risk as they often suffer from vascular problems. There are cases where hematomas appeared spontaneously without any reason. Newborns are also at high risk of suffering from this problem. The cause of this outcome is injury during childbirth, premature birth or fetal hypoxia. Also, a baby may encounter a hematoma due to head injuries after birth.
From the editor: Symptoms and dangers of VSD in adolescents
Mechanism of development and symptoms
A lump is a neoplasm that appears on the head due to bruising of soft tissues. It occurs as a result of head trauma. Why does injury occur? There are several reasons:
- A fall. Most often it is observed in young children. For example, babies fall out of a stroller or bed. This happens due to parental neglect. Older children also fall while exploring the world (when taking their first steps, while running or riding a bike). When falling, not only the elbows and knees are often affected, but also the head.
- Strikes. The bump can occur from a blow to a hard surface or from a heavy object falling on the head.
- Beatings. If a bump appears on the head, this may indicate that the person was intentionally or accidentally injured.
What is the mechanism for the appearance of a lump? This tumor occurs due to damage to blood vessels. They burst, and blood flows out of them into the space between the skin and the skull. Thus, the more blood accumulates under the skin, the larger the lump appears.
In order not to confuse a lump after a bruise with another formation on the head, you should pay attention to some of its symptoms. Among them:
- The lump is localized directly in the place where the bruise occurred. It will not appear on the back of the head if a person hits his forehead.
- The bump from a bruise can be of different sizes. It depends on the force of the blow.
- The color of the cone is no different from the color of the skin. Sometimes it may look slightly red.
- Swelling is observed in the area of the bruised area.
- The lump is accompanied by pain. Often the child experiences itching in the area of the bruise.
The lump itself is not very dangerous. Its appearance is due to the fact that there is nowhere for blood to be absorbed after the blood vessels rupture. There is no layer of fiber on the head that absorbs blood, so it collects directly under the skin in the form of a tubercle. After some time (from 2 days to a week), the lump goes away.
Sometimes some signs appear that should not be ignored. If they occur, you must urgently seek qualified help. Among them are:
- bleeding;
- presence of open wounds on the head;
- development of severe pain in the head and cervical region, which is constantly intensifying;
- pain in the head is accompanied by an attack of nausea (sometimes vomiting);
- bleeding from the nose or mouth;
- persistent high body temperature (above 38 degrees Celsius);
- blurred vision (cloudness, blurriness of objects);
- speech disorder;
- temporary or long-term loss of consciousness.
Such symptoms may indicate a concussion, intracerebral bleeding, or skull fractures. Therefore, the patient needs immediate medical attention. If alarming signs appear in a child, you should call an ambulance, and until it arrives, provide him with peace.
What to do if a lump appears
The appearance of a bump on the forehead after a blow, like all other injuries, requires some actions to help reduce it. After a person has suffered a head injury and a convex hematoma has appeared, you need to:
- Give a light massage. This action can be performed immediately after the blow, until a bruise appears. If you massage an already formed lump, it can be dangerous. Light massage movements will help the outflow of blood and lymph from the injured area, which will prevent the appearance of a large hematoma. Do not knead your forehead too intensely and for more than one minute.
- Apply a cold compress to the injury site. To do this, wrap pieces of ice or frozen food in a cloth. A wet cloth or a bottle of cold water will also work, although the effect will not be as strong as ice. Cold constricts blood vessels, which reduces pain and subcutaneous hemorrhage.
- Place a tight bandage on your head. This method works exactly the same as cold. The capacity of compressed vessels decreases, which leads to stopping internal bleeding.
- Warm the injury site. This can only be done from the second day after injury. Thanks to the thermal effect, the hematoma on the forehead gradually resolves and the swelling subsides.
- Stick to bed rest. You need to lie down for at least a day after the impact without getting up. This will help your overall recovery.
Basically, such actions are enough for the formation to disappear faster. But sometimes, after a strong blow, you should resort to pharmaceuticals that help resolve hematomas.
Preventive methods for compaction to occur
To prevent a lump from forming after a fracture or bruise, it is necessary to apply cold to the damaged area as soon as possible after receiving the injury. Any item from the freezer will do. Hold for 15-20 minutes, and if medical assistance is not required, then after another hour.
At the same stage, the elevated position of the limb will also be relevant. The outflow of venous blood will reduce the degree of edema formation to a minimum. Without swelling, the likelihood of a lump appearing in the future is reduced.
You should not bandage the affected area immediately after receiving an injury. In the case of a recent injury, this method can disrupt tissue trophism and lead to unpleasant consequences.
If it is not possible to carry out the above steps, you should at least leave the injured limb alone. Physical activity in this situation will only worsen the clinical picture and increase the chance of a lump appearing during the recovery period.
When to see a doctor if you have a head injury
If the symptoms of a bruise are only swelling of the lump and pain at the site of the impact, which gradually subsides, then it is not necessary to go to the hospital; it is enough to use the remedies described above. But sometimes the situation can be much more serious. The injured person may experience not only a bump on the head from a blow, but also signs of a sharp deterioration in their condition as a result of a concussion, intracerebral bleeding, or a fracture of the skull. Urgent medical assistance is absolutely necessary.
Signs of such particularly severe conditions of the injured person are
- The appearance of open wounds and bleeding from them, which does not stop for more than 10 minutes.
- Feeling of severe pain in the head and neck area.
- Increasing nature of pain.
- Simultaneously with severe pain, attacks of nausea are observed.
- Blood or other fluid is leaking from the ears and nose.
- Increase in body temperature to a value greater than 38 degrees.
- Speech impairment.
- There is a feeling that there is “floating” in the eyes; the pupils are of different sizes.
- Confused consciousness.
If these signs occur, the victim must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible, and until the ambulance arrives, the person should be ensured complete rest and closely monitor his breathing and consciousness.
A bump on the head from a blow may appear to a lesser extent or not appear at all. It all depends on how quickly the situation is assessed and the necessary actions are taken to improve the condition of the injured person.
Ekaterina Morozova
Reading time: 4 minutes
A A
A child's skull is more fragile and vulnerable than that of an adult. Accordingly, the risk of serious injury increases significantly. Especially in the 1st year of life, when the bones have not yet fused and can easily move from a blow. Babies fall out of strollers and cribs, roll off the changing table and just plop down out of the blue. It’s good if everything turns out to be a bump or abrasion, but what should a mother do if the baby hits his head hard?
Severity of lumps under the skin
First, you need to clearly understand the mechanism of development of such phenomena. There are three degrees of severity for the consequences of bruises:
- the seal forms during the day and is almost not painful (only when touched);
- the bruised area swells a little, constant pain appears, which disrupts general well-being;
- an extensive diffuse hematoma, compaction in the tissues after a bruise is sharply painful, especially when touched, the body temperature may rise.
In what cases is it necessary to go to the hospital?
At any of the above stages, you should consult a doctor. But if the first two can be treated on an outpatient basis, then the third is an absolute indication for a hospital.
There are also a number of alarming symptoms that require a more detailed examination in a hospital setting:
- if the compaction does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to examine it in detail, even in the absence of pain. It is advisable to do this as quickly as possible, but the optimal period is up to 6 months.
- sharp pain that increases with palpation;
- bright pronounced redness of the skin over the seal;
- increased body temperature;
- decreased or loss of sensation in the bruised area.
Treatment of education in children and adults
If a minor head injury occurs and a lump appears, treatment is carried out at home. In severe cases and with extensive damage, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible.
Home help
Emergency help in this case consists of applying cold to the affected area. It helps relieve pain and promotes blood resorption, which leads to a reduction in the size of the lump. To do this, use the following means:
Ice. You can take it out of the freezer or take it outside in winter. Apply pieces of ice to the injury site for 15 minutes, after wrapping it in cloth
It is important not to overexpose, since prolonged exposure to cold leads to the death of skin cells. If there is no ice, you can cool the bruised area using a napkin or gauze soaked in cold water. This compress is changed periodically, preventing it from drying out. Bottle filled with water
It needs to be applied to the bump and kept for about half an hour. A heating pad filled with ice or water. A piece of frozen meat. Cold metal object (for example, a tablespoon, an iron cup).
All these remedies should be applied to the bruise on the head immediately after the blow. They relieve pain, reduce swelling and help shrink the lump. The next day, the use of cold is no longer acceptable. To make the lump go away, you need to use the following folk methods:
- Hot salt compress. It is heated and applied to the cone until it cools completely. A boiled egg is used for the same purpose.
- Applying a tincture of medicinal herbs (St. John's wort, chamomile, calendula) to the site of the injury.
- Vegetable oil (sunflower, olive). A piece of cloth is moistened with it and applied to the bump for half an hour. It removes swelling and redness.
- Alcohol and iodine. They are mixed in a 1:1 ratio and applied to the cone.
- Infusion of camphor with vodka. 10 g of camphor and 500 ml of vodka are mixed and infused for several days. Then soak a piece of cotton wool in this tincture and apply it to the bump for an hour.
- A mixture of iodine, lemon juice (1:2) and aspirin tablets. It is placed in a plastic bag and wrapped in warm cloth. After this, it is applied to the bruised area.
From the editor: In what cases is brain bypass performed?
Such drugs have virtually no contraindications. They safely treat a lump even in a child. When used correctly, formation should occur within 3-5 days.
Drug effects
There are medications that help resolve the lump, as well as eliminate the accompanying symptoms (pain, swelling, redness). They are prescribed for external use in the form of an ointment or gel. The following medicines are distinguished:
- Ointments based on troxerutin (a semi-synthetic substance used in the treatment of vein diseases). This is Troxevasin, Troxerutin. They have the following actions:
- venotonic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- decongestant;
- antioxidant. They reduce the fragility of blood vessels, increase their tone, and also relieve inflammation. The product is applied in a thin layer 2 times a day. It should not be used for open head injuries.
angioprotective;
To treat bumps on the head, there are many methods that can be used at home. Are these folk remedies or medications?
When choosing a remedy for treating a lump that appears after a head injury, you should take into account the patient’s age, the degree of head injury, as well as the person’s general condition. If symptoms intensify, it is better to immediately seek help from a doctor, since a head injury can cause dangerous pathologies
Medicines to treat lumps under the skin
A frequently asked question is “How to treat a lump after a bruise without surgery?” If this option is possible and the help of a surgeon is really not needed, then some medications may be effective. However, it is still best to discuss their use with your doctor.
Applications with a solution of dimexide diluted with water in a ratio of 1:4 - 1:2 give a good effect. Dimexide relieves pain and inflammation, and also reduces swelling. There is another useful property of this solution - it helps other substances (NSAIDs, hormones, antibiotics) penetrate deeper into the body’s tissues, thereby enhancing their effect.
You can apply ointment to the affected area to resolve bumps after a bruise. Today there are a huge number of them with different names, prices and, most importantly, completely different medicinal effects. Therefore, before using the ointment, you should consult your doctor.
In case of hematoma, the use of heparin-based ointment will be more effective. If we are talking about severe inflammation, then non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments will help (they also eliminate pain well) or ointment with a hormonal component
In any case, an ointment that resolves lumps after a bruise should be prescribed based on the mechanism of formation of the lump itself. And it’s better to sort this issue out with your doctor.
There is another good way to treat lumps on the extremities, which is especially effective for post-traumatic hematomas. You should try to keep the injured limb elevated to improve the outflow of venous blood and relieve swelling. For example, if a lump has formed after bruising your leg, you can place one or two pillows under the injured leg at night.
To improve the effect, doctors sometimes recommend bandaging the limb with an elastic bandage. This method also improves microcirculation and helps relieve swelling.
Main symptoms of head injury
Even children know that a bruised arm or leg will hurt. And your head will also hurt after you hurt your forehead or the back of your head. Only the headache cannot last longer than a few minutes, or at most, up to an hour.
Typically, pain after a soft tissue injury goes away quickly. But if a headache occurs, and in places remote from the injury, which does not stop, or, on the contrary, arose in the evening, when the person forgot to think about the injury, this may be a symptom of a concussion, or damage to the bones of the skull.
If your head hurts after a bruise with throbbing pain, then this is due to poor circulation and the development of vascular spasm. This is usually how the consequences of minor injuries occur in patients with migraines: an attack simply begins.
Another symptom is a hematoma, or bruise at the site of the injury. In this case, a condition is considered a soft tissue contusion if an x-ray of the skull bones is taken and all fractures are excluded.
Severe head injury - what is it?
The concept of “severe head contusion” has no medical meaning. Is this a click on the forehead, a slight bruise to the head? Or is it not a bruise at all? Or is it a forehead bruise?
In medicine there are clear criteria for making a diagnosis. And the qualitative characteristic “strong” is unknown what it means. Possibly severe pain, but no fractures. Then it would be more accurate to say that the patient, for example, “has a concussion and a severe contusion of the back of the head, the size of a soft tissue hematoma is about 3 by 5 cm.”
In any case, specifics are needed when making a diagnosis.
Contusion of soft tissues of the head
Contusion of the soft tissues of the head is the most common diagnosis among all head injuries. Bruises are divided by location (forehead, back of the head, temporal, parietal areas, soft tissues of the face). Also, a bruise may or may not be complicated by a hematoma.
Every second diagnosis of a concussion or brain contusion is “paired” with the soft tissues of the head, and this is understandable. Only DAP, or diffuse axonal injury, can occur during sudden braking of a car, when the head does not hit, and the damaging element is sharp negative acceleration.
Of course, sometimes blunt head trauma can occur in multiple locations. So, if a person was hit on the head while he was standing close to the wall, then the bruise will be in two places. This also needs to be taken into account.
Surgical methods for treating seals after a bruise
Surgical treatment of such seals involves opening the seal and draining the resulting cavity under local anesthesia. The choice of access is at the discretion of the surgeon. This can be a simple puncture or incisions in one or several places. For example, if a lump on the knee does not go away after a bruise, then it can be eliminated in one way or another (the final decision is made after performing all the necessary diagnostic procedures).
After opening, the surgeon clears the resulting cavity from the contents and, if necessary, installs a temporary drainage through which, within a few days, what could not be removed will come out of the wound.
Brain hematoma
The brain tissue contains a lot of blood vessels, and when damaged or ruptured, hematomas are formed. This problem can threaten human life and disrupts the normal functioning and activity of all body systems, and therefore requires immediate medical attention.
Brain hematoma - symptoms and types
The protection of the main organ in the human body is carried out through a special liquid called cerebrospinal fluid. In case of mechanical injuries, this substance is not able to provide proper shock absorption and vascular damage occurs. It can be localized both inside the brain and in the area between the skull and soft tissues. Thus, there are intracerebral, epidural and subdural hematomas of the brain. The first type of hemorrhage is characterized by ruptures of blood vessels directly in the organ itself, which entails damage to the white matter and disruption of the functioning of neurons. The second type affects the area between the hard shell of the organ and the bones of the skull. The third is the zone of contact between the brain substance and its covering. In turn, the latter form is classified as follows:
- Acute - the clinical picture is clearly expressed immediately after injury.
- Subacute – symptoms develop after a few hours.
- Chronic subdural hematoma of the brain - manifestations of damage are noticeable only weeks, and even months after injury.
- weakness and decreased motor activity of one half of the body;
- headache ;
- dizziness;
- confusion;
- chronic fatigue. drowsiness;
- nausea;
- speech apparatus disorders;
- decreased vision;
- different pupil sizes.
Intracerebral, epidural and subdural hematoma of the brain - consequences
The absence of the above signs and the victim’s normal state of health does not mean that the disease can not be treated. Without treatment, a hematoma can lead to serious complications:
Moreover, the disease provokes mental disorders, contributes to the development of depression, distortion of perception and thinking, increasing irritability and aggression.
Treatment of cerebral hematoma
Depending on the size of the damaged tissue and the presence of swelling, medical and surgical methods of therapy are used.
Small hematomas with mild clinical signs are treated with anticoagulants, blood thinners, corticosteroid hormones and diuretics. This complex of medications allows you to quickly eliminate the inflammatory process, relieve swelling and speed up the resorption of blood clots.
Extensive damage requires surgery. It is performed in two ways. If there is a visible accumulation of fluid localized in one place, it is sucked out through a small hole in the skull. A large hemorrhage requires trephination and complete removal of all clots to avoid pressure on the soft tissue.