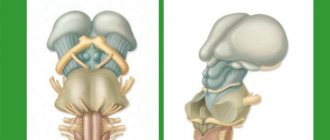
How does the disease develop and what are the consequences?
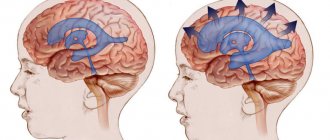
The activity of the endocrine glands, which produce cerebrospinal fluid, is disrupted. As a result, there is too much cerebrospinal fluid, and the small body is unable to ensure its normal outflow. On the left of the diagram is a normal brain, and on the right is one affected by hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalic babies are easily recognized by their disproportionately large heads. Water cannot compress and increases the volume of the skull, and since in children under one year old rigid connections between the cranial bones have not yet formed, the increase in volume of the head occurs unhindered.
When hydrocephalus of the brain develops in an older child, excess fluid manifests itself exclusively as damage to the central nervous system.
The disease is quite dangerous: the cerebrospinal fluid does not leave the head and begins to put pressure on the nervous tissue, destroying neural connections. Without proper treatment, this usually leads to swelling of the brain and ultimately the death of the child.
Classification of the disease
In children, there are four main types of hydrocephalus of the brain:
- External - fluid accumulates in the subarachnoid space - the cavity between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater.
- Internal - cerebrospinal fluid remains in the cerebral ventricles. The substance of the brain begins to thin out.
- Open (communicating) - all ventricular systems of the brain expand, but there are no obstacles to the movement of fluid through the cerebrospinal fluid system.
- Closed (occlusive) - disruption of the liquor flow is caused by pathologies of the ventricles: their adhesions, neoplasms.
The open form of childhood hydrocephalus can be either external or internal. But occlusal in 99% of cases is internal.
In addition, dropsy is also divided according to the form of its flow:
- Acute – a rapid increase in intracranial pressure, the baby’s condition worsens in the period from one to three days.
- Subacute - normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted for three to six months, after which severe brain damage occurs.
- Chronic – the development of the disease also lasts up to six months, but there is no such serious damage to the brain. Characteristic of open hydrocephalus.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of intrauterine hydrocephalus in your baby, you need to prepare for pregnancy. All chronic infections must be eliminated. At the same time, take a course of vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
It is necessary to eat right and engage in moderate physical activity. If possible, avoid large crowds of people during viral colds.
The formation of hydrocephalus in newborns in many cases is caused by infection of the mother during pregnancy, leading to disruption of the ventricular system of the brain. Timely detection of abnormalities and subsequent therapy provide a high chance for a child to live a full life.
Causes of pathology
As a rule, this is a congenital disease. There are also acquired forms, but they are quite rare.
The causes of cerebral hydrocephalus in children are intrauterine infections, birth injuries, genetic disorders, and central nervous system defects.
Depending on the stage at which the disease developed, its causes vary:
- Fetal hydrocephalus in the vast majority of cases develops due to defects of the central nervous system. Infectious infections are to blame for the pathology of every fifth intrauterine hydrocephalus. Only a small proportion is due to genetic disorders.
- When the disease begins to develop immediately after birth, it is most likely due to infections in the womb. Such situations account for 75%. In 15% of cases, a newly born baby begins to suffer from dropsy due to a birth injury that led to meningitis or intracranial hemorrhage. The remaining 10% are malformations of either the spinal cord or brain, as well as disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels.
- In children aged one year and older, hydrocephalus is almost equally formed as a result of one of the following reasons: hemorrhage; brain tumor (spinal or brain); consequences of TBI; consequences of brain inflammation; genetic problems; malformations of cerebral vessels.
These generalized reasons also have their own classification.
So, among the infections that cause the disease, the following are common:
- rubella;
- cytomegalovirus;
- neurosyphilis;
- herpes virus type 1 or 2;
- toxoplasmosis;
- bacteria and viruses that cause meningitis;
- parotitis.
Defects responsible for the formation of dropsy:
- Narrowing of the canals connecting the cerebral ventricles.
- Arnold-Chiari syndrome (underdevelopment of the posterior fossa of the skull, due to which the brain structures located there do not fit into it).
- Anomalies of the cerebral venous system.
- Underdevelopment of the openings through which cerebrospinal fluid drains into the subarachnoid space.
- Dandy-Walker syndrome (anomaly of the development of the cerebellar spaces and cerebellum).
Also, among oncological diseases, hydrocephalus can be caused by:
- brain cancer;
- papilloma;
- tumor of the skull bones;
- brain ventricle tumor;
- vascular plexus meningioma;
- various forms of spinal cord oncology that impair fluid circulation.
Diagnosis of internal hydrocephalus
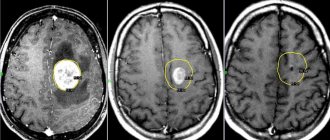
The clinical symptoms of internal hydrocephalus are usually so characteristic that they allow the neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital to suspect its presence during the first examination of the patient. To determine the type and degree of hydrocephalus, as well as to identify the pathological process that caused the disease, doctors conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, which includes radiography of the skull, ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
X-ray signs of hydrocephalus are thinning of the skull bones and divergence of the sutures between them; a symptom of “finger impressions” is observed on the inner surface of the cranial vault. With hydrocephalus caused by stenosis of the cerebral aqueduct, a decrease in the volume of the posterior cranial fossa is determined on radiographs of the skull. An increase in the volume of the posterior cranial fossa on craniograms is a sign of hydrocephalus in Dandy-Walker syndrome. If one of the interventricular communications is closed, the asymmetry of the skull is visible on the craniogram.
Echoencephalography (ultrasound) allows you to determine the degree of increase in intracranial pressure. In children of the first year of life, an ultrasound scan of the brain is performed through an open fontanel using ultrasonography. The most informative are tomographic diagnostic methods. They make it possible to determine the nature of hydrocephalus, identify the location of blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid tract or an existing congenital anomaly, and diagnose a neoplasm, cyst or hematoma. Monoventricular internal hydrocephalus is characterized by an increase in the volume of one ventricle of the brain.
If vascular disorders are suspected, magnetic resonance angiography is performed. For congenital hydrocephalus of infectious origin, PCR diagnostics are performed to determine the type of pathogen that caused it. Visual disturbances and the condition of the optic discs are assessed by an ophthalmologist at the Yusupov Hospital. Neurosurgeons at partner clinics decide on the need or advisability of surgical intervention.
Risk factors
There are accompanying conditions that contribute to the development of hydrocephalus of the brain in a child:
- Early birth (gestation period did not exceed 34 weeks).
- A narrow maternal pelvis and, as a result, a difficult birth process.
- The newborn's light weight is less than one and a half kilograms.
- During childbirth, hypoxia or asphyxia was observed in the fetus.
- Active methods of obstetrics: manual techniques, vacuum, forceps.
- The mother suffered viral infections during pregnancy: herpes, influenza, ARVI, toxoplasmosis.
- Bad habits of the mother that manifested themselves during pregnancy.
- Untreated sexually transmitted diseases in the mother during pregnancy.
Most risk factors for hydrops are related to maternal health.
Even indirect reasons, such as a premature baby with low weight, indicate an abnormal pregnancy. Every problem with a woman’s health during pregnancy weakens the embryo’s body.
Early Pregnancy Study
Seeing the desired - or sudden - “two stripes” on the test, many of us panic. Life is instantly divided into “before” and “after”. Someone feverishly remembers three glasses of champagne, someone took antibiotics during their fertile cycle, someone does not understand how this could happen, because “we were so careful.” Seventeen positive pregnancy tests are not an exotic exception at all, but a completely common reaction of a woman to a new circumstance.
The very first analysis
Pregnancy can be reliably confirmed or excluded by determining the level of the hormone β-hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin. As early as 6–10 days after fertilization of the egg, β-hCG can be detected in a woman’s blood serum or urine.
I am one of the principled opponents of the very early study of β-hCG. Just as not every grain planted in the ground sprouts, so not every zygote (fertilized egg) becomes an embryo and fetus. It is reasonable to start doing such tests if there is a slight delay in menstruation, at least after the 28th–30th day of the cycle.
Determining the level of total β-hCG in the blood serum is significantly more informative than urinary tests, but a single test will not provide any information. With a well and correctly progressing early pregnancy, the level of β-hCG approximately doubles every 48 hours. This growth dynamics is a good prognostic factor. Wherein:
- insufficient increase in the indicator - an ectopic or non-developing pregnancy is possible;
- doubling of hCG occurs at a very high rate - multiple pregnancies or hydatidiform moles are possible;
- decrease in hCG level - regressing pregnancy;
- hCG level does not increase or decrease - non-developing pregnancy.
When β-hCG levels reach 1200 mU/ml, the growth rate slows down, taking approximately 72–96 hours to double. And after 9–11 weeks, the concentration of β-hCG naturally begins to decrease.
Important!
Conduct the study in the same laboratory so that the attending physician does not have to compare incomparable things.
When is an ultrasound needed?
The need for ultrasound diagnostics in very early stages of pregnancy remains one of the controversial issues in modern obstetrics. On the one hand, visualization of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity allows us to exclude the possibility of ectopic pregnancy (except for those rare cases when the patient is “lucky” to have one fertilized egg in the uterus and another in the fallopian tube).
On the other hand, ultrasound examination in the early embryonic period cannot be considered completely safe. The embryo is still too small, and the rate of cell division and the likelihood of “breakage” are very high.
It is well known that ultrasound is capable of causing thermal and non-thermal (mechanical) bioeffects, therefore, to minimize the risk, it is recommended to conduct the study for the 1st trimester only in a protected mode - not going beyond the range of 3-4 MHz, the duration of the study should be as short as possible, use Power Doppler is not advisable.
That is why, when deciding to conduct ultrasound diagnostics in the early stages, the doctor must evaluate the ratio of the expected risk and the expected benefit.
Ultrasound is mandatory even in very early stages if:
- bloody discharge or pain in the lower abdomen appeared;
- there are serious concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, rheumatic diseases, cardiovascular pathologies, etc.);
- during the fertile cycle or in the early stages of pregnancy, the patient was exposed to teratogenic factors (ARVI or other infections, taking medications, radiation);
- pregnancy occurred due to intrauterine contraception;
- there is a suspicion of multiple pregnancy;
- pregnancy occurred thanks to assisted reproductive technologies (IVF);
- there is a suspicion of hydatidiform mole;
- high risk of developing fetal abnormalities; previously born children with malformations or chromosomal abnormalities;
- pregnancy in patients with uterine fibroids or formations in the ovaries;
- there is a suspicion of a non-developing or ectopic pregnancy.
Don't miss an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy may well become a life-threatening condition, especially if it is terminated as a result of a ruptured fallopian tube. Moreover, the only symptom of intra-abdominal bleeding that has begun may be sudden, severe weakness with loss of consciousness. How quickly will passers-by come to your aid? When will the ambulance arrive? How soon will a diagnosis be made and help provided?
How does hydrocephalus manifest?
Depending on the form of development of the pathology and the age of the child, the external signs of the disease change.
For children under two years of age, in which in 95% of cases hydrocephalus is a congenital pathology, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- Severe course of the disease. A rapidly deteriorating condition caused by damage to brain structures.
- The main symptom is a rapid increase in head volume. Growth of 1.5 cm or more every month is typical, for at least three months in a row. Starting from the ninth month of life, growth drops to 8-9 mm.
- A child is born with a head whose girth is larger than the girth of the chest. If by six months the ratio does not change, and the head is still larger than the chest, there is reason to suspect hydrocephalus.
- The veins on the occipital, temporal and frontal parts of the head are clearly visible.
- At three months the child does not yet hold his head up and begins to sit up late, crawl, and walk.
- The fontanel on the top of the head is convex.
- The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid primarily occurs in the frontal lobes of the brain. Head enlargement starts from the forehead.
- While fixating the baby's gaze, the baby's pupil twitches chaotically.
- The scalp becomes thin and has a painful shine.
- Overhang of the brow ridges over the facial bone - the eyes appear to be very deep-set.
A number of less characteristic signs can confuse the initial diagnosis of hydrocephalus in children and complicate treatment. For example, tearfulness, poor appetite, slow weight gain, frequent regurgitation, drowsiness, legs constantly bent at the knees, head tilting - all these symptoms are characteristic of hydrocephalus. But at the same time, they can be observed in dozens of other childhood diagnoses.
In the acute form of dropsy, when the disease progresses rapidly, other signs can be observed:
- convulsions;
- long cry on one note;
- loss of acquired physical skills (sitting, following other people's movements, vocal functions);
- vomit.
For children aged two years and older, other manifestations of hydrocephalus of the brain are typical:
- Headaches that begin in the morning (after sleep) and gradually subside in the evening. Nausea and vomiting often begin at the same time.
- Migraines that appear after stress, mental or physical work. Often accompanied by nosebleeds.
- A feeling of a rush to the head when bending over and bursting headaches.
- Pain in the fundus of the eye.
- Visual impairment: loss of sharpness, double vision.
- Urinary incontinence.
- Decreased muscle strength, accompanied by rapid fatigue.
- Cramps and fainting.
- Loss of coordination and uncontrolled movements of the limbs.
Treatment of hydrocephalus in children
Due to the complexity of the disease and its danger, treatment for a child with hydrocephalus is prescribed not only by a neurosurgeon, but also by a neurologist.
Treatment can be conservative (that is, without surgery, only with the help of medications) or surgical.
During drug treatment, the first step is to reduce intracranial pressure using the drug Diacarb. It reduces the production of cerebrospinal fluid and promotes the removal of potassium from the body.
In the hospital, strong osmotic diuretics are prescribed - oral Glycerin and Mannitol. Salt diuretics, for example Furosemide, are also prescribed. It, like Diacarb, should be taken in conjunction with drugs that maintain normal potassium levels - Panangin or Asparkam.
Doctor's advice
Hydrocephalus - this conclusion can often be found after an ultrasound scan of infants. However, in most cases it is compensatory in nature, everything returns to normal by the first year of life. In addition to birth injuries, protracted labor, structural features, the cause of such dropsy is the immaturity of the nervous system. True hydrocephalus is characterized by the entire clinical picture of increased intracranial pressure - an increase in the size of the head, monotonous crying, and the presence of neurological symptoms. Conclusion Ultrasound is not a diagnosis, it is the result of an examination; the diagnosis is made based on a combination of complaints, anamnesis, examination, and research data.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Any medicinal forms of treatment for acute hydrocephalus must be carried out under the strict supervision of doctors, and intermediate results must be checked using computed tomography and neurosonography.
Along with diuretic enzyme blockers, medications are prescribed that stimulate the functioning of brain neurons. For example, "Encephabol".
As for surgical intervention, the most effective method of surgical treatment of the brain in children is bypass surgery. Often this is the only way to save a child's life.
Shunting is the creation of a flow path (shunt) for cerebrospinal fluid to bypass an existing blockage. For closed hydrocephalus, it is used when tumors have already grown into the brain.
In the open form of the disease, three types of bypass surgery are provided:
- Ventriculoatrial.
- Ventriculo-peritoneal.
- Lumbo-peritoneal.
In addition to shunting, another type of surgical intervention is possible for closed forms of hydrops - dissection of arachnoid adhesions. This method involves the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
Watch the video about the causes and treatment of hydrocephalus:
The life span and quality of life of a child with hydrocephalus, his chances of recovery depend on many factors: the reasons that caused the development of the disease, the speed of diagnosis, the quality of treatment. But even a healthy baby can become a victim of the disease.
Don't forget about prevention. Protect your child from head injuries in every possible way; be sure to use protective equipment during active recreation. If the baby was born premature, be sure to undergo routine examinations with a neurologist, do an ultrasound and an MRI.
Women who are about to become mothers or planning to conceive a child should be aware of their health. Get rid of bad habits a few months before pregnancy. Get screened for infections. If you happen to get sick while pregnant, consult a geneticist and undergo an additional ultrasound.
Your unborn baby is sensitive to literally everything, so take care of him even before birth.
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://docs.cntd.ru/document/499002598
Rate how useful this article was
3.5 4 people voted, average rating 3.5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!