In everyday life, a person performs a number of actions aimed at ensuring daily activities in the cultural, public and social sphere. So during the day a person spends a lot of physical effort. As a result, fatigue sets in, which is cured by resting for a short time. However, if such fatigue occurs for no reason and accompanies a person constantly, even after a long rest, then you should think about visiting a qualified specialist. Perhaps these are the first signs of a serious disease in the human body.
So, chronic fatigue syndrome is a disease that is not associated with a person’s physical activity, is not associated with his daily activities, has nothing to do with seasonal changes, but causes a person to constantly feel tired and overworked. As a result, an able-bodied person experiences a breakdown.
In practice, using a statistical method, it has been proven that about 90% of this disease occurs in densely populated cities and is associated with human psycho-emotional activity. This disease affects people aged 25-45 years. Most people get sick in countries such as the USA and Australia. Thus, in the US state of Nevada, about 200 cases were recorded in 1984. Women get sick more often than men by 80%. The name of the disease has been established since 1988.
Disease prevention
After specialists identified this disease, an appropriate set of measures was developed to prevent it. A person can live with chronic fatigue syndrome for months or years. It occurs in people of different age groups from teenagers to adults.
To prevent this disease, you need to adhere to certain medical recommendations and use medications that enhance immunity. In a separate case, it is worth focusing on the prevention of disease in children.
The following reasons can lead to this disease:
- Incorrect work schedule for the child.
- Difficult school curriculum.
- Lots of homework.
- Constantly spending time watching TV or computer.
- Difficult relationships with other people.
As a rule, the disease chronic fatigue syndrome occurs in children aged 6-7 years, 11-14 years. The occurrence and development of this disease may be indicated by the following symptoms (strong manifestation in the afternoon):
- Moodiness.
- Constant crying.
- Fidget.
- Superficial sleep.
- Anxiety.
- Headache.
- Dependence on weather conditions.
- Loss of concentration.
Children with asthenic conditions
Children with asthenic conditions
The failure of some public school students is due to so-called asthenic conditions.
Depending on the reasons that caused the asthenic state, cerebral asthenia and somatogenic asthenia are usually distinguished. The latter is often intensified due to traumatic mental factors. Of course, the possibility of asthenia of a purely psychogenic nature cannot be excluded. But they are rarely limited only to asthenic manifestations and often lead to severe conflict experiences.
It is known that any external unfavorable factors, be it general somatic infections, minor injuries or very mild focal lesions of the brain, as well as prolonged and severe mental experiences, overwork, primarily affect the central nervous system and can cause functional mental disorders
A characteristic feature of asthenic and, especially, cerebroasthenic conditions is a violation of intellectual activity with primary preserved intelligence. In the process of studying, such children quickly become fatigued, nervous exhaustion, and have headaches. As a result, performance is impaired, memory and attention are weakened, children have difficulty concentrating when performing a task or are distracted.
All this creates real learning difficulties for the child. They are expressed in the fact that children with asthenic conditions, despite the absence of local speech disorders, experience difficulties in the process of mastering reading, writing, and counting. When reading, they often lose a line, do not highlight sentences, read by guesswork, and do not make semantic accents. Various mistakes are made in writing: letters and words are not completed, several words are combined into one, while individual letters and syllables are omitted, etc.
When learning mathematics, these children often do not master the concept of number, mental calculation techniques, do not remember the multiplication table well, and do not remember the terms of the problem, which makes it difficult to solve. The degree of severity of these manifestations depends both on the child’s condition and on the conditions in which his activities take place. With increasing fatigue and the absence of calm working conditions, the productivity of the educational activities of such children decreases sharply. Some features are also observed in their behavior: some of them are excited, restless, overly mobile, irritable, and tearful; others, on the contrary, are lethargic, timid, slow, inhibited, and unsure. Often, for fear of answering incorrectly, they refuse to answer at all.
In cases where a disorder of mental activity occurs at earlier stages of a child’s life, mental retardation manifests itself in a limited understanding of the surrounding reality, in a poor vocabulary and some underdevelopment of thinking.
All of these symptoms are often more pronounced with cerebral asthenia.
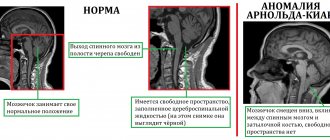
Cerebral asthenia is more often caused by impaired circulation of fluid in the brain, or occurs as a result of a concussion, or an inflammatory focus in the brain, even a small, narrowly local one. This happens because during inflammatory processes in the brain, as well as during cranial injuries, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid may increase slightly and then its circulation is disrupted. An increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid is called hydrocephalus. It goes without saying that the severity of this disorder can be very different - from the mildest to the most severe painful conditions. But even the mildest forms of hydrocephalus affect the development of the child and often lead to functional disorders of his mental activity. Here, much depends on the age at which the disruption of fluid circulation in the brain occurred, to what extent it is expressed, what is the general condition of the child, and many other factors. Cerebral asthenia often causes poor academic performance in children, but with a correct understanding of these conditions and timely provision of pedagogical and therapeutic assistance, many of these children can overcome their learning difficulties.
Constant overwork
In some cases, it is necessary to involve a qualified specialist to carry out psychological correction of the child’s activities. This will minimize psychological risks. And it will speed up the child’s recovery.
According to the information presented, in order to prevent the causes of this disease, you must adhere to the following recommendations from specialists:
- Control of the daily routine.
The work schedule of a child and an adult must be balanced. You need to spend more time outdoors, alternate between work and sleep. - Control of bad habits.
If a person has a tendency to drink alcohol and smoke tobacco, then he should limit himself in many ways. Children should be limited from drinking energy drinks. - Control of physical activity.
Optimal physical activity will help cope with this disease. - A change of scenery.
Sometimes, in order to get back to normal, you need to change your environment. Visit various public places, parks and squares. - Power control.
To eliminate the etymology of the disease, a balanced diet with a vitamin complex will help.
Causes of the disease
Fortunately, people are not born with this disease. It is acquired throughout life. It does not depend on the will of a person, but is acquired as a result of a person’s professional activity. Therefore, let’s move on to consider the main causes of this disease.
Main reasons:
- Wrong lifestyle.
Occurs as a result of prolonged consumption of drinks and items prohibited for consumption. This also includes lack of sleep, improper working hours, mental and physical fatigue, lack of air and sun, as well as a person’s sedentary lifestyle. - Psychological fatigue.
Sometimes, as a result of psychological fatigue, various emotional disorders occur. The result is obsessive fears, depression, depression, and anxiety. - Chronic diseases.
In this case, the disease is a consequence or accompanies a more serious disease. The result is not only exhaustion of the body, but also a weakening of the immune system. - Wrong diet.
This disease occurs when a person eats low-quality foods as a result of overeating and undereating. - Level of environmental safety.
A poor level of environmental safety not only has a negative impact on human health, but also on his psycho-emotional state. - Various viruses.
Various viruses and herpes viral infections can affect normal functioning and the occurrence of disease.
Causes of asthenia in children
The appearance of asthenia in children is caused by the following factors:
- metabolic disorders;
- nutritional deficiency;
- excessive expenditure of physical energy.
In addition, acute exhaustion of the body is possible under the influence of such reasons as:
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, gastritis, stomach ulcers, etc.);
- chronic infection (often asthenic syndrome develops after pneumonia);
- diseases of the blood and cardiovascular system;
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, hormonal imbalance);
- organic brain damage.
These diseases provoke exhaustion of the body, which leads to a neurotic syndrome in the child.
An increased risk of developing a mental disorder in children is observed in the presence of the following circumstances: heredity, frequent stress, unfavorable living conditions (poor environment, negative family environment), unbalanced diet.
Asthenia develops slowly. Therefore, the symptoms of the pathological condition become noticeable several months or years after, for example, a brain injury.
Symptoms of the disease
Before conducting a diagnosis and contacting the appropriate specialist, you need to establish some of the features of this disease yourself, which will inevitably be expressed in the manifestation of various symptoms, which should include:
- The occurrence of insomnia (sensitive, superficial sleep).
- The appearance of an obsessive feeling of fear (anxiety, restlessness).
- The occurrence of headaches and migraines.
- The appearance of pulsation at the temples.
- Overfatigue of the human nervous system.
- Decreased memory and concentration.
- Persistent weakness (apathy).
- The appearance of psycho-emotional disorders.
- The occurrence of depression.
- Painful symptoms in the muscles, three arms.
- General decrease in immunity.
- Manifestation of previously acquired chronic diseases.
Diagnosis of the disease
After establishing the above symptoms. It is best to contact a specialist. He will conduct an appropriate examination of the patient and make the correct diagnosis. Depending on the etymology of the disease, the diagnosis can be made by the following specialists:
- Neuropathologist.
It will help when the disease is associated with stress, anxiety and insomnia. - Psychologist.
This specialist will help when the nervous system is too overworked. - Endocrinologist.
A concomitant factor of chronic fatigue syndrome may be disruption of the endocrine system. - Immunologist.
Such a specialist is needed when it is determined that the disease is associated with colds or previous illnesses. - Therapist.
This is the main specialist who will conduct an external examination of the patient and send him to the appropriate specialist for treatment and a speedy recovery. After all, such a disease is easy to cure at any stage.
The specialist makes a diagnosis only after a thorough examination of the patient. After this, the doctor makes the following management decisions:
- Refer the patient to a specialist (neurologist, psychologist, endocrinologist, immunologist).
- Refer the patient for clinical tests (blood, urine).
- Refer the patient to donate blood hormones.
Asthenopia - symptoms and treatment
The doctor develops a comprehensive treatment strategy based on the patient’s individual indications and the stage of development of the disorder:
- In the compensation phase, in the absence of pathological changes, patients are recommended to give their eyes the necessary rest during visual stress: every 35-45 minutes, take a break for 15-20 minutes;
- In the subcompensation phase, patients are prescribed hardware treatment - laser stimulation to stabilize the work of the ciliary muscle, the use of a special synoptophore instrument for training the eye muscles, and therapeutic glasses. Glasses will help you get rid of the consequences of accommodative spasms and select the right tools for optical correction of myopia and farsightedness.
- In the decompensation phase, more serious measures will be required: the choice of glasses or contact lenses and eye drops. Drops for asthenopia:
- mydriatics - to relax the muscles responsible for contraction and dilation of the pupil;
- drops with antibacterial and antihistamine effects - used for infectious diseases of the eye;
- tear drops - for severe dryness of the mucous membranes;
- keratoprotectors - in the presence of microtraumas of the cornea.
When using drops, it is important to know that they differ in composition and properties. The dosage and duration of therapy must be observed. Some drops have no restrictions on the duration of use, others are addictive. Medicines for asthenopia are selected by an ophthalmologist.
When treating asthenopia, it is important to consider the main points:
- the correct choice of means of correcting visual impairment (glasses or contact lenses);
- eye drops to reduce the tone of the ciliary muscle and eliminate spasm of accommodation, use one drop every day or every other day at night for a month;
- proper nutrition containing sufficient amounts of vitamins;
- compliance with the work and rest regime.
Vitamins and traditional treatment
The benefits of taking vitamin complexes for asthenopia have not been proven. It is likely that symptoms of eye strain can be alleviated by taking blueberry extract and fish oil, but further research into the effectiveness of these products is needed [12].
Homeopathy
Homeopathy is a type of alternative medicine; there is no scientifically proven evidence of its effectiveness.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
To train accommodation reserves, hardware treatment methods are used: laser stimulation, color pulse therapy, magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation. However, there is no clear opinion about the effectiveness of physiotherapeutic treatment in the medical community.
Surgery
There is no surgical treatment for asthenopia.
Features of treatment depending on the form of the disease
In the case of symptomatic asthenopia, correction is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of underlying concomitant diseases. Treatment of the muscular form of ocular asthenopia begins with the elimination of strabismus (using orthoptics, diploptics) and correction of myopia. In the asthenic form, the cause should be determined and eliminated, the immune system should be strengthened, work and rest regime should be observed, and nutrition should be nutritious. The neurogenic form is treated by a neurologist.
Treatment of asthenopia takes a long time. When treating children, preventive measures and limiting visual load are of particular importance.
To relax the eye muscles, special daily exercises are performed. A set of eye exercises is chosen by an ophthalmologist based on the form of asthenopia.
Set of exercises
People whose activities regularly involve eye strain are recommended to do the following exercises daily:
Exercise 1. Closing your eyes. While sitting, close your eyes for five seconds, then open both eyes at the same time. Repeat seven times. Taking it will help relax the eye muscles, strengthen the muscles of the eyelids and normalize blood circulation.
Exercise 2. Blinking. While sitting, look straight ahead and blink intensely for a minute. Exercise normalizes blood supply to the eyes.
Exercise 3. Moving your gaze . Performed while standing. Look into the distance for a few seconds, then bring your index finger to your face at a distance of thirty centimeters from your eyes. Move your gaze to the tip of your finger and hold for five seconds. Lower your hand. Repeat ten times.
Exercise 4. Eyelid massage. Take a comfortable position on a chair, close your eyes and gently massage your eyelids with your fingertips. When massaging the upper eyelid, they move from the inside out, the lower eyelid - in the opposite direction. Perform for one minute. The procedure relaxes muscles and stimulates blood circulation.
Exercise 5. Alternating eye exercises. While standing, place your index finger at a distance of thirty centimeters from the eyes along the midline. Look closely at the tip of your finger for five seconds. Then, with the palm of your second hand, close your left eye, without taking your eyes off the object with your right eye. Then remove your palm and look at your finger for five seconds. Repeat the manipulation with the other eye. Repeat five times.
Exercise 6. Horizontal eye movements. Stand up and move your right hand to the side in a half-bent position, extending your index finger. Slowly move your hand to the side in the opposite direction, while carefully watching your finger. Then return your hand to its original position without taking your eyes off it. Do it ten times. Exercise helps strengthen the muscles responsible for horizontal eye movement.
Exercise 7. Pressing on the eyelids. Sitting on a chair, place three fingers on your closed eyes. Gently press on your eyelids for two seconds, then remove your hands. Repeat five times. Taking it helps improve the circulation of intraocular fluid.
Exercise 8. Fixation of gaze. Take a comfortable position on a chair and unfocus your gaze for five seconds, then move it to the tip of your nose. Repeat six times. Exercise improves the ability to keep your gaze on objects.
Exercise 9. Vertical eye movements. While standing, raise your half-bent arm up and extend your index finger. Fix your gaze on it and slowly move your hand down, then return to the starting position. Do it ten times. The technique strengthens the muscles responsible for the vertical movement of the eyeballs and trains the coordination of the visual apparatus.
Exercise 10. Circular movements. Sitting, the head is motionless. Raise your eyes up and move clockwise, and then in the opposite direction. Repeat five times.
Exercise 11. Movements in different directions. Standing, head motionless. Raise your gaze as high as possible, then lower your gaze. Look left and right. Repeat eight times. The exercise trains the visual apparatus.
Exercise 12. Static voltage. Sitting, the head is motionless. Close your eyelids and look up, then down, turn right and left. Do six times [4][3].
Treatment options
Since 1988, specialists have developed a number of techniques that allow effective treatment of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. The following treatment options are used for this:
ethnoscience
(treatment at home). A disease such as chronic fatigue syndrome can be treated at home using various effective methods and methods:
- Diet.
So, to treat this disease, choosing and creating a specialized diet is suitable. In other words, a person himself must correctly balance his diet with the content of various microelements. The diet must include various types of teas, carbonated drinks, coffee and alcohol. The best juice to use is grape juice. Salted fish should be eaten no more than once a week. - Normal sleep.
To normalize circadian rhythms, you must have normal sleep. To do this, you need to create a correct daily routine (work, rest). - Taking baths.
This disease is easily treated by taking warm baths. The temperature in the bath should be 38 degrees. The duration of the procedure is no more than 30 minutes. The heart area should not be submerged in water. - Physical exercise.
For a speedy recovery, various walks will be required. - Psychological therapy.
If you involve a qualified specialist, he can carry out psychological correction of the person. - Ethnoscience.
Now there are many traditional recipes for the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome. In this case, using tinctures of ginger and cinnamon will help.
Newspaper "News of Medicine and Pharmacy" 3 (353) 2011
Asthenic syndrome, or asthenia, is a component of the autonomic dysfunction syndrome, which often occurs in both adults and children.
It is polyetiological and is caused by violations of the regulatory functions of the higher parts of the autonomic nervous system, which is clinically manifested by emotional and volitional disorders, a decrease in the body’s adaptive capabilities and asthenia. Asthenia is a condition characterized by general weakness, increased fatigue and exhaustion, weakening or loss of ability for prolonged physical or mental activity, manifestations of anhedonia (decreased activity, loss of interest in normal activities and a sense of pleasure from them), cephalgia, dizziness, frequent changes mood, lack of positive motivation for recovery. Asthenia is always pathological weakness [5, 6]. Today, there are two types of asthenia - reactive (functional, or primary) and organic (secondary), as one of the manifestations of the disease.
In the pathogenesis of asthenia, hypoperfusion of the brain is of great importance with the formation of neurotransmitter disorders and, as a consequence, autonomic dysfunction, anxiety and depression, irritability and sleep disorders, as well as hypoperfusion of skeletal muscles. It is accompanied by hypoxia, increased ammonia levels, increased processes of anaerobic glycolysis, accumulation of lactate with the formation of acidosis and, as a consequence, muscle weakness [7].
In the pathogenesis of asthenia, the leading role belongs to metabolic disorders, which lead to hypoxia and acidosis with further disruption of the processes of formation and use of energy [2]. It is known that normally adequate energy production in the body is ensured by aerobic and anaerobic systems of glucose oxidation, which result in the formation of 38 ATP molecules (in anaerobic glycolysis - 2, in the Krebs cycle - 36). That is, the most appropriate for the body is aerobic metabolism of glucose. When the inclusion of pyruvate in the Krebs cycle is disrupted and its transformation into lactate, conditions arise for the formation of a significant energy deficiency in the cell with the development of acidosis, metabolic disorders, excessive protein catabolism with the formation of hyperammonemia and inhibition of the citrate and malate mechanisms of energy production [4]. It is known that malate is a dicarboxylic acid that normalizes the Krebs cycle, reduces lactate levels in the blood and tissues, prevents the development of lactic acidosis, enhances metabolism, promotes ATP synthesis and is the main supplier of energy for metabolic processes. An important role in the normalization of metabolic disorders is played by the intermediate product of the urea cycle—the amino acid citrulline, which activates the removal of ammonia compounds from the body. Both amino acids are present normally in the body. They catalyze metabolic and energy-synthesizing processes in the cell, and are insufficient in asthenia [4, 5].
Understanding the mechanism of development of asthenia at the cellular level makes it possible to rationally and purposefully influence its main links using metabolic drugs. A special place among these agents is occupied by the corrector of energy disorders of cellular metabolism Stimol® (Biocodex, France), which contains malate and citrulline. This drug has an energy-producing, metabolic and detoxifying effect, which is realized by eliminating hyperlactate and hyperammonemia. Malate has the ability to bypass the ammonia block of the oxidative pathway and limit the accumulation of lactic acid by reorienting it towards gluconeogenesis, and citrulline enhances the excretion of ammonia [3, 4]. In addition, Stimol® has a general tonic effect, helps normalize metabolism and activate nonspecific body defense factors, does not cause mental and physical dependence and drug withdrawal syndrome, is well tolerated, practically does not cause adverse reactions, and is therefore safe when used in children. An important advantage of the drug is that it does not contain glucose and can be used for any psychosomatic disease, including diabetes.
Purpose of the work: to determine the effectiveness of metabolic correction of asthenia in the treatment of psychosomatic pathology in children with and without NPFR.
Materials and methods
We examined 194 children aged 7 to 17 years with PSP (BA and PUD), of which 101 were without NPFR and 93 with NPFR. Diagnoses were verified according to ICD-10. Psychological testing was carried out to determine reactive and personal anxiety and was assessed using a self-esteem scale according to the Spielberger-Khanin method. The state of the autonomic nervous system was studied using cardiointervalography with a clinoorthostatic test.
To determine the effectiveness of the proposed therapy, two representative groups were identified: I (main), which included 50 children with PSP and NPFR, and II (control group) - 50 patients with PSP without NPFR. Patients in both groups received basic therapy depending on the underlying disease according to treatment protocols approved by the Ministry of Health of Ukraine. For patients in the main group, complex therapy included the drug Stimol®, which was prescribed 1-2 sachets 2-3 times a day for 14 days.
The results obtained were processed statistically using the MathCAD software package to determine the level of reliability. The work used an analysis of the scoring of the main clinical manifestations of asthenia with the calculation of the integral index of pathology (IPI) and the coefficient of comparative effectiveness of therapy (S.G. Makeev, 1985).
Research results and discussion
The clinical picture of PSP in children with and without NPFR was characterized by a polymorphism of complaints and clinical syndromes. The main syndromes in the examined children were: pain (69.1 and 51.4%), dyspeptic (71.2 and 60.3%), chronic intoxication syndrome (45.7 and 36.6%, respectively), which did not differ significantly in both groups (p > 0.05). Asthenoneurotic syndrome was significantly more common in children with PSP and NPFR than in children without NPFR (97.8 and 57.4%) (p < 0.05). Manifestations of asthenia were dizziness and decreased ability to work (35.1 and 14.9%), weather sensitivity (40.4 and 9.9%), sleep and memory disorders (44.7 and 11.9%), irritability (37.2 and 11.9%) and emotional lability (57.4 and 18.8%).
The dynamics of clinical symptoms in those examined are presented in Table 1. Thus, the pain symptom disappeared faster and after treatment was observed only in 6.6 ± 0.1% of patients in group I. At the same time, 18.0±0.1% of children in the control group complained of pain (p<0.05). Similar results concern manifestations of dyspepsia (5.6 ± ± 0.1 and 14.0 ± 0.1%), chronic intoxication syndrome (7.2 ± 0.1 and 20.4 ± 0.1%) and impaired bronchial ventilation (14.1 ± 0.1 and 45.6 ± 0.1% of those examined in accordance with group distribution) (p < 0.05).
Asthenic manifestations after treatment persisted only in 19.6 ± 0.1 and 20.0 ± 0.1% of patients in groups I and II, decreasing by almost 5 and 2.5 times according to the group distribution (p < 0.05). Cephalgia in the control group was observed in 18.0 ± 0.1% versus 5.6 ± 0.1% in the main group. The dynamics of meteosensitivity were more positive in the main group—5.6 ± 0.1% and 8.4 ± 0.1% in the control group. Dizziness at the end of the course of treatment was not observed in children of the main group, while in the control it was observed in 6.0 ± 0.1% of patients (p < 0.05).
Only 2.2±0.1% of patients in group I and 16.0±0.9% of children in the control group complained of weakness, which was significantly less than before treatment. Sleep disturbances disappeared in children of the main group and remained in 9.2 ± 0.2% of the control group (p < 0.05). At the end of the observation, 10.0 ± 0.2% of children in group II noted irritability, while patients receiving metabolic correction with Stimol® felt completely balanced.
At the beginning of the observation, 47% of children in group I and 45% of children in group II had a normal level of autonomic reactivity. Asympathicotonic (AST) type was established in 28% of children in group I and in 33% of children in group II. Hypersympathicotonic (HST) autonomic reactivity was observed in 25 and 22% of subjects according to group distribution.
After treatment, a more significant positive dynamics of autonomic reactivity was noted in patients of group I: asympathicotonia decreased to 12%, hypersympathicotonia to 8%, and the number of patients with the normotonic type increased to 80% in group I. In the control group, at the end of treatment, asympathicotonia was observed in 18%, hypersympathicotonia in 19%, and a normal type of autonomic reactivity (NTVR) was observed in only 63% of children (Table 2).
As can be seen from table. 3, for patients with PSP and NPFR who took the drug Stimol®, the level of personal (PT) and reactive anxiety (RT) significantly decreased and amounted to 36.47 ± 1.04 and 25.43 ± 0.75 points, respectively. In those examined with PSP without NPFR, the indicators of personal and reactive anxiety did not significantly decrease and amounted to 44.34 ± ± 1.24 and 29.32 ± 1.02 points, respectively (p > 0.05).
Objectifying the research data using the method of scoring the leading clinical manifestations of asthenia, it should be noted that in children in whose treatment complex Stimol® was included, the positive dynamics were more significant than in the control group (Table 4). This is confirmed by the values of PPI2, which after treatment in group I was 0.9 ± 0.15 versus 1.9 ± 0.11 points (p < 0.05) in the control group. That is, the dynamics of reverse changes in the main clinical manifestations of asthenia in children of group I occurred twice as fast.
Determination of the coefficient of comparative effectiveness of therapy (K = 1.54) gives grounds to assert that the inclusion of the drug Stimol® in basic therapy increases the effectiveness of complex treatment of children with PSP and NPFR by 1.54 times. Improved therapy significantly more quickly eliminates manifestations of asthenia, improves the general condition of children, normalizes the main indicators of the autonomic nervous system, and reduces reactive and personal anxiety of patients.
Thus,
1. The course of PSP in children and adolescents with and without NPFR is accompanied by significant manifestations of asthenia, which requires its metabolic correction.
2. The inclusion of the drug Stimol®, as a psychopharmacotherapeutic agent, in the complex therapy of PSP doubles the regression of clinical manifestations of asthenia and increases the effectiveness of treatment by 1.54 times.
3. The metabolic drug Stimol® reduces the level of personal anxiety and normalizes reactive anxiety and the state of the autonomic nervous system in the vast majority of patients with PSP (80%), which indicates its vegetative and psychomodulatory properties.
4. The high efficiency and good tolerability of Stimol® allow us to recommend it for widespread use in complex therapy of children and adolescents with PSP to eliminate manifestations of asthenia.
Drug treatment
In some cases, drug treatment is prescribed. To do this, the appropriate specialist, after making a correct diagnosis, prescribes the following medications:
- Medications with sleeping pills and sedatives;
- Medicines to stimulate the production of serotonin;
- Various vitamin complexes;
- Psychotropic drugs (in consultation with a specialist);
- Immunological modulators;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal).
- Optimized physical activity.
To treat a disease such as chronic fatigue syndrome, the following methods in the field of physical activity are used:
- Carrying out a massage.
When performing this procedure, a general relaxation of the muscles in the head and joints occurs. Massage procedures relieve tension, reduce pain, improve blood circulation and muscle saturation. - Performing acupuncture.
A targeted effect on special points that make it possible for a person to relax. This allows you to relieve pain, minimize irritation of the nervous system, and restore the vitality of the body. - Performing physical therapy.
Minor physical activity will help restore the overall tone of the body, as well as improve the energy metabolism of the body's cells. - Magnetotherapy.
A magnetic field can be actively used for treatment. As a result, the endocrine and immune systems are restored. - Hydrotherapy.
Impact on the body of water procedures. This reduces pain. Calms the nerves. - Laser therapy.
A laser system can be used to restore the human body. As a result, the nervous system is stimulated and metabolism improves.