- What does a brain CT scan show?
- CT with contrast
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Preparing for the examination
- How is the procedure performed?
- Decoding the results
- Is the examination safe?
- How often can you do it
CT scan of the brain is a high-tech, informative examination method that allows you to obtain detailed and clear images of the structures of the brain, blood vessels, nerves, bones of the cranial vault, and soft tissues of the head.
Computed tomography allows you to obtain black and white images, which are layer-by-layer sections of the brain and its surrounding structures. The thickness of the sections can be about 1 mm. This makes it possible to detect even small tumors and other pathological changes that occur in the brain at the earliest stages of the development of the disease.
What does a brain CT scan show?
The images can reveal signs of the following pathological processes::
- cerebral edema of varying severity;
- displacement of brain structures such as ventricles, etc.;
- hemorrhages in the brain tissue, even minimal in size;
- hematomas of various locations: epidural (located between the bones of the skull and the dura mater), and subdural (located between the dura and arachnoid membranes);
- brain cysts;
- tumors of the brain and meninges;
- inflammatory processes: arachnoiditis, encephalitis, abscess, pus between the meninges.
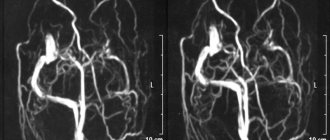
Modern computed tomographs have special modes that allow you to examine the vessels of the problem area of the body and build a three-dimensional color image of the arteries and veins. This examination is called CT angiography of the brain.
CT angiography allows you to examine the condition of vessels with a diameter of more than 1 mm and identify pathological changes in the blood supply to the brain:
- protrusions of vessel walls (aneurysms);
- malformations (congenital abnormalities of vascular development);
- atherosclerotic changes in the walls of blood vessels;
- thrombosed and embolized areas of blood vessels;
- narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels;
- kinks of blood vessels;
- proliferation of blood vessels by a tumor.
A CT scan of the brain and cerebral vessels can be performed in one clinic visit, but this will be two studies in one.
How does a CT scan differ from an MRI of the brain?
| COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHER | MAGNETIC RESONANCE TOMOGRAPHER |
The principle of operation of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner
Diagnosis of brain diseases using MRI is one of the most harmless and harmless examination methods.
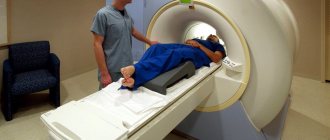
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the ability of high-frequency radio waves to cause vibrations in the hydrogen atoms present in the body's cells when they are exposed to a powerful magnetic field. The MRI machine records the received impulses, which are then processed by a computer. Due to the fact that different tissues of the body are characterized by signals of varying intensities, high-frequency images of the substance, meninges and vascular bed are formed with high spatial resolution. The increased power and ultra-sensitivity of modern tomograph models have made it possible for doctors to diagnose millimeter changes at an early stage of their occurrence. An MRI machine, depending on the type of model (open or closed), resembles a large installation with a narrow pipe in the center or a magnetic canopy. During the examination, the patient lies, as still as possible, on a mobile table that is placed inside the tomograph. An MRI scan lasts from 20 to 40 minutes, depending on the purpose and examination protocol. It is quite comfortable for the patient. Only loud noises from the machine can cause slight concern. This noise is safe for the patient. It occurs due to vibration of the metal coils in the device, which is caused by rapid pulses of electricity. The induction power of a tomograph (fullness) is one of the most important parameters of a tomographic installation. It is measured in Tesla. There are three types of devices that differ in magnetic field strength: low-field (0.3-0.5 Tesla), high-field (1-1.5 Tesla) and ultra-high-field (3 Tesla or more). The higher the induction level of the tomograph, the better the quality of the images it produces.
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
The principle of operation of a computed tomograph
CT scans of the brain are performed using a device called a spiral CT scanner.
During the examination, the patient's body is exposed to several beams of X-rays released by the emitter sensor at different angles. Unlike conventional radiography, which offers only a flat image from several positions, a CT scan of the brain produces a set of images in the form of small sections in different projections. To do this, the device's sensors move in a spiral around the patient's body, recording information received from different angles. On a computer, this information is combined into three-dimensional models (tomograms) of a specific area or lobe of the brain. The power of a CT scanner depends on the number of slices the scanner makes per revolution of the gantry ring. The higher the shearing ability of the unit, the more accurate the scanning results will be. In St. Petersburg clinics today you can undergo examination using 4-340 slice computed tomographs. A high-quality CT scan of the brain will require a device of 32 slices or higher.
To obtain CT images of the vessels of the head, the patient is injected intravenously with an iodine-containing contrast agent, which stains the vascular bed well. Without it, high-quality visualization of the vascular system of the head and neck is impossible. The CT scan procedure is absolutely silent and fast. The average scan duration is about 5-7 minutes.
Computed tomography of the brain with contrast
Native (performed without contrast) CT scan of the brain allows one to obtain informative images of bones, as well as hematomas and areas of hemorrhage. Neoplasms, blood vessels, and soft tissues of the head will not be visible on native images. To increase the information content of the examination, special contrast agents based on iodine are used, which “stain” individual anatomical structures and tissues valuable for diagnosis.
For contrast-enhanced computed tomography, contrast is administered intravenously immediately before the study begins or as a bolus throughout the scan. For bolus administration of contrast, a special device is used - an injector, which delivers the drug into the blood at a constant speed.
CT scan of brain vessels is performed only with contrast.
CT head
Main diagnostic features
Features of Head CT
Thin-slice images allow high-quality three-dimensional reconstructions such as VR (volume imaging) or MPVR (multi-plane volumetric reconstructions), especially used in the evaluation of post-traumatic and vascular studies.
Diagnosis of the head in computed tomography consists of several separate procedures that require different patient preparation.
Computed tomography of the brain allows you to evaluate:
- nervous tissue (distinguishing between gray and white matter);
- spaces containing liquid;
- spinal (ventricular system and arachnoid reservoir system).
In emergency cases - in case of injuries, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, as well as in the diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhages (SAH), the examination is carried out without preparing the patient.
This technology is proving to be extremely useful, especially in imaging structures located inside the human head. The quality of the result is influenced by the power and capabilities of the equipment on which the research is carried out. Computed tomography of the head in Moscow is available in our clinic using the latest generation tomograph, a high-precision 64-SLICE CT PHILIPS BRILLIANCE.
Preparing for diagnosis
Preparing for a CT scan of the head
Head tomography is performed on an empty stomach; before the procedure, approximately three hours before the examination, it is recommended to drink about 2 liters of still water. Before the test, tell the doctor performing the test about any chronic illnesses, medications you take, allergies or other conditions. Before performing a CT scan of the head, jewelry, glasses, and hearing aids (if the patient is wearing them) must be removed.
It is also important to bring your current blood creatinine and TSH results with you if the test will be done with contrast (contrast is removed from the blood naturally by the kidneys, so the doctor must assess their status before administering contrast).
Computed tomography technique
You do not need to dress in any special way for a CT scan of the head. However, items such as jewelry, glasses, or hearing aids should be removed as metallic objects may interfere with the examination image. The patient is wearing a protective gown (especially to protect the reproductive organs, which are sensitive to radiation).
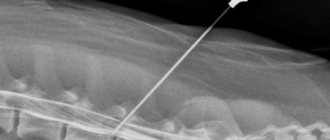
The subject is placed on a special table, which then slowly slides into the round hole of the tomograph. Sometimes an additional pillow is placed on the table so that the head is fixed in one position and does not move. During tomography, X-ray tubes move around the patient 360° in a special frame and produce a series of layer-by-layer X-ray images. The entire procedure is painless and usually lasts only a short time.
It is important for the patient to remain still and, in addition, to hold his breath when the special light comes on or when the radiologist performing the CT scan asks to do so. During the diagnosis, the doctor is in a separate room, but throughout the entire examination he maintains contact with the subject through a special internal system of microphones and speakers. In this way, any alarming symptoms caused by, for example, the administration of a contrast agent (which is administered during a break in the study through an intravenous tube) can be immediately reported at any time during the study.
After the examination
If a contrast agent is administered, the patient is rarely asked to remain in the clinic after the examination is completed to ensure that there is no serious acute allergic reaction. Immediately after the examination, as well as in the days following it, you should drink plenty of fluids in order to remove the contrast from the body as quickly as possible.
If no contrast agent was used, the patient can return to their daily activities, eat normally, and maintain a normal rhythm immediately after the examination. Only if you use sedatives, which slightly impair concentration and reflexes, should you avoid driving and other activities that require concentration for several hours.
Indications for CT scanning
Head imaging is most often performed for head injuries such as brain contusions, skull fractures, and hematomas. Neoplastic diseases of the central nervous system are also indications for tomographic examination. For example, glioma, lymphoma, astrocytoma, malignant neoplasms of the middle ear, meningioma and tumor metastases to the face.
Head tomography is also performed for unclear bacterial and viral inflammations, for tuberculous meningitis, abscesses and brain abscesses, for toxoplasmosis and cysticercosis. Indications for head tomography also include any vascular changes in the brain, hematomas, intracerebral hemorrhage, cerebral ischemia, hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral infarction, suspected pituitary disease, and monitoring of postoperative condition.
In children, head tomography is performed if developmental defects or, for example, hydrocephalus are suspected. This examination is also necessary for inflammation of the paranasal sinuses and meninges. Alzheimer's disease, cerebral dementia, craniofacial changes, cysts, and septal pellucid defects are other examples of complaints when performing a CT scan of the head.
Contraindications
Computed tomography of the head is performed in pregnant women in rare cases when the value of the diagnosis significantly outweighs the possible risks associated with the procedure. Also, CT is not recommended for young patients under the age of 14 years.
The decision to prescribe this study or replace it with another is always made by the attending physician based on the clinical characteristics of a particular case.
CT scanning of the head with contrast should not be performed in patients with allergies to iodine-containing drugs. It is also not recommended for patients with kidney failure and people whose thyroid hormone levels are too high.
Also, the weight of the subject over 200 kg will be a contraindication, since this is the maximum capabilities of the device.
Advantages and disadvantages of tomography
Advantages of head CT
Advantages of multi-row spiral computed tomography:
- non-invasive and painless examination method;
- short duration and reduced radiation dose;
- the ability to simultaneously obtain images of bones, soft tissues and blood vessels;
- the ability to examine a larger area of the body with one breath-hold;
- reducing the amount of contrast administered, which is equivalent to reducing the risk of complications;
- increasing patient comfort during the examination;
- CT provides very detailed images of various types of tissue, in contrast to classical x-ray studies, and makes it possible to obtain images with high spatial resolution;
- In most cases, a CT scan is faster than a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan; in both modalities, it is important that the patient does not move because any movement can cause errors in the resulting images (CT scans have a potentially lower risk if they have a shorter duration patient movements);
- it can also be performed on patients with implanted medical devices such as a pacemaker or neurostimulator (as opposed to MRI);
- it is performed quickly and easily, in emergency situations it allows you to immediately visualize internal injuries and bleeding, which can save the patient’s life;
- allows real-time imaging, making it a suitable tool for invasive procedures such as needle biopsies of various organs, particularly the lungs, abdomen, pelvis and bones.
CT scan of the head vessels may eliminate the need for surgery or surgical biopsy.
Disadvantages of diagnostics include the impossibility of examination during pregnancy, the dose of radiation received, and the need for additional preparation if the procedure is performed with contrast.
Research results
A CT scan provides valuable information about a patient's health and plays an important role in the diagnosis of diseases by assessing the condition of internal organs and possible abnormalities throughout the body.
The price for a head CT scan in our clinic is one of the best in Moscow. We provide diagnostic services at a guaranteed high level. You can quickly make an appointment and get tested.
Sign up for a head CT scan
Computed tomography is a non-invasive, accurate and fast diagnostic method. You can get a CT scan of your head at the Open Clinic. You can sign up for an examination by calling the specified phone number or using the feedback form.
You can also sign up for a head CT scan in Moscow upon arrival at the clinic at the registration desk in the Presnensky Center or on Mira Avenue, but we suggest calling in advance to choose a time that is suitable and convenient for you for the examination.
Indications for CT scan of the brain
You can get a referral from your doctor for an examination in the following cases::
- head injury;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- violation of higher brain functions such as speech, memory;
- convulsions;
- fainting;
- neurological signs of damage to parts of the brain if symptoms appeared for the first time or began to progress over time.
Indications for CT angiography of cerebral vessels:
- suspicion of the presence of congenital vascular anomalies (malformations);
- syndrome of compression of blood vessels by a space-occupying formation (tumor);
- proliferation of blood vessels by a cancerous tumor.
Which is better - CT or MRI of the brain?
In the case of complex anomalies of the brain and vascular system, CT and MRI perfectly complement each other and together provide the most complete and comprehensive information.
However, any diagnosis has its own nuances and subtleties that are understandable only to medical specialists. Therefore, it is best when the choice of diagnostic method is made by your attending physician, guided by the primary diagnosis, the purposes of the tomographic examination and your state of health. Medical centers are constantly improving examination protocols in order to increase diagnostic accuracy. Therefore, if you are concerned about your well-being, and you have no direct contraindications or restrictions, it is better not to put off going to the diagnostic center for too long. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will quickly and efficiently help you find out if everything is okay in your head. Author: Belik Ekaterina Mikhailovna
Radiologist with 19 years of experience
Contraindications for computed tomography of the brain
Absolute contraindications include:
- pregnancy at any stage;
- patient weight over 120 kg.
Relative contraindications:
- age up to 12 years;
- allergy to drugs containing iodine;
- feeding the baby with breast milk;
- chronic renal failure;
- multiple myeloma.
If the examination is planned to be carried out using a contrast agent, then the:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- insufficiency of kidney and liver function;
- intolerance to iodine-based drugs.
When is a head CT scan recommended?
A neurologist, traumatologist, surgeon, oncologist, or general practitioner can refer the patient for this examination. But a head CT scan can be done without a doctor’s referral. Tomography is also recommended if the patient is bothered by headaches, dizziness, fainting of unknown etiology after injuries, in particular those received during an accident.
In what situations is it recommended to do a CT scan of the head?
- Traumatic brain injuries. A CT scan will show fractures, hematomas, joint dislocations, and hemorrhages.
- After a stroke or if acute cerebrovascular accident is suspected. In case of hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to exclude hemorrhage in the brain; diagnosis is carried out immediately. The consequences of an ischemic stroke are best assessed after 4-5 hours, since the signs of this type of stroke are visualized later.
- If tumors and brain metastases are suspected. Neoplasms can compress nerve endings and blood vessels; their compression can cause chronic pain and disorders of the central nervous system and vision.
- Before operations and surgical interventions. A CT scan of the head is prescribed before the removal of tumors and cysts, reconstructive operations for injuries and fractures of the skull bones, removal of hernias and cysts of the cervical spine, and some types of operations on the facial bones of the skull (before septoplasty, rhinoplasty, osteotomy).
- After surgery and chemotherapy. Follow-up CT is necessary to monitor treatment results.
- If vascular diseases, malformations, or thrombosis of cerebral vessels are suspected. Blockage of the arteries can cause ischemia, atrophic changes, and poor health.
- Foreign objects. A CT scan of the head will show foreign bodies in the scanned area and traumatic changes. The examination can be performed on patients with internal metal structures and implants.
- With frequent otitis. An ENT doctor may prescribe an examination of the temporal bone and paranasal sinuses.
- Before aesthetic surgeries (rhinoplasty, septoplasty, Olivari surgery).
- In case of disruption of the salivary glands. A CT scan of the neck is prescribed as part of the examination for salivary stone disease (sialolithiasis).
How to do a CT scan of the brain
The patient is placed on the moving table of the CT scanner in the supine position. The head is fixed with a special pillow and a belt so that the patient remains completely still during the examination. The clarity and information content of the resulting images depends on this.
A contrast agent can be administered before the examination begins or after native images are taken. If a bolus injection of the drug is planned, a special catheter is inserted into the patient’s vein, to which a thin tube from the injector is connected.
The machine table together with the patient is moved inside the tomograph and the examination begins.
The best examination results are obtained by spiral computed tomography of the brain, when the scanner continuously moves around the human body. One revolution of the scanner produces one image of a tissue section of the area under study.
When the examination is completed, the doctor checks the quality of the images obtained. If all the images are clear and detailed, then the table along with the patient is pulled out of the tomograph capsule, and the patient is allowed to stand up.
To make our explanation more clear, we have prepared a video about what a CT scan of the brain shows.
Contraindications
X-ray radiation and contrast agents cannot be called completely harmless, therefore there are a number of contraindications to CT scans of the brain. You cannot undergo the procedure if you have severe pain syndromes or hyperkinesis, when you cannot remain completely still. Contraindications to contrast administration are diabetes mellitus, iodine allergy and renal failure. It will not be possible to find out what a brain tomography shows if the procedure is necessary for a pregnant woman at any stage - the radiation can negatively affect the fetus. Nursing mothers will have to wean their baby off the breast for two days until the contrast wears off. Patients with acute mental illness, as well as claustrophobia, will need to either choose a different research method or undergo a CT scan under anesthesia.
How often can a CT scan of the brain be done?
You can’t just find out what a CT scan of the brain shows. The procedure is prescribed by the attending physician if there are a number of symptoms indicating disturbances in the functioning of the brain, as a rule, no more than once a year. In severe cases, you can undergo tomography up to three times a year with an interval of at least 4 weeks.
Alternative Methods
If for a number of reasons it is impossible to find out what a CT scan of the brain shows, you can undergo an MRI
. This procedure will allow you to examine the structure of the brain in detail and identify any abnormalities. CT is aimed at studying the chemical structure of tissues that absorb x-rays, depending on their density. MRI does an excellent job of visualizing soft tissue. It often happens that CT and MRI are prescribed together to obtain a more detailed picture. However, it is worth knowing that magnetic resonance imaging makes it practically impossible to examine the bones of the skull; in this case, computed tomography better shows all structural changes.
Is a CT scan of the brain harmful?
CT scanners use X-rays to obtain images of tissue slices on the patient's body. The radiation dose that the patient receives during the examination is 1.4±0.4 mSv. For comparison, the permissible annual radiation exposure from background radiation is 3-4 mSv. One such examination will not cause harm to the patient. But one should take into account the fact that performing several such procedures in a short time can lead to radiation sickness. In this regard, for computed tomography, restrictions have been introduced on the volume of one examination and the frequency of procedures.
THE SECOND MAIN DIFFERENCE OF MRI FROM CT IS TISSUE SENSITIVITY
CT scans are similar to x-rays and are best suited to view bone structures. Therefore, computed tomography provides a good image of bones, which allows it to be used to determine bone injuries and various injuries. CT is also good for diagnosing “fresh” hemorrhages, tumor processes in the brain, chest and abdominal cavity. If a contrast agent is injected before the study, then it will be possible to make a high-quality image of the intestines, kidneys and large vessels. CT is often used in pulmonology to diagnose pathology of the lungs and mediastinum.
MRI clearly shows not so much bone structures as soft tissues:
parenchymal organs muscles vessels cartilage spinal cord reproductive system
MRI is often used in neurology and neurosurgery, as it provides much more information on the diagnosis of various diseases (tumors of the brain and spinal cord, stroke and traumatic conditions of the brain, vascular ruptures). The gold standard is the use of MRI for headaches. There is also a difference between MRI and CT in that in the first case it is possible to visualize blood vessels without using a contrast agent. In gynecology, MRI is also widely used, as it makes it possible to diagnose diseases of the pelvic organs.
Difference between MRI and CT