The brain is one of the most important organs, the central computer of the body. His research was always fraught with difficulties and precautions. However, with the advent and implementation of magnetic resonance imaging, diagnosing brain pathologies has become faster and easier. MRI is a non-invasive test. It is based on the use of high-frequency pulses, magnetic fields, a computer system and special software that allow you to obtain the most detailed image of the brain. “Treatment and Diagnostic Center on Vernadsky” offers MRI at a cost that is one of the lowest in the capital.
Types of MRI examinations
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head is performed with or without a contrast agent. In the first case, the subject is injected with special substances (usually based on gadolinium salts), which make it possible to create a contrast between different tissues. In some cases, the contrast agent may cause allergic reactions. The type of study (with or without contrast) is determined by the specialist.
Indications for prescribing CT scan of the brain with contrast
If a person experiences such symptoms, doctors will first order a high-quality and useful examination using a CT scan. These include:
- Regular and severe pain.
- The appearance of dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Constant fainting.
- Presence of noise in the ears.
- Injuries, in particular TBI and concussions.
- The likelihood of a stroke.
- Dental complaints.
- Diseases of the intraosseous sinuses.
- Suspicion of formations of unknown origin in the central nervous system.
- The need to check for hemorrhage.
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging
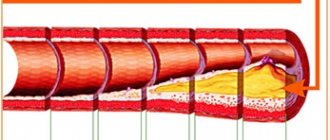
- Pathologies and diseases of cerebral vessels.
- Head injuries and bruises, which are accompanied by internal bleeding.
- Speech impairment and hearing loss.
- Tumors of the brain, cerebellopontine angle.
- Paroxysmal states.
- Infectious diseases of the central nervous system (abscess, meningitis, HIV infection).
- Pituitary adenoma.
- Abnormal development of the blood vessels of the head (thrombosis, aneurysms).
- Epilepsy.
- Systematic headaches of unknown origin.
- Sinusitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Neurodegenerative diseases.
- Pathology of the base of the skull.
How often should an MRI be done?
This is a more correct question, which should be asked, first of all, to the attending physician. However, there are some general patterns:
- For herniated discs, it is advisable to undergo an MRI every 2-3 years
- For stroke – once every 1-3 years
- For the initial diagnosis of multiple sclerosis - 1 examination every six months, for an already established disease - 1 session per year
- In the presence of stable tumors - 1 examination every six months to a year
- In the presence of unstable tumors - 1 examination every 3 months to six months
- After surgery to remove a tumor - 2-4 examinations in the first year, then - once a year
Too frequent, randomly performed MRI examinations are only a blow to your wallet, but not to your health. To save money, do not neglect consulting a doctor!
Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
Relative:
- severe claustrophobia;
- the presence of non-ferromagnetic implants, insulin pumps, heart valve prostheses;
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- drug or alcohol intoxication;
- presence of tattoos containing metallic compounds in the ink;
- heart failure.
Absolute:
- the presence of metallic foreign objects in the patient’s body;
- hematopoietic anemia (with magnetic resonance imaging with contrast);
- use of electronic devices such as pacemakers, etc.
Harm from contrast media and contraindications
Side effects from contrast administration are rare and include the following:
- severe allergic reaction (Quincke's edema or anaphylaxis);
- acute renal failure with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis;
- pain in bones and joints;
- dyspeptic disorders: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting;
- skin rashes.
According to statistics, hypersensitivity to pharmaceuticals occurs in 0.004-0.7% of cases. More often, allergy manifestations are mild and are expressed by hives, nasal congestion, sneezing, and itchy skin.
Swelling and difficulty breathing occur with more serious reactions. Anaphylaxis is extremely rare, occurring in 0.001-0.01% of cases. The risk of encountering this pathology is slightly higher in patients with bronchial asthma or a history of frequent allergy symptoms.
For this case, there is a special first aid kit, the drugs from which help to relieve an acute condition.
Due to acute renal failure, a condition in which the functional ability of the kidneys to produce and excrete urine, and with it toxic waste products, is lost, nephrogenic systemic fibrosis can develop. Gadolinium accumulates in the kidneys and other organs, where it causes the formation of coarse fibrous tissue, and the structural units - nephrons - die.
But contrast agents in MRI, unlike iodine-containing radiopharmaceuticals in computed tomography, extremely rarely provoke the development of acute renal failure.
If you have any urological or nephrological diseases, you need to be warned about this in advance. To minimize risks from the urinary organs, take a blood test for creatinine before diagnosis - the main indicator of kidney function. This test can be done at your local clinic or at our diagnostic center using the express method 20 minutes before the procedure. A creatinine test when performing enhanced magnetic resonance imaging is not mandatory.
We list the contraindications to MRI with contrast. These include:
- severe kidney disease, liver disease in the stage of decompensation or a history of transplantation (waiting for transplantation) of these organs;
- allergic reactions to contrast administration in previous studies;
- pregnancy (1st trimester) or suspicion of it;
- any metal implants, pacemakers, pumps, fastening structures, terminals, etc., with the exception of dental pins;
- the patient's weight is more than 120 kg.
During lactation, examination is possible, but it is recommended to refrain from breastfeeding for the next 24 hours.
If a patient has bronchial asthma, multiple myeloma, or severe cardiovascular insufficiency, in each case the issue of conducting contrast-enhanced MRI is decided on an individual basis.
During pregnancy after the first trimester, MRI with contrast is performed only for health reasons.
Although the scan is safe, the long-term effect of exposing a developing fetus to a strong magnetic field is unknown.
Preparing for an MRI of the brain
Usually, there is no need to do any complicated steps before the examination. Sometimes the specialist may ask the patient to refrain from eating and drinking before the procedure. The person being examined must remove all metal jewelry. In many centers, the patient is given a loose shirt, in some they are allowed to remain in their own clothes, provided that they are loose and free of metal parts. Before a brain MRI, women should inform their doctor about the possibility of pregnancy. The patient is also obliged to inform the doctor about recent operations and diseases, allergies and the presence of metal implants. If the person being examined suffers from claustrophobia or is very worried before the procedure, he may ask the doctor for a sedative.
How is an MRI of the brain performed?
- An MRI machine is a cylinder with holes at both ends. The patient sits on a movable table that is placed inside the device during the MRI procedure.
- The length of the tunnel depends on the specific type of apparatus. Some devices only partially surround the table. Tomographs can also be open on the sides. They are used for patients with severe claustrophobia. In closed-type devices, the table slides in completely.
- During the examination, the patient is secured with belts. The less it moves, the more accurate the diagnostic results.
- During magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, devices with wires that receive and send radio waves are placed around the head.
- Patients are often given earplugs. This helps protect your hearing from the loud noise that comes from the MRI machine when it is in operation.
- The table is placed inside the tomograph, and the specialist moves to an adjacent office, which houses a computer system that processes the data. The device takes a series of pictures. Each one takes a few minutes to shoot. As a rule, an MRI of the brain without contrast takes about 20–30 minutes, with a contrast agent – approximately 45–50 minutes.
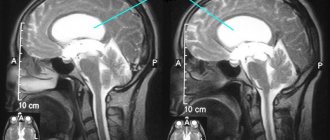
- An MRI machine takes layer-by-layer images of tissue. During a head scan, data is collected from approximately 20 levels, each 4–5 mm thick. The higher the magnetic field strength of the tomograph and the thinner the sections, the more accurate the research result.
Decoding the data obtained after a CT scan of the brain
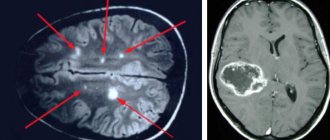
Images that are simulated on a doctor's computer in raw format are not able to provide reliable and detailed information. In order to obtain accurate and correct data, they need to be processed in the installed program. The study shows black and white images, with the help of which a specialist can create a three-dimensional picture. With all this, the doctor sees information about the condition of all the required areas of the organ, located at different depths.
In addition, the patient can receive the results on a portable medium, which will contain not only the finished material, but also a draft version of the image. One of the advantages of such diagnostics is that the analysis allows you to see a full picture of the development of all stages of the disease, as well as monitor changes in real time. Most often, the time it takes to complete a report takes about 60 minutes, but in special situations (with a high workload) the specialist may need more time and will have to come back for an answer the next day.
Prices for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in Moscow
Various factors influence how much an MRI costs in each case. The price may change depending on whether the specialist will use a contrast agent, whether the results will need to be recorded on disk, etc. The approximate cost of magnetic resonance imaging is indicated on the page.
You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Diagnostic and Treatment Center on Vernadsky. To do this, call us by phone at any time convenient for you. You can also leave an online application through a special form presented on the website.
Why do MRIs with contrast be done?
Intravenous enhancement is a way to improve diagnostic reliability. The contrast agent helps:
- differentiate different anatomical structures;
- identify areas of neovascularization (pathological proliferation of blood vessels that accompanies the formation of tumors);
- consider hollow, parenchymal organs;
- study blood vessels;
- examine organ function and perfusion.
If cancer is suspected, magnetic resonance imaging with contrast allows:
- clarify the structure of the pathological focus or the area of the altered MR signal;
- determine the exact number of affected areas, the degree of invasion of surrounding tissues, distant prevalence (metastases);
- track the dynamics of changes.
Using contrast, you can evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and monitor the condition of tissues and organs after surgery.
MR angiogram of the vessels of the head and neck
The main purposes of using intravenous enhancement are:
| MRI of the brain, spinal cord and neck organs |
|
| MRI of the chest |
|
| MRI of the abdominal cavity |
|
| MRI of the pelvic organs |
|
| MRI of the musculoskeletal system |
|
| MRI of peripheral vessels |
|