Indications for MRI of the brain in children
An examination is prescribed if a child has the following problems:
- deterioration of hearing and vision;
- unexplained changes in behavior;
- dizziness and headaches;
- convulsions and periodic fainting;
- head injury with concussion;
- speech development delay.
Frequent headaches or dizziness as usual
The cause of pain may be disturbances in the blood supply to the brain and inner ear. For correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a modern, highly informative study.
Fainting occurs periodically without visible external influences
Fainting in children that occurs repeatedly may indicate serious illness. If such signs occur, an MRI of the head and brain with contrast is prescribed; a special substance is injected into a vein for better visualization.
Convulsive syndrome occurs periodically
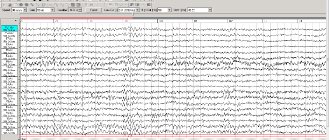
This is a nonspecific reaction of the body to irritants, which manifests itself in involuntary muscle contractions. To determine the causes of seizures, specialists are consulted and an MRI of the child’s head is performed.
Markedly progressive decrease in vision and/or hearing
The study provides an image of the structures located inside the skull. The presence of layer-by-layer images is an opportunity to conduct an accurate diagnosis.
When is a child's head MRI necessary?
It is always important for both doctors and patients to correctly identify the problem and make the correct diagnosis. The person’s subsequent recovery and quality of life depend on this. If it is not possible to identify a possible pathology or disease by other means, MR imaging seems to be the safest and most justified method.
The procedure is carried out only as prescribed by the treating doctor. Parents cannot voluntarily “prescribe” and conduct this examination for their child for the sake of interest. Tomography is performed for the following indications:
- regular headaches;
- “unexplained” loss of consciousness in the absence of external causes;
- convulsions;
- the appearance of regular dizziness;
- sudden deviations in behavior;
- developmental lag behind peers;
- gradual or sudden deterioration of hearing or vision.
What the examination may reveal:
- congenital abnormalities in brain development;
- post-traumatic changes in tissues as a result of a difficult birth process;
- neoplasms of various etiologies;
- damage to structures as a result of the influence of toxic or infectious substances;
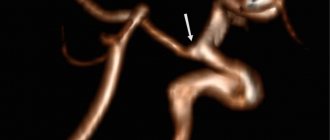
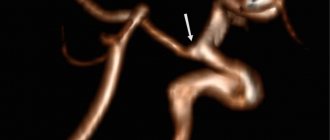
- changes in the vascular network of the brain of the head.
Most often, traumatic health problems accompany hyperactive children or children involved in strength sports. It is almost impossible to avoid traumatic injuries. Doctors monitor such children especially closely. Parents need to be prepared for the fact that the doctor may refer the child for a head tomography even with mild symptoms of the disease.
Features of the procedure in children
Parents are interested in how MRIs of the brain are done for children. The main problem is the difficulty of getting the child to remain still while the tomograph takes pictures. You are required to remain motionless for 15-20 minutes. The device is noisy and can frighten the baby. However, patient immobility is a mandatory requirement, so tomography in some cases is performed under anesthesia. Indications for the use of anesthesia are age under 5 years, fear of confined spaces, panic fear of examinations, hyperactivity, and the presence of mental illness. To conduct examinations in infants, special incubators are used, which are used in conjunction with a magnetic tomograph. Anesthetic agents are propofol-based drugs, which are characterized by:
- short action;
- low level of toxicity;
- minimizing side effects;
- falling asleep quickly;
- minimal impact on the central nervous system;
- no effect on the respiratory centers;
- rapid elimination from the body.
When using anesthesia that does not affect the central nervous system, the baby's infancy is not a contraindication. Doctors at specialized diagnostic centers have extensive experience in conducting examinations of children of different ages. Parents ask what an MRI of the child’s brain shows. The study allows you to visually analyze the state of the brain and identify pathological changes that appear due to difficult pregnancy and childbirth. Using the method, problems in brain development caused by intrauterine development disorders, previous diseases, bruises and injuries are identified.
How is an MRI of a child's brain performed?
The study is done using a tomograph consisting of a mobile table and a wide tunnel. To improve scanning quality, additional gradient magnetic coils are used that create an alternating force field. The data is converted into a series of layered images by a complex computer program.
The child lies face up on the tomograph table. If contrast enhancement is necessary, an intravenous catheter connected to an automatic injector is installed. The head and body are fixed with special fasteners and bolsters, and headphones are worn to protect against noise.
The doctor and x-ray technicians are in the next room; one of the parents can stay with the child. Communication with the subject is maintained through an intercom.
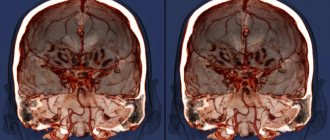
MRI of a child's brain
The table with the patient is rolled into the tomograph tube. Scanning occurs in the axial, sagittal and frontal planes. The doctor studies the photo and, if necessary, reconstructs a 3D model of the brain.
Contrast MRI involves a break in scanning. After a series of native images, the child is injected with a gadolinium solution. As the “staining” preparation fills the vascular bed in the area of interest, the study continues.
MRI of the child’s brain is performed both on tunnel tomographs and on open devices. The latter are characterized by weak power, so photographs do not always allow a detailed study of the state of cerebral structures.
How is the research performed?
Doctors create the most comfortable atmosphere for the child so as not to frighten him. It is necessary to ensure the patient's immobility; if this is not possible, anesthesia is used for children. Older children undergo the test in the presence of their parents, who can help reassure them. The child is placed on a special table, which slides into the apparatus. The use of an open type tomograph allows the baby to see his parents and feel comfortable. The equipment is equipped with a feedback system for communication, listening to fairy tales and music. You can watch a video of how an MRI of the brain is done for children
.
Preparing for an MRI for a child
Preparing a child for an MRI is, first of all, emotional preparation:
- Inform your child about the peculiarities of the procedure: the hum of the tomograph and the need to lie still. Sometimes it helps the child to associate the examination with a game in which it is necessary to remain motionless for as long as possible.
- Before the examination, allow your child to get comfortable in the room.
- Before entering the room with the tomograph, leave all metal toys, mobile phones, and glasses outside. Be sure to tell your radiologist about the presence of braces.
An MRI of the brain takes about 20 minutes; after the examination, the doctor makes a conclusion and gives the images to the parents. Based on them, the attending physician will be able to understand what pathology is hidden in the child’s body and prescribe competent treatment!
If you have any questions, ask our specialist!
Ask a Question
Contraindications for the procedure for children
The study is not carried out if the child has: foreign metal objects (staples, stents, prosthetic heart valves);
- electronic devices (pacemaker, insulin pump);
- hematopoietic anemia (in case of administration of a contrast agent).
If a teenager has a tattoo on his body, the doctor determines whether the procedure can be performed.
The solution depends on the dye used (paints should not be metal-based). Examination under anesthesia is not carried out if there is a history of:
- rickets;
- developmental delay;
- lack of body weight;
- feverish conditions;
- bronchial asthma during exacerbation;
- mental disorders;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- acute neurological diseases.
How to prepare a child for an MRI?
It is necessary to tell the child how the procedure goes and how long it takes. Being in a confined space and noise during the examination can frighten the child, so it is better to warn in advance about the peculiarities of the scan.
Before an MRI of the brain, doctors recommend maintaining a sleep schedule and avoiding stressful situations. An excited state, nervousness, and fear can negatively affect the reliability of the research results. It is advisable to avoid the use of tonic drinks; compotes, water, and juices are suitable to quench thirst.
An hour before an MRI with contrast, the child needs to have a snack. This will help avoid nausea and dizziness.
If you experience severe pain, claustrophobia, or increased nervousness, you can discuss taking analgesic and sedative medications with your doctor. Self-administration of medications is prohibited. If you have concomitant diseases, you must notify the specialist about available appointments.
Before scanning, jewelry and metal accessories are removed; it is advisable to dress the child in a comfortable home suit or pajamas that do not restrict movement.
MRI is not performed if:
- metal non-removable medical structures in the area of interest;
- implanted electromagnetic devices;
- tattoos made with metal-containing inks (in teenagers).
Contrast scanning is prohibited for severe liver and kidney diseases. Possible contraindications should be reported to your doctor.
Brain tumor on MRI in a child
Most clinics in St. Petersburg provide free telephone consultations, where specialists will tell you how to properly prepare a child for an MRI. Following the recommendations will help increase the efficiency of the diagnostic procedure.
In what cases is a child prescribed an MRI?
MR imaging is used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, such as injury, disease, or congenital anomalies. When issuing a referral for diagnostics, the specialist indicates which area requires examination.
MRI scanning is used to study:
- brain;
- cervical spine;
- spinal column and bone structure;
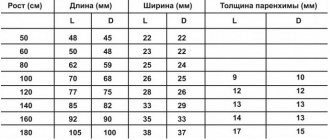
An MRI scan of the brain and spine is recommended by a doctor if abnormal development is suspected, for example, encephalopathy, problems with the pituitary gland, changes in the intervertebral discs, changes in nervous tissue in the spinal cord, etc.
Cardiac MRI is used as an adjunct to echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart), computed tomography (CT) and angiography (vascular examination) to provide information both before and after treatment.
Imaging of joints and bones using magnetic resonance imaging is required to detect sports injuries and fractures.
- Available: doctor’s appointment from 1500 rubles
- Convenient: open daily from 8:00 to 21:00
- Quickly: we will carry out all the diagnostics at the first appointment
- Complete: has all the necessary equipment