Characteristics of the symptom
Goosebumps is a comparative description of a sensation that is similar to a slight tingling, tightening, or moving of the skin. In medical terminology, this phenomenon is called paresthesia. It arises as a response to irritating factors of an endogenous and exogenous nature.
Paresthesia can be either episodic or chronic, depending on the triggering agents.
The symptom is a type of sensory disorder and has several characteristic features.
The following properties of pathology are distinguished:
- wave contraction of the middle layer of skin (dermis), with changes in sensitivity;
- spontaneous occurrence of sensations, without a specific chronological periodicity;
- the duration of the episodes increases, depending on the worsening of the provoking factors.
As the symptoms increase, the goosebumps may spread to the cervical spine, upper and lower extremities, or enter a more severe phase, which is accompanied by numbness and soreness of the skin.
When the kidney has abnormal mobility and falls below the diaphragm, the patient suffers from pain in the hypochondrium and lower back. Nephroptosis begins to develop, which should be treated immediately, preventing the development of complications and inflammation. Read more in the article: “kidney prolapse: treatment, causes and consequences.”
Features of the symptom
Advertising:
In some cases, paresthesia is of a reflex nature and is called the pilomotor reflex or piloerection. The condition occurs in response to a pronounced emotional outburst, which can be caused by the following emotions:
- joy;
- fear;
- sexual arousal and other feelings.
In addition to the causes of the emotional spectrum, pilomotor paresthesia can be triggered by a feeling of cold, a reaction to anti-stress toys, or unexpected sounds (grinding metal, creaking foam). The effect can also be caused by dosed physical activity and massage, even if a simple hand massager is used.
Piloerection is a rudimentary reflex and is not a sign of disease.
The origin of this reflex is the stimulation of peripheral nerve endings and is manifested in the contraction of smooth muscle of conical connective tissue fibers. As a result of the contraction of the hair follicles, the hairs rise and the “goose bumps” effect is observed. The mechanical movement of the skin is accompanied by the sensation of goosebumps running over the head.
Syphilis is an infectious disease caused by Treponema pallidum and is sexually transmitted. The initial symptom of a syphilitic infection is a hard chancre that appears at the site of entry of the pathogen. Read more in the article: “syphilitic infection: symptoms and signs.”
Causes of pathology
Advertising:
Paresthesia is a consequence of the influence of external and internal negative factors acting on nerve tissue. These include:
- exogenous factors, in which unpleasant sensations arise from external mechanical influence on the scalp (impacts, prolonged compression);
- endogenous factors in which disruption of innervation is caused by somatic pathologies (diseases of internal organs and tissues) and mental illnesses.
As a result of changes occurring under the influence of these aggressive agents, the conductivity of the nerve fibers responsible for the innervation of the dermis is disrupted. Interruptions in impulses passing through the occipital, transverse, trigeminal and other nerves innervating the scalp lead to microspasms.
If the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted, not only goosebumps can be felt. Increased symptoms are accompanied by pain (the face and neck hurt), and the scalp becomes numb. Intense manifestation of paresthetic symptoms indicates an acute course of the underlying pathology.
Paresthesia in somatic diseases
The cause of the feeling of goosebumps running on the scalp is often diseases of the internal organs or tissues. The main diseases that can cause paresthesia of the skin are associated with the following factors:
Advertising:
- disruption of the innervation of nerve tissue;
- difficulty in peripheral and cerebral circulation.
Somatic causes of unpleasant sensations can be classified according to pathogenetic reactions and the mechanism of development of the root cause of symptoms.
Neurological pathologies
Degenerative or tumor processes (trigeminal neuralgia, cervical plexus neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, Bell's palsy, vegetative-vascular dystonia, diabetic and alcoholic polyneuropathy) cause changes in the tissues and fibers of the central or peripheral nervous system. Demyelination, tissue compression or gradual destruction of trigeminal nerve cells and cervical plexus ganglion fibers occurs, which leads to disruption of nerve conduction in the skin and the appearance of goosebumps on the face, back of the head, neck and upper part of the head.
Inflammatory diseases of the spine
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine and adjacent tissues (osteochondrosis, arthrosis, spondylitis and other pathologies of the upper spine) are accompanied by the development of inflammatory processes within the fibers of smooth and skeletal muscles. Inflamed muscle tissue compresses blood vessels and nerve lines, which causes difficulty in the synaptic transmission of nerve impulses.
Cardiovascular diseases
Arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, stenosis, atrial fibrillation, ischemic stroke and other pathologies, which are characterized by thickening of the vascular walls and narrowing of their lumen, are accompanied by impaired cerebral circulation. Narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels leads to insufficient nutrition of the brain. Hypoxia and nutrient deficiency cause discirculatory encephalopathy (with gradual death of neurons). Focal damage to brain tissue is accompanied by various neurological symptoms, including paresthetic ones.
Paresthesia in mental disorders
Sensitivity disorders in patients with mental illness are observed quite often. The sensation of tingling and crawling is recorded in symptom complexes of such nervous disorders as:
Advertising:
- depression;
- schizophrenia;
- neurotic somatoform disorder (hypochondriacal, dysfunctional);
- anxiety disorders.
In most patients, the sensory disorder is hallucinogenic or imaginary and refers to perceptual disorders. This manifestation of symptoms is called sensopathy.
Sensopathy is characterized by a sensation of pins and needles not only on the surface of the body, but also under the skin.
The similarity of paresthesia and sensopathy makes diagnosis difficult only at the initial stage of symptoms. If the pathogenesis of a symptom is of physiological origin, then it is characterized by constant localization. The sensitive symptom can move and is determined in the arms, legs and other parts of the body, since it is a projection of the patient’s state of mind.
Additional factors
There are several other pathological causes that can cause paresthetic symptoms. The table shows some conditions that may be accompanied by a feeling of goosebumps.
| Pathology | Cause of symptom development |
| Respiratory diseases | When you have a cold, the sensitivity of the skin and body temperature increase, which contributes to an exacerbation of the pilomotor reflex. |
| Mechanical impact (non-traumatic) | Skin receptors are irritated, which provokes microspasm |
| Endocrine system disorders | Insufficient release of parathyroid hormone in the thyroid gland causes the development of hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcemia, which are characterized by the appearance of spastic conditions |
The feeling of crawling sensations, not associated with a violation of innervation, can be caused by pediculosis (lice), seborrheic dermatitis, follicular hyperkeratosis, a reaction to shampoo or hair styling and coloring products (the skin becomes covered with keratinized scales). An allergic reaction to medications may also be a factor in causing symptoms.
What else to pay attention to - accompanying symptoms
If your head is numb and you have goosebumps, you should pay close attention to the accompanying symptoms. This will help you choose the right doctor. For example, if you constantly feel dry mouth, the frequency and volume of urination has increased, and there is irritation on the skin, then it is advisable to first visit an endocrinologist. This doctor will rule out the possibility of developing diabetes mellitus and accompanying neuropathy.
If there is pain in the neck, difficulty turning and tilting the head, then you need to make an appointment with a vertebrologist. Most likely you are developing osteochondrosis, protrusion, spondyloarthrosis, spondylitis and a number of other degenerative diseases. The vertebrologist will prescribe an X-ray examination of the cervical and cervicothoracic spine. In the image, he can see a decrease in the height of the intervertebral spaces, which will indicate the development of osteochondrosis to the protrusion stage. If the intervertebral joints are destroyed, it is highly likely that a diagnosis of deforming spondyloarthrosis will be made.
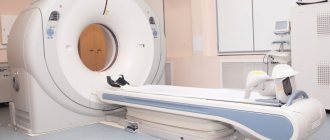
An MRI examination may be required to clarify the diagnosis. It shows the condition of all soft tissues: cartilaginous intervertebral discs, radicular and cranial nerves, muscles, ligaments and tendons. Doppler ultrasound will help identify pathologies of the vascular bed.
If on the eve of the appearance of goosebumps on your scalp there was a traumatic impact (a fall, emergency braking while driving in a car, a blow, an awkward turn of the head), then you should first visit a traumatologist. This specialist will eliminate the possibility of displacement of the vertebral bodies, violation of their integrity (fracture or crack), and tissue ruptures. If injuries are found, the doctor will suggest initial surgical treatment.
Features of symptoms in women
Advertising:
If goosebumps appear on the head in women, the reason may lie in the hormonal changes in the body that occur during menopause. Symptoms of paresthesia can occur at any stage of the menopause, but they are more pronounced in the premenopausal and menopausal phases, when hormonal surges are most active.
Provoking factors that cause sensitivity disorders in women include vitamin deficiency. The feeling of goosebumps occurs when there is a lack of elements such as:
- vitamins A, D, E, C and B vitamins (cyanocobalamin, folic acid);
- trace elements zinc, copper, iodine.
If the content of useful substances in the body is low, especially during pregnancy, dry skin, dizziness, general weakness and sensitivity disorders of the skin may occur.
Significance in diagnosis
Symptoms, accompanied by a feeling of goosebumps running in the head, have important diagnostic significance. Such manifestations mean that a pathological process is occurring in the body, which may be a consequence of the following factors:
- disruption of the innervation of the neck, head and brain;
- problems with blood circulation;
- hormonal disorders;
- consequences of mechanical damage.
Paresthesia is also of differential importance in the diagnosis of mental disorders.
The benefit of goosebumps is the possibility of early diagnosis. Making a diagnosis at an early stage allows you to avoid the development of acute life-threatening conditions (vascular obliteration, stroke). Since paresthetic effects appear in the first stages of the pathological process, timely treatment helps prevent chronic disease.
Diagnosis of head tremor
First of all, it is necessary to establish the diseases that cause head shaking. As a rule, the development of tremor is based on a malfunction in the functioning of internal organs.
After clarifying the patient’s complaints, rapid video recording is carried out and tremor is checked using a tremograph (a special device that records tremor in 3 planes). Electromyography, which determines electrical muscle activity, is required.
Additionally, studies are prescribed to assess the general condition of the patient’s body, as well as the activity of internal organs (ultrasound examination, laboratory blood tests, magnetic resonance imaging). If necessary, the patient is recommended to visit specialists.